Immunogenic Potential Of Tnbc
The tumour microenvironment plays an important role in defining the interaction of our immune system with tumours. In TNBC, the TME is characterized by higher levels of vascular endothelial like growth factor , tumour infiltrating lymphocytes and tumour associated macrophages in contrast to other types of breast cancer. Additionally, there is a high level of expression of TILs in patients with TNBC. These have been shown to be a useful prognostic indicator across malignancies. TNBC has been shown to have consistently elevated TILs in contrast to other subtypes and TILs have been shown to be associated with improved survival. Ibrahim et al found that patients with lymphocyte-predominant breast cancer had a 40% pathological complete response rate compared to 7% of those patients without. High TILS are more frequent in TNBC compared to HER2-positive and luminal tumours and are associated with improved disease free survival and OS in early stage breast cancer. This is consistent with findings in other malignancies demonstrating the important role of the immune system in cancer biology and prognostication. All of these features demonstrate that the TME of TNBC is highly immunogenic.
How Does Staging Relate To Types Of Breast Cancer
In addition to cancer stage, doctors will determine the tumor grade and subtype.
Tumors are graded on a scale of 1 to 3, based on how abnormal the cells appear compared to normal cells. The higher the grade, the more aggressive the cancer, meaning that it tends to be growing quickly.
The subtype is important because treatment and outlook will vary depending on which subtype of breast cancer that you have. Subtypes include:
What Is The Staging Of Triple
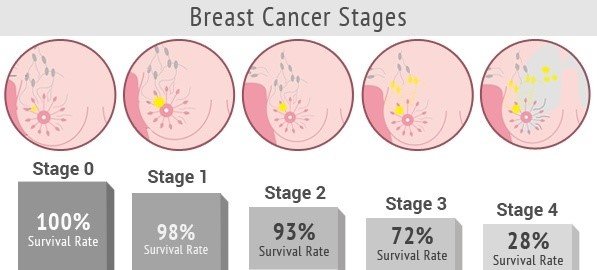
Staging is the process of determining the extent of the cancer and its spread in the body. Together with the type of cancer, staging helps determine the appropriate therapy and predict the chances for survival.
To determine if the cancer has spread, medical professionals may use several different imaging techniques, including X-ray, CT scans, bone scans, and PET scans. Staging depends upon the size of a tumor and the extent to which it spread to lymph nodes or distant sites and organs in the body. Examination of lymph nodes removed at surgery and the results of ER, PR, and HER2 tests performed on the tumor tissue also help determine the stage of a tumor. Stage I is the lowest stage, while stage IV is the highest stage and refers to tumors that have metastasized, or spread to areas distant from the breast.
Most doctors specifically adjust breast cancer treatments to the type of cancer and the staging group.
Surgery
Many women with breast cancer will require surgery. Broadly, the surgical therapies for breast cancer consist of breast-conserving surgery and mastectomy .
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy destroys cancer cells with high-energy rays. Doctors commonly administer radiation therapy to patients after breast cancer surgery, most commonly after lumpectomy.
Chemotherapy
Types of chemotherapy include the following:
Other therapies for triple-negative breast cancer
Read Also: Anne Hathaway Breast Cancer
Read Also: Stage 3b Breast Cancer Prognosis
Inoperable Breast Cancer Is Often Still Treatable
Stage 3C breast cancer is divided into operable and inoperable stage 3C breast cancer. However, the term inoperable is not the same as untreatable.
If your physician uses the word inoperable, it may simply mean that a simple surgery at this time would not be enough to get rid of all the breast cancer that is within the breast and the tissue around the breast. There must be healthy tissue at all of the margins of the breast when it is removed. Keep in mind that the breast tissue goes beyond the breast mound it goes up to the clavicle and down to a few inches below the breast mound. There must also be tissue to close the chest wound after the surgery is performed.
Another treatment method may be used first to shrink the breast cancer as much as possible before surgery is considered.
Also Check: Treatment For Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast
Grading Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
In 1957, Bloom and Richardson first developed a histology grading system for invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast, based on the degree of tubule formation, cell nuclear pleomorphism and mitotic count. This system was replaced or modified in 1991 by the Nottingham grading system, which is still based on a points scoring system of the histologic features of the cancer mild, moderate or severe or Grade 1, 2 or 3 .
Recommended Reading: Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer Curable
Don’t Miss: Healing Cancer With Baking Soda
Sociodemographic And Clinical Characteristics Of Tnbc Patients
We enrolled 152 patients aged 26-85, median age 58 years , just over two-thirds of them menopausal. In routine medical records, family history data were lacking in a high percentage of cases, i.e. 42 for any cancer and 43 for BC. We kept these data in descriptive , but did not interpret them. In patients for whom we had properly collected data, 18/109 had a positive family history of BC. Patients with a positive family history of BC were younger, median age 43 years compared to patients without family BC, median age 57 years. The vast majority of patients had ductal invasive carcinoma with a median tumor size of 2.2 cm, 62 with positive lymph nodes, 124 with grade III tumor, and median Ki67 proliferation index 57 . Just over one-third of patients underwent radical surgery , and almost all of them underwent axillary dissection. Adjuvant chemotherapy was used in 130/148 patients, in 114/128 cases with anthracyclines or a combination of anthracyclines and taxanes. A total of 103/140 patients were treated with adjuvant radiotherapy. None of the patients was treated with the neoadjuvant approach.
Risk Factors And Epidemiologic Features
In addition to a distinct molecular and pathologic profile, the epidemiology and risk factors associated with triple-negative breast cancer are distinct, especially when compared with endocrine-sensitive luminal breast tumors. The Carolina Breast Cancer Study, a population-based, case-control study aimed at determining clinical associations and distributions across distinct breast cancer subtypes, has refined our understanding of the epidemiologic and risk factors associated with triple-negative breast cancer. In the initial study of women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer, the prevalence of breast cancer subtypes within racial and menopausal subsets were determined. Immunohistochemical staining was used to classify specific subtypes in approximately 500 tumors, and basal-like tumors were defined as triple negative and cytokeratin 5/6 positive and/or HER1 positive. Results indicated that those with basal-like tumors were more likely to be African American compared with nonAfrican American and premenopausal compared with postmenopausal . There was a particularly high prevalence of basal-like tumors among premenopausal African American women compared with postmenopausal African American women and nonAfrican American women of any age . The observation that triple-negative breast cancers more commonly arise in younger African American women has been confirmed in several additional studies, although the exact cause for this association is not yet fully understood.,
You May Like: How Long Can U Live With Stage 4 Cancer
Early Stage Clinical Trials
In a proof of concept study published in the Lancet, authors investigated olaparib in patients with advanced metastatic breast cancer with germline BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations. They investigated two doses of olaparib at 400 mg BD and 100 mg BD. Approximately half of patients in this study had TNBC with the remainder having other histological subtypes. Patients were heavily pretreated with a median of 3 prior chemotherapy regimens and platinum sensitivity was not needed for trial enrolment. Overall response rates were impressive in this heavily pre-treated population at 41% in the group receiving the higher dose and 22% in the group receiving the lower dose.
Kaufman et al investigated olaparib further in a large phase 2 basket trial with 298 patients in a single-arm study. Patients with any advanced solid-organ malignancy were included if they harboured a gBRCA mutation. In the breast cohort, patients may have received multiple lines of treatment and there was no requirement for platinum sensitivity. Response rates were modest with only 8 of 62 patients responding in this unselected population.
How Quickly Breast Cancer Develops
You may have heard remarks that cancer has been present for five years before it is diagnosed, and this may sometimes be true.
The actual time it takes for breast cancer to grow from a single cancer cell to a cancerous tumor is unknown, as estimates based on doubling time assume that this is constant throughout the duration of tumor growth.
If doubling time were constant, cancer with a doubling time of 200 days would take 20 years to develop into a detectable tumor, and a doubling time of 100 days would take 10 years to be evident on exam.
In contrast, a breast tumor with a doubling time of 20 days would take only 2 years to develop.
Since the majority of studies have found the average doubling time to be between 50 days and 200 days, its likely that most breast cancers that are diagnosed began at least 5 years earlier .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Don’t Miss: How Fast Does Triple Negative Cancer Grow
How Is Tnbc Diagnosed
Imaging tests are usually the first tests done:
- Mammography, the most common screening tool for breast cancer, uses X-rays to take images of the breast and can uncover tumors that may be too small to feel.
- MRI uses a magnet, radio waves and a computer to make detailed images of the breast with a much greater resolution than a mammogram offers.
The next step is a biopsy to remove a sample of suspicious cells from the breast to analyze them. Techniques include:
The appropriate type of biopsy for you depends on factors such as the size and location of the tumor. You may also have a biopsy of your underarm lymph nodes at the same time to see if any cancer is there.
Your Prognosis Depends On Several Factors
- The size of your cancer
- Whether your tumor has spread to other areas of your body
- The type of breast cancer you have
- The hormone receptor and HER2 status of your tumor
- The rate of cell growth
- Your age and menopausal status
- Your general health
Each person is different, and your doctor will likely run several tests before giving you a formal prognosis.
Also Check: Stage 4 Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment
The Tumor Microenvironment: Creating A Pre
TNBC exhibits numerous CSC-like traits and is more likely to lead to BM. The short time to BM occurrence in TNBC and the short survival time after BM diagnosis may be indicative of an innate ability of TNBC cells to adapt to the brain microenvironment.67 The vascular basement membrane presents the soil in BM. Although more than 95% of early brain micrometastases were shown to coexist with blood vessels, there is little evidence for isolated neurogenic growth.68 When TNBC cells invade the brain parenchyma, an adequate blood supply is needed to provide the nutrients necessary for tumor growth and proliferation. Tumor angiogenesis depends on the balance between pro- and anti-angiogenic factors at the local tissue level and is regulated by the local microenvironment.69
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Genetics

One of the leading causes of triple-negative is a womans genetic makeup, specifically the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are genes that are supposed to produce tumor suppressant proteins in the body.
In the case of triple-negative breast cancer, 10% to 15% of Caucasians with triple-negative breast cancer have a BRCA1 gene mutation, while 35% of African Americans with triple-negative breast cancer have a BRCA1 gene mutation.
For a while the BRCA1 gene was the only gene known for increasing the risk of triple-negative breast cancer.
These genes, if defected can increase their risk of getting any type of breast cancer by 20% as well as elevating the chances that their breast cancer diagnosis be triple negative breast cancers .
You May Like: What Does Invasive Breast Cancer Mean
I Have Now Finished My 4 Cycles Of Ec Chemotherapy Which I Had Every 3
Triple negative breast cancer grade 3. The cells are growing at a speed of and look like cells somewhere between grades 1 and 3. But triple negative breast cancer. I am facing the challenge of my life battling very aggressive triple negative grade 3 only 20 cure rate breast cancer.
Get thousands of teacher-crafted activities that sync up with the school year. Triple negative breast cancer grade 3. See J Clinical Inv 2011 12172750-2767 for more information.
Think of cancer cells as a house. Triple-negative breast cancer TNBC accounts for about 10-15 of all breast cancers. On a scale of 1 to 3 with 3 being the most serious TNBC is often labeled grade 3.
Triple-negative breast cancer is a kind of breast cancer that does not have any of the receptors that are commonly found in breast cancer. What Is Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Ad Over 1000000 vacation rentals and hotels worldwide.
This is my story with stage 3 triple negative breast cancer. Special rates for members. I am 55 years old 34 years happily married to Mark I have a daughter 25 Katie son Brad 24.
Find Signs For Lung Cancer. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer. Triple negative breast cancer is a less common type of breast cancer.
Triple negativegrade 3 is an aggressive type of cancer and even though a mammogramcatscan may not show any evidence of cancer its. Ad Access the most comprehensive library of third grade learning resources. The cells test negative on all 3.
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several types of breast cancer, and any of them can metastasize. Most breast cancers start in the ducts or lobules and are called ductal carcinomas or lobular carcinomas:
- Ductal carcinoma. These cancers start in the cells lining the milk ducts and make up the majority of breast cancers.
- Lobular carcinoma. This is cancer that starts in the lobules, which are the small, tube-like structures that contain milk glands.
Less common types of breast cancer include:
-
Medullary
-
Metaplastic
-
Papillary
-
Inflammatory breast cancer is a faster-growing type of cancer that accounts for about 1% to 5% of all breast cancers.
-
Pagets disease is a type of cancer that begins in the ducts of the nipple.
Breast cancer can develop in women and men. However, breast cancer in men is rare. Less than 1% of all breast cancers develop in men.
Read Also: Metastatic Breast Cancer Stage 3
Tnbc Chemotherapy Drugs And Efficacy Evaluation
Compared to other types of breast cancer, TNBC has limited treatment options, is prone to recurrence and metastasis, and has a poor prognosis. The main reason is that the expression of ER, PR, and HER2 are all negative, making specific endocrine therapies and targeted therapies ineffective. Therefore, chemotherapy has become the main approach for the treatment of TNBC. In recent years, a large body of literature has shown that the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimens in the treatment of TNBC has a significantly higher pathological remission rate than for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer and can significantly improve the prognosis of TNBC patients. The national comprehensive cancer network guidelines recommend using combination regimens based on taxane, anthracycline, cyclophosphamide, cisplatin, and fluorouracil. At present, taxel/docetaxel + adriamycin + cyclophosphamide , docetaxel + cyclophosphamide , adriamycin + cyclophosphamide , cyclophosphamide + methotrexate + fluorouracil , cyclophosphamide + adriamycin + fluorouracil , and cyclophosphamide + epirubicin + fluorouracil + paclitaxel/docetaxel are the preferred adjuvant regimens for TNBC. Therefore, the selection of appropriate chemotherapy drugs and the optimization of chemotherapy regimens are important for ensuring good treatment outcome and prognosis of TNBC patients.
Risk Factors For Triple
Doctors arent sure what makes you more likely to get triple-negative breast cancer. Not many women do it only affects up to 20% of those who have breast cancer. Youre most at risk for triple-negative breast cancer if you:
- Are African-American or Latina
Also Check: What Percentage Of Breast Cancer Is Hereditary
Don’t Miss: Whats Stage 3 Cancer
Advanced Cancer That Progresses During Treatment
Treatment for advanced breast cancer can often shrink the cancer or slow its growth , but after a time, it tends to stop working. Further treatment options at this point depend on several factors, including previous treatments, where the cancer is located, and a womans age, general health, and desire to continue getting treatment.
Stage 3a Breast Cancer
If you are diagnosed with Stage 3A breast cancer, it means that one of the following applies to you:
Either:
The tumour is less than 5 cm and breast cancer cells have been found in:
- 4-9 lymph nodes in the armpit. or
- 1 or more lymph nodes under the breastbone
The tumour is larger than 5 cm and breast cancer cells have spread to 1-9 lymph nodes.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Breast Cancer Definition
Receptor Status And Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Your pathology report and your healthcare providers may describe your breast cancer as estrogen receptor , progesterone receptor or human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 positive or negative. Or, they may say that your breast cancer is triple negative or triple positive.
Estrogen and progesterone receptors are proteins found in some cancer cells that allow a hormone to attach and feed the cancer cells. Hormone receptor status is reported as positive or negative and sometimes a percent is also provided. For example, 90% estrogen receptor positive. ER/PR+ breast cancers will, at a minimum, receive some form of hormone therapy such as Tamoxifen.
HER2 is a protein involved in normal cell growth, which may also be present on breast cancer cells. If too much of the HER2 protein is produced, the tumor is considered HER2+ . Breast cancers that are HER2+ will receive HER2 directed therapy such as Herceptin.
Triple positive breast cancer is positive for HER2, ER and PR. You will receive HER2 directed therapies as well as hormone therapy.
Triple negative breast cancer is negative for HER2, ER and PR. Therefore, HER2 directed therapy and hormone therapy are not utilized. Typical treatment is chemotherapy.
Related Topics
Read Also: What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Breast Cancer