What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
This breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. In stage 1, the tumor measures up to 2 cm and no lymph nodes are involved. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue.
Because a stage 1 tumor is small, it may be difficult to detect. However, breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.Stage 1 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 1A: The tumor measures 2 cm or smaller and has not spread outside the breast.
Stage 1B: Small clusters of cancer cells measuring no more than 2 mm, are found in the lymph nodes, and either there is no tumor inside the breast, or the tumor is small, measuring 2 cm or less.
At stage 1, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. For example, there may or may not be cancer cells in the lymph nodes, and the size of the tumor may range from 1 cm to 2 cm. Most commonly, stage 1 breast cancer is described as:
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4, depending on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor
- N0: Usually, cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
- M0: The disease has not spread to other sites in the body.
Stage 1 breast cancer survival rate
The survival rate for stage 1A breast cancer may be slightly higher than for stage 1B. However, all women with stage 1 breast cancer are considered to have a good prognosis.
What Is Histologic Grade Or Nottingham Grade Or Elston Grade
These grades are similar to what is described in the question above about differentiation. Numbers are assigned to different features seen under the microscope and then added up to assign the grade.
- If the numbers add up to 3-5, the cancer is grade 1 .
- If they add up to 6 or 7, it means the cancer is grade 2 .
- If they add up to 8 or 9, it means the cancer is grade 3 .
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 breast cancer is divided into three groups:
- Stage 3A
- Stage 3C
Stage 3A can mean:
No cancer is seen in the breast, but cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast measures up to 5cm and cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is larger than 5cm, and cancer is found in up to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone.
Stage 3B means the cancer in the breast can be any size and has spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall. Cancer is found in up to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breast bone.
Stage 3C means the cancer in the breast can be any size, may have spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall and cancer is found in 10 or more lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone, or to nodes above or below the collarbone.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3b Breast Cancer Prognosis
The Tnm Staging System
The TNM staging system gives the complete stage of the cancer:
- T describes the size of the tumour.
- N describes whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and which nodes are involved. For example, N0 means no lymph nodes are affected. N1 means there are cancer cells in 1 to 3 of the lymph nodes.
- M describes whether the cancer has spread to another part of the body. For example, M0 means the cancer has not spread to other parts of the body.
Sometimes the final TNM staging may not be certain until after surgery to remove the cancer.
What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer
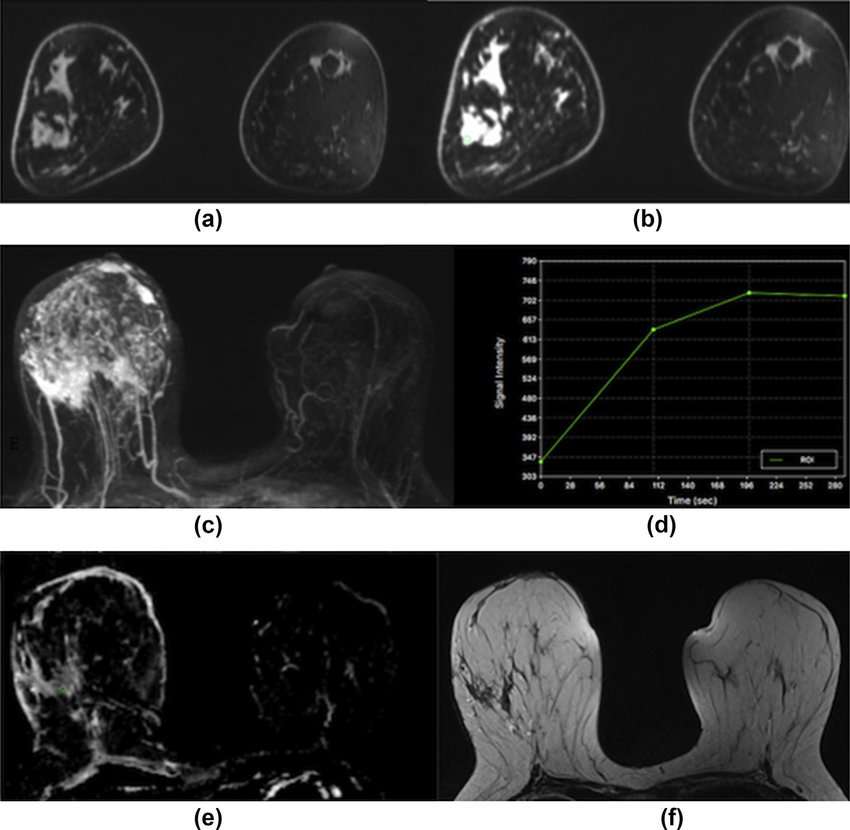
As its name suggests, inflammatory breast cancer often causes the breast to become red, swollen, and inflamed. Some women with IBC also notice thickened or discolored breast skin with tiny dimples, puckers, or ridges that make it look like an orange peel. While the symptoms may sound like an infection, the real culprit is cancer that is blocking lymphatic vessels in the skin and breast tissue, causing a buildup of fluid and, in some cases, pain, discoloration, and sudden swelling of the breast. Also called inflammatory breast carcinoma or locally advanced breast cancer, IBC can spread quickly, making prompt diagnosis and treatment essential.
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
You May Like: Tamoxifen Metastatic Breast Cancer
What Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Also known as invasive breast cancer, the tumor in this stage measures between 2 cm to 5 cm, or the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer. Stage 2 breast cancer indicates a slightly more advanced form of the disease. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue, and the tumor is larger than in stage 1 disease. However, stage 2 means the cancer has not spread to a distant part of the body.
At stage 2, a tumor may be detected during a breast self-exam as a hard lump within the breast. Breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.
Stage 2 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 2A: One of the following is true:
- There is no tumor within the breast, but cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast is 2 cm or smaller and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast measures 2 cm to 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage 2B: One of the following is true:
- The tumor measures 2 cm to 5 cm and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
At stage 2, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Most commonly, stage 2 breast cancer is described as:
Stage 2 breast cancer survival rate
Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Stage 4 breast cancer is also known as secondary breast cancer.
Stage 4 breast cancer means:
- The tumour can be any size
- The lymph nodes may or may not contain cancer cells
- The cancer has spread to other parts of the body such as the bones, lungs, liver or brain
If your cancer is found in the lymph nodes under the arm but nowhere else in the body you do not have stage 4 breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer Stage 3
What Is A Cancer Stage
While a grade describes the appearance of cancer cells and tissue, a cancers stage explains how large the primary tumor is and how far the cancer has spread in the patients body.
There are several different staging systems. Many of these have been created for specific kinds of cancers. Others can be used to describe several types of cancer.
Coping With A Diagnosis Of Dcis
Being told you have DCIS can be a difficult and worrying time. Everyone reacts differently to their diagnosis and have their own way of coping.
Although DCIS is an early form of breast cancer with a very good prognosis, people understandably may feel very anxious and frightened by the diagnosis. People can often struggle to come to terms with being offered treatments such as a mastectomy, at the same time as being told their DCIS may never do them any harm.
Some people are reluctant to say theyre anxious about a diagnosis of DCIS because they worry others will see it as less important than other types of breast cancer. Because of this they might feel less able to ask for support. But there are people who can support you so dont be afraid to ask for help if you need it. By letting other people know how you feel, particularly your family and friends, they can be more supportive.
Some people find it helpful to discuss their feelings and concerns with their breast care nurse or specialist. If youd like to talk through your feelings and concerns in more depth over a period of time, a counsellor or psychologist may be more appropriate. Your breast care nurse, specialist or GP can arrange this.
Find out more about coping emotionally with breast cancer.
If you want to talk you can also call our Helpline on 0808 800 6000.
Recommended Reading: How Bad Is Stage 3 Cancer
What Does It Mean If My Report Mentions Estrogen Receptor Or Progesterone Receptor
Receptors are proteins on cells that can attach to certain substances, such as hormones, that circulate in the blood. Normal breast cells and some breast cancer cells have receptors that attach to the hormones estrogen and progesterone. These 2 hormones often fuel the growth of breast cancer cells.
An important step in evaluating a breast cancer is to test a portion of the cancer removed during the biopsy to see if they have estrogen and progesterone receptors. Cancer cells may contain neither, one, or both of these receptors. Breast cancers that contain estrogen receptors are often referred to as ER-positive cancers, while those containing progesterone receptors are called PR-positive cancers. Women with hormone receptor-positive cancers tend to have a better prognosis and are much more likely to respond to hormone therapy than women with cancers without these receptors.
All breast cancers and pre-cancers, with the exception of lobular carcinoma in situ , should be tested for these hormone receptors when they have the breast biopsy or surgery.
Results for ER and PR are reported separately and can be reported in different ways:
- Negative, weakly positive, positive
- Percent positive
- Percent positive and whether the staining is weak, moderate, or strong.
How the results of your tests will affect your therapy is best discussed with your doctor.
What Is Vascular Lymphovascular Or Angiolymphatic Invasion What If My Report Mentions D2
If cancer cells are seen in small blood vessels or lymph vessels under the microscope, it is called vascular, angiolymphatic, or lymphovascular invasion. When cancer is growing in these vessels, there is an increased risk that it has spread outside the breast. If your report does not mention this type of invasion, it means it is not there. Even if it is there, it does not always mean that your cancer has spread. How this finding affects your treatment is best discussed with your doctor.
D2-40 and CD34 are special tests that the pathologist may use to help identify these types of vascular invasion. These tests are not needed in every case.
Don’t Miss: Stage Three Breast Cancer Prognosis
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
Treatment Options For Stage 3 Cancer
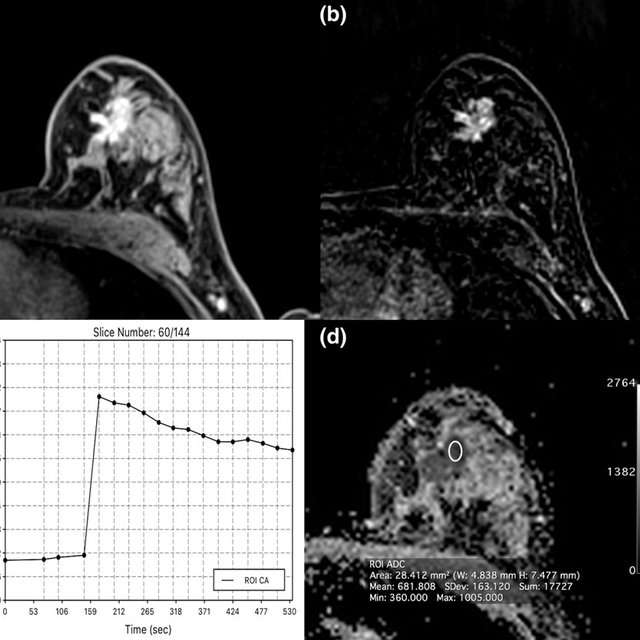
In general, regimens for stage 3 cancers typically start with either surgery or treatment to shrink the tumor before surgery, such as chemotherapy, radiation, or a combination of both.
Stage 3 breast cancer treatment: The first step is typically either chemotherapy or surgery.
Called neoadjuvant chemotherapy, because its given before other treatment, this may help shrink a tumor enough that breast-conserving surgery is possible. If it doesnt shrink enough, the patient may need a mastectomy instead. HER2-positive cancers may also be treated with targeted drugs before surgery.
After surgery, depending on the type of breast cancer, your treatment may continue with radiation. Chemotherapy and/or targeted drugs may be part of your treatment plan after surgery as well.
Stage 3 lung cancer treatment: This is highly dependent on how large the tumor is and which lymph nodes are affected. Generally, treatment begins with chemotherapy and/or radiation. You may have chemotherapy and radiation at the same time, or you may have them one after another. Surgery may follow this treatment if your care team thinks the remaining cancer may be successfully removed. After surgery, additional chemotherapy and/or radiation may be part of your treatment plan.
If chemotherapy, radiation or surgery arent appropriate options, immunotherapy drugs may be.
Recommended Reading: Where To Buy Breast Cancer Merchandise
Don’t Miss: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Definition
What Are The Different Grades Of Breast Cancer
There are three grades of invasive breast cancer:
- Grade 1 looks most like normal breast cells and is usually slow growing
- Grade 2 looks less like normal cells and is growing faster
- Grade 3 looks different to normal breast cells and is usually fast growing
Sometimes the grade given to a cancer after a biopsy can change after surgery. This is because after surgery theres more tissue for the pathologist to look at, which can give them more detailed information about the cancer.
What Does It Mean If My Carcinoma Has Tubular Mucinous Cribriform Or Micropapillary Features
These are different types of invasive ductal carcinoma that can be identified under the microscope.
- Tubular, mucinous, and cribriform carcinomas are “special types” of well-differentiated cancers that often have a better prognosis than the more common type of invasive ductal carcinoma .
- Micropapillary carcinoma is a type of invasive breast carcinoma that often has a worse prognosis.
If your doctor knows that your tumor is made up of one of these special types of breast cancer, he or she may recommend different treatment.
Since some tumors are made up of more than one type, the entire tumor must be removed in order to know what types your tumor contains. A needle biopsy doesnt give enough information to guide treatment.
Recommended Reading: Type 3 Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
In the early stages, invasive ductal carcinoma may not cause any obvious symptoms. Some people may develop certain warning signs, including:
- A new lump in the breast.
- Swelling of the breast.
- Prior radiation to the chest.
- Early start of menstrual periods.
- Late menopause.
- Never being pregnant or having children later in life.
In approximately 5% to 10% of breast cancer cases, invasive ductal carcinoma has been linked to hereditary factors. These include mutations of the breast cancer gene 1 , breast cancer gene 2 and other genes such as PALB2, CHEK2 and ATM.
What To Know About Breast Cancer Growth
Breast cancer occurs when normal cells mutate and multiply faster than usual. One cell divides to become two cells, then each of those cells divides to become four cells, and so on. The uncontrolled multiplication of cancer cells creates tumors within the breast tissue.
The speed at which a cancer progresses depends on the growth rate of the cancer cells. It is hard to estimate cancer growth because not all cancer cells multiply and divide at the same speed.
In most cases, breast cancer initially develops in either the milk ducts or the lobules, which are the glands that produce milk, before expanding into the breast tissue.
Breast cancer that develops in ducts or lobules can spread to the connective tissue. From there, it can spread to the surrounding lymph nodes.
Once in the lymph nodes, the cancer cells can enter the lymphatic system or the bloodstream, where they can move to other areas of the body.
One recent
Also Check: First Stage Of Breast Cancer Symptoms
Rare Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Medullary ductal carcinoma accounts for only 3%5% of breast cancers. It may appear on a mammogram, and it does not always feel like a lump rather, it can feel like an abnormally spongy area in the breast tissue.
Mucinous ductal carcinoma is also called colloid breast cancer. It occurs when cancer cells within the milk duct of the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma tends to grow slowly, and has a better prognosis than some other types of IDCs.
Papillary carcinoma forms finger-like projections that can be seen under a microscope. Many papillary tumors are benign, but even those that become cancerous are usually very treatable with a good prognosis. Papillary carcinoma most commonly occurs in people older than 60.
Tubular ductal carcinoma is a rare diagnosis of IDC, comprising only 2% of breast cancer diagnoses. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
What If A Carcinoma Is Infiltrating Or Invasive
These words are used to mean that the cancer is not a pre-cancer , but is a true cancer.
The normal breast is made of tiny tubes that end in a group of sacs . Cancer starts in the cells lining the ducts or lobules, when a normal cell becomes a carcinoma cell. As long as the carcinoma cells are still confined to the breast ducts or lobules, without breaking out and growing into surrounding tissue, it is considered in-situ carcinoma .
Once the carcinoma cells have grown and broken out of the ducts or lobules, it is called invasive or infiltrating carcinoma. In an invasive carcinoma, the tumor cells can spread to other parts of your body.
Also Check: Non Inflammatory Breast Cancer