Side Effects Of Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
Chemotherapy works by targeting fast-growing cancer cells. But it may also kill other cells in the body that grow quickly, such as those in hair follicles, bone marrow and the digestive system. As a result, chemotherapy for breast cancer may cause a variety of side effects, including:
- Hair loss
- Suppressed immunity
Invasive Breast Cancer: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma And Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma are the most common types of invasive breast cancer. Invasive means cancer has spread from the original site through the bloodstream and lymph nodes to other areas, like nearby breast tissue, lymph nodes, or elsewhere.
Invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast canceraccounting for roughly 70 to 80 percent of all cases. IDC starts in a milk duct and grows into other parts of the breast. With time, it may spread further, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
Invasive lobular carcinoma is the second most common type, accounting for roughly 5 to 10 percent of all breast cancers. ILC starts in lobules and then spreads into the nearby breast tissue. Like IDC, it may metastasize and spread to other parts of the body. This cancer is harder to detect on mammograms than IDC and one in five women with ILC have both breasts affected.
What Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Also known as invasive breast cancer, the tumor in this stage measures between 2 cm to 5 cm, or the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer. Stage 2 breast cancer indicates a slightly more advanced form of the disease. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue, and the tumor is larger than in stage 1 disease. However, stage 2 means the cancer has not spread to a distant part of the body.
At stage 2, a tumor may be detected during a breast self-exam as a hard lump within the breast. Breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.
Stage 2 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 2A: One of the following is true:
- There is no tumor within the breast, but cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast is 2 cm or smaller and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast measures 2 cm to 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage 2B: One of the following is true:
- The tumor measures 2 cm to 5 cm and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
At stage 2, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Most commonly, stage 2 breast cancer is described as:
Stage 2 breast cancer survival rate
Read Also: Breast Cancer Curable
Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
It is recommended to go for regular screening tests and know how your breasts normally look so you will be aware of any changes and seek medical help. The most common sign of breast cancer is a new mass or lump. It is crucial to understand that not all breast lumps are caused by breast cancer. Other symptoms include
· Swelling on part or all of your breast even if you cant feel a lump
· Nipple or breast pain
· Red, flaking, dry, or thickened nipple or breast skin
· Swollen lymph nodes near the collar bone or under the arm.
Although other conditions can cause these symptoms, it is advisable to have any lumps or other changes in your breasts checked by a healthcare practitioner.
M Categories For Breast Cancer
M followed by a 0 or 1 indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs — for example, the lungs, liver, or bones.
M0: No distant spread is found on x-rays or by physical exam.
cM0: Small numbers of cancer cells are found in blood or bone marrow , or tiny areas of cancer spread are found in lymph nodes away from the underarm, collarbone, or internal mammary areas.
M1: Cancer has spread to distant organs as seen on imaging tests or by physical exam, and/or a biopsy of one of these areas proves cancer has spread and is larger than 0.2mm.
Read Also: Is High Grade Cancer Curable
Prognostic Impact Of Tumor
It has been previously reported that tumor-specific expression of the rate-limiting enzyme, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutharyl-coenzyme A reductase , in the mevalonate pathway is associated with more favorable tumor parameters in breast cancer. In the present study, it is examined the prognostic value of HMG–CoAR expression in a large cohort of primary breast cancer patients with long-term follow up.
Does A Benign Breast Condition Mean That I Have A Higher Risk Of Getting Breast Cancer
Benign breast conditions rarely increase your risk of breast cancer. Some women have biopsies that show a condition called hyperplasia . This condition increases your risk only slightly.
When the biopsy shows hyperplasia and abnormal cells, which is a condition called atypical hyperplasia, your risk of breast cancer increases somewhat more. Atypical hyperplasia occurs in about 5% of benign breast biopsies.
Don’t Miss: What Does Stage 4 Breast Cancer Mean
Grade Of Breast Cancer
The grade describes the appearance of the cancer cells.
- low grade the cells, although abnormal, appear to be growing slowly
- medium grade the cells look more abnormal than low-grade cells
- high grade the cells look even more abnormal and are more likely to grow quickly
Read further information:
Read further information about secondary breast cancer
How Much Do Anastrozole And Exemestane Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Studies have shown that both anastrozole and exemestane can lower the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women who are at increased risk of the disease.
In one large study, taking anastrozole for five years lowered the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by 53 percent. In another study, taking exemestane for three years lowered the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by 65 percent.
The most common side effects seen with anastrazole and exemestane are joint pains, decreased bone density, and symptoms of menopause .
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/31/2018.
References
Read Also: Stage 3a Breast Cancer Prognosis
Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
In its early stages, breast cancer may not cause any symptoms. In many cases, a tumor may be too small to be felt, but an abnormality can still be seen on a mammogram.
If a tumor can be felt, the first sign is usually a new lump in the breast that was not there before. However, not all lumps are cancer.
Each type of breast cancer can cause a variety of symptoms. Many of these symptoms are similar, but some can be different. Symptoms for the most common breast cancers include:
- a breast lump or tissue thickening that feels different than surrounding tissue and has developed recently
- breast pain
- changes to the appearance of the skin on your breasts
- a lump or swelling under your arm
If you have any of these symptoms, it doesnt necessarily mean you have breast cancer. For instance, pain in your breast or a breast lump can be caused by a benign cyst.
Still, if you find a lump in your breast or have other symptoms, you should see your doctor for further examination and testing.
Diagnosis Of Breast Cancer
To determine if your symptoms are caused by breast cancer or a benign breast condition, your doctor will do a thorough physical exam in addition to a breast exam. They may also request one or more diagnostic tests to help understand whats causing your symptoms.
Tests that can help diagnose breast cancer include:
- Mammogram. The most common way to see below the surface of your breast is with an imaging test called a mammogram. Many women ages 40 and older get annual mammograms to check for breast cancer. If your doctor suspects you may have a tumor or suspicious spot, they will also request a mammogram. If an abnormal area is seen on your mammogram, your doctor may request additional tests.
- Ultrasound. A breast ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the tissues deep in your breast. An ultrasound can help your doctor distinguish between a solid mass, such as a tumor, and a benign cyst.
Your doctor may also suggest tests such as an MRI or a breast biopsy.
If you dont already have a primary care doctor, you can browse doctors in your area through the Healthline FindCare tool.
You May Like: Stage 3 Advanced Breast Cancer
Types Of Breast Carcinomas
Within the large group of carcinomas, there are many different types of breast cancer. The first major division is between in situ and invasive carcinoma. In situ carcinoma is “pre-invasive” carcinoma that has not yet invaded the breast tissue. These in situ cancer cells grow inside of the pre-exisiting normal lobules or ducts. In situ carcinoma has significant potential to become invasive cancer, and that is why it must be adequately treated to prevent the patient from developing invasive cancer. Invasive cancers have cancer cells that infiltrate outside of the normal breast lobules and ducts to grow into the breast connective tissue. Invasive carcinomas have the potential to spread to other sites of the body, such as lymph nodes or other organs, in the form of metastases.
Approximately 80% of breast carcinomas are invasive ductal carcinoma, followed by invasive lobular carcinomas which account for approximately 10-15% of cases. Invasive ductal carcinomas and invasive lobular carcinomas have distinct pathologic features. Specifically, lobular carcinomas grow as single cells arranged individually, in single file, or in sheets, and they have different molecular and genetic aberrations that distinguish them from ductal carcinomas. Ductal and lobular carcinomas may have different prognoses and treatment options, depending upon all of the other features of the particular cancer.
Benign hyperplasia of the breast epithelial cells lining the ducts and lobules.
A mass.
Types Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Most breast cancers are invasive, meaning the cancer has spread from the original site to other areas, like nearby breast tissue, lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body. Invasive breast cancer cells break through normal breast tissue barriers and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream and lymph nodes. The two most common types of invasive breast cancer are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma.
Invasive ductal carcinoma
The most common type of breast canceraccounting for roughly 70 to 80 percent of all casesis called invasive ductal carcinoma . IDC is a cancer that starts in a milk duct and grows into other parts of the breast. With time, it may spread further, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
Invasive lobular carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma is the second most common type, accounting for roughly 5 to 10 percent of all breast cancers. ILC starts in lobules and then spreads into nearby breast tissue. Like IDC, it may metastasize. However, this cancer is harder to detect on mammograms and other exams than IDC. One in five women with ILC have both breasts affected.
Inflammatory breast cancer
Pagets disease of the breast
Angiosarcoma of the breast
Phyllodes tumors
Other, even more rare, types of invasive breast cancer include adenoid cystic carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, papillary carcinoma and tubular carcinoma.
Also Check: Whats The Youngest You Can Get Breast Cancer
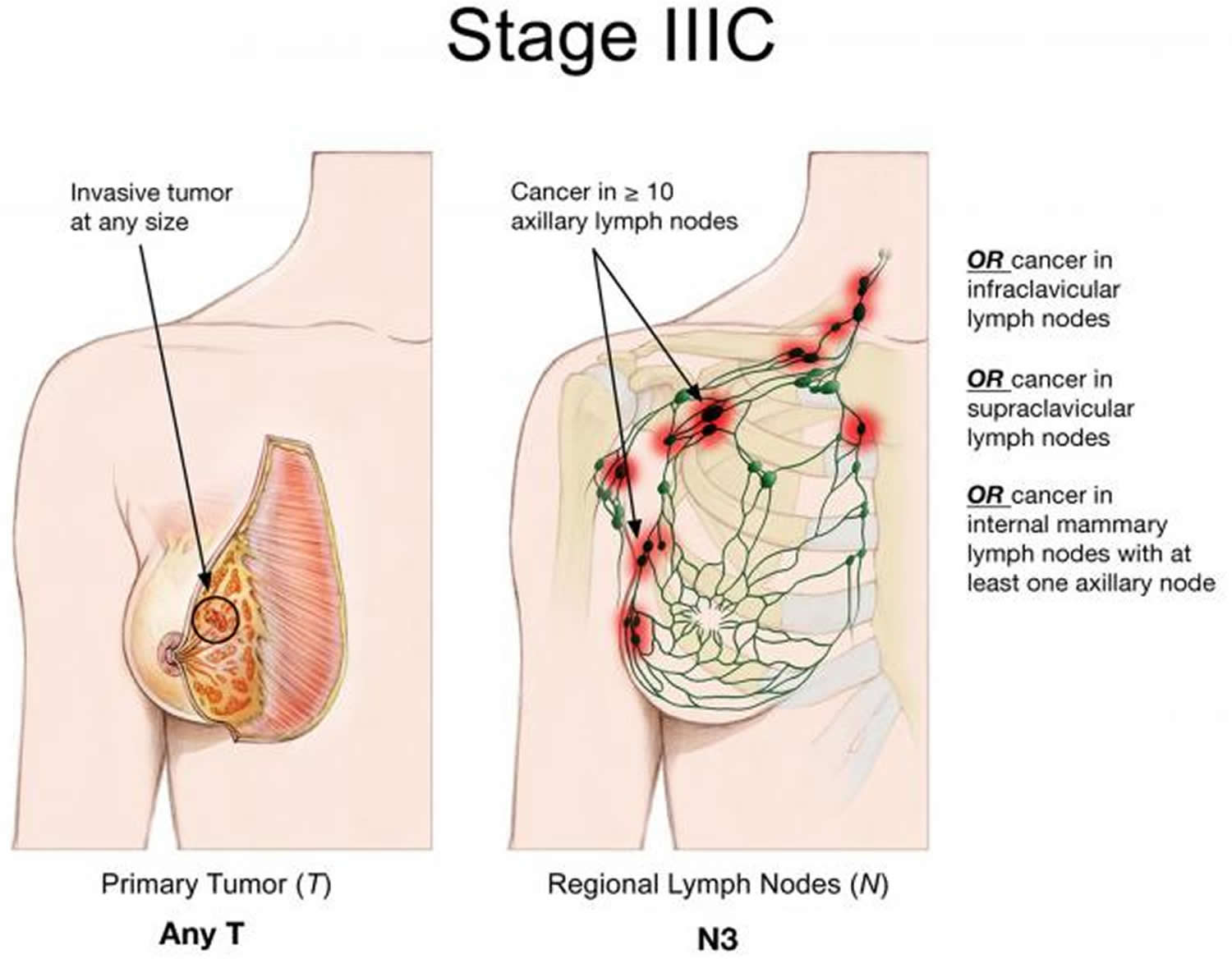
What Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Also known as locally advanced breast cancer, the tumor in this stage of breast cancer is more than 2 inches in diameter across and the cancer is extensive in the underarm lymph nodes or has spread to other lymph nodes or tissues near the breast. Stage 3 breast cancer is a more advanced form of invasive breast cancer. At this stage, the cancer cells have usually not spread to more distant sites in the body, but they are present in several axillary lymph nodes. The tumor may also be quite large at this stage, possibly extending to the chest wall or the skin of the breast.
Stage 3 breast cancer is divided into three categories:
Stage 3A: One of the following is true:
- No tumor is found in the breast, but cancer is present in axillary lymph nodes that are attached to either other or other structures, or cancer may be found in the lymph nodes near the breast bone, or
- The tumor is 2 cm or smaller. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that are attached to each other or other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breastbone, or
- The tumor is 2 cm to 4 cm in size. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that are attached to each other or to other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breast bone, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that may be attached to each other or to other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breastbone.
Stage 3C:
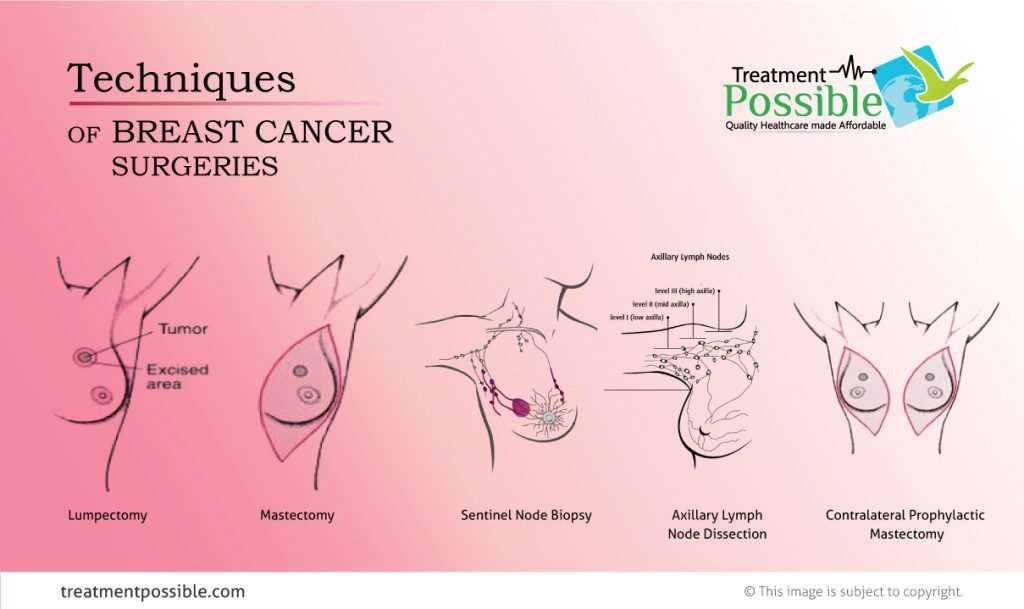
Side Effects Of Breast Cancer Surgery
Surgery for breast cancer may result in side effects that require additional medical treatment and supportive care services.
Side effects may include:
- Reduced shoulder and chest mobility
- Seroma, a build-up of fluid around a scar in in the armpit
- Lymphedema, a collection of lymph fluid that may cause swelling and discomfort
- Fatigue brought on by stress and the emotional toll of the surgery
You May Like: Non Hormonal Breast Cancer
Birads : Overall After Biopsy The Rate Of Breast Cancer Diagnosis Is About 30%
When the finding is suspicious enough for breast cancer to require a biopsy, about 30% of these turn out to be breast cancer. Conversely, about 60% to 70% are benign.
Among initial findings on mammograms that require a biopsy, the most common category is a BIRADS 4 breast lesion. These lesions are suspicious for malignancy and occur about 70% of the time.
BI-RADS category 5 lesions account for about 13% of screening mammograms requiring biopsy. Breast lesions that are BI RADS category 3 on a mammogram. account for about 11% of biopsy requests.
Human Antimicrobial Protein Hcap18/ll
Human cathelicidin antimicrobial protein, hCAP18, and its C-terminal peptide LL-37 is a multifunctional protein. In addition to being important in antimicrobial defense, it induces chemotaxis, stimulates an giogenesis and promotes tissue repair. We previously showed that human breast cancer cells express high amounts of hCAP18, and hypothesised that hCAP18/LL-37 may be involved in tumor progression.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Her2 Positive Breast Cancer
Breast Exam By Your Doctor
The same guidelines for self-exams provided above are true for breast exams done by your doctor or other healthcare professional. They wont hurt you, and your doctor may do a breast exam during your annual visit.
If youre having symptoms that concern you, its a good idea to have your doctor do a breast exam. During the exam, your doctor will check both of your breasts for abnormal spots or signs of breast cancer.
Your doctor may also check other parts of your body to see if the symptoms youre having could be related to another condition.
Who Gets Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women other than skin cancer. Increasing age is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer, with 66% of breast cancer patients being diagnosed after the age of 55.
In the US, breast cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death in women after lung cancer, and it’s the leading cause of cancer death among women ages 35 to 54. Only 5 to 10% of breast cancers occur in women with a clearly defined genetic predisposition for the disease. The majority of breast cancer cases are “sporadic, meaning there is no definitive gene mutation.
Recommended Reading: Stage 4 Breast Cancer Symptoms Treatments
What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer
As its name suggests, inflammatory breast cancer often causes the breast to become red, swollen, and inflamed. Some women with IBC also notice thickened or discolored breast skin with tiny dimples, puckers, or ridges that make it look like an orange peel. While the symptoms may sound like an infection, the real culprit is cancer that is blocking lymphatic vessels in the skin and breast tissue, causing a buildup of fluid and, in some cases, pain, discoloration, and sudden swelling of the breast. Also called inflammatory breast carcinoma or locally advanced breast cancer, IBC can spread quickly, making prompt diagnosis and treatment essential.
Are You Under 40 You’re Not Alone

While most cases of breast cancer occur in women over 50, around 400 New Zealand women under the age of 44 are diagnosed with breast cancer every year. These days, breast cancer is much more treatable if detected early, and there are many women still thriving decades after experiencing breast cancer at a young age. Discover the specific concerns for young women with breast cancer.
Also Check: What Are The Odds Of Surviving Breast Cancer
In Situ Vs Invasive Breast Cancers
The type of breast cancer can also refer to whether the cancer has spread or not. In situ breast cancer is a pre-cancer that starts in a milk duct and has not grown into the rest of the breast tissue. The term invasive breast canceris used to describe any type of breast cancer that has spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Invasive breast cancer has spread into surrounding breast tissue. The most common types are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma. Invasive ductal carcinoma makes up about 70-80% of all breast cancers.