What Is Breast Reconstruction
Breast reconstruction may help restore the look and feel of the breast after a mastectomy. Many women who have had a breast removed opt for breast reconstructionin some limited cases, at the same time as the mastectomy, but more often after the mastectomy procedure. With immediate reconstruction, a surgeon performs the first stage to rebuild the breast during the same operation as the mastectomy. A method called skin-sparing mastectomy may be used to save enough breast skin to cover the reconstruction.
Breasts may be rebuilt using saline implants or autologous tissue . Most breast reconstructions performed today use implants. For some reconstructions, more than one surgery may be needed.
Mastectomy with reconstruction done on the same day is an option for many women, but the best approach for an individual should be determined through a discussion of various options between the patient and her surgeon.
The decision to have reconstruction is a personal one. Some women choose not to have reconstruction. Others believe it helps their appearance and recovery.
How Genetic Test Results May Influence Treatment Decisions
If youve already been diagnosed with breast cancer, genetic test results may identify the reason for your cancer and influence treatment decisions, such as which surgical procedure or what kind of follow-up is recommended .
Some patients are confident about their surgical and other treatment decisions regardless of what genetic testing shows. Others use genetic testing to guide their treatment plan.
When it comes to breast surgery, for example, some patients who know they have a higher chance of developing a second breast cancer decide to have more extensive surgery, such as a mastectomy or a double mastectomy. Conversely, when others discover they dont have a BRCA or other mutation, they sometimes decide to have a lumpectomy to remove the tumor instead of a double mastectomy to remove both breasts.
Knowing this information prior to surgery may help some people make a decision they wouldnt otherwise have made, or it may allow them to make a decision with more confidence.
The results of genetic testing sometimes allow the oncologist to consider other treatments, such as targeted therapy and different types of chemotherapy, that may not otherwise have been an option.
Emotional Risks For Family Members
Genetic testing may also have an emotional impact on family members.
Your genetic counselor may suggest you talk to your family about BRCA1/2 or expanded panel testing before you get tested or before you learn your results. That way you can find out if they want to know about your results.
For people with a BRCA1/2 or other high-risk inherited gene mutation, figuring out how to tell relatives can be hard.
Some family members may value the option of BRCA1/2 or panel testing. Others may be upset, anxious or angry about hearing the news.
If you have concerns about the best way to share the news with your family members, talk with a genetic counselor. You may prefer to write a letter to your relatives , especially if you have a big family. Your genetic counselor may be able to help you write this letter.
Don’t Miss: How Likely Is Breast Cancer To Come Back
Components Of The Risk Assessment Process
This section provides an overview of critical elements in the cancer risk assessment process.
A number of professional guidelines on the elements of cancer genetics risk assessment and counseling are available. Except where noted, the discussion below is based on these guidelines.
The cancer risk assessment and genetic counseling process consists of one or more consultative sessions and generally includes the following:
- A detailed, multifaceted assessment including medical, psychosocial, and family history.
- A determination of the risk of cancer and/or indication for genetic testing based on evidence of an inherited cancer syndrome.
- Education and counseling about familial/hereditary cancer risks.
- If appropriate, review of genetic testing options as well as potential limitations, risks, and benefits of testing.
- Establishment of a cancer risk management plan.
- Discussion of follow-up plans, provision of referrals, educational materials, etc.
Potential Future Directions For Research On The Psychosocial Implications Of Treatment

This overview of the psychosocial literature shows that treatment-focused genetic testing for BRCA1 and/or BRCA2 mutations is not associated with adverse psychological and quality of life outcomes. However, these studies included almost exclusively women with a family history that indicated an increased risk for hereditary breast/ovarian cancer, and very little is known about the psychosocial impact of treatment-focused genetic testing in women without a family history. This review also shows that very few data are currently available on: the anticipated implications of genetic testing for the patient and other family members patient preferences in terms of timing of genetic testing information mode of delivery of information and preferred format and amount of information. Furthermore, no educational interventions have been developed to supplement expert advice and counselling of women considering treatment-focused genetic testing.
Read Also: Can Metastatic Breast Cancer Go Into Remission
What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Considered a rare disease, inflammatory breast cancer typically forms in the soft tissues, blocking lymph vessels in the breast skin. Thatâs why the breast often becomes firm, tender, itchy, red and warm, from the increase in blood flow and a build-up of white blood cells. IBC differs from other forms of breast cancer, especially in symptoms, prognosis and treatment. The term inflammatory is not meant to reflect whatâs happening inside the breast, only in how the breast appears. When an infection or injury causes the breasts to become inflamed, they often become tender, swollen, red and itchy, but the underlying cause is not inflammation.
Genetic Counseling For Hereditary Breast And Ovarian Cancer
If you have a personal or family health history of breast or ovarian cancer that indicates that you could have a BRCA1, BRCA2, or other inherited mutation, your doctor may refer you for genetic counseling. Understanding and dealing with a strong family health history of breast or ovarian cancer can be challenging for you and your family. Genetic counselors can help by providing information, resources, and support to you and your family.
Genetic counseling can help you and your family make informed decisions about genetic testing for BRCA1, BRCA2, and other inherited mutations. A genetic counselor or other health care provider with specialty training in cancer genetics can provide genetic counseling.
Read Also: How Do I Self Check For Breast Cancer
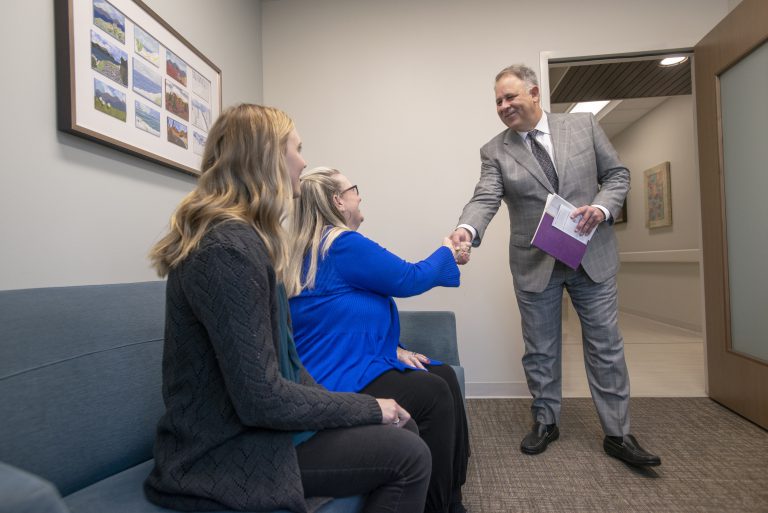
What To Expect During A Visit With A Genetic Counselor In Oncology
About 5 to 10 percent of all cancers are estimated to be caused by an inherited risk for cancer, according to the American Cancer Society . Genetic counseling and testing can help people understand their risks for developing cancer. These tools may also help them learn how to manage their risks with personalized cancer screening and identify steps they may take to reduce their cancer risks.
Genetic counselors perform risk assessments by asking questions about personal and family histories to create a family tree that goes back three to four generations. This information helps assess the chances of an inherited risk for cancer in a family and determine whether medical criteria for genetic testing are met. Information is provided about the link between cancer and genetics and inherited cancer conditions. The counselor also reviews the availability of and considerations for genetic testing.
As outlined by the ACS, the National Society of Genetic Counselors and other organizations, genetic counselors help people consider how the results of genetic testing will affect them and their families. Prior to genetic testing, and as part of the genetic counseling session, the counselor reviews and discusses these topics:
Ultimately, genetic counselors provide a supportive environment to empower people to learn about genetics and the risks for health conditions and make informed decisions about genetic testing.
If The Result Is Inconclusive
If theres not enough information to know whether you have the genetic changes, the test result is said to be inconclusive. You may still be at a higher risk of developing cancer. Taking steps to lower your risk or look for cancer early can be helpful for some people, but not having a sure result can still cause anxiety and frustration. Your health care provider or genetic counselor can help you understand what the results might mean for you and your family and help you cope with them. In some cases, testing blood relatives can help clarify this result.
Recommended Reading: Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer Deadly
Testing For Other Gene Mutations Linked With Breast Cancer Risk
Mutations in one of the BRCA genes account for most inherited breast cancers. But inherited changes in some other genes, including PALB2, CHEK2, ATM, PTEN , and TP53 can also increase breast cancer risk. Testing for changes in these genes is done less often, but it might be considered in some situations.
Talk With Your Health Care Provider Or A Genetic Counselor
The process of genetic testing is complex. Its best to meet with a genetic counselor or a trained health care provider to make decisions about testing. They can help you choose a test that meets your needs.
Your health care provider or a genetic counselor can help you correctly interpret the test results. If the testing was not done in a certified lab, your health care provider can help you get a clinical genetic test to confirm the results.
If clinical genetic testing finds a gene mutation related to breast cancer, your health care provider or a genetic counselor can help you make informed decisions about breast cancer screening and any risk-lowering options that may be right for you.
Learn about genetic test results.
Read Also: What Does Breast Cancer Affect
Variant Of Uncertain Significance
A VUS test result is not conclusive. However, most of the time, minor changes in a gene turn out to be normal variants. Most VUS results do not impact the genes ability to work, meaning they dont increase the risk of breast cancer. VUS results are usually treated similar to negative results.
VUS results are much more common with expanded panel testing than with BRCA1/2 genetic testing. Panel testing looks at many genes . With more genes in the test, its more likely youll get a VUS.
Over time, the lab may clarify the meaning of the VUS and send an updated test report to the health care provider who ordered the test. You should be notified if the VUS gets updated.
You can also check with the health care provider who ordered the test every 1-2 years to see if there is any new information about the VUS. While this may seem like a long time to wait, the information isnt likely to change very often.
A VUS test result can be confusing. If you have any questions about a VUS result, meet with a genetic counselor to go over the results.
Cascade Genetic Testing Of Family Members
Cascade genetic testing refers to the process of offering genetic testing to biologic family members who are at risk of inheriting the pathogenic variant previously identified in their relative. The process is repeated as additional pathogenic variant carriers are identified within a family. Cascade testing provides the opportunity to identify carriers of a pathogenic variant prior to cancer presentation, which allows opportunities for cancer prevention, early detection, risk reduction, and ultimately, improved health outcomes. There is wide variation in how cascade testing is conducted internationally this section currently focuses on cascade testing in the United States.
Uptake of cascade genetic testing
The dissemination of genetic risk information, from the proband to at-risk relatives, is essential for the uptake of cascade testing. Traditionally, this has consisted of discussions regarding the importance of result dissemination to at-risk relatives identified through the probands pedigree this may be supplemented with a letter or educational materials that the proband can use to facilitate disclosure to family members.
Barriers to cascade genetic testing
Communication barriers
Information interpretation
Strategies to facilitate cascade genetic testing
Several strategies aimed at facilitating family dissemination and testing uptake have been studied.
Group counseling
Proband training
Low- or no-cost genetic testing
Online direct-to-consumer testing
Chatbots
Don’t Miss: Is Radiation For Breast Cancer Dangerous
Literature Research Process And Results
Articles that met the inclusion criteria were evaluated, and data from these articles were extracted . The included articles were checked by a second reviewer to determine if they met the inclusion criteria . The literature search identified 309 references as potentially relevant. After reviewing these, 22 references were selected for detailed review .
Table 1 Mutation frequency in women with early onset breast cancer unselected for family history
Counseling And Testing Issues
Once an accurate personal and family history has been obtained, the issue of genetic testing can be explored, but when should the test be ordered, who should order the test and how should results be communicated? Individuals at risk for hereditary cancer can be identified at multiple different times. They may be identified after diagnosis and definitive treatment of breast cancer, after diagnosis but before definitive treatment, and when unaffected. Each scenario presents its own set of challenges and different approaches to the patients with respect to counseling, testing, and risk management are required . Since the testing is expensive, insurance coverage can be a concern. Most insurance companies have established criteria for coverage of genetic testing based on the National Comprehensive Cancer Networks guidelines . Some of the newer panel tests are not covered by some insurers.
Read Also: Can Cancer Spread To The Breast
Whats The Role Of A Genetic Counselor
Most people are referred to a genetic counselor by their physician or an advanced practitioner, such as a physicians assistant or a nurse practitioner.
Genetic counselors dont recommend testing. Our role is to perform a risk assessment and review the reasons people may or may not be interested in genetic counseling to empower them to make a decision thats right for them.
During pre-test counseling, genetic counselors:
- Discuss genetics and the connection to cancer
- Review your personal and family history information to assess the likelihood that genetic testing may find an inherited risk
- Prepare you for what genetic testing may or may not find and the potential consequences of the results
- Review reasons people may decline genetic testing
Should you choose to go ahead with genetic testing, we discuss your results and their potential consequences during a post-testing counseling session.
If we find a mutation, we discuss your options, according to the medical guidelines for that specific mutation, to help you determine your next steps. If youre a patient at CTCA, we work with your medical team to outline the guidelines to be considered going forward.
Why Refer To A Uva Genetic Counselor
UVA geneticcounselors have experience with large-panel tests, so they can interpret theresults and translate them into clinical recommendations, which can often be achallenge. They have a full hour with patients to counsel them on their testresults and, as an added benefit, the genetic counseling team handles all ofthe insurance billing and any snafus that arise.
UVA geneticcounselors are always available to step in at any phase of a patient evaluationand will work with referring physicians to ensure patients are well informed oftheir options for testing and the recommended approach to treatment.
To refer a patient to UVA Cancer Center, call UVA PhysicianDirect at 800.552.3723.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Know If I Have Breast Cancer
Who Should Be Tested For Brca
While BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations may increase your odds of developing breast cancer, your odds of having either mutation are pretty small. An estimated 0.25% of the general population carries a mutated BRCA gene, or about one out of every 400 people.
For some people, though, the chances of having a BRCA gene mutation are much higher. Genes are inherited, which is why knowing your family history is important when determining breast cancer risks. If one of your parents has a BRCA mutation, you have a 50% chance of inheriting the mutated gene.
Odds can also vary depending on a persons ethnicity. For example, people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent have a 2.5% chance of inheriting a BRCA mutation, or about 10 times the rate of the general population.
Because the overall odds are so low, most experts recommend that only people with a heightened risk get tested for BRCA mutations. Likewise, insurance companies often only cover genetic counseling and testing for individuals who are at high risk. A person could be considered at high risk for BRCA mutations if they have a family history of:
There are also other gene mutations besides BRCA that could increase the risk of breast cancer. The most prominent of these is PALB2. As with BRCA1 and BRCA2, testing for other genetic mutations is recommended only if you are at high risk for that particular gene.
What Does A Genetic Counselor Do
A genetic counselor can evaluate your individual risk of getting certain types of cancer based on your family’s medical history. They also explain which genetic tests can give you more information about your risk level.
It can be complex to decide whether you should have genetic testing to find out more about your hereditary cancer risk. Your counselor will explain the testing process, what the tests can and cannot do, and how well they work. Together, you will also discuss how knowing the test results may affect your emotions, mental health, and family. This information can help you decide if having genetic testing is right for you.
Genetic counselors can also advise you on:
-
The privacy of your genetic information
-
How to talk with family members about inherited cancer risk
You May Like: How Treatable Is Breast Cancer
When Is Genetic Testing Not Recommended
Theres only a very small chance your family carries a BRCA1/2 inherited gene mutation if you or a family member is the only person in your family with breast cancer .
Although you always have the option of being tested, in most cases, genetic testing isnt recommended when theres a very low chance of finding a mutation. Its strongly recommended you speak with a genetic counselor before deciding whether to have genetic testing.
Most breast cancers are not due to a BRCA1/2 or other inherited gene mutation linked to breast cancer .