Always Seek Medical Attention Even During The Coronavirus Pandemic
The key point is that a woman should seek medical attention for any concerning lumps in her breasts, says Harold Burstein, MD, PhD, a breast oncologist with the Susan F. Smith Center.
Simple imaging techniques, such as a mammogram or breast ultrasound, can usually provide reassurance that the breast lump is benign. If necessary, a breast MRI or biopsy can be used to evaluate whether the lump is cancerous.
Effect Of Hormonal Changes On Breasts
As women develop from pre-puberty through puberty, pregnancy and to menopause, the breasts will be affected by a variety of fluctuations in hormones.
During puberty, hormones produced by the ovaries cause growth and development of the breast. After puberty, the hormones oestrogen and progesterone will change throughout a womans monthly menstrual cycle. This may cause women to have swollen or tender breasts at different times of the month.
During pregnancy the body will produce additional oestrogen and progesterone, which trigger further growth and development of the breast to prepare mothers for breastfeeding.
Around the time of menopause , the ovaries stop producing female hormones including oestrogen. Without oestrogen, the breast tissue decreases in size. After menopause , monthly menstrual periods stop.
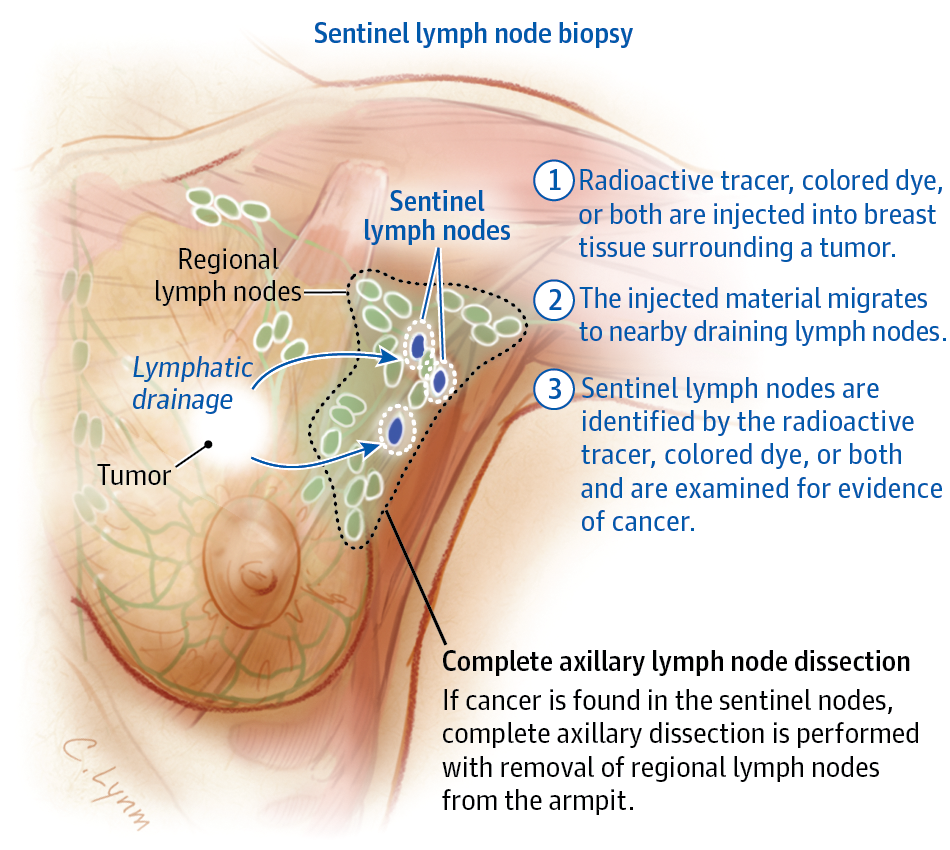
The Lymphatic System Of The Breast The Breast Has Many Blood Vessels And Lymph Vessels Lymph Vessels Are Thin Tubes Similar To Blood Vessels They Collect And Move Lymph Fluid Away From The Breast Into Small Bean
The axillary lymph nodes are under the arm . There are about 3050 lymph nodes in the axilla. They are divided into 3 levels based on how close they are to the large muscle of the chest . When breast cancer spreads, it usually spreads to level I lymph nodes, then to level II and then to level III.
- Level I, or low axilla, are along the outer border of the muscle under the pectoralis major
- Level II, or mid axilla, are beneath the pectoralis minor.
- Level III, or high axilla, are along the inner border of the pectoralis minor.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer In The Duct Glands
Breast Lumps: Why Size Movability And Pain Matter
Your breasts are made up of fat, nerves, blood vessels, fibrous connective tissue, and glandular tissue, as well as an intricate system of milk-producing lobules , and ducts . This anatomy in and of itself creates a lumpy, uneven terrain.
A lump in the breast distinguishes itself from this background of normal irregularities. Harmless breast lumps can be solid and unmovable, like a dried bean or movable, soft, and fluid-filled you can roll it between your fingers like a grape. A lump may be pea-size, smaller than a pea, or even several inches across, although this larger size is rare.
What typically differentiates a benign breast lump from a cancerous breast lump is movement. That is, a fluid-filled lump that rolls between the fingers is less likely to be cancerous than a hard lump in your breast that feels rooted in place.
Another rule of thumb has to do with pain. Breast cancer does not usually cause pain. Benign conditions sometimes do, although there are exceptions to this rule as well. For instance, a rare form of breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer, may cause symptoms such as aching, tenderness, pain, or burning in the breast.
The only way to know the status of a lump for sure is through medical tests, such as an ultrasound, a mammogram, or a fine needle aspiration , in which your doctor uses a tiny needle to extract a bit of the lump for laboratory examination.
RELATED: What Is a Skin Lump? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
The most common types of breast cancer are:
- Infiltrating ductal carcinoma. This cancer starts in the milk ducts of the breast. It then breaks through the wall of the duct and invades the surrounding tissue in the breast. This is the most common form of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of cases.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ is ductal carcinoma in its earliest stage, or precancerous . In situ refers to the fact that the cancer hasn’t spread beyond its point of origin. In this case, the disease is confined to the milk ducts and has not invaded nearby breast tissue. If untreated, ductal carcinoma in situ may become invasive cancer. It is almost always curable.
- Infiltrating lobular carcinoma. This cancer begins in the lobules of the breast where breast milk is produced, but has spread to surrounding tissues in the breast. It accounts for 10 to 15% of breast cancers. This cancer can be more difficult to diagnose with mammograms.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ is a marker for cancer that is only in the lobules of the breast. It isn’t a true cancer, but serves as a marker for the increased risk of developing breast cancer later, possibly in both or either breasts. Thus, it is important for women with lobular carcinoma in situ to have regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
You May Like: How Bad Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Is More Likely To Occur On The Left Side Of The Body Than The Right
Breast cancer continues to hold mysteries that scientists dont understand. And while there may be more important mysteries out there than why breast cancer is more likely to occur on the left side than the right side, we likely wont know for sure how vital the answer to this question is until we find it.
For now, what we know is that breast cancer is more likely to occur in the left breast than in the right, accounting for about 53 percent of unilateral breast cancer cases. An investigation into data from the Icelandic Cancer Registry found that, out of 2011 unilateral breast cancer cases occurring from the years 1948 to 1987, 1139 of those cases were in the left breast, an excess of 13%. Similarly, an analysis of 18 U.S. studies found that breast cancer occurred in the left breast 4% more often than the right.
We dont know why this happens, but we do have some plausible theories.
Its entirely possible that the increased incidence of breast cancer on the left side of the body is a coincidence. But then again, maybe its not. One thought is that the left breast tends to be larger than the right breast, meaning there is more tissue on that side to develop breast cancer in. One study showed a slight connection between the chances of cancer and left- or right-handedness. These and potentially dozens of other factors could be at play in determining which side of the body breast cancer originates in.
Provide Mammograms
Other Types Of Breast Cancer
Other less common types of breast cancer include invasive lobular breast cancer, which develops in the cells that line the milk-producing lobules, inflammatory breast cancer and Paget’s disease of the breast.
It’s possible for breast cancer to spread to other parts of the body, usually through the lymph nodes or the bloodstream. If this happens, it’s known as “secondary” or “metastatic” breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Can Stage 1 Breast Cancer Be Cured
How Are Fibroadenomas Diagnosed And Treated
Your healthcare provider may diagnose this type of lump simply by feeling it. But, he or she will want to confirm the diagnosis with a mammogram or ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration. Sometimes, in very young women, the fibroadenoma is not removed. However, since sometimes these tumors enlarge with pregnancy and breastfeeding, your provider may suggest having it surgically removed.
While most fibroadenomas do not lead to cancer, there is a type of fibroadenoma that has been linked to an increased risk of cancer, particularly in women with a family history of the disease.
Appearance Of Cancer Cells
The appearance, or differentiation, of the cancer cells is another factor in cancer staging. Doctors grade cancer cells according to how similar they appear to noncancerous cells under a microscope.
Healthcare professionals classify cancer cells that are close to resembling healthy cells as being low grade or well differentiated. These cancers typically grow more slowly.
High grade, or poorly differentiated, cancer cells appear very different from normal cells and tend to grow faster.
After assessing the different characteristics of the breast cancer, doctors use the information to determine its overall stage from 04.
Here is an overview of each breast cancer stage :
- Stage 0: This cancer is noninvasive and is only present inside the milk duct. This stage includes ductal carcinoma in situ.
- Stage 1: These are small tumors that either have not spread to the lymph nodes or have only affected a small area of the sentinel lymph node.
- Stage 2: These are larger tumors that have spread to some nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: These tumors are large or growing into surrounding tissues, such as breast skin, muscle, and lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: These are tumors that started in the breast but have spread to other parts of the body.
When recommending treatment options for breast cancer, a doctor will take into account:
Treatment options can include:
Early detection and diagnosis of breast cancer can significantly improve a persons outlook.
- lymph node involvement
Read Also: Estrace Breast Cancer
Signs Of Benign Breast Masses
In contrast to breast cancer tumors, benign lumps are often squishy. They may feel like a soft rubber ball with well-defined margins. They’re often easy to move around and may be tender.
Infections in the breast can cause redness and swelling. Sometimes it can be difficult to tell the difference between mastitis and inflammatory breast cancer, but mastitis often causes symptoms of fever, chills, and body aches. Those symptoms aren’t associated with cancer.
Relationships With Friends And Family
It’s not always easy to talk about cancer, either for you or your family and friends. You may sense that some people feel awkward around you or avoid you.
Being open about how you feel and what your family and friends can do to help may put them at ease. However, don’t be afraid to tell them that you need some time to yourself, if that’s what you need.
Want to know more?
- Healthtalkonline: How breast cancer affects families
You May Like: Can Nipple Piercing Cause Cancer
How Much Do Tamoxifen And Raloxifene Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Multiple studies have shown that both tamoxifen and raloxifene can reduce the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in healthy postmenopausal women who are at high risk of developing the disease. Tamoxifen lowered the risk by 50 percent. Raloxifene lowered the risk by 38 percent. Overall, the combined results of these studies showed that taking tamoxifen or raloxifene daily for five years reduced the risk of developing breast cancer by at least one-third. In one trial directly comparing tamoxifen with raloxifene, raloxifene was found to be slightly less effective than tamoxifen for preventing breast cancer.
Both tamoxifen and raloxifene have been approved for use to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in women at high risk of the disease. Tamoxifen is approved for use in both premenopausal women and postmenopausal women . Raloxifene is approved for use only in postmenopausal women.
Less common but more serious side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include blood clots to the lungs or legs. Other serious side effects of tamoxifen are an increased risk for cataracts and endometrial cancers. Other common, less serious shared side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.
Normal Breast Changes Through Life
The female breast will go through various normal changes over the course of a lifetime. Many of these changes are driven by hormones. They can be related to the menstrual cycle, pregnancy or the normal aging process. Most breast changes are not cancer, however, if you do notice an unusual breast change, it is important that you speak with your doctor so that it can be checked as soon as possible.
Normal breast changes throughout life include:
You May Like: Can Breast Cancer Cause Stomach Pain
What Are Breast Lobes And Breast Ducts
Each female breast contains 15-20 sections called lobes. Each lobe is made up of many smaller sacs called lobules . It is these lobules that produce milk in breastfeeding women. The lobes and lobules are connected to the nipple by tubes called ducts, which carry milk to the nipple. Milk flows through the nipple to the outside during breastfeeding.
Benign Breast Lumps And Future Cancer Risk
- Women who had a history of benign breast disease are more likely to develop breast cancer than those who have never had any breast disease. According to a 2019 study in the International Journal of Cancer, benign breast disease increases the risk of developing breast cancer in the future, in addition to the risk that a woman may already have due to family history, personal breast cancer history, or a genetic mutation.
Also Check: Nipple Piercing And Breast Cancer
Can Breast Cancer Be Prevented
A lot of breast cancers are detected at an early stage, by breast screening. However, a small number are not. Some women may have developed breast cancer before they have their first mammogram and some may develop breast cancer between mammograms. All women of every age should be breast aware. That is, get to know how your breasts and nipples normally look and feel. Try to recognise any changes that occur before and after your periods. See your GP if you notice any changes, lumps, or other abnormalities in your breasts or nipples. Don’t wait until your next scheduled screening appointment.
There is some evidence that regular exercise may reduce your risk of breast cancer by as much as a third. If you have been through the menopause, it is particularly important you are not overweight or obese. This is because being overweight causes more oestrogen to be produced, which can increase the risk of breast cancer.
Studies have shown that women who breast-feed their children are less likely to develop breast cancer than those who do not. The most likely reason for this is that women do not produce an egg as regularly while they are breast-feeding and oestrogen levels remain stable.
Cosmetic Implants And Breast Cancer Survival
The general agreement, based on , is that silicone breast implants do not increase the risk of breast cancer. A 2015 meta-analysis of 17 studies that included participants who had undergone cosmetic breast augmentation discovered no increase in the risk of breast cancer associated with the procedure. In fact, the research showed that the incidence among these participants was lower than expected.
In 2021, another study found that women with cosmetic implants have significantly lower rates of breast cancer than those who do not have them.
Meanwhile, a 2013 meta-analysis found that women who received a diagnosis of breast cancer after getting cosmetic breast implants may have a higher risk of dying from the disease.
However, this research did not factor in other variables that may influence breast cancer mortality, such as body mass index, age at diagnosis, or cancer stage at diagnosis. And at least one of the studies in the analysis looked at overall mortality, instead of breast cancer-specific mortality, thereby potentially skewing the results. As such, a person should consider the finding with caution.
most common type is ductal carcinoma, which begins in a milk duct. Another type is lobular carcinoma, which begins in a lobule, one of the tiny glands that produce milk.
Invasive breast cancer involves cancerous cells spreading to nearby tissue. It is then more likely that the cancer will spread to other parts of the body.
Read Also: Malignant Neoplasm Of Female Breast
Early Warning Signs Of Breast Cancer
Common symptoms of breast cancer include:
- A lump in your breast or underarm that doesnât go away. This is often the first symptom of breast cancer. Your doctor can usually see a lump on a mammogram long before you can see or feel it.
- Swelling in your armpit or near your collarbone. This could mean breast cancer has spread to lymph nodes in that area. Swelling may start before you feel a lump, so let your doctor know if you notice it.
- Pain and tenderness, although lumps donât usually hurt. Some may cause a prickly feeling.
- A flat or indented area on your breast. This could happen because of a tumor that you canât see or feel.
- Breast changes such as a difference in the size, contour, texture, or temperature of your breast.
- Changes in your nipple, like one that:
- Pulls inward
- Develops sores
What Are Dense Breasts
Breasts contain glandular, connective and fatty tissue. Breast density is a term used to describe the different proportions of these tissue types as detected by a mammogram. Dense breasts have relatively high amounts of connective and/or glandular tissue and low amounts of fatty tissue. Only a mammogram can show if a woman has dense breasts. Breast density is not related to how the breasts look, feel, their size or firmness.
On a mammogram, connective or fibrous tissue appears white while fatty tissue appears dark. Because breast cancers also appear white, this may make it more difficult for specialists to identify cancer in women with dense breasts. However, even with dense breasts, a screening mammogram is still the most effective method to detect breast cancer early for women over age 50.
Dense breasts also tend to be more common in younger women or women with a lower body mass index. In addition, breast density tends to decrease as women become older.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Spread To Lungs Prognosis