How Do Hormone Therapies Work
Hormone therapies slow or stop the growth of hormone receptor-positive tumors by preventing the cancer cells from getting the hormones they need to grow.
They do this in a few ways:
- Some hormone therapies, such as;tamoxifen, attach to the receptor in the cancer cell and block estrogen from attaching to the receptor.
- Some hormone;therapies, such as aromatase inhibitors and ovarian suppression, lower the level of estrogen in the body so the cancer cells cant get the estrogen they need to grow.
What Is The Life Expectancy For Each Cancer Stage
Your outlook depends on the stage of your cancer when its discovered. Cancer is staged by number, starting with 0 and going to 4. Stage 0 is the very beginning and stage 4 is the last stage, also called the metastatic stage because its when cancer has spread to other areas in the body.
Each number reflects different characteristics of your breast cancer. These include the size of the tumor and whether cancer has moved into lymph nodes or distant organs, like the lungs, bones, or brain.
The cancer subtype doesnt play a role in staging, only in treatment decisions.
Survival statistics of women with the major subtypes of breast cancer such as ER-positive, HER2-positive, and triple-negative are grouped together. With treatment, most women with very early stage breast cancers of any subtype can expect a normal life span.
Survival rates are based on how many people are still alive years after they were first diagnosed. Five-year and 10-year survival are commonly reported.
According to the American Cancer Society, 5-year survival rates are:
- stage 0 100 percent
- stage 3 72 percent
- stage 4 22 percent
One thing to note is that these statistics also included women with the more aggressive HER2-positive and triple-negative cancers. And it takes five years to get to a five-year statistical survival rate, so newer therapies are not included in these numbers.
Its likely that a woman with ER-positive breast cancer diagnosed today may have a higher chance of survival.
What Is The Prognosis For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Triple negative breast cancer can be more aggressive and difficult to treat. ;Also, the cancer is more likely to spread and recur. ;The;stage;of breast cancer and the;grade of the tumor;will influence your prognosis. Research is being done currently to create drug therapies that are specific for triple negative breast cancer.
Interested in learning more? i3Health is hosting an upcoming webinar Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Applying Treatment Advances to Personalized Care. Learn more here.
Material on this page courtesy of Johns Hopkins Medicine
Don’t Miss: How Can I Know If I Have Breast Cancer
Basal Cell Breast Cancer
Basal cell breast cancer is a type of breast cancer with a clear pattern of changes in proteins in the cells.
Cancer doctors recognise basal cell breast cancer when they examine the cancer cells under a microscope. It is often linked with triple negative breast cancer.
Basal cell breast cancers are usually triple negative. And most triple negative breast cancers are basal cell cancers. They are similar types of breast cancer, but not exactly the same.
See also
The symptoms;of triple negative breast cancer are the same as for other breast cancer types.
See also
Prospective Ascertainment Of Breast Cancer Cases And The Coding Of Receptor Status
In all countries incident breast cancer cases were identified using record linkage with cancer and pathology registries. In France, Germany and Greece, cancer occurrence was prospectively ascertained through linkage with health insurance records and regular direct contact with participants and their next of kin, and all reported breast cancer cases were then systematically verified against clinical and pathological records. Mortality data were coded according to the 10th Revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Injuries, and Causes of Death , and cancer incidence data were coded according to the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology . Invasive breast cancer cases were classified as per the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology , second revision . Breast tumor receptor status was standardized across EPIC centers using the following criteria for a positive expression: 10% cells stained, any plus-system description, 20 fmol/mg, an Allred score of 3, an IRS 2, or an H-score 10 .
Vital status was collected from regional or national mortality registries. The last updates of endpoint data for cancer incidence and vital status were between 2005 and 2010, depending on the center. Women were considered at risk from the time of recruitment until breast cancer diagnosis or censoring respectively. A total of 7,095 breast cancer cases had information on ER status ; of which, 5,843 had further information on PR status .
Read Also: Is Radiation For Breast Cancer Dangerous
What Is Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy slows or stops the growth of hormone-sensitive tumors by blocking the bodys ability to produce hormones or by interfering with effects of hormones on breast cancer cells. Tumors that are hormone insensitive do not have hormone receptors;and do not respond to hormone therapy.
Hormone therapy for breast cancer should not be confused with menopausal hormone therapy treatment with estrogen alone or in combination with progesterone to help relieve symptoms of menopause. These two types of therapy produce opposite effects: hormone therapy for breast cancer blocks the growth of HR-positive breast cancer, whereas MHT can stimulate the growth of HR-positive breast cancer. For this reason, when a woman taking MHT is diagnosed with HR-positive breast cancer she is usually asked to stop that therapy.
Do I Need Genetic Counseling And Testing
Your doctor may recommend that you see a genetic counselor. Thats someone who talks to you about any history of cancer in your family to find out if you have a higher risk for getting breast cancer. For example, people of Ashkenazi Jewish heritage have a higher risk of inherited genetic changes that may cause breast cancers, including triple-negative breast cancer. The counselor may recommend that you get a genetic test.
If you have a higher risk of getting breast cancer, your doctor may talk about ways to manage your risk. You may also have a higher risk of getting other cancers such as ovarian cancer, and your family may have a higher risk. Thats something you would talk with the genetic counselor about.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Breast Cancer
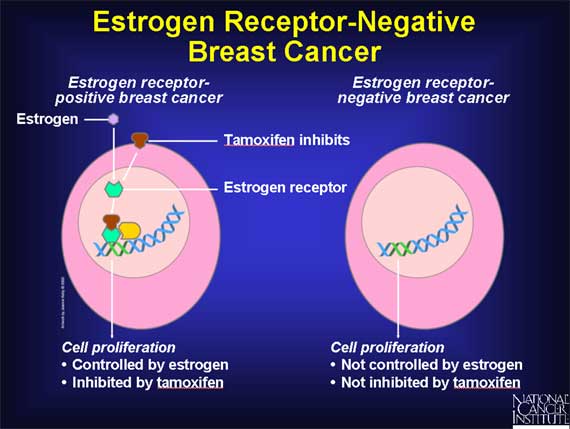
What Are Estrogen And Progesterone Receptors
Receptors are proteins in or on cells that can attach to certain substances in the blood. Normal breast cells and some breast cancer cells have receptors that attach to the hormones estrogen and progesterone, and depend on these hormones to grow.
Breast cancer cells may have one, both, or none of these receptors.
- ER-positive: Breast cancers that have estrogen receptors are called ER-positive cancers.
- PR-positive: Breast cancers with progesterone receptors are called PR-positive cancers.
- Hormone receptor-positive: If the cancer cell has one or both of the receptors above, the term hormone-receptive positive breast cancer may be used.
- Hormone receptor-negative: If the cancer cell has neither the estrogen nor the progesterone receptor, it’s called hormone-receptor negative .
Keeping the hormones estrogen and progesterone from attaching to the receptors can help keep the cancer from growing and spreading. There are drugs that can be used to do this.
What This Means For Patients
Because the results of ER and PR testing can make a difference in a persons treatment and chance of recurrence, it’s important that these tests are accurate. This guideline was developed to help both doctors and laboratories know how to improve the accuracy of ER and PR testing for those with breast cancer. Understanding the ER/PR status of the primary tumor and any distant or recurrent tumors can help doctors make sure that patients receive the appropriate treatment and avoid side effects of a treatment that may not work. Use this guideline to talk with your doctor about the accuracy of your ER and PR test results and what that means for your treatment.
Read Also: What To Eat During Breast Cancer Treatment
Hormone Receptor Status And Prognosis
Hormone receptor status is;related to the risk of breast cancer recurrence.
Hormone receptor-positive tumors have a slightly lower risk of breast cancer recurrence than hormone receptor-negative tumors in the first;5 years after diagnosis .
After;5 years, this difference begins to decrease and over time, goes away .
|
For a summary of research studies on hormone receptor status and survival,;visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section.;; |
How Often Does Stage 1 Breast Cancer Come Back After Treatment
If stage 1 cancer is treated comprehensively, it rarely comes back. A new, unrelated breast cancer is more likely to emerge after stage 1 breast cancer is treated than a recurrence. Your healthcare provider will recommend a surveillance schedule for you so that new breast cancer or a recurrence can be identified and treated as quickly as possible.
You May Like: What Age Should You Get Checked For Breast Cancer
How Your Breast Cancer Type Will Affect Your Treatment
Because breast cancer is not a one-size-fits-all disease, neither is treatment. Typically, your breast cancer treatment plan will be personalized and based on your specific stage and type of breast cancer. However, it is critical to determine which hormones, if any, are involved in the growth of your breast cancer.;
Your RMCC oncologist will run some tests that indicate the hormone receptor status and HER2/neu status of your breast cancer tumor. These results will play a large role in the type of breast cancer treatment that we recommend for you.;
How Long Does It Take For Stage 1 Breast Cancer To Develop Into Stage 2

It is not possible to determine exactly how long it will take for newly diagnosed breast cancer to progress from stage 1 to stage 2. It can happen within months if it is an aggressive high-grade tumor, or it can take longer. It’s important to know that stage 1 breast cancer could have already been present for a while before being detected, so it may progress quickly.
You May Like: How Quickly Does Triple Negative Breast Cancer Grow
How Her2 Status Affects Treatment
For more than 30 years, researchers have been studying HER2-positive breast cancer and ways to treat it.
Targeted therapies have now changed the outlook of stage 1, 2, and 3 breast cancers from poor to good.
While targeted therapies are part of the standard treatment for HER2-positive breast cancer, theyre only used occasionally in HER2-negative breast cancer.
Another difference between HER2-positive treatments and HER2-negative treatments is that HER2-negative treatments are often oral medications. HER2-positive treatments are usually administered intravenously or by injection.
For HER2-positive or HER2-negative breast cancers that are estrogen-positive or progesterone-positive, treatment with hormonal therapy may also be recommended.
Medications that may be used to treat HER2-negative breast cancers that are hormone-negative include:
- sacituzumab govitecan , an IV treatment
- talazoparib
Medications that may be used to treat HER2-negative breast cancers that are hormone-positive include:
- abemaciclib
- palbociclib
- ribociclib
Some of these medications are taken on their own, while others must be administered with other medications. Factors that affect your treatment regimen include whether:
- youve gone through menopause
- youve already received hormone therapy or chemotherapy
- you have certain gene mutations
Trastuzumab is a biologic therapy thats administered intravenously.
Other treatments for HER2-positive breast cancer include:
The Signs Of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Symptoms of triple negative breast cancer arent different from other types of breast cancer, Dr. Mayer says. According to the ACS, these symptoms include:
- A new breast lump that may be hard, soft, painful, or painless
- Swelling of the breast
- Skin peeling, thickening, or redness
- Skin that resembles an orange peel
- Nipple discharge
- Swollen lymph nodes
You May Like: Which Type Of Breast Cancer Has The Poorest Prognosis
Can Other Drugs Interfere With Hormone Therapy
Certain drugs, including several commonly prescribed antidepressants , inhibit an enzyme called CYP2D6. This enzyme plays a critical role in the body’s;use of tamoxifen;because CYP2D6 metabolizes, or breaks down, tamoxifen into molecules, or metabolites, that are much more active than tamoxifen itself.
The possibility that SSRIs might, by inhibiting CYP2D6, slow the metabolism of tamoxifen and reduce its effectiveness is a concern given that as many as one-fourth of breast cancer patients experience clinical depression and may be treated with SSRIs. In addition, SSRIs are sometimes used to treat hot flashes caused by hormone therapy.
Many experts suggest that patients who are taking antidepressants along with tamoxifen should discuss treatment options with their doctors, such as switching from an SSRI that is a potent inhibitor of CYP2D6, such as paroxetine hydrochloride , to one that is a weaker inhibitor, such as sertraline or citalopram , or to an antidepressant that does not inhibit CYP2D6, such as venlafaxine . Or doctors may suggest that their postmenopausal patients take an aromatase inhibitor instead of tamoxifen.
Other medications that inhibit CYP2D6 include the following:
- Quinidine, which is used to treat abnormal heart rhythms
Estrogen And Progesterone Receptor Testing For Breast Cancer
To help doctors give their patients the best possible care, the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the College of American Pathologists developed evidence-based guidelines to improve the accuracy of testing for estrogen and progesterone receptors for breast cancer. This guide for patients is based on ASCO’s and CAP’s 2020 updated recommendations.
Recommended Reading: What Does Triple Negative Mean For Breast Cancer
What Type Of Drug Treatment Might I Get
Most women with breast cancer in stages I to III will get some kind of drug therapy as part of their treatment. This may include:
- Chemotherapy
- Hormone therapy
- HER2 targeted drugs, such as trastuzumab and pertuzumab
- Some combination of these
The types of drugs that might work best depend on the tumors hormone receptor status, HER2 status, and other factors.
Evaluation Of Immunohistochemical Staining
Positive controls and internal areas of normal breast tissues showed strong and uniform staining of the epithelial cells lining the ducts and lobules with minimal back ground reactivity for various cytokeratins, smooth muscle actin, BRCA-1, E-cadherin and GCDFP. For evaluating EGFR, CerbB2 and p53 immunostaining, a known positive external control was utilized. Two cores were evaluated from each tumor. Each core was scored individually then the mean of the two readings was calculated. If one core was uninformative, the overall score applied was that of the remaining core. Assessment of staining was based on a semiquantitative approach. A modified histochemical score was used which includes an assessment of both the intensity of staining and the percentage of stained cells. For the intensity, a score index of 0, 1, 2 and 3 corresponding to negative, weak, moderate and strong staining intensity was used and the percentage of positive cells at each intensity was estimated subjectively. A final score of 0300 is the product of both the intensity and the percentage. Staining of ER and p53 was evaluated in the nuclei of the malignant cells and scored as positive or negative. An H-score of 0 and 50 were considered as cutoff points for positive staining of ER and rest of the markers, respectively. One observer scored the staining pattern , without previous knowledge of the outcomes on two separate occasions and a good correlation between the results was found.
You May Like: Can Breast Cancer Develop In One Year
All About Er Positive Her2 Negative Breast Cancer
About one;in eight women in the United States will develop breast cancer, according to commonly used statistics.
But other reports indicate that breast cancer rates are on the decline, likely because of improved recognition, prevention, and treatment. One advancement is the ability to identify different breast cancer types based on specific molecules found in tumors. The distinction greatly aids in breast cancer treatment selection and helps doctors predict how aggressive cancers will advance.
A;crucial step in the process of beast cancer evaluation;is testing tumor tissue removed during a;biopsy or surgery to determine if it has estrogen and progesterone receptors ;molecules that the hormones bind to.
Cancerous cells may have none, one, or both receptors. Breast cancers that have estrogen receptors are called;ER-positive . Those with progesterone receptors are referred to as;PR-positive .
In addition to hormone receptors, some breast cancers have high levels of a growth-promoting protein called HER2/neu. If a tumor has this property, it is called;HER2-positive. HER2 positive cancers are more aggressive than HER2 negative cancer.
Knowing breast cancer;type, leads doctors to determining;best treatments.
HER2 negative cancers will not respond to treatment with drugs that target HER2, such as trastuzumab and lapatinib .
Overall, estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer is treatable, especially when diagnosed early.
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a non-invasive breast cancer where abnormal cells have been contained in the lining of the breast milk duct. Although it isnt considered life-threatening, DCIS can increase the risk of developing an invasive breast cancer later on. Most recurrences happen within 5-10 years after initial diagnosis.;;
You May Like: Do Breast Cancer Tumors Hurt
Treatment Of Breast Cancer Stages I
The stage of your breast cancer is an important factor in making decisions about your treatment.;
Most women with breast cancer in stages I, II, or III are treated with surgery, often followed by radiation therapy. Many women also get some kind of drug therapy. In general, the more the breast cancer has spread, the more treatment you will likely need.;But your treatment options are affected by your personal preferences and other information about your breast cancer, such as:
- If the cancer cells contain hormone receptors. That is, if the cancer is estrogen receptor -positive or progesterone receptor -positive.
- If the cancer cells have large amounts of the HER2 protein
- How fast the cancer is growing
- Your overall health
- If you have gone through menopause or not
Talk with your doctor about how these factors can affect your treatment options.