Breast Cancer Staging Guidelines
The TNM system is the most widely used cancer staging system and looks at the following cancer characteristics:
- Tumor The size of the tumor and whether it has grown into nearby tissue.
- Node Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. And if so, how many.
- Metastasis Indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs, like the lungs or liver.
But when it comes to breast cancer staging, the TNM system was expanded to include additional cancer characteristics, including:
- Estrogen-receptor status or progesterone-receptor status Whether the cancer has estrogen or progesterone receptors. A positive status means the cancer can use either hormone to grow.
- HER2 status Whether the cancer produces HER2, a protein that promotes the growth of cancer cells.
- Grade Indicates how much the cancer cells look like healthy cells.
- Oncotype DX recurrence score Indicates how likely a group of genes may respond to treatment, depending on ER, PR and HER2 status.
What Is Stage 3 Cancer
Stage 3 cancer is sometimes referred to as locally advanced cancer. In this stage, the tumor may have grown to a specific size, the cancer may consist of multiple tumors, and/or the cancer may have spread to adjacent lymph nodes, organs or tissue. In some cases, stage 3 cancers may be considered metastatic cancers, meaning they may have spread beyond their organ of origin.
Many stage 3 cancers have multiple subcategories, usually designated as stages 3A, 3B and 3C. These subcategories are often determined by the size of the tumors, whether multiple tumors are present and the degree to which the cancer has spread locally.
Liquid cancers, or blood cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma or multiple myeloma, are staged differently than most other cancers because they may not always form solid tumors. Liquid cancers may be staged by a variety of factors, including:
- The ratio of healthy blood cells to cancerous cells
- Whether cancer cells are found in lymph nodes or the diaphragm
- The degree to which lymph nodes, the liver or spleen may be swollen
Stage 3 cancer is determined in the five most common cancers this way:
Starting With Neoadjuvant Therapy
Most often, these cancers are treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy . For HER2-positive tumors, the targeted drug trastuzumab is given as well, sometimes along with pertuzumab . This may shrink the tumor enough for a woman to have breast-conserving surgery . If the tumor doesnt shrink enough, a mastectomy is done. Nearby lymph nodes will also need to be checked. A sentinel lymph node biopsy is often not an option for stage III cancers, so an axillary lymph node dissection is usually done.
Often, radiation therapy is needed after surgery. If breast reconstruction is done, it is usually delayed until after radiation is complete. In some cases, additional chemo is given after surgery as well.
After surgery, some women with HER2-positive cancers will be treated with trastuzumab for up to a year. Many women with HER2-positive cancers will be treated first with trastuzumab followed by surgery and then more trastuzumab for up to a year. If after neoadjuvant therapy, any residual cancer is found at the time of surgery, trastuzumab may be changed to a different drug, called ado-trastuzumab emtansine, which is given every 3 weeks for 14 doses. For people with hormone receptor-positive cancer in the lymph nodes who have completed a year of trastuzumab, the doctor might also recommend additional treatment with an oral drug called neratinib for a year.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Five Signs Of Breast Cancer
What Are The Signs Of Stage 4 Breast Cancer
The symptoms of Stage 4 breast cancer may not show up until the disease is progressed. If there are symptoms, however, the woman may exhibit one or more of the following: weight loss, lack of appetite, headaches, weakness, bone pain, dry cough or shortness of breath. The existence of a metastasis may be established at the time
Tumor Size Or Clinical Features On Diagnosis

Tumor size, as a single prognostic factor in DCIS, has remained controversial amongst medical experts.
Whilst many cases of DCIS are diagnosed by mammography and are not palpable on diagnosis some present as a clinical, palpable mass .
Narod, following a 2014 medical study, asserts that:-
Tumour size and palpability are risk factors for breast cancer recurrence and mortality.
One small, 2006 medical study concluded that higher rates of invasive caner were detected according to tumor size. Progression to invasive cancer occurred in 10% of DCIS patients with a tumor size between 2.5 to 3.5 cms, 57% for tumor size 3.6 to 4.5 cms and 71% for tumors between 4.5 and 6 cms.
This study concluded that tumors over 2.5 cms have a higher risk of progressing to invasive cancers. However, the study stresses the correlating importance of axillary node involvement.
Recommended Reading: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
Also Check: How To Know If You Have Breast Cancer Female
What Is Stage Iii
In this stage, I tell my patients the real war against the cancer begins, Cruz said. Spreading is much more advanced.
According to Cruz, stage III is unique in that it has three subcategories: IIIA, IIIB and IIIC.
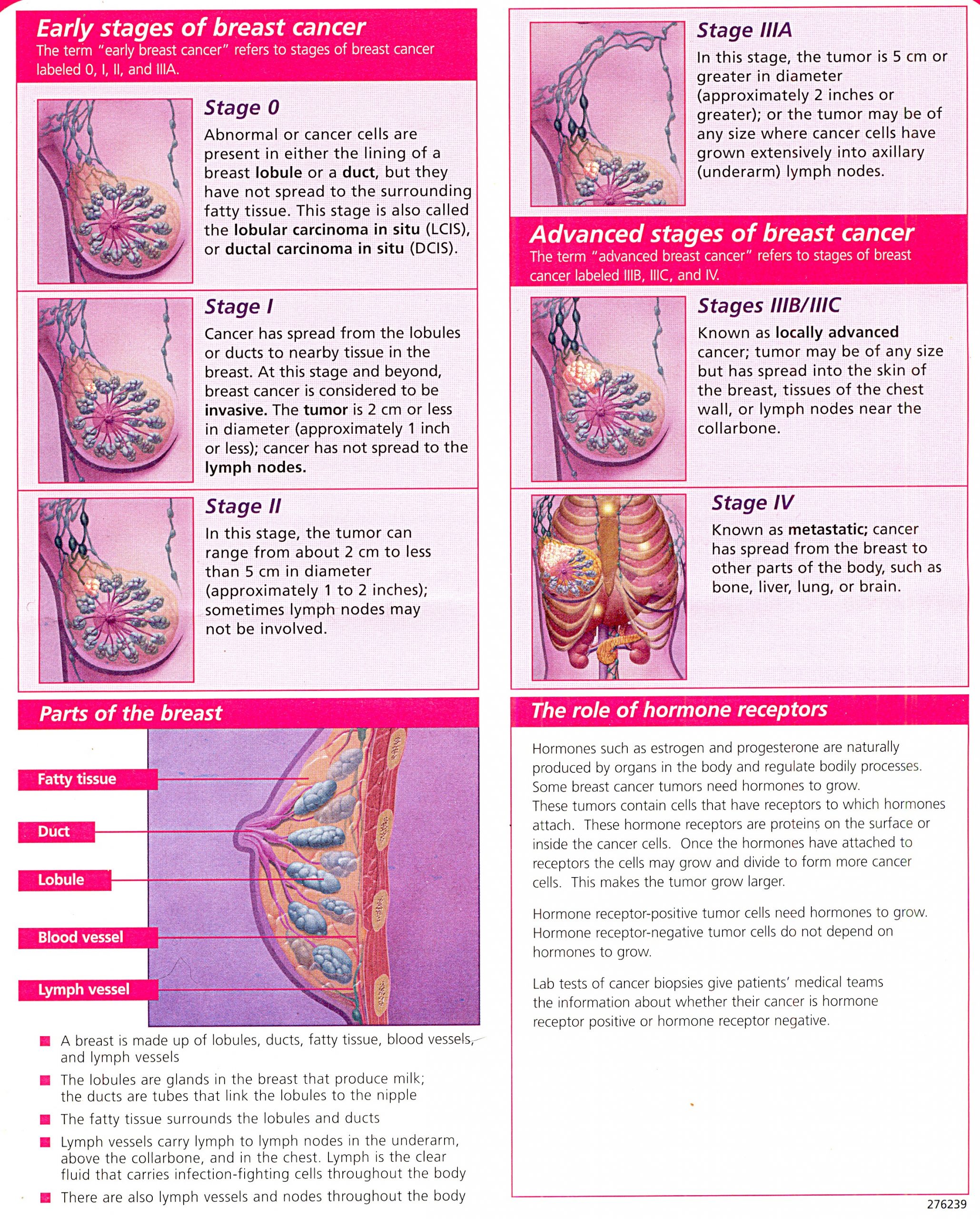
IIIA has tumors all larger than five millimeters and has spread to lymph nodes. Cruz said the higher number of lymph nodes with cancer cells, the more advanced it is.
In stage IIIB, the tumor has spread to the chest wall and skin of the breast. In many cases, this spreading can result in swelling or ulcers. The cancer cells have also spread to nine lymph nodes.
There is advanced spreading in stage IIIC: the cancer has spread to the chest wall, skin of the breast, 10 or more lymph nodes and the collarbone.
In stage III, yes there is advanced spreading. Yes it is harder to treat, but not untreatable, Cruz said. Thats what we tell our patients, although the spreading is scary, we can still fight it.
You May Like: How Long Does Chemo Take For Breast Cancer
The Effects Of Breast Cancer On The Body
At first, breast cancer affects the breast area only. You may notice changes in your breasts themselves. Other symptoms arent so obvious until you detect them during a self-exam.
Sometimes your doctor may also see breast cancer tumors on a mammogram or other imaging machine before you notice symptoms.
Like other cancers, breast cancer is broken down into stages. Stage 0 is the earliest stage with the fewest noticeable symptoms. Stage 4 indicates the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
If breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it may cause symptoms in those particular areas, too. Affected areas may include the:
- liver
- bones
- brain
The early effects of breast cancer can depend on the exact type of breast cancer you have.
Recommended Reading: Has Anne Hathaway Had Breast Cancer
The Tnm Staging System
The TNM staging system gives the complete stage of the cancer:
- T describes the size of the tumour.
- N describes whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and which nodes are involved. For example, N0 means no lymph nodes are affected. N1 means there are cancer cells in 1 to 3 of the lymph nodes.
- M describes whether the cancer has spread to another part of the body. For example, M0 means the cancer has not spread to other parts of the body.
Sometimes the final TNM staging may not be certain until after surgery to remove the cancer.
Grade 3 Breast Cancer
Just looking for info on other peoples treatment. I’m 39, I’ve just had 2nd surgery to remove 8mm IDC as the margins aren’t clear – hopefully will be now . It is grade 3 but luckily no lymph nodes involved .
My consultant says I won’t need chemo as there were no lymph nodes with cancer in them, but I’ve been reading some things that in younger women with grade 3, oncology may suggest chemo? I haven’t had my appointment with oncology yet.
Anyone else with similar – would love to hear your story/treatment.
Recommended Reading: What To Do If You Suspect Breast Cancer
Idc Type: Mucinous Carcinoma Of The Breast
Mucinous carcinoma of the breast sometimes called colloid carcinoma is a rare form of invasive ductal carcinoma . In this type of cancer, the tumor is made up of abnormal cells that float in pools of mucin, a key ingredient in the slimy, slippery substance known as mucus.
Normally, mucus lines most of the inner surface of our bodies, such as our digestive tract, lungs, liver, and other vital organs. Many types of cancer cells including most breast cancer cells produce some mucus. In mucinous carcinoma, however, mucin becomes part of the tumor and surrounds the breast cancer cells. Under a microscope, it looks like the cancer cells are scattered throughout pools of mucus.
Research suggests that only about 2-3% of invasive breast cancers are pure mucinous carcinomas meaning that this is the only type of cancer present within the tumor. About 5% of invasive breast cancers appear to have a mucinous component within them, with other types of cancer cells present as well. Mucinous carcinoma is extremely rare in men.
Although mucinous carcinoma can be diagnosed at any age, it tends to affect women after theyve gone through menopause. Some studies have found that the average age at diagnosis is in the 60s or early 70s.
On the following pages, you can learn more about:
Changes To Your Breasts
Breast cancer usually starts in one breast. According to the American Cancer Society, the most common sign of breast cancer is a newly formed mass or lump in your breast.
The mass or lump is usually irregularly shaped and painless. However, some cancerous masses can be painful and round in shape. This is why any lump or mass ought to be screened for cancer.
Invasive ductal carcinoma causes lumps and bumps in the breasts. This is a type of breast cancer that forms inside the milk ducts.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer. It makes up about 80 percent of all diagnoses. Its also more likely to spread to other areas of the body.
Invasive lobular carcinoma can cause breast thickening. This type of breast cancer starts in the glands that produce breast milk. The Cleveland Clinic estimates that up to 15 percent of all breast cancers are invasive lobular carcinomas.
You may notice your breasts have changed color or size. They may also be red or swollen from the cancerous tumor. While breast cancers themselves arent usually painful, the resulting swelling can cause breast pain. The cancer lumps may still be painful in some cases, though.
With breast cancer, your nipples may also undergo some noticeable changes.
Don’t Miss: What Does Breast Cancer Look Like On The Outside
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
- the skin
How Is Breast Cancer Recurrence Managed Or Treated
Your treatment depends on the type of cancer recurrence, as well as past treatments. If cancer develops in a reconstructed breast, your surgeon may want to remove the breast implant or skin flap.
Treatments for local and regional breast cancer recurrence may include:
- Mastectomy: Your surgeon removes the affected breast and sometimes lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy:Chemotherapy circulates in blood, killing cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy:Tamoxifen and other hormone therapies treat cancers that thrive on estrogen .
- Immunotherapy:Immunotherapy engages your bodys immune system to fight cancer.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy X-ray beams damage and destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Treatments target specific cancer cell genes or proteins.
Recommended Reading: Has Anyone Survived Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Data Acquisition And Patient Selection
We used the SEER dataset that was released in April 2015, which included data from 18 population-based registries and covered approximately 28% of U.S. cancer patients. Data for tumour location, grade and histology were recorded according to the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology Version 3 . The inclusion criteria used to identify eligible patients were the following: females aged between 18 and 79, unilateral breast cancer, breast cancer as the first and only cancer diagnosis, diagnosis not obtained from a death certificate or autopsy, only one primary site, pathological confirmation of infiltrating ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified and papillary carcinoma with invasion , surgical treatment with either mastectomy, breast-conserving surgery or unknown type, known ER and PR statuses, American Joint Committee on Cancer stages IIII and known time of diagnosis from January 1, 2003 to December 31, 2012. Patients diagnosed with breast cancer before 2003 were excluded because the World Health Organization did not recognize IPC as a distinct pathological entity until 2003. In addition, patients who were diagnosed with breast cancer after 2012 were not included because the database was only updated up to December 31, 2012 and we wanted to ensure adequate follow-up time. A total of 233,171 patients were included. Of these patients, 524 were diagnosed with IPC and 232,647 were diagnosed with IDC.
What Type Of Drug Treatment Might I Get
Most women with breast cancer in stages I to III will get some kind of drug therapy as part of their treatment. This may include:
- Chemotherapy
- Hormone therapy
- HER2 targeted drugs, such as trastuzumab and pertuzumab
- Some combination of these
The types of drugs that might work best depend on the tumors hormone receptor status, HER2 status, and other factors.
Don’t Miss: Do Hormones Cause Breast Cancer
What To Do If You Have Breast Cancer
When you learn about such an unpleasant diagnosis, the first thing to do is to avoid panic in any way. Try to pull yourself together. After that, be sure to look for an experienced doctor who will tell you what to do and how to proceed. Only an experienced doctor will be able to give you the right diagnosis, assess your overall condition, and be able to provide assistance that will lead to a positive result.
The main thing, in this case, is to see a professional doctor. Unfortunately, many countries have adopted a radical fight against this disease. Therefore, the question, whether it is possible to cure without surgery, the answer is a resounding no. But in the USA, such treatment can be carried out much more gently. Clinics here offer to conduct surgery for breast cancer, but try to keep as much healthy tissue as possible. In addition, after surgery in such centers, you will certainly be offered plastic surgery to restore the breast.
So, if you or your loved one was diagnosed with breast cancer, even if it is stage 4, do not panic. Find a great oncologist, select the best treatment option, and start it immediately. With this approach, the probability of a positive outcome increases many times. Remember even the worst and most difficult diagnosis can be a thing of the past if you start the right treatment on time and believe in the best outcome.
The Number Staging System
Breast cancer can also be divided into four number stages. We have put these into a table to make them easier to understand. You can .
This information is about stage 1 to 3 breast cancer.
Stage 1 breast cancer is when the cancer is 2cm or smaller. There may be no cancer cells in the lymph nodes in the armpit or tiny numbers of cancer cells are found. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast, but cancer cells have spread to lymph nodes in the armpit.
Stage 2 breast cancer is when the cancer is up to or bigger than 5cm. It may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes under the arm. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast. But cancer cells have spread to 1 to 3 lymph nodes in the armpit or near the breast bone.
Stage 3 breast cancer is sometimes called locally advanced breast cancer. The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit and sometimes to other lymph nodes nearby. It may have spread to the skin of the breast or to the chest muscle. The skin may be red, swollen or have broken down. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast or is small but has spread to 4 to 9 lymph nodes in the armpit.
Stage 4 breast cancer is also called secondary or metastatic breast cancer. This is when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones, the liver or lungs. We have separate information about secondary breast cancer.
Also Check: How Long Can You Live With Breast Cancer Without Treatment