Drug Treatment Before Surgery
You might have chemotherapy as a first treatment to shrink the cancer down.
You might have hormone therapy first if your cancer cells have hormone receptors. But you usually only have this if chemotherapy isnt suitable.
If your cancer cells have particular proteins called HER2 receptors you might also have a targeted cancer drug called trastuzumab .
These treatments might shrink the tumour enough to allow your surgeon to remove just the area of cancer. This is called breast conserving surgery or a wide local excision.
If the cancer doesnt shrink enough, you need to have the whole breast removed . You may be able to have a new breast made . Do speak to your surgeon about this.
Before your surgery the lymph nodes in the armpit are checked for cancer cells.
You usually have radiotherapy to the breast after surgery.
Want To Learn More About Your Breast Cancer Treatment Options Were Here For You
Whether you just received your diagnosis or youre looking for new treatment options, were here to help.
If youve just been diagnosed with breast cancer, your next stop will be to meet with a nurse navigator or breast surgeon, depending on your initial diagnosis, and start building your treatment plan. We offer cancer care clinic locations across the Twin Cities and western Wisconsin, so get started by selecting a location to make an appointment at.
Examples Using The Full Staging System
Because there are so many factors that go into stage grouping for breast cancer, it’s not possible to describe here every combination that might be included in each stage. The many different possible combinations mean that two women who have the same stage of breast cancer might have different factors that make up their stage.
Here are 3 examples of how all of the factors listed above are used to determine the pathologic breast cancer stage:
Don’t Miss: How To Check Breast For Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Staging Guidelines
The TNM system is the most widely used cancer staging system and looks at the following cancer characteristics:
- Tumor The size of the tumor and whether it has grown into nearby tissue.
- Node Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. And if so, how many.
- Metastasis Indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs, like the lungs or liver.
But when it comes to breast cancer staging, the TNM system was expanded to include additional cancer characteristics, including:
- Estrogen-receptor status or progesterone-receptor status Whether the cancer has estrogen or progesterone receptors. A positive status means the cancer can use either hormone to grow.
- HER2 status Whether the cancer produces HER2, a protein that promotes the growth of cancer cells.
- Grade Indicates how much the cancer cells look like healthy cells.
- Oncotype DX recurrence score Indicates how likely a group of genes may respond to treatment, depending on ER, PR and HER2 status.
M Categories For Breast Cancer

M followed by a 0 or 1 indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs — for example, the lungs, liver, or bones.
M0: No distant spread is found on x-rays or by physical exam.
cM0: Small numbers of cancer cells are found in blood or bone marrow , or tiny areas of cancer spread are found in lymph nodes away from the underarm, collarbone, or internal mammary areas.
M1: Cancer has spread to distant organs .
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If Breast Cancer Has Metastasized
Stage 1 Breast Cancer
What is Stage 1 breast cancer?
Stage 1 breast cancers are still relatively small, and theyve either not yet spread to the lymph nodes or theres only been a tiny bit of spread in the sentinel lymph node which is where the cancer is most likely to spread first. There are two types of Stage 1 breast cancer:
- Stage 1A Stage 1A breast cancer means the tumor is no larger than 2 centimeters, and the cancer has not spread outside the breast or to lymph nodes.
- Stage 1B Stage 1B breast cancer means there are small groups of cancer cells in the lymph nodes. There may or may not be a tumor smaller than 2 centimeters in the breast.
What are the treatment options for Stage 1 breast cancer?
- Surgery Like with Stage 0, a lumpectomy and mastectomy are both options at this stage:
- Lumpectomy This kind of breast conservation surgery is a viable option when the cancerous cells are confined to one area of the breast.
- Mastectomy A mastectomy may be recommended if cancer is found throughout the breast.
Stage 1 breast cancer treatment timeline
M Refers To Metastasis
Metastasis is the spread of cancer to other areas of the body, otherwise known as distant spread. Some breast cancer cells have the ability to invade lymphatic and/or blood vessels where they can circulate to distant organs and tissues e.g. bones, liver, lungs and brain. Imaging such as CT scans and bone scans can be performed if the tumour is high risk and/or metastases are suspected.
Until recently breast cancer staging used only these measures to classify the stage of the cancer but in January 2018 the system was updated to take into account additional tumour biology factors that can affect outcomes.
These are:
You May Like: What Does An Ultrasound Show For Breast Cancer
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stages
Invasive ductal carcinoma stages provide physicians with a uniform way to describe how far a patients cancer may have spread beyond its original location in a milk duct. This information can be helpful when evaluating treatment options, but it is not a prognostic indicator in and of itself. Many factors can influence a patients outcome, so the best source of information for understanding a breast cancer prognosis is always a physician who is familiar with the patients case.
In general, breast cancer stages are established based on three key variables: the size of a tumor, the extent of lymph node involvement and whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. This information may be obtained through a combination of clinical examinations, imaging studies, blood tests, lymph node removal and tissue samples . If, based on the initial test results, a physician believes that the cancer may have spread to other parts of the body, further testing may be ordered, such as a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or liver function test.
Invasive ductal carcinoma is usually described through a numeric scale ranging from 1 to 4 . Specifically, the invasive ductal carcinoma stages are:
If youd like to learn more about invasive ductal carcinoma stages and treatment options, call or complete a new patient registration form online.
- BROWSE
Is Stage 2 Cancer Serious
Stage II cancer refers to larger tumors or cancers that have grown more deeply into nearby tissue. In this stage, the cancer may have spread to the lymph nodes, but not to other parts of the body. At Cancer Treatment Centers of America® , our cancer experts recognize that stage II cancer is a complex disease.
Read Also: Is Radiation For Breast Cancer Dangerous
Breast Lumps Or Thickening
The earliest symptoms of breast cancer are easier to feel than see. Performing a monthly self-exam of your breasts will help you get familiar with their normal look and feel.
Theres no evidence that self-exams will help you detect cancer earlier, but it will help make it easier for you to notice any changes in your breast tissue.
Get into a routine of examining your breasts at least once per month. The best time to examine your breasts is a few days after the start of your menstrual cycle. If youve already begun menopause, choose a specific date to check your breasts every month.
With one hand positioned on your hip, use your other hand to run your fingers over both sides of your breasts, and dont forget to check underneath your armpits.
If you feel a lump or thickness, its important to realize that some women have thicker breasts than others and that if you have thicker breasts, you may notice lumpiness. A benign tumor or cyst can also cause lumpiness.
Even though it might be not be cause for alarm, tell your doctor about anything you notice that seems unusual.
Stage Iv Breast Cancers May Be Recurrences Following Initial Treatment
Up to 5% of initial breast cancer diagnoses are of the most advanced or metastatic stage. However, this number has significantly reduced with the implementation of widespread breast cancer screening programs.
Metastatic breast cancer can appear to be a rapid deterioration of a disease that has been present for some time undetected.
But metastatic breast cancer can also be the result of a recurrence of breast cancer after successful initial treatment. Sometimes the terms local and regional recurrence indicate a return of breast cancer to the original tumor site or elsewhere in the breast or contralateral breast.
If the cancer returns in other areas of the body it is a distant metastasis or distant recurrence.
For more detail on Stage IV survival rates, recurrence rates and treatment please see our new post HERE.
Read Also: How Does Metastatic Breast Cancer Start
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
Changes In The Size And Shape Of The Breast
Its not uncommon for breasts to swell, and you may notice a change in size around the time of your menstrual cycle.
Swelling can also cause breast tenderness, and it may be slightly uncomfortable to wear a bra or lie down on your stomach. This is perfectly normal and rarely indicative of breast cancer.
But while your breasts may undergo certain changes at different times of the month, you shouldnt overlook some changes. If you notice your breasts swelling at times other than your menstrual cycle, or if only one breast is swollen, talk to your doctor.
In cases of normal swelling, both breasts remain symmetrical. That means one wont suddenly be larger or more swollen than the other.
Also Check: What Medications Are Used For Breast Cancer
What Are The Survival Rates For Stage 3 Breast Cancer By Stage
Survival rates can be confusing. Remember that they dont reflect your individual circumstances.
The relative 5-year survival rate for stage 3 breast cancer is 86 percent, according to the American Cancer Society. This means that out of 100 people with stage 3 breast cancer, 86 will survive for 5 years.
But this figure doesnt consider breast cancer characteristics, like grade or subtype. It also doesnt distinguish between people with stage 3A, 3B, and 3C.
In comparison, the relative 5-year relative survival rate for stage 0 breast cancer is 100 percent. For stages 1 and 2, its 99 percent. For stage 4, the survival rate drops to 27 percent.
What Are The Different Grades Of Breast Cancer
There are three grades of invasive breast cancer:
- Grade 1 looks most like normal breast cells and is usually slow growing
- Grade 2 looks less like normal cells and is growing faster
- Grade 3 looks different to normal breast cells and is usually fast growing
Sometimes the grade given to a cancer after a biopsy can change after surgery. This is because after surgery theres more tissue for the pathologist to look at, which can give them more detailed information about the cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 1 Breast Cancer Mean
N Categories For Breast Cancer
N followed by a number from 0 to 3 indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are involved.
Lymph node staging for breast cancer is based on how the nodes look under the microscope, and has changed as technology has improved. Newer methods have made it possible to find smaller and smaller collections of cancer cells, but experts haven’t been sure how much these tiny deposits of cancer cells affect outlook.
Its not yet clear how much cancer in the lymph node is needed to see a change in outlook or treatment. This is still being studied, but for now, a deposit of cancer cells must contain at least 200 cells or be at least 0.2 mm across for it to change the N stage. An area of cancer spread that is smaller than 0.2 mm doesn’t change the stage, but is recorded with abbreviations that indicate the type of special test used to find the spread.
If the area of cancer spread is at least 0.2 mm , but still not larger than 2 mm, it is called a micrometastasis . Micrometastases are counted only if there aren’t any larger areas of cancer spread. Areas of cancer spread larger than 2 mm are known to affect outlook and do change the N stage. These larger areas are sometimes called macrometastases, but are more often just called metastases.
NX: Nearby lymph nodes cannot be assessed .
N0: Cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes.
N1c: Both N1a and N1b apply.
N3: Any of the following:
N3a: either:
N3b: either:
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
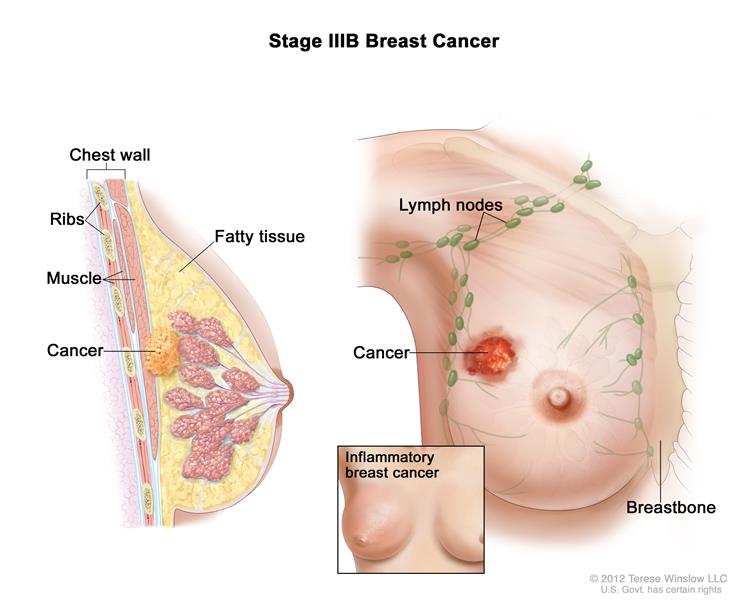
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
- the skin
Recommended Reading: Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer Curable
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares women with the same type and stage of breast cancer to women in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of breast cancer is 70%, it means that women who have that cancer are, on average, about 70% as likely as women who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
What Are Breast Cancer Stages
The stage of a cancer describes the size of the cancer and how far it has spread.
Your breast cancer may be described as stage 1, stage 2, stage 3 or stage 4.
An early form of breast cancer called DCIS is sometimes referred to as stage 0 breast cancer.
The stage takes into account:
- The size of the cancer
- Whether the lymph nodes are affected
- If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
The stage of your cancer may not be fully known until after you have had surgery.
Recommended Reading: What To Eat To Cure Breast Cancer
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 means that the cancer has spread from the breast to lymph nodes close to the breast or to the skin of the breast or to the chest wall.
It is also called locally advanced breast cancer.
The stage of a cancer tells you how big it is and how far it has spread. It helps your doctor decide which treatment you need.
Staging for breast cancer is very complex. Many different factors are considered before doctors can confirm your final stage. For example, they also use a sample of your cancer to test for:
- receptors for the female hormones
- HER2 status
- the grade of your cancer
You may also have a CT scan to check that the cancer has not spread to other parts of your body.
Do speak to your breast doctor or nurse if you have any questions about staging.
Breast Changes During Pregnancy And Lactation Period
Breast changes are one of the first signs of pregnancy, since these are also related to the lactation period. There is rapid breast swelling during pregnancy. Most pregnant women experience tenderness down the sides of the breasts and soreness of the nipples. This is because of the growth of the milk duct system and the formation of many more lobules. By the fifth or sixth month of pregnancy, the breasts are fully capable of producing milk. Other physical changes, like the prominence of the blood vessels in the breast and the enlargement and darkening of the areola happen. All of these changes are in preparation for breastfeeding stage after the child birth.
Also Check: Can Breast Cancer Cause Menstrual Irregularities