Request An Appointment At Moffitt Cancer Center
Please call for support from a Moffitt representative. New Patients and Healthcare Professionals can submit an online form by selecting the appropriate buttonbelow. Existing patients can call . for a current list of insurances accepted at Moffitt.
NEW PATIENTS To request a new patient appointment, please fill out the online form or call 1-888-663-3488.
REFERRING PHYSICIANS Providers and medical staff can refer patients by submitting our online referral form.
Moffit now offers Virtual Visits for patients. If you are eligible for a virtual appointment, our scheduling team will discuss this option further with you.
Moffitt Cancer Center is committed to the health and safety of our patients and their families. For more information on how were protecting our new and existing patients, visit our COVID-19 Info Hub
British Columbia Specific Information
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women in British Columbia. Breast cancer can occur in men as well, but it is not as common. Tests and treatments for breast cancer vary from person to person, and are based on individual circumstances. Certain factors such as your age, family history, or a previous breast cancer diagnosis may increase your risk of developing breast cancer. For information about your specific risk factors, speak with your health care provider.
A number of screening methods, including mammograms in women, can help find and diagnose breast cancer. The decision to have a mammogram or use any other screening method may be a difficult decision for some women. While screening for breast cancer is often recommended, it is not mandatory. Speak with your health care provider for information regarding how to get screened, the facts and myths about screening tests, how to maintain your breast health, and to get help making an informed decision.
For more information about breast cancer and breast cancer screening, visit:
If you have questions about breast cancer or medications, speak with your health care provider or call 8-1-1 to speak with a registered nurse or pharmacist. Our nurses are available anytime, every day of the year, and our pharmacists are available every night from 5:00 p.m. to 9:00 a.m.
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Treated
Inflammatory breast cancer is usually treated aggressively. In most cases, doctors begin treatment with chemotherapy.
Many women also have surgery to remove the entire affected breast and nearby lymph nodes. This procedure is known as a mastectomy or modified radical mastectomy.
Following surgery, your doctor may recommend radiation therapy or other treatments, like hormone therapy, to target remaining cancer cells. Some people also participate in clinical trials to gain access to exploratory treatments that are not yet widely available.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Staging Inflammatory Breast Cancer
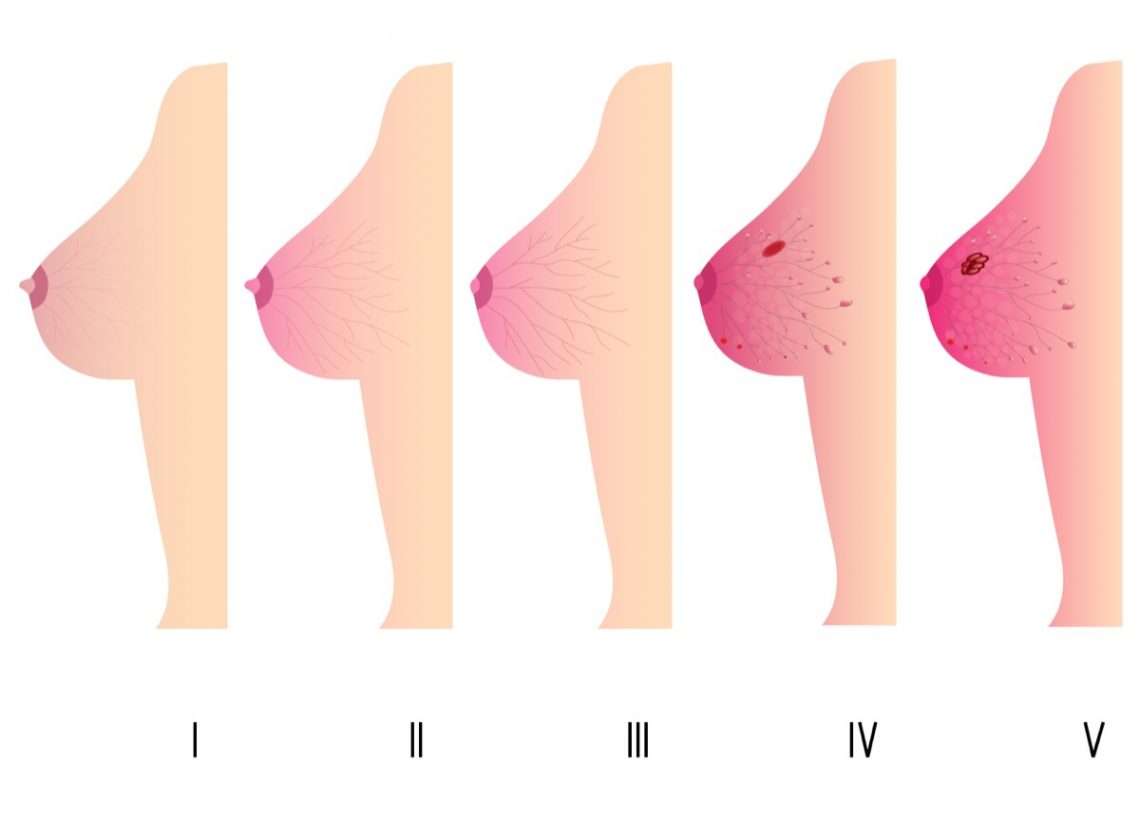
Inflammatory breast cancer is always at least locally-advanced when its first diagnosed because the breast cancer cells have grown into the skin. This means it is at least stage III.
In about 30% of cases, the inflammatory breast cancer has already spread to parts of the body away from the breast when it is diagnosed. This means the cancer is metastatic or stage IV.
After inflammatory breast cancer is diagnosed, your doctor will do more tests to collect information on the characteristics of the cancer. These tests, as well as the results of your biopsy and any imaging tests, make up the parts of your pathology report.
Other information commonly collected on inflammatory breast cancer includes:
Survivorship care after inflammatory breast cancer treatment
Because of treatments theyve received, many breast cancer survivors have a higher risk of developing other diseases as they age, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and osteoporosis. To make sure breast cancer survivors are regularly screened for these and other diseases, experts have developed the idea of survivorship care planning.
Survivorship care plans are written documents made up of two parts.
The first part is a treatment summary, a record of all the breast cancer treatments youve received.
When To See A Health Care Provider About Changes To The Skin Of The Breast
Even though breast skin changes usually dont mean anything serious, it’s important to know when you might actually need medical attention.
If wearing more breathable fabrics avoiding soaps and detergents that cause skin sensitivity and keeping your breasts clean and dry doesnt seem to help with the skin changes youre seeing, or if you notice your symptoms worsening, be sure to check in with a health care provider. And be sure to visit a health care provider if you notice any of these accompanying symptoms:
- Pain
Don’t Miss: Anne Hathaway Boob Size
Symptoms Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Because the lymph channels are blocked, the breast might become:
- swollen
- firm or hard
- hot to the touch
The breast can also be painful in inflammatory breast cancer, but this is not always the case.
Other possible symptoms include:
- ridges or thickening of the skin of the breast
- pitted skin, like orange peel
- a lump in the breast
- a discharge from the nipple
- an inverted nipple the nipple is pulled into the breast
Inflammatory breast cancer symptoms can appear quite suddenly.
Inflammatory breast cancer is often confused with an infection of the breast . This is because the symptoms are very similar. Mastitis is uncommon in women who aren’t pregnant or breast feeding and it is particularly rare in women who have had their menopause.
Your doctor might give you a course of antibiotics if they think that you could have mastitis. But they will refer you to a specialist if they think you are unlikely to have an infection or if your symptoms dont clear up after antibiotics.
While inflammatory breast cancer can cause these particular symptoms, its worth being aware of the general symptoms of breast cancer.
Make an appointment to see your doctor if you notice any change in the look or feel of your breasts.
Your GP usually refers you to a breast clinic for tests.
You might have a:
- mammogram, which is an x-ray of the breast
- breast ultrasound
- biopsy of the skin in the breast
- biopsy of a breast lump
- MRI scan of the breast
Other tests may include a CT scan or PET-CT scan, and bone scan
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Healthcare providers, including primary care clinicians, radiation, surgical and medical oncologists, and pathologists should form a dynamic team in the management of this complicated and challenging cancer. An individual patient-centered approach should be developed to address the patient’s ethical and social needs. All available community resources should be provided to the patient at the time of obtaining medical care. At the institutional level, conducting mobile screening mammograms for communities, tumor boards, and continuation of medical education conferences for clinicians play a vital role in understanding and improving the awareness of diagnosis and treatment for providers.
Also Check: Stage 3a Breast Cancer Survival
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Lumps usually do not form with inflammatory breast cancer, making the condition harder to diagnose. A mammogram usually does not identify IBC.
Your doctor diagnoses IBC based on your symptoms, a physical examination, and test results. In some cases, doctors rule out other issues that may cause similar symptoms, like infections of the breast tissue . Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat a suspected infection. Let your doctor know immediately if antibiotics do not resolve your symptoms.
To confirm your diagnosis, your doctor takes a tissue sample for further evaluation in a laboratory. The biopsy results allow your doctor to stage the cancer, or determine whether it has spread outside the breast tissue. Biopsies also help doctors discover whether cancer cells may benefit from certain targeted therapies, like hormone drugs.
Your doctor may also order one of these tests to determine whether IBC has spread to other tissues:
- Mammogram: A screening test using low-energy X-rays to create a picture of the inside of the breast
- Ultrasound: Sound waves create pictures of the interior of breasts
- Positron emission tomography : Uses dye containing radioactive drugs to view internal structures and check for diseases
- Computed tomography : Takes several X-rays of the breast, combining them to create a cross-sectional image
- Magnetic resonance imaging : Using radio waves, magnets and a computer, this imaging technique forms pictures of interior body structures and processes
- Bone scan
What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer
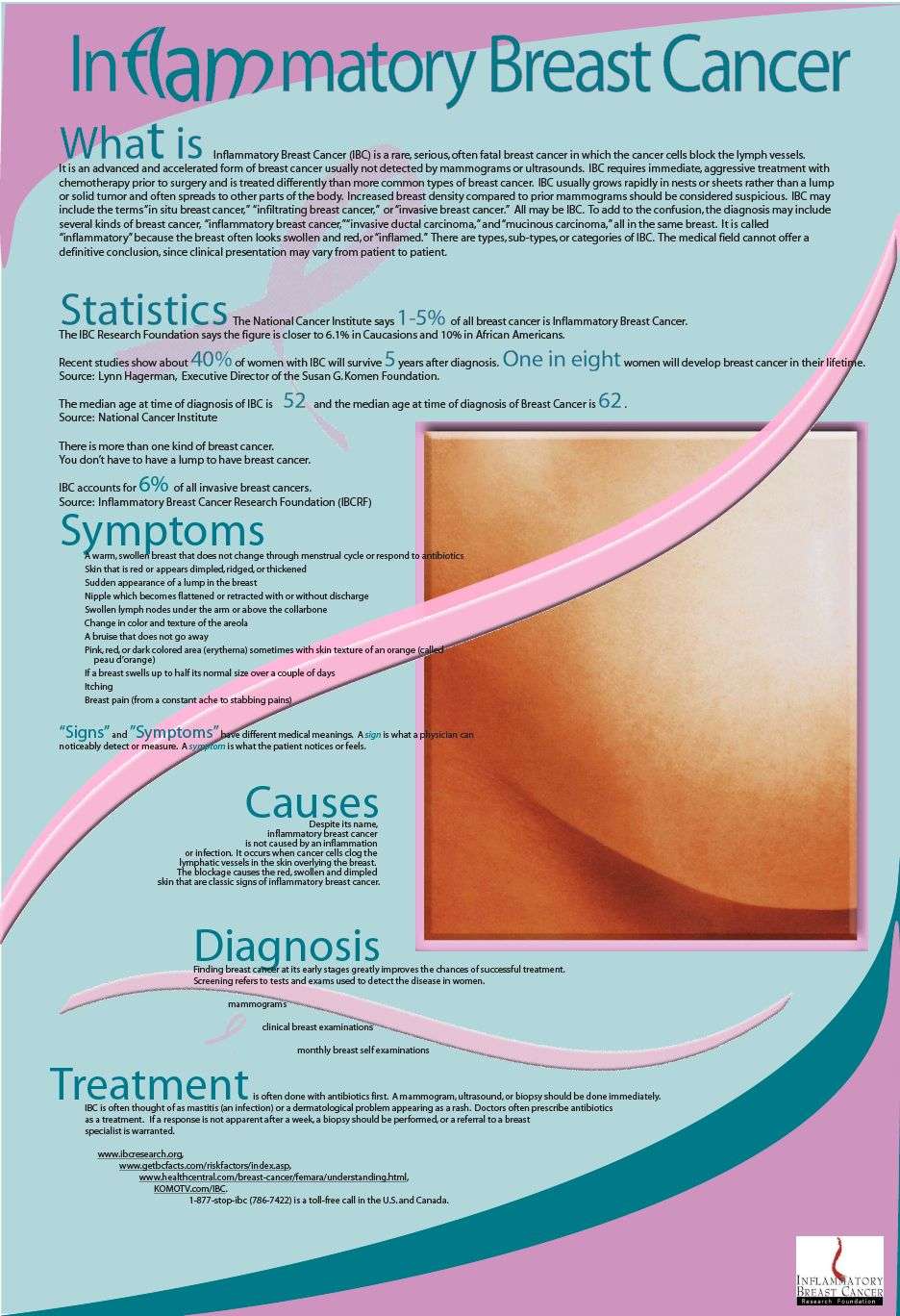
Inflammatory breast cancer is rare and is sometimes thought to be some kind of infection. However, this kind of cancer can develop and spread quickly . It causes redness, swelling, and dimpling in the affected breast. IBC does not usually cause lumps to form in breast tissue. Instead, it appears as a rash or skin texture similar to an orange peel.
The condition results when cancer cells block lymph vesselssmall, hollow tubes allowing lymph fluid to drain out of the breast.
Because IBC can grow quickly , it requires immediate treatment. Doctors usually treat IBC with a combination of therapies, including chemotherapy, surgery and radiation therapy.
Recommended Reading: Does Having Breast Cancer Shorten Life Expectancy
Ibc Signs And Symptoms
Typically, breast cancer symptoms develop slowly over time. With inflammatory breast cancer, however, symptoms progress quickly over days or weeks. Women often report receiving an inaccurate diagnosis of mastitis or breast infection because the symptoms are similar:
- Changed breast appearance, including darkened skin coloring, dimpling, ridges or thickening of the skin
- Flattened or inverted nipple
- Redness covering more than one-third of the breast
- Swelling of lymph nodes near the neck or under the arm
- Swelling that affects one breast, causing it to be larger than the other
- Warm or hot skin
If you experience these symptoms and receive an antibiotic treatment for infection, but your symptoms dont resolve within a week, its important to follow up with your provider.
What Are The Early Signs And Symptoms Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Unlike more common types of breast cancer, this type generally doesnât show up as a lump. The disease grows as nests or sheets under the skin.
Symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer may include:
- Pain in the breast
- Skin changes in the breast area. You may find pink or reddened areas often with the texture and thickness of an orange.
- A bruise on the breast that doesn’t go away
- Sudden swelling of the breast
- Itching of the breast
- Swelling of the lymph nodes under the arm or in the neck
These changes often happen quickly, over a period of weeks.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Cancer Lymph Nodes
Clinical Presentation And Differential Diagnosis
As its name implies, IBC presents as an inflamed-appearing breast with generalized edema and skin thickening, which is often referred to aspeau dorange. The spectrum of IBC symptoms is broadsome patients have diffuse breast involvement associated with skin dimpling and nipple retraction others have more subtle findings, with only faint central skin erythema, and these symptoms can be particularly challenging to discern in women with darker skin tones.
IBC can be categorized as one of three different types: primary IBC, secondary IBC, and locally recurrent breast cancer presenting as IBC. International IBC experts have defined primary IBC as those cases where the breast symptoms had a rapid onset and where at least one-third of the breast skin is involved. Secondary IBC implies the presence of an untreated/neglected breast cancer that progressed into an inflammatory state. Sadly, some patients will experience an inflammatory recurrence following appropriate treatment for an early-stage breast cancer. Regardless of the prior cancer history, the clinical management of all three IBC patterns is the same.
Sanford H. Barsky, … Richard Love, in, 2009
Quick Facts About Inflammatory Breast Cancer
- IBC doesn’t look like other breast cancer.
- There usually isn’t a lump.
- It doesn’t always show up on a mammogram.
- IBC is more aggressive and is almost always “locally advanced” when diagnosed. One-third of patients have metastatic cancer at diagnosis.
- It’s more common in black women, whereas other breast cancers are more common in white women.
- IBC occurs more often in overweight or obese women.
- IBC can be mistaken to be mastitis, a breast infection usually seen in women who are nursing.
- IBC is a not a new disease IBC was first identified and described in 1814 by Sir Charles Bell.
- Black women are at higher risk for IBC.
- Men can also develop IBC.
Read Also: What Is Stage 3a Cancer
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for breast cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the breast.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the breast to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
Survival Rates For Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer is considered an aggressive cancer because it grows quickly, is more likely to have spread at the time its found, and is more likely to come back after treatment than other types of breast cancer. The outlook is generally not as good as it is for other types of breast cancer.
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
You May Like: Baking Soda And Molasses Cure Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Ibc And When Do They Develop
IBC symptoms can develop in three to six months. They are a result of lymph vessels becoming blocked and white blood cells building up. These symptoms include:
- Large patches of redness
- Swelling and warmth on your breast
- Dimpling or a thickness to the skin, giving it the texture and appearance of an orange peel
- Flat, inverted, bruised-looking nipple
- Itching
- Generalized pain
These blockages may also cause the lymph nodes under your arm or around your collarbone to become swollen. If youre pregnant or breastfeeding, some of these symptoms might be mistaken for a common breast infection called mastitis. This is caused by breast tissue inflammation that usually affects people who are lactating, and they may or may not have an infection. You may initially be diagnosed with this condition and sent home with antibiotics. Its important to talk to your doctor if your symptoms dont go away in seven to 10 days.
Targeted Therapies And Hormone Therapy
Many inflammatory breast cancers are HER2 positive , so treatment with HER2-targeted therapies can be effective in controlling the tumor. These drugs are usually given along with the other treatments after a diagnosis of IBC. If the cancer is sensitive to estrogen, hormone therapy may also be an option.
Most inflammatory breast cancers are estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor negative, so hormonal therapy with tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors isn’t commonly used.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Advanced Breast Cancer
Special Case: Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer is an aggressive form of cancer marked by the classic finding of peau d’orange and a relatively poor prognosis.6 These cancers may require aggressive surgical resection in addition to chemotherapy and irradiation, and have a relatively high recurrence rate.7,8 Reconstruction in this setting can be particularly challenging as the diffuse skin and lymphatic involvement can require extensive resection of the breast, chest wall, and skin, resulting in an extensive mastectomy defect. Furthermore, the need for radiotherapy increases the rate of poor patient outcomes. While some surgeons consider inflammatory breast cancer a relative contraindication to reconstruction, others note the utility of autogenous flaps in helping to provide durable, vascularized coverage over the chest wall in anticipation of postmastectomy radiation.9,10
Relatively little reconstructive data exists on this rare cohort.10 In the largest study to date,9 59 women, all of whom received chemotherapy and radiation, underwent 52 delayed and 7 immediate autogenous reconstructions. Complications occurred in nearly 36% of patients, with one total flap loss.
A. Sahin, H. Zhang, in, 2014
Inflammatory Breast Cancer And Hormone Receptor Status
Inflammatory breast cancer tumors often have increasedangiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.
Furthermore, IBC tumors also frequently show an overexpression of HER-2, RhoC GTPase, and NF–B genes.
Inflammatory breast cancers are more likely to be negative for Estrogen receptor status and/or progesterone receptor status .
Inflammatory breast cancer tumors have a higher frequency of ER- and PR- tumors in comparison to other advanced breast cancer tumors. Indeed, some studies show that up to 83% of IBC tumors are ER-. This tends to affect the efficacy of treatment as the tumors do not respond to hormone therapy.
Data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database show a higher median survival rate in inflammatory breast cancer ER+ tumors compared with ER- tumors .
Recommended Reading: Tamoxifen Metastatic Breast Cancer
Inflammatory Breast Cancer: Symptoms & Signs
- Medical Author: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD
Medically Reviewed on 9/10/2019
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare type of breast cancer that spreads to the lymphatic system, causing signs and symptoms of inflammation in the involved breast. It is an aggressive form of breast cancer.
Many breast cancers do not cause symptoms or signs at diagnosis, but inflammatory breast cancer is different. It produces characteristic symptoms including swelling, warmth, and redness of the breast. Other associated symptoms can include pitting, skin changes, dimpling, bruising, inversion of the nipple, burning pain, tenderness, and a rapid increase in the size of the breast. Enlarged lymph nodes in the underarm or beneath the collarbone may be present.
Causes of inflammatory breast cancer
The causes of inflammatory breast cancer are unknown.
Other inflammatory breast cancer symptoms and signs
- Breast Dimpling or Pitting Like an Orange Peel
- Breast Discoloration or Bruising