Paget Disease Is A Rare Type Of Breast Cancer
- Approximately accounts for 1% of all breast cancers
- Cancer starts in the breast ducts, then spreads to the skin of the nipple, and areola
- Usually associated with ductal carcinoma in situ or invasive ductal carcinoma
- Symptoms may consist of the nipple and areola being: Crusted, scaly, red, bleeding, oozing, burning, or itching
National Breast Cancer AssistanceAccess For All
ABCF makes access to breast health care and services easier for everyone. By eliminating barriers for screenings and increasing the availability of other medical resources, we are helping women and men detect breast cancer at its earliest stage.
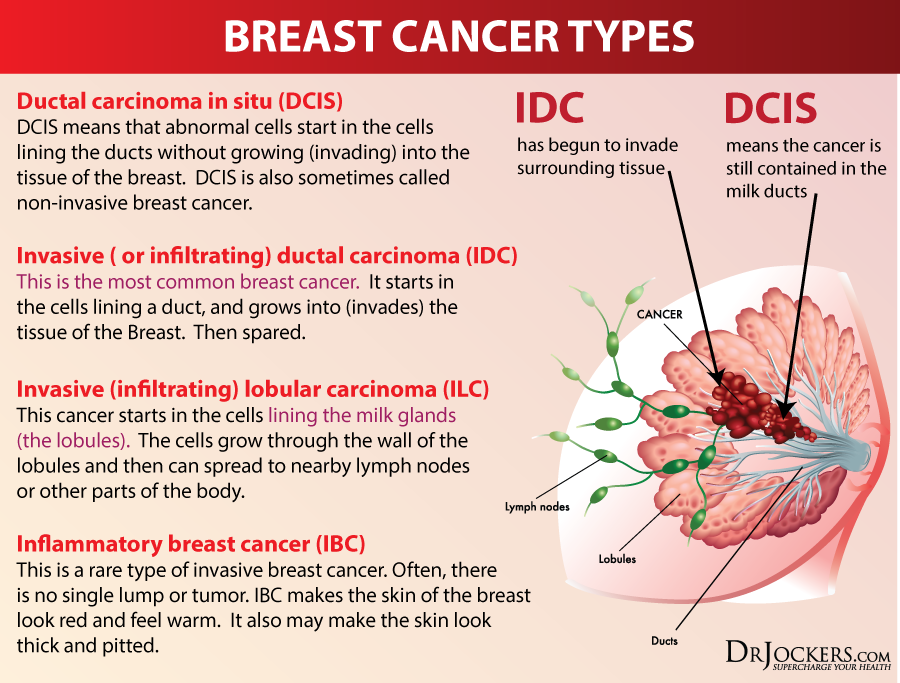
What Are The Four Types Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer may be called lobular carcinoma if it begins in glands that make milk, or ductal carcinoma if it begins in the ducts that carry milk to the nipple. The cancer may grow and invade other areas around the breast, such as skin or chest wall.
Different types of breast cancer grow and spread at different rates. Both types of breast cancer may be invasive or non-invasive.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ : DCIS is a noninvasive condition. With DCIS, the cancer cells are confined to the ducts in the breast and have not invaded the surrounding breast tissue.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ : LCIS is cancer that grows in the milk-producing glands of the breast. Like DCIS, the cancer cells do not invade the surrounding tissue.
- Invasive ductal carcinoma : It is the most common type of breast cancer. This type of breast cancer begins in the milk ducts and then invades nearby tissue in the breast. Once the breast cancer has spread to the tissue outside milk ducts, it can spread to other nearby organs and tissue.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma first develops in lobules of the breast and then invades nearby tissues.
Apart from above four types, below are few less-common types of breast cancer:
How Much Do Tamoxifen And Raloxifene Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Multiple studies have shown that both tamoxifen and raloxifene can reduce the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in healthy postmenopausal women who are at high risk of developing the disease. Tamoxifen lowered the risk by 50 percent. Raloxifene lowered the risk by 38 percent. Overall, the combined results of these studies showed that taking tamoxifen or raloxifene daily for five years reduced the risk of developing breast cancer by at least one-third. In one trial directly comparing tamoxifen with raloxifene, raloxifene was found to be slightly less effective than tamoxifen for preventing breast cancer.
Both tamoxifen and raloxifene have been approved for use to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in women at high risk of the disease. Tamoxifen is approved for use in both premenopausal women and postmenopausal women . Raloxifene is approved for use only in postmenopausal women.
Less common but more serious side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include blood clots to the lungs or legs. Other serious side effects of tamoxifen are an increased risk for cataracts and endometrial cancers. Other common, less serious shared side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Mayo
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed
During your regular physical examination, your doctor will take a thorough personal and family medical history. He or she will also perform and/or order one or more of the following:
- Breast examination: During the breast exam, the doctor will carefully feel the lump and the tissue around it. Breast cancer usually feels different than benign lumps.
- Digital mammography: An X-ray test of the breast can give important information about a breast lump. This is an X-ray image of the breast and is digitally recorded into a computer rather than on a film. This is generally the standard of care .
- Ultrasonography: This test uses sound waves to detect the character of a breast lump whether it is a fluid-filled cyst or a solid mass . This may be performed along with the mammogram.
Based on the results of these tests, your doctor may or may not request a biopsy to get a sample of the breast mass cells or tissue. Biopsies are performed using surgery or needles.
After the sample is removed, it is sent to a lab for testing. A pathologist a doctor who specializes in diagnosing abnormal tissue changes views the sample under a microscope and looks for abnormal cell shapes or growth patterns. When cancer is present, the pathologist can tell what kind of cancer it is and whether it has spread beyond the ducts or lobules .
What To Know About Breast Cancer Symptoms

The symptoms of breast cancer can vary widely and some types of breast cancer may not have any noticeable symptoms.
Sometimes a lump may be too small to be felt or to cause any changes to your breast or surrounding area. In these cases, cancerous cells are often first detected through screening techniques like a mammogram.
When there are symptoms, they can include:
- a lump or thickening of breast tissue that you can feel with your fingers
- breast swelling or changes to your breast size or shape
- changes to the skin on your breast, such as dimpling, redness, or skin irritation
- the nipple turning inward or nipple pain
- a lump in your underarm area
- nipple discharge other than breast milk
Its important to be familiar with how your breasts usually look and feel. This will help you notice any changes and to follow up with your healthcare professional promptly if anything looks or feels different.
Noninvasive breast cancer develops in the cells of a duct or lobule and remains in that location. Its also referred to as in situ which means in the original place.
There are two types of noninvasive breast cancer:
- ductal carcinoma in situ
- lobular carcinoma in situ
Lets take a closer look at each type.
Read Also: What Causes Hormonal Breast Cancer
Prognostic Impact Of Tumor
It has been previously reported that tumor-specific expression of the rate-limiting enzyme, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutharyl-coenzyme A reductase , in the mevalonate pathway is associated with more favorable tumor parameters in breast cancer. In the present study, it is examined the prognostic value of HMG–CoAR expression in a large cohort of primary breast cancer patients with long-term follow up.
What Is A Breast Papilloma And Is It Cancer
Also called intraductal papilloma, a breast papilloma is a small, wartlike growth in the breasts milk ducts. This benign condition may cause a clear or bloody discharge from the nipple, or you may feel a small lump behind or next to the nipple. Having one papilloma does not raise your breast cancer risk, though having several of these growths has been linked to higher risk.
Don’t Miss: Anne Hathaway Cup Size
Can You Get Two Different Types Of Breast Cancer
TypesTypes of breast cancercarcinomacarcinomabreast cancerbreast cancercancerhavebreast
. Herein, can you have 2 types of breast cancer at the same time?
Multifocal breast cancer occurs when there are two or more tumors in the same breast. All of the tumors begin in one original tumor. The tumors are also all in the same quadrant or section of the breast. Multicentric breast cancer is a similar type of cancer.
Subsequently, question is, which is the most aggressive form of breast cancer? The most aggressive breast cancers include: Triple-negative breast cancer: This type of breast cancer tests negative for the hormones estrogen and progesterone, and the protein HER2.
Similarly one may ask, is there more than one type of breast cancer?
Invasive breast cancer Invasive breast cancer has spread into surrounding breast tissue. The most common types are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma. Invasive ductal carcinoma makes up about 70-80% of all breast cancers.
What is the best type of breast cancer to have?
Certain breast cancer subtypes have a better statistical prognosis
| breast cancer sub-type |
|---|
| almost 100% |
| Infiltrating lobular carcinoma |
What Are The Common Warning Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
- Lump in the breast or armpit discovered during bathing may be the first symptom of breast cancer
- Changes to the nipple and the surrounding area like nipple retraction and inverted nipple.
- Bloody discharge from nipple: If an individual notices blood stains on the bra, and if the secretions are unusual, they may need urgent medical attention.
- Change in color and/or thickening of skin on the breast, dimpling or thickening of breast skin that resembles an orange rind is a warning sign of breast cancer. If the breast skin changes color, typically to a pink or reddish hue that covers more than half the breast, that may also be a warning sign.
- A non-healing sore anywhere on the breast, including the nipple: A red, scaly, flaky nipple, and any persistent skin change, including blood or fluid from the nipple with non-healing sore, may be a warning sign of breast cancer.
- Increased warmth in the breast
- Pain, itching or tenderness in the breast
Recommended Reading: What Is Stage 3 Cancer In Lymph Nodes
Types Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Most breast cancers are invasive, meaning the cancer has spread from the original site to other areas, like nearby breast tissue, lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body. Invasive breast cancer cells break through normal breast tissue barriers and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream and lymph nodes. The two most common types of invasive breast cancer are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma.
Invasive ductal carcinoma
The most common type of breast canceraccounting for roughly 70 to 80 percent of all casesis called invasive ductal carcinoma . IDC is a cancer that starts in a milk duct and grows into other parts of the breast. With time, it may spread further, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
Invasive lobular carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma is the second most common type, accounting for roughly 5 to 10 percent of all breast cancers. ILC starts in lobules and then spreads into nearby breast tissue. Like IDC, it may metastasize. However, this cancer is harder to detect on mammograms and other exams than IDC. One in five women with ILC have both breasts affected.
Inflammatory breast cancer
Pagets disease of the breast
Angiosarcoma of the breast
Phyllodes tumors
Other, even more rare, types of invasive breast cancer include adenoid cystic carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, papillary carcinoma and tubular carcinoma.
Stages Of Breast Cancer
When cancer is diagnosed, a stage is assigned to it, based on how advanced it is. The stage helps doctors determine the most appropriate treatment and the prognosis. Stages of breast cancer may be described generally as in situ or invasive. Stages may be described in detail and designated by a number .
Also Check: Did Anne Hathaway Have A Nose Job
Who Gets Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women other than skin cancer. Increasing age is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer, with 66% of breast cancer patients being diagnosed after the age of 55.
In the US, breast cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death in women after lung cancer, and it’s the leading cause of cancer death among women ages 35 to 54. Only 5 to 10% of breast cancers occur in women with a clearly defined genetic predisposition for the disease. The majority of breast cancer cases are “sporadic, meaning there is no definitive gene mutation.
Hormone And Protein Receptors
Breast cancer can sometimes be described by the types of hormones or protein receptors on the surface of the cancer cells.
For example:
- Oestrogen receptor and progesterone receptor positive cancers are encouraged to grow by the female hormones oestrogen or progesterone. Read more about ER positive breast cancer.
- HR2 positive breast cancer means that the tumour produces too much of a protein called HER2, which helps breast cancer to grow. Read more about HER2+ breast cancer.
- Triple negative breast cancer doesnt have receptors for HER2, oestrogen or progesterone. More about triple negative breast cancer.
Also Check: Stage 3b Breast Cancer Prognosis
What Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a very early form of breast cancer thats confined to the milk ducts, which is why its called ductal. Carcinoma is the name for any cancer that begins in cells that line the inner or outer surfaces of tissues, such as the breast ducts. In situ is a Latin term meaning in its original place. DCIS is the most common form of noninvasive breast cancer.
DCIS is classified as low, intermediate, or high grade. Grades are based on what the cells look like under a microscope. The lower the grade, the more closely DCIS resembles normal breast cells. The higher the grade, the more different it is from normal cells. DCIS can sometimes involve the nipple, causing it to look red and scaly. This is a rare form of cancer known as Pagets disease of the breast .
In some women, DCIS may not progress to invasive cancer in their lifetime. This has fueled debate about DCIS about whether women with low-risk disease need any treatment, or if they could be safely checked with annual mammograms and breast exams to see if the cancer is progressing. Currently, the standard treatment for DCIS includes surgery, often a lumpectomy.
Types Based On Where Cancer Starts Or Spreads
One of the ways doctors describe breast cancer is based on where in your body it starts or spreads.
Carcinoma and Adenocarcinoma. Carcinomas start in the tissues that line your breasts and other organs. Most breast cancers are carcinomas.
Breast cancers are often a type of carcinoma called an adenocarcinoma. These cancers start in the cells lining the milk ducts or the glands that produce milk .
Ductal Carcinoma. Ductal carcinoma is cancer of the cells that line the milk ducts in your breast.
Ductal carcinoma in situ is the earliest form of ductal carcinoma. “In situ” means it’s only in the milk ducts, and isn’t likely to spread to other parts of your body. About 1 in 5 people who are newly diagnosed with breast cancer have DCIS. This type is very curable.
Invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer, affecting about 80% of people who are diagnosed. “Invasive” means the cancer is able to spread outside of the milk duct where it started.
There are several subtypes of invasive ductal carcinoma:
You might also hear about lobular carcinoma in situ . But LCIS isn’t really cancer, and won’t spread outside of the lobule. Doctors usually find it when they do a breast biopsy.
Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast. These rare tumors grow in the breast’s connective tissue. They’re more common in women who have an inherited condition called Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Only 1 in 4 phyllodes tumors are cancer. The rest are noncancerous .
Also Check: Breast Cancer Growth Rate
Are You Under 40 You’re Not Alone
While most cases of breast cancer occur in women over 50, around 400 New Zealand women under the age of 44 are diagnosed with breast cancer every year. These days, breast cancer is much more treatable if detected early, and there are many women still thriving decades after experiencing breast cancer at a young age. Discover the specific concerns for young women with breast cancer.
What Makes A Normal Cell Turn Cancerous
There are trillions of cells in the body having regulated cell cycle that controls their growth, maturity, division and death. During childhood normal cells divide faster to allow the person to grow. In adulthood the cells divide to replace worn-out cells and to repair injuries. This cell division and growth is controlled by DNA and genes that lie within the cells nucleus.
Cancer begins when cells in a part of the body start to grow out of control. All types of cancer, irrespective of their origin, occur due to this disturbed growth of cells that leads to formation of tumors and lesions.A normal cell can become a cancer cell if it undergoes damage to the DNA. It is the DNA that regulates the cycle of growth and death and any changes or damage of the cell.
For most cells if the DNA is damaged the cell either repairs the damage or the cell dies. In cancer cells, the damaged DNA is not repaired and the damage is spread to new abnormal cells that are born of the defective cell. Damaged DNA by mutation can also be inherited or can also occur due to exposure to toxins like cigarette smoking, alcohol etc.
You May Like: Baking Soda And Honey Cancer
How Is It Treated
Your treatment will depend on the stage of your cancer. If the cancer is early stage meaning the tumors are only in one quadrant of your breast breast-conserving surgery is possible. This procedure removes as much of the cancer as possible, while preserving the healthy breast tissue around it.
After surgery, youll get radiation to kill any cancer cells that might have been left behind. Chemotherapy is another option after surgery.
Large tumors or cancers that have spread may require mastectomy surgery to remove the whole breast. Lymph nodes may also be removed during the surgery.
Although breast cancer treatments can improve your survival odds, they can have side effects.
Side effects from breast-conserving surgery include:
- pain in the breast
- swelling in the breast or arm
- change in the shape of the breast
- bleeding
- redness, itching, peeling, and irritation of the skin
- fatigue
Cosmetic Implants And Breast Cancer Survival
The general agreement, based on , is that silicone breast implants do not increase the risk of breast cancer. A 2015 meta-analysis of 17 studies that included participants who had undergone cosmetic breast augmentation discovered no increase in the risk of breast cancer associated with the procedure. In fact, the research showed that the incidence among these participants was lower than expected.
In 2021, another study found that women with cosmetic implants have significantly lower rates of breast cancer than those who do not have them.
Meanwhile, a 2013 meta-analysis found that women who received a diagnosis of breast cancer after getting cosmetic breast implants may have a higher risk of dying from the disease.
However, this research did not factor in other variables that may influence breast cancer mortality, such as body mass index, age at diagnosis, or cancer stage at diagnosis. And at least one of the studies in the analysis looked at overall mortality, instead of breast cancer-specific mortality, thereby potentially skewing the results. As such, a person should consider the finding with caution.
most common type is ductal carcinoma, which begins in a milk duct. Another type is lobular carcinoma, which begins in a lobule, one of the tiny glands that produce milk.
Invasive breast cancer involves cancerous cells spreading to nearby tissue. It is then more likely that the cancer will spread to other parts of the body.
You May Like: Anne Hathaway Boob Size