Results Of A Breast Ultrasound
A radiologist will examine the images from your breast ultrasound and send the results to your primary care doctor, if you have one.
The images that a breast ultrasound produces are in black and white. Cysts, tumors, and growths will appear as dark areas on the scan.
However, a dark spot on your ultrasound doesnt mean that you have breast cancer. Most breast lumps are benign, or noncancerous.
Several conditions can cause benign lumps in the breast, including:
- fibrocystic breast disease, in which hormonal changes cause the breasts to become lumpy and tender
- fibroadenoma, which is a benign tumor of the breast tissue
Read Also: Natural Cures For Breast Cancer
What Does Breast Cancer Look Like On An Ultrasound Topic Guide
How Do I Get Ready For A Breast Ultrasound
-
Your healthcare provider will explain the procedure to you. Ask any questions you have about the procedure.
-
You may be asked to sign a consent form that gives permission to do the test. Read the form carefully and ask questions if anything is not clear.
-
You do not need to stop eating or drinking before the test. You also will not need medicine to help you relax.
-
You should not put any lotion, powder, or other substances on your breasts on the day of the test.
-
Wear clothing that you can easily take off. Or wear clothing that lets the radiologist or technologist reach your chest. The gel put on your skin during the test does not stain clothing, but you may want to wear older clothing. The gel may not be completely removed from your skin afterward.
-
Follow any other instructions your healthcare provider gives you to get ready.
Also Check: Stage 2 Breast Cancer Metastasis
Read Also: Can Human Papillomavirus Cause Breast Cancer
When Might A Person Need One
A doctor typically does not order an ultrasound on its own. Instead, they will use an ultrasound to get more information about abnormalities found during other testing methods.
For example, they may order an ultrasound to check a lump that a person can feel during a physical examination but that a mammogram does not detect. The ultrasound image can also help a doctor distinguish between a solid mass and a fluid-filled sac, which healthcare professionals refer to as a cyst.
A healthcare professional may use a breast ultrasound as a guide for a biopsy. If they detect a lump that may be cancerous, they can use the technique to guide a needle to acquire a small tissue sample for testing.
If the biopsy results indicate a lump is cancerous, a doctor can use an ultrasound to examine the tissue around the lump in more detail and help determine its size.
A healthcare professional can then use the size of the lump to determine the clinical stage of the cancer.
Breast Cancer Tumor Cells
Under the microscope, breast cancer cells may appear similar to normal breast cells. They also may look quite different, depending on the tumor’s growth and grade.
Cancer cells differ from normal cells in many ways. The cells may be arranged in clusters. They also may be seen invading blood vessels or lymphatic vessels.
The nucleus of cancer cells can be striking, with nuclei that are larger and irregular in shape. These centers will stain darker with special dyes. Often, there are extra nuclei rather than just one center.
You May Like: What Is Localized Breast Cancer
Mammogram And Breast Ultrasound
If you have symptoms and have been referred to a specialist breast unit by a GP, you’ll probably be invited to have a mammogram, which is an X-ray of your breasts. You may also need an ultrasound scan.
If cancer was detected through the NHS Breast Screening Programme, you may need another mammogram or ultrasound scan.
Your doctor may suggest that you only have a breast ultrasound scan if you’re under the age of 35. This is because younger women have denser breasts, which means a mammogram is not as effective as ultrasound in detecting cancer.
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of the inside of your breasts, showing any lumps or abnormalities.
Your breast specialist may also suggest a breast ultrasound if they need to know whether a lump in your breast is solid or contains liquid.
Find out more about breast screening.
How Painful Is A Breast Biopsy
You will be awake during your biopsy and should have little discomfort. Many women report little pain and no scarring on the breast. However, certain patients, including those with dense breast tissue or abnormalities near the chest wall or behind the nipple, may be more sensitive during the procedure.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Know If I Have Breast Cancer
What Does The Equipment Look Like
Ultrasound machines consist of a computer console, video monitor and an attached transducer. The transducer is a small hand-held device that resembles a microphone. Some exams may use different transducers during a single exam. The transducer sends out inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body and listens for the returning echoes. The same principles apply to sonar used by boats and submarines.
The technologist applies a small amount of gel to the area under examination and places the transducer there. The gel allows sound waves to travel back and forth between the transducer and the area under examination. The ultrasound image is immediately visible on a video monitor. The computer creates the image based on the loudness , pitch , and time it takes for the ultrasound signal to return to the transducer. It also considers what type of body structure and/or tissue the sound is traveling through.
How You Have It
The ultrasound scanner has a microphone that gives off sound waves. The sound waves bounce off the organs inside your body, and the microphone picks them up.
The microphone links to a computer that turns the sound waves into a picture on the screen. A sonographer will do your ultrasound. A sonographer is a trained professional who is a specialist in ultrasound scanning.
Also Check: How Does It Feel When You Have Breast Cancer
Can Radiologist Tell If It Is Cancer
While even the most advanced imaging technology doesnt allow radiologists to identify cancer with certainty, it does give them some strong clues about what deserves a closer look. Today well discuss a few things that radiologists are on the lookout for when examining mammography and breast ultrasound images.
What Is Breast Ultrasound
Breast ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to look at the inside of your breasts. It can help your healthcare provider find breast problems. It also lets your healthcare provider see how well blood is flowing to areas in your breasts. This test is often used when a change has been seen on a mammogram or when a change is felt, but does not show up on a mammogram.
The healthcare provider moves a wand-like device called a transducer over your skin to make the images of your breasts. The transducer sends out sound waves that bounce off your breast tissue. The sound waves are too high-pitched for you to hear. The transducer then picks up the bounced sound waves. These are made into pictures of the inside of your breasts.
Your healthcare provider can add another device called a Doppler probe to the transducer. This probe lets your healthcare provider hear the sound waves the transducer sends out. He or she can hear how fast blood is flowing through a blood vessel and in which direction it is flowing. No sound or a faint sound may mean that you have a blockage in the flow.
Ultrasound is safe to have during pregnancy because it does not use radiation. It is also safe for people who are allergic to contrast dye because it does not use dye.
You May Like: What Shape Are Breast Cancer Lumps
How Does Elastography Help With Breast Cancer
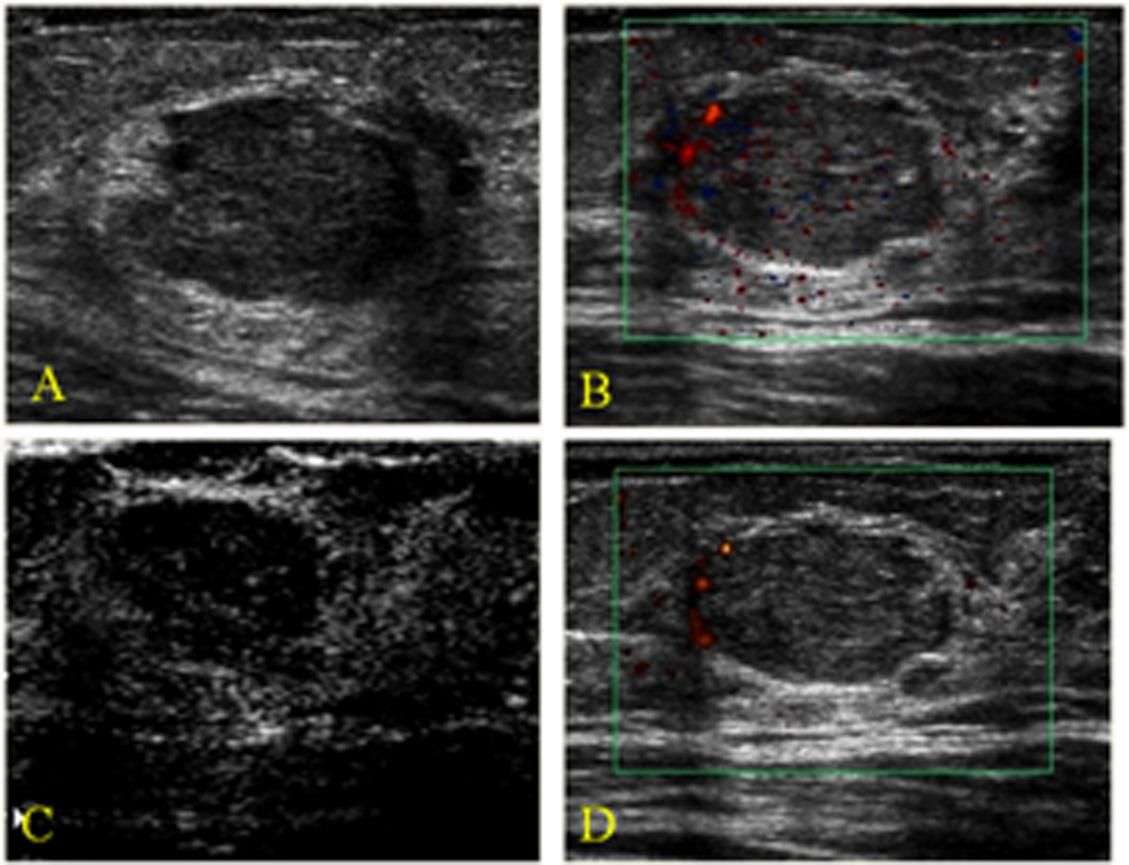
Ultrasound elastography is an additional software to assess tissue elasticity. Many papers have shown that it enhances diagnostic accuracy. Malignant lesions are generally harder than benign lesions. Therefore, elastography appears to increase the sensitivity and specificity of breast ultrasound by demonstrating the firmness of the mass. In the example shown, the colour bar at the left top corner is set to show red as soft and blue as hard. In the image shown, the blue region in the middle of the image corresponds to the mass seen on the scan. This indicates that the mass is stiff or hard in consistency.
What Does Breast Cancer Look Like On A Mammogram
Any area that does not look like normal tissue is a possible cause for concern. The radiologist will look for areas of white, high-density tissue and note its size, shape, and edges.
A lump or tumor will show up as a focused white area on a mammogram. Tumors can be cancerous or benign.
If a tumor is benign, it is not a health risk and is unlikely to grow or change shape. Most tumors found in the breasts are non-cancerous.
Small white specks are usually harmless. The radiologist will check their shape and pattern, as they can sometimes be a sign of cancer.
As well as dense breast tissue and possible tumors, a radiologist will look for anything unusual on a mammogram.
Other abnormalities include:
A mass may refer to a tumor, cyst, or fibroadenoma, whether it is cancerous or not.
A mammogram can also give a person information about their breast density. People with dense breasts have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer. Dense breasts can make it more difficult to find abnormalities on a mammogram.
Mammograms are still possible if a person has had breast cancer surgery or implants. However, it may be necessary to take more images of each breast, and it might take longer to check the images.
A radiologist will often compare a mammogram against previous images. This can help them to spot any changes and decide whether an unusual area could be a sign of cancer.
Also Check: What Age Does Breast Cancer Start
Appearance With A Biopsy
When a breast biopsy is done, tissue is removed and sent to a pathologist. They will look at it under a microscope. Usually, special genetic studies are done as well.
The pathologist looks at the size and shape of the cells, as well as their arrangement if the tissue sample was taken by using a core needle biopsy. That’s also true for an open biopsy done by making a cut through the skin to remove the sample.
What Are The Limitations Of Ultrasound Imaging Of The Breast
- Ultrasound is one of the tools used in breast imaging, but it does not replace annual mammography.
- Many cancers are not visible on ultrasound. Many calcifications seen on mammography cannot be seen on ultrasound. Some early breast cancers only show up as calcifications on mammography. MRI findings that are due to cancer are not always seen with ultrasound.
- Biopsy may be recommended to determine if a suspicious abnormality is cancer or not.
- Most suspicious findings on ultrasound that require biopsy are not cancers.
- Many facilities do not offer ultrasound screening, even in women with dense breasts, and the procedure may not be covered by some insurance plans.
- It is important to choose a facility with expertise in breast ultrasound, preferably one where the radiologists specialize in breast imaging. Ultrasound depends on the abnormality being recognized at the time of the scan as it is a “real-time” examination. This requires experience and good equipment. One measure of a facility’s expertise in breast ultrasound can be found in its ACR accreditation status. Check the facilities in your area by searching the ACR-accredited facilities database.
Also Check: Who Is Most Likely To Get Breast Cancer
Signs Of Benign Breast Masses
In contrast to breast cancer tumors, benign lumps are often squishy. They may feel like a soft rubber ball with well-defined margins. Theyâre often easy to move around and may be tender.
Infections in the breast can cause redness and swelling. Sometimes it can be difficult to tell the difference between mastitis and inflammatory breast cancer, but mastitis often causes symptoms of fever, chills, and body aches. Those symptoms arenât associated with cancer.
How Does The Procedure Work
Ultrasound imaging uses the same principles as the sonar that bats, ships, and fishermen use. When a sound wave strikes an object, it bounces back or echoes. By measuring these echo waves, it is possible to determine how far away the object is as well as its size, shape, and consistency. This includes whether the object is solid or filled with fluid.
Doctors use ultrasound to detect changes in the appearance of organs, tissues, and vessels and to detect abnormal masses, such as tumors.
In an ultrasound exam, a transducer both sends the sound waves and records the echoing waves. When the transducer is pressed against the skin, it sends small pulses of inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body. As the sound waves bounce off internal organs, fluids and tissues, the sensitive receiver in the transducer records tiny changes in the sound’s pitch and direction. A computer instantly measures these signature waves and displays them as real-time pictures on a monitor. The technologist typically captures one or more frames of the moving pictures as still images. They may also save short video loops of the images.
Doppler ultrasound, a special ultrasound technique, measures the direction and speed of blood cells as they move through vessels. The movement of blood cells causes a change in pitch of the reflected sound waves . A computer collects and processes the sounds and creates graphs or color pictures that represent the flow of blood through the blood vessels.
Don’t Miss: How Big Are The Lumps In Breast Cancer
What Are The Benefits Of A Breast Ultrasound
Ultrasound examination allows the detection and identification of most breast lumps. It is especially useful in distinguishing between solid and fluid-filled lumps.
If the ultrasound does not identify a lump that you or your doctor can feel, then other tests, such as mammography or magnetic resonance imaging , may be required to examine the breast.
Read Also: Signs Of Breast Cancer Recurrence After Mastectomy
What Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Invasive breast cancer develops when abnormal cells originally found in the linings of the breast milk ducts invade surrounding tissue. A breast mass is shown here with indistinct, spiculated borders, which suggest the presence of tissue invasion in invasive ductal carcinoma.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Breast Cancer In Men
Normal Breast Parenchymal Patterns
In the young non-lactating breast, the parenchyma is primarily composed of fibroglandular tissue, with little or no subcutaneous fat. With increasing age and parity, more and more fat gets deposited in both the subcutaneous and retromammary layers .
Normal breast. Mid transverse scan of a normal breast. The fibroglandular parenchyma is echogenic and is surrounded by hypoechoic fat
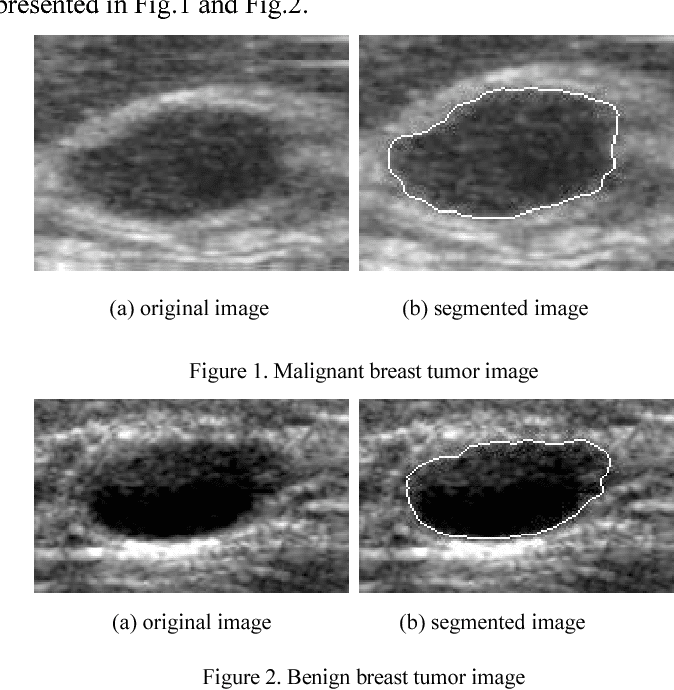
Appearance On An Ultrasound
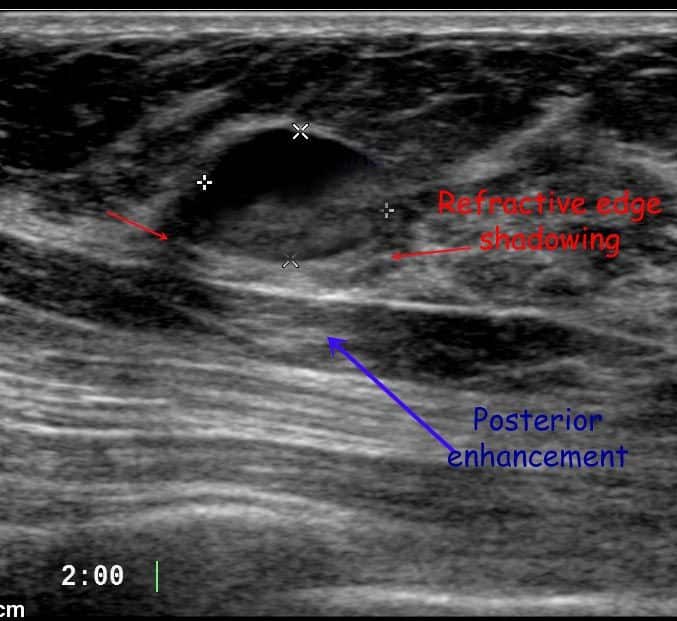
Breast ultrasound can detect some lumps that a mammogram cannot. It is also used to help diagnose masses found on a mammogram.
Ultrasound can help tell the difference between fluid-filled cysts, which aren’t likely to be cancerous, and hard cysts that need further testing. Hard cysts are more likely to be cancerous.
On an ultrasound report, the term “hypoechoic” refers to an area that appears darker in the images. This means the area is solid.
Also Check: What Types Of Breast Cancer Are There
Color Doppler Sonography: Characterizing Breast Lesions
Atif Hashmi, Susan Ackerman and Abid Irshad
Department of Radiology, Medical University of South Carolina, PO Box 250322, 169 Ashley Avenue, Charleston, SC 29425, USA
- *Corresponding Author:
- Department of Radiology, Medical University of South Carolina PO Box 250322, 169 Ashley Avenue CharlestonSC 29425, USA Tel: +1 843 792 1957 Fax:+1 843 792 9503 E-mail:
How Is The Procedure Performed
You will lie on your back or on your side on the exam table. The sonographer may ask you to raise your arm above your head.
The radiologist or sonographer will position you on the exam table. They will apply a water-based gel to the area of the body under examination. The gel will help the transducer make secure contact with the body. It also eliminates air pockets between the transducer and the skin that can block the sound waves from passing into your body. The sonographer places the transducer on the body and moves it back and forth over the area of interest until it captures the desired images.
There is usually no discomfort from pressure as they press the transducer against the area being examined. However, if the area is tender, you may feel pressure or minor pain from the transducer.
Doctors perform Doppler sonography with the same transducer.
Once the imaging is complete, the technologist will wipe off the clear ultrasound gel from your skin. Any portions that remain will dry quickly. The ultrasound gel does not usually stain or discolor clothing.
Recommended Reading: Are Male Breast Cancer Lumps Painful
What Does Red And Blue On Ultrasound Mean
Vessels in which blood is flowing are colored red for flow in one direction and blue for flow in the other, with a color scale that reflects the speed of the flow. Because different colors are used to designate the direction of blood flow, this Doppler technique simplifies interpretation of the ultrasound data. Types.