Why Receptor Status Matters
Breast cancer is not a single disease, and researchers now have the ability to break down breast cancer into different subtypes based on the receptor status of the tumors. Among the variations between different types of breast cancers are the proteins found on cell surfaces, which are involved tumor growth. These proteins are related to the genetic material of cancer cells.
For example, with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer, estrogen binds to specific receptors on breast cancer cells, stimulating proliferation. Similarly, HER2 receptors on the surface of breast cancer cells are stimulated by HER2 protein, promoting the growth and spread of breast cancer.
It’s important to note, however, that all breast cellsboth cancerous and noncanceroushave HER2 receptors on their surfaces. The difference is that HER2-positive breast cancer cells have 40 to 100 times more receptors than HER2-negative breast cancer cells or normal breast cells. In positive cases, the abundance of receptors fuels the cancer.
Breast Cancer Discussion Guide
Get our printable guide for your next healthcare provider’s appointment to help you ask the right questions.
How Is Lobular Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Your doctor will likely order a mammogram and ultrasound to look for abnormal breast tissue. A breast MRI scan is a more sensitive test for detecting breast cancer. Your doctor may order this test if you are at higher risk of breast cancer or if mammogram or ultrasound findings raise concerns that should be investigated further.
If abnormal breast tissue is seen on breast imaging, a small sample of tissue is taken from the area of concern using a needle and examined under a microscope. The results of the biopsy either confirm or rule out a diagnosis of breast cancer.
Why Do I Need Her2 Breast Cancer Testing
If you’ve been diagnosed with breast cancer, you may need this test to find out if your cancer is HER2-positive or HER2-negative. If you are already being treated for HER2-positive breast cancer, you may need this test to:
- Find out if your treatment is working. Normal levels of HER2 may mean you are responding to treatment. High levels may mean the treatment is not working.
- Find out if cancer has come back after treatment.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Side Effects Of Breast Cancer
How Are Breast Tumors Tested For Her2
Either a test called an immunohistochemistry test or fluorescence in situ hybridization test is used to find out if cancer cells have a high level of the HER2 protein.
See Testing Biopsy and Cytology Specimens for Cancer and Understanding Your Pathology Report: Breast Cancerto get more details about these tests.
Prognosis For Metastatic Her2+ Cancer
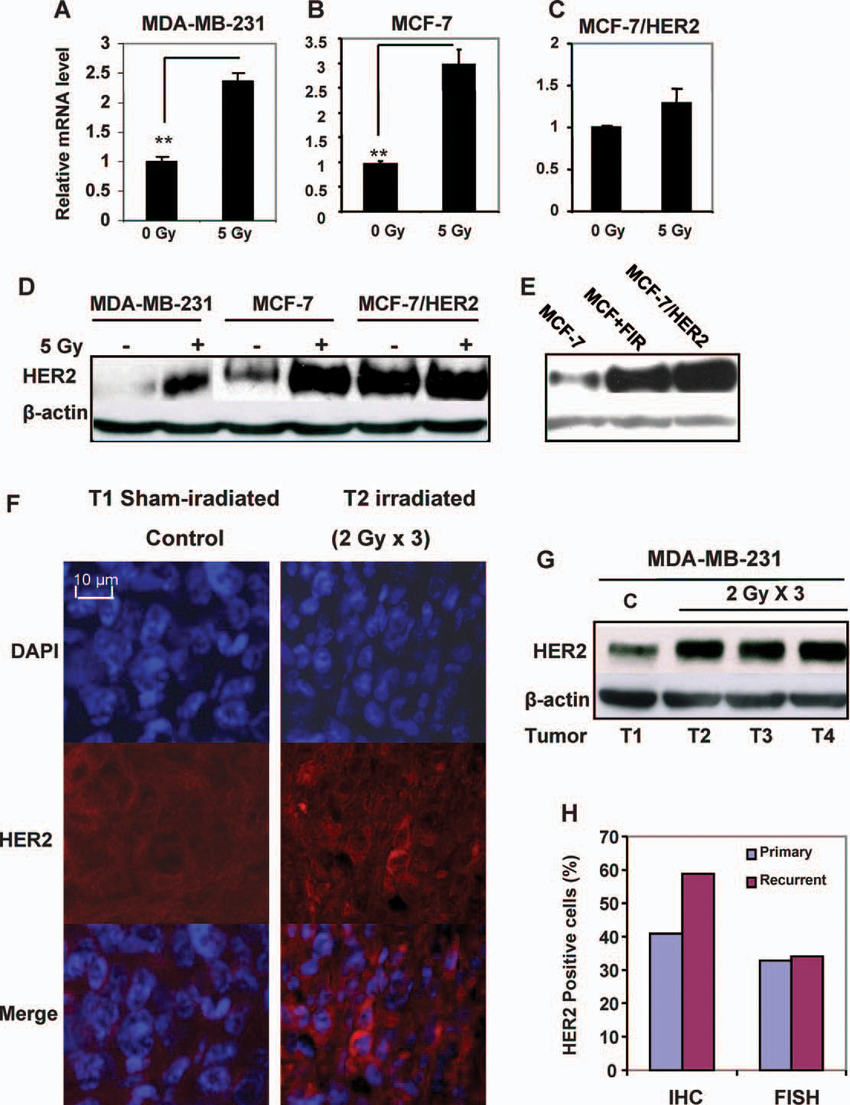
Generally, when breast cancer becomes metastatic, it is not possible to cure the cancer. This does not mean that the cancer isnt treatable, though. Data from the National Cancer Institute estimates that for those diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer, 29% have a five-year survival rate. This means that 29% of the people with that cancer are still alive in five years.
Recommended Reading: Whats The Youngest You Can Get Breast Cancer
Examples Using The Full Staging System
Because there are so many factors that go into stage grouping for breast cancer, it’s not possible to describe here every combination that might be included in each stage. The many different possible combinations mean that two women who have the same stage of breast cancer might have different factors that make up their stage.
Here are 3 examples of how all of the factors listed above are used to determine the pathologic breast cancer stage:
Histopathological Subtypes: Morphologic Heterogeneity
The histopathological classification of BC is set by the 2012 World Health Organization . Most of the breast cancers are adenocarcinomas, with around 7080% defined as invasive ductal carcinomas not otherwise specified . The rest, around 2530%, are characterized by histological special types such as papilar, metaplastic, cribiform, apocrine, or mucinous carcinomas, among others . The majority of special types is rare and differ strongly about prognosis and response to the treatments . The tumor grade is the other important intrinsic characteristic of tumoral heterogeneity .
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Breast Cancer
How Can I Tell If My Treatment Is Working
One way youll know is if your pain starts going away, Brufsky says. Your doctor will also monitor your progress every few months with a variety of assessments, which may include a physical exam, blood tests to check for tumor markers, and imaging tests: X-ray, CT scan, PET scan, or bone scan. The results of these tests, combined with the symptoms you report, will help your cancer team understand whether your treatment is helping to control tumor growth, according to Breastcancer.org.
Treatment is typically continued if its working and your side effects are manageable, but if the treatment is no longer working or the side effects are problematic, your doctor may switch you to a different drug. We expect that just about every treatment we choose will work for a period of time and then likely stop working as the cancer develops resistance, Brufsky says. Fortunately, we have many treatments that are effective with HR-positive/HER-2-negative metastatic breast cancer.
Determining Your Her2 Status
A breast biopsy is used to determine HER2 status. The biopsy can be sent for laboratory testing with an immunohistochemistry test. The fluorescence in situ hybridization test looks for the HER2 gene in breast cancer cells.
The results of an immunohistochemistry test show different levels of HER2 positivity. For example, a tumor may be reported as 0, 1+, 2+, or 3+. Tumors with a higher number may be referred to as having an overexpression of HER2.
According to the American Cancer Society, immunohistochemistry test results should be considered as follows:
| Designation | |
|---|---|
| Equivocal | |
| 3+ | HER2-positive |
The impact of being HER2-positive on breast cancer survival is, of course, a top concern. Unfortunately, statistics can be misleading without considering other aspects of your diagnosis, including cancer stage at diagnosis and whether the tumor is also estrogen and/or progesterone receptor-positive.
With this in mind, you may also be tested for progesterone and estrogen receptors. Triple-negative breast cancers are negative for HER2, estrogen, and progesterone, while triple-positive breast cancers are positive for all three.
Read Also: Low Grade Breast Cancer Prognosis
Other Factors To Consider
Breast cancer staging is difficult. A tumor grading system and the presence of specific receptors in breast cancer cells are two more elements that might influence the overall staging diagnosis. A tumor grading system indicates how quickly cancer cells are expected to develop and spread. The cancer is regarded as more aggressive at higher grades.
What Does Phesgo Treat
PHESGO® is a prescription medicine approved for use in combination with chemotherapy for:
- use prior to surgery in adults with HER2-positive, locally advanced, inflammatory, or early stage breast cancer . PHESGO should be used as part of a complete treatment regimen for early breast cancer.
- use after surgery in adults with HER2-positive early breast cancer that has a high likelihood of coming back.
PHESGO is a prescription medicine approved for use in combination with docetaxel in adults who have HER2-positive breast cancer that has spread to different parts of the body and who have not received anti-HER2 therapy or chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer.
Also Check: Stage 4 Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment
Breast Cancer Chemotherapy Can Use Agents Which Specifically Target Her
Sometimes medics will also treat HER-2 positive tumors with targeting agents such as
Physicians will also sometimes employ hormonal therapy, such as anthracylines, and taxanes, to minimize the growth effect of HER-2 positive breast cancers.
Since the rate of local recurrence is typically quite high with HER-2 postive tumors, radiation therapy is sometimes useful in addition to trastuzumab-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and generally with good effect.
There Are Two Ways To Measure The Her
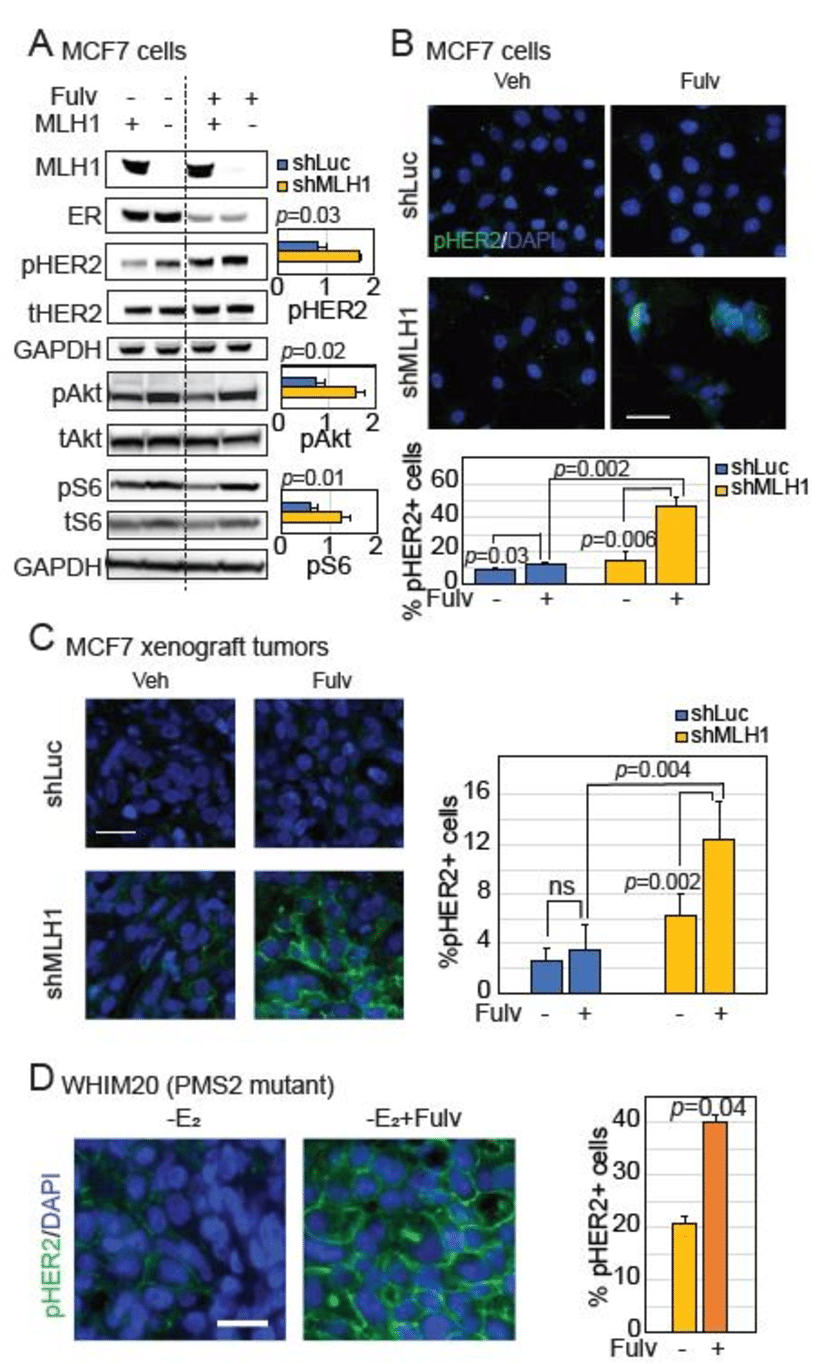
The most common way to measure the HER-2 status of a potential breast cancer tumor is through an immunohistochemistry test. This will likely be part of an overall histological/pathological evaluation of the tumor.
Various tumor markers, including the HER-2 status indicators, give the pathologist a characterization of the tumor. This helps to predict the future behavior and probable responses, of the tumor to different types of treatments.
The immunohistochemistry test of the HER-2 status measures the over-expression of a particular protein and is typically given a score of 0 to +3.
The pathologist actually counts the number of receptors on the surface of the cancer cells. Indeed, the pathologist can see the cells microscopically because they are receptive to certain protein-based dyes and change color.
Scores of 0 and +1 are indicative of a negative status , whilst +2 and +3 are HER-2 positive . There is no in-between state.
You May Like: What Does Stage 4 Breast Cancer Mean
Stage The Stage Is The Main Prognostic Factor For Breast Cancer There Is Less Risk That Early Stage Breast Cancer Will Come Back So It Has A More Favourable Prognosis Breast Cancer Diagnosed At A Later Stage Has A Greater Risk Of Recurrence So It Has A Less Favourable Prognosis Doctors Will Consider If Cancer Has Spread To Lymph Nodes And The Size Of The Tumour When They Predict A Prognosis
If cancer has spread to lymph nodes
Whether or not cancer has spread to lymph nodes is the most important prognostic factor for breast cancer. Breast cancer that has spread to lymph nodes has a higher risk of coming back and a less favourable prognosis than breast cancer that has not spread to the lymph nodes.
The number of lymph nodes that contain cancer is also important. The more positive lymph nodes there are, the higher the risk that breast cancer will come back. Breast cancer that has spread to 4 or more lymph nodes has the highest risk for recurrence.
The size of the tumour
The size of the tumour is the 2nd most important prognostic factor for breast cancer. The tumour size will affect prognosis no matter how many lymph nodes have cancer in them.
Breast tumours that are 5 cm or larger are more likely to come back after treatment than smaller tumours. Breast tumours that are smaller than 1 cm and have not spread to the lymph nodes have a very favourable prognosis.
Should I Have Breast Reconstruction And When
This is another question that has a multi-layered answer. It involves both medical and personal considerations. Some women opt not to have reconstruction. Others believe it benefits their appearance and psychological recovery.
This is another question that has a multi-layered answer. It involves both medical and personal considerations. Some women opt not to have reconstruction. Others believe it benefits their appearance and psychological recovery.
If youre having one or both breasts removed and are considering reconstruction, the stage of your cancer may dictate the timing of the reconstructive surgery. For patients with early-stage breast cancer, Dr. Abraham says immediate reconstruction is reasonable. With a Stage III cancer, you should discuss with your oncologist and surgeon whether immediate reconstruction is advisable.
Don’t Miss: Can Weight Gain Be A Symptom Of Breast Cancer
Who May Not Be Able To Have Herceptin
Herceptin should not be used to treat people with breast, oesophageal or stomach cancer that is not HER2 positive.
It may also not be suitable if:
- you have a pre-existing heart condition, such as heart failure, severe angina or a problem with your heart valves
- you have poorly controlled high blood pressure
- you’re pregnant
- you’re breastfeeding
Avoid becoming pregnant while taking herceptin and for at least 7 months after treatment stops, as it could harm your developing baby.
Also avoid breastfeeding until at least 7 months after treatment stops, as the medicine can enter breast milk and may be harmful for babies.
M Categories For Breast Cancer
M followed by a 0 or 1 indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs — for example, the lungs, liver, or bones.
M0: No distant spread is found on x-rays or by physical exam.
cM0: Small numbers of cancer cells are found in blood or bone marrow , or tiny areas of cancer spread are found in lymph nodes away from the underarm, collarbone, or internal mammary areas.
M1: Cancer has spread to distant organs as seen on imaging tests or by physical exam, and/or a biopsy of one of these areas proves cancer has spread and is larger than 0.2mm.
You May Like: How To Detect Breast Cancer Early
Will I Ever Be Cured
Oncologists dont talk about curing stage 4 breast cancer as much as managing it as you would other chronic diseases, according to Brufsky. Were not likely going to get rid of every single bit of cancer, but were learning that people can live with this disease and be asymptomatic for years and years, he explains. While the mean survival of patients with HR-positive/HER-2-negative metastatic breast cancer is now over five years, its hard to say what the future holds for a woman diagnosed with the disease today. The field is changing so quickly and dramatically that in two or three years, this will be a different conversation.
Complications And Side Consequences
All therapies have some degree of adverse effect, ranging from minor to severe. Most clear up after therapy, but there may be some long-term consequences. Its critical to inform your oncologist about any symptoms, no matter how small they seem. Your healthcare team will collaborate with you to manage side effects and problems.
Recommended Reading: Lymph Node Metastasis Breast Cancer
What Should I Know About Side Effects With Phesgo
- Not all people have serious side effects however, side effects with PHESGO therapy are common. It is important to know what side effects may happen and what symptoms you should watch for
- Your doctor may stop treatment if serious side effects happen. Be sure to contact your healthcare team right away if you have questions or are worried about any side effects
What Is The Staging For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
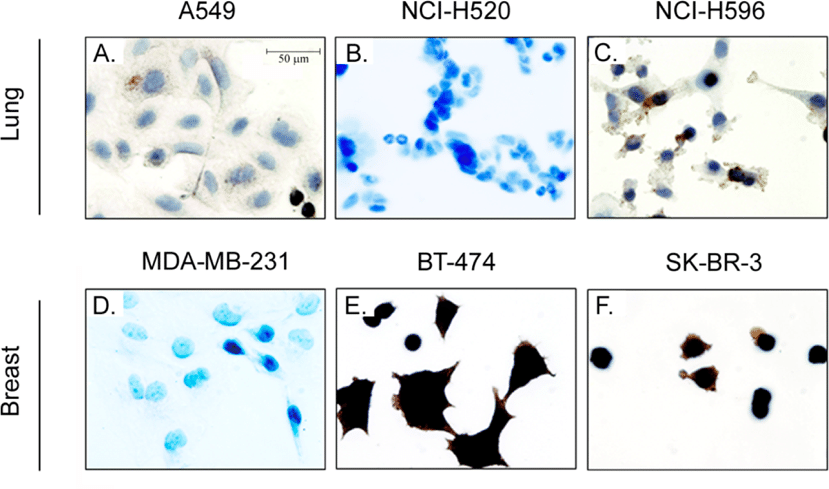
Staging refers to the extent of a cancer. A cancer is always referred to by the stage it was determined to be at diagnosis, even if it spreads.
Stages of invasive ductal carcinoma include:
- Stage I: Breast tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters in diameter and the cancer has not spread beyond the breast
- Stage II: Breast tumor measures 2 to 4 centimeters in diameter or cancerous cells have spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area
- Stage III: Cancer is more extensive but it is confined to the breast, surrounding tissues, and lymph nodes
- Stage IV: Breast cancer has spread to lymph nodes beyond the underarm area or to distant sites, such as the lungs, liver, bones, or brain
You May Like: Chemotherapy For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What Happens During A Her2 Breast Cancer Test
Most HER2 testing involves taking a sample of tumor tissue in a procedure called a biopsy. There are three main types of biopsy procedures:
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy, which uses a very thin needle to remove a sample of breast cells or fluid
- Core needle biopsy, which uses a larger needle to remove a sample
- Surgical biopsy, which removes a sample in a minor, outpatient procedure
Fine needle aspiration and core needle biopsies usually include the following steps:
- You will lay on your side or sit on an exam table.
- A health care provider will clean the biopsy site and inject it with an anesthetic so you won’t feel any pain during the procedure.
- Once the area is numb, the provider will insert either a fine aspiration needle or core biopsy needle into the biopsy site and remove a sample of tissue or fluid.
- You may feel a little pressure when the sample is withdrawn.
- Pressure will be applied to the biopsy site until the bleeding stops.
- Your provider will apply a sterile bandage at the biopsy site.
In a surgical biopsy, a surgeon will make a small cut in your skin to remove all or part of a breast lump. A surgical biopsy is sometimes done if the lump can’t be reached with a needle biopsy. Surgical biopsies usually include the following steps.
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
DCIS is the most common type of noninvasive breast cancer, with about 60,000 new cases diagnosed in the United States each year. About one in every five new breast cancer cases is ductal carcinoma in situ.
Also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer, its considered a noninvasive breast cancer. With DCIS, abnormal and cancerous cells havent spread from the ducts into nearby breast tissue nor anywhere else, such as the lymph nodes.
DCIS is divided into several subtypes, mainly according to the appearance of the tumor. These subtypes include micropapillary, papillary, solid, cribriform and comedo.
Patients with ductal carcinoma in situ are typically at higher risk for seeing their cancer return after treatment, although the chance of a recurrence is less than 30 percent. Most recurrences occur within five to 10 years after the initial diagnosis and may be invasive or noninvasive. DCIS also carries a heightened risk for developing a new breast cancer in the other breast. A recurrence of ductal carcinoma in situ would require additional treatment.
The type of therapy selected may affect the likelihood of recurrence. Treating DCIS with a lumpectomy , and without radiation therapy, carries a 25 percent to 35 percent chance of recurrence. Adding radiation therapy to the treatment decreases this risk to about 15 percent. Currently, the long-term survival rate for women with ductal carcinoma in situ is nearly 100 percent.
Recommended Reading: Cancer Stages 3