Removal Of The Whole Breast
You might have a mastectomy if:
- the area of the DCIS is large
- there are several areas of DCIS
- you have small breasts and too much of the breast is affected by DCIS to make breast conserving surgery possible
You may have surgery to your armpit called a sentinel lymph node biopsy if you have a mastectomy. This means having about 1 to 3 lymph nodes removed.
If you want to, you can choose to have a new breast made at the time of the mastectomy, or some time afterwards.
Hormone therapy is recommended for 5 years if you have breast conserving surgery for DCIS and:
- your cancer calls have oestrogen receptors
- you do not have radiotherapy
Research shows that taking hormone therapy after breast conserving surgery for DCIS reduces the risk of it coming back .
Trials show that hormone therapy can reduce the number of further invasive breast cancers or DCIS. But in these trials, the people taking a hormone therapy tablet called tamoxifen did not live any longer than those who didn’t take it.
What Is High Grade Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Standard treatment options for DCIS include: Lumpectomy followed by radiation therapy: This is the most common treatment for DCIS. Lumpectomy is sometimes called breast-conserving treatment because most of the breast is saved. Mastectomy: Mastectomy, or removal of the breast, is recommended in some cases.
Additionally, is ductal carcinoma in situ really cancer? Ductal carcinoma in situ means the cells that line the milk ducts of the breast have become cancer, but they have not spread into surrounding breast tissue. DCIS is considered non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer.
does high grade DCIS always come back?
DCIS that is high grade, is nuclear grade 3, or has a high mitotic rate is more likely to come back after it is removed with surgery. DCIS that is low grade, is nuclear grade 1, or has a low mitotic rate is less likely to come back after surgery.
How long does it take for high grade DCIS to become invasive?
Research has shown that the interval between DCIS detection and the occurrence of invasive cancer averages five years in high–grade cases. For the retrospective study, researchers divided 733,905 women aged 50 to 69 years participating for the first time in a screening program into five-year age groups.
What Does It Mean If My Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Is Described As Being Low Grade Intermediate Grade Or High Grade Or Nuclear Grade 1 Nuclear Grade 2 Or Nuclear Grade 3 Or Low Mitotic Rate Intermediate Mitotic Rate Or High Mitotic Rate
These are all different ways of describing how the DCIS looks under the microscope:
- DCIS that is high grade, is nuclear grade 3, or has a high mitotic rate is more likely to come back after it is removed with surgery.
- DCIS that is low grade, is nuclear grade 1, or has a low mitotic rate is less likely to come back after surgery.
- DCIS that is intermediate grade, is nuclear grade 2, or has an intermediate mitotic rate falls in between these two.
Patients with higher grade DCIS may need additional treatment.
Also Check: Stage 2 Carcinoma Breast Cancer
Recovering From Breast Surgery
Will I have pain?
Most people have some pain after surgery.
Talk with your doctor or nurse before surgery about ways to control pain after surgery. Also, tell them if your pain control is not working.
How long before I can return to normal activities?
| Breast-Sparing Surgery | Most women are ready to return to most of their usual activities within 5 to 10 days. |
|---|---|
| Mastectomy | It may take 3 to 4 weeks to feel mostly normal after a mastectomy. |
| Mastectomy with Reconstruction | Your recovery will depend on the type of reconstruction you have. It can take 6 to 8 weeks or longer to fully recover from breast reconstruction. |
What other problems might I have?
| Breast-Sparing Surgery |
|---|
You may not like how your breast-like shape looks.If you have an implant:
If you have flap surgery, you may lose strength in the part of your body where a muscle was removed. |
What other types of treatment might I need?
If you chose to have breast sparing surgery, you will usually need radiation therapy. Radiation treatments are usually given 5 days a week for 5 to 8 weeks.
If you have a mastectomy, you may still need radiation therapy.
No matter which surgery you choose, you might need:
- Chemotherapy
What will my breast look like?
To get a better idea of what to expect, ask your surgeon if you can see before and after pictures of other women who have had different types of surgery.
Who Gets Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast
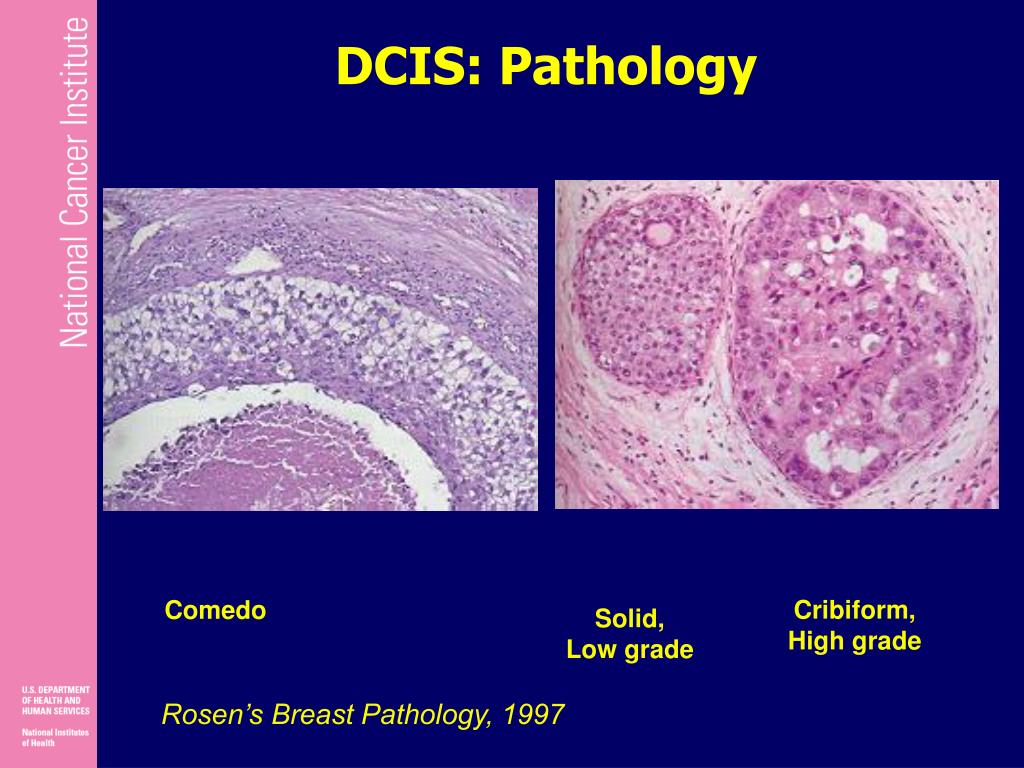
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast is a very common type of breast cancer. Almost 70-80% of breast cancers are Ductal Carcinoma NOS types
- Middle-aged and older women past the age of 40 years are affected, though women over 65 years have the highest risk
- Although both women and men are capable of developing the condition, it is much more common in women
- All racial and ethnic groups are affected and no specific predilection is seen
- Developed countries show higher prevalence rate for breast cancer than developing countries average of 80 cases per 100,000 populations, as against 18 cases per 100,000 populations seen in the developing countries. Thus, America, Europe, Australia have greater incidences than Asia and Africa
Read Also: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Factors At Diagnosis That Affect Prognosis For Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Many people used to think that Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ was a precursor for invasive breast cancer or a pre-cancerous condition. However, researchers have struggled for many years to work out which ductal carcinomas in-situ develop into invasive breast cancer and why.
Indeed, not all of these early changes progress to a more invasive, problematic cancer. The high survival rates of 98% to 99% for Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ, in 2010 reflect the effectiveness of treatment.
At present, there does not seem to be onedefinitive prognostic marker. Indeed, it is difficult to find research on one single factor alone, such as age, or tumor grade, because they are all inter-linked.
This clearly shows that each individual case is different and outcome and prognosis is based upon many factors.
However, research suggests that 5 main factors of DCIS on diagnosis seem to predict a less favourable outcome. These include:-
- Younger age at Diagnosis
- Tumor Grade
- Large Tumor size or clinically palpable at diagnosis
Treatment Options For Dcis: Lumpectomy Or Mastectomy
In most cases, the first line of treatment when DCIS is diagnosed is some form of breast surgery.
There are two basic surgical approaches for DCIS treatment:-
Lumpectomy is usually adequate if the area of breast abnormality is very small or only one abnormality is found on a mammogram.
Also, lumpectomy is usually recommended if the DCIS is of a less aggressive type such as non-comedo DCIS.
Lumpectomy is most effective for DCIS patients with small, low-grade DCIS which is easily identifiable on mammogram. In some cases the amount of DCIS is so small that the first exploratory biopsy is enough to remove all of the carcinoma and a subsequent lumpectomy is not required.
You May Like: Can Stage 3 Breast Cancer Be Cured
Are You Facing A Decision About Surgery For Dcis Or Breast Cancer
Do you have ductal carcinoma in situ or breast cancer that can be removed with surgery? If so, you may be able to choose which type of breast surgery to have. Often, your choice is between breast-sparing surgery and a mastectomy .
Once you are diagnosed, treatment will usually not begin right away. There should be enough time for you to meet with breast cancer surgeons, learn the facts about your surgery choices, and think about what is important to you. Learning all you can will help you make a choice you can feel good about.
How Is Dcis Diagnosed
DCIS doesnt usually appear as a breast lump or breast change. As a result, most women with DCIS do not show any signs or symptoms of having breast cancer.
Mammograms and ultrasounds are the most common ways in which DCIS is diagnosed. If DCIS is suspected, a biopsy is usually required to confirm whether DCIS is present.
Pathologists usually attribute a grade to DCIS. The grade indicates the patterns of cancer cell growth and how fast the cells are growing. Based on what the DCIS cancer cells look like under a microscope, DCIS can be graded as high, intermediate or low.
If left untreated, high grade DCIS is likely to develop into invasive breast cancer. Low or intermediate grades of DCIS may remain as they are for many years. In some cases, however, low or intermediate grades of DCIS can develop into invasive breast cancer.
While the size and grade of DCIS can help doctors predict whether the cancer is likely to become invasive, there are no certain answers. Unfortunately it is not currently possible to know for certain if a woman will go on to develop invasive breast cancer.
Read Also: Did Anne Hathaway Have Cancer
What Is The Optimal Treatment For A Local Recurrence
Although local recurrences are uncommon after initial treatment for DCIS, they can be psychologically devastating for the patient, particularly if it is an invasive recurrence. The treatment of a recurrence depends on the initial treatment of DCIS, whether the recurrence is DCIS or invasive, and whether the patient has received radiotherapy to the breast. After diagnosis is confirmed histologically, a screen for distant metastatic disease is usually performed.
For a patient treated by BCS alone, management options may include re-excision followed by radiation or mastectomy with or without breast reconstruction. If BCS and XRT were used initially, then mastectomy is usually the only option available. If mastectomy alone was the original treatment modality, then surgical removal of a chest wall recurrence may be possible, followed by chest wall RT, but this situation is extremely rare. Treatment of the axilla and consideration of systemic therapy is also required. Most recurrences can be salvaged by mastectomy. One study showed that following mastectomy, subsequent freedom from chest wall recurrence was high .
What Does It Mean If My Report On Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Mentions Estrogen Receptor Or Progesterone Receptor
ER and PR are special tests that the pathologist does that are important in predicting response of the DCIS to hormone therapy . Testing for ER is done for most cases of DCIS, but testing for PR is not typically needed. Results for ER and PR are reported separately and can be reported in different ways:
- Negative, weakly positive, positive
- Percent positive with something saying whether the staining is weak, moderate, or strong
Ask your doctor how these results will affect your treatment.
Also Check: De Novo Metastatic Breast Cancer Symptoms
Dcis Can Happen At Any Age
“DCIS can happen to anybody, anytime,” says Dr. Meyers, but it’s usually diagnosed in women over 40, the age at which many women begin getting mammograms. According to the American Cancer Society, DCIS rates increase with age, and peak around age 70 to 79.
Women diagnosed with DCIS under age 50 have a higher rate of recurrence or of an invasive cancer, and therefore more aggressive treatment is usually recommended, says Dr. White. Those over 50, on the other hand, can take comfort in knowing that a diagnosis does not raise their risk of early death.
What Are The Symptoms Of Dcis
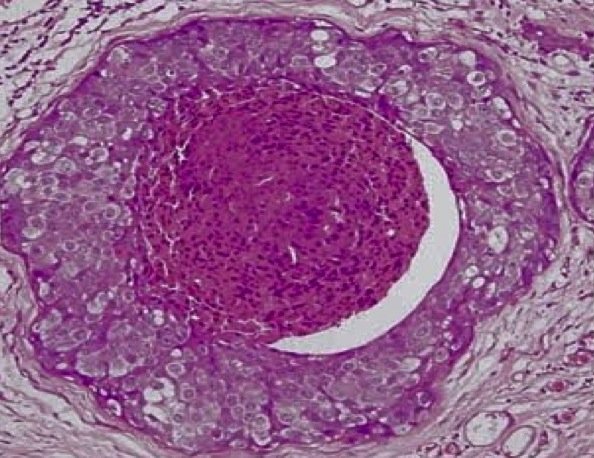
DCIS usually has no symptoms. Most cases of DCIS are found during routine breast screening or if a mammogram is done for some other reason.
Occasionally DCIS is found when someone has a breast change such as a lump or discharge from the nipple. However, if someone with DCIS has a breast change its more likely they will also have an invasive breast cancer.
Some people with DCIS also have a type of rash involving the nipple known as Pagets disease of the nipple, although this is rare.
Don’t Miss: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Treatment
You Can Still Breastfeed After Dcis
Even though DCIS affects the milk ducts, it doesn’t necessarily mean a woman can’t produce milk if she gets pregnant after diagnosis and treatment. “As long as a woman has surgery alone, and assuming the lesion is not too close to the nipple, DCIS should not cause problems with conceiving or breastfeeding,” says Dr. Meyers.
If a woman has been treated with radiation or hormone therapy in addition to surgery, on the other hand, “we usually recommend that a woman see her gynecologist or a fertility doctor to ensure there won’t be an issue,” Dr. Meyers adds.
Morphological Features Of Carcinoma In Situ
Features of a low-grade DCIS. Low-grade DCIS in a core needle biopsy intermediate and high-magnification of the lesion showing a cribriform growth pattern DCIS with negative margins, but the distance between neoplasia and inked margin is < 2 mm ER positivity in a low-grade DCIS Her-2 positivity in a low-grade DCIS.
Reporting stromal reaction and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is also recommended. High-grade DCIS is predominantly associated with a desmoplastic reaction of the periductal stroma and seems to correlate with a higher risk of recurrence . TIL is a dense, chronic inflammatory infiltrate surrounding DCIS. Several studies demonstrated that breast carcinomas with a marked intra-tumoral stromal lymphocytic infiltrate have a better prognosis than carcinomas with lymphocyte depletion . Triple-negative and HER2-positive DCIS lesions are the subgroups of breast carcinomas that show the greatest degree of enrichment of the stroma by lymphocytes . A shorter recurrence-free interval is seen if TILs are associated with younger age, larger size, comedonecrosis and ER negative, and HER2 overexpression. However, no significant association was identified for longer follow-ups . It should be noted that the evaluation of TILs has a prognostic value and not a predictive value of response to therapies, therefore, this criterion is not used to decide whether or not to administer chemotherapy or other systemic therapies.
Recommended Reading: What Blood Test Can Detect Breast Cancer
After Dcis The Risk Of Another Cancer Is Higher
Stage 0 breast cancer still comes with risks. “When you have DCIS, it means your risk of developing another DCIS or an invasive breast cancer is higher than the general population,” says Dr. Meyers. Studies show that people with DCIS have a 1% to 2% chance of developing invasive breast cancer after a mastectomy and a slightly higher chance after a lumpectomy.
“Whatever caused the cells to mutate will generally occur in more than one ductand sometimes, those mutated cells can break through a duct and become invasive breast cancer,” adds Dr. Meyers. “We don’t know why some DCIS have the ability to do this while others don’t, so right now we want to treat all of them with at least surgery, and maybe more.”
Dcis Has The Same Risk Factors As Invasive Breast Cancers
“The same things that increase a woman’s risk for DCIS are really the same things that increase her risk of invasive breast cancer,” says Dr. Meyers. For example, having a strong family history can be a factorespecially if a woman tests positive for a high-risk BRCA gene mutation.
Women who have a longer period of estrogen stimulation, meaning they started menstruation early and/or entered menopause late, also have an increased risk of DCIS as well as invasive cancer. That also goes for women who don’t have children, or who have their first pregnancy after age 30.
Also Check: What Percentage Of Breast Cancer Is Hereditary
I Have Dcis Will I Develop Invasive Breast Cancer In The Future
Not every woman with DCIS will develop invasive breast cancer. Your risk of developing invasive breast cancer is, however, increased if you have been diagnosed with DCIS.
Recent results from an Australian study found that between 1995 and 2005, 13,749 women were diagnosed with DCIS and that, by the end of 2005, 706 of those women had developed invasive breast cancer even though they had received treatment for DCIS.2
According to the study, women who are diagnosed with DCIS are, on average, 3.9 times more likely to develop invasive breast cancer than Australian women of a similar age who have not had DCIS.
Appendix: Constructing Survival Curves From Casecontrol Data For Population
To estimate the absolute risks of recurrence for the population-based cohort by clinical and histopathologic characteristics, we converted the results from the matched casecontrol study to survival curves by using the following method. First, we assigned a simulated value for a variable of interest to each member of the cohort not included in the casecontrol study and to those members selected for the casecontrol study who had missing values. We generated the simulated value based on the prevalence of the variable of interest among the control and case subjects. After all participants in the entire cohort had been assigned a value for a variable of interest, we used standard methods to generate KaplanMeier survival curves. We repeated this process 1000 times, each time using a new, simulated value assigned for the variable of interest that was based on the same proportion calculated for case and control subjects. Finally, we generated an overall KaplanMeier curve by averaging the KaplanMeier curves at each event time point, t. We repeated this process for each clinical and histopathologic variable of interest. The 95% confidence intervals for the averaged KaplanMeier curves were obtained by evaluating the .025 and .975 quantiles at each time point, t. All survival estimates and simulations were generated with the use of the statistical package R .
Also Check: Breast Cancer Symptoms Weight Gain
The Sojourn Time For Early Breast Tumor Development Is Faster In Younger Women
Breast tumors in younger women do seem to progress faster than with older women, particularly in the pre-clinical phases .
This is sometimes called the sojourn time. The sojourn time is the difference in time between abnormalities found on mammogram and the time it takes for them to be clinically detectable, .
Sojourn time sometimes formally defined as, the mean duration of pre-clinical disease, has been consistently shown to be longer for older women and for slower-growing breast tumors.
estimate