How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast Treated
Treatment options available for individuals with Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast are dependent upon the following:
- Type of cancer
- The staging of the cancer
- Whether the cancer cells are sensitive to certain particular hormones, and
- Personal preferences
In general, breast cancer stages range from 0 to IV. 0 may indicate a small and non-invasive cancer, while IV indicates that the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. Briefly, as per US National Cancer Institute , breast cancer is staged as follows:
- Stage 0 : The abnormal cancer cells are confined to their site of origin
- Stage I: The tumor is 2 centimeters in diameter or less, and has not spread outside the breast
- Stage II: The tumor may be up to 5 centimeters in diameter and may have spread to lymph nodes. Another criteria is that the tumor may be larger than 5 centimeters in diameter, but has not spread to surrounding lymph nodes
- Stage III: The tumor may be more than 5 centimeters in diameter and may have spread to several axillary lymph nodes, or to the lymph nodes near the breastbone. The cancer may also have spread to the breast skin/chest wall, causing ulcer-like sores, or a swelling
- Stage IV: The tumor has spread outside the breast and to other organs, such as the bones, liver, lungs, or brain, regardless of its size
If breast cancer is diagnosed, staging helps determine whether it has spread and which treatment options are best for the patient.
Hormone therapy:
Dont Miss: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Mean
Reducing Your Risk Of Noninvasive Breast Cancer
The main strategy for lowering your risk of any cancer is changing risk factors you can control. Maintaining a healthy body weight, exercising regularly, and drinking alcohol in moderation will help lower your risk of breast cancer. Because you cant control all your risk factors, screening is recommended as the most effective tool for finding breast cancer early, including DCIS.
Some women have a high risk of breast cancer due to a family history or known gene mutations. These women may want to consider other prevention strategies including estrogen blockers or prophylactic mastectomy. A double , with or without breast reconstruction can reduce the risk of breast cancer by about 97%. Genetic testing for breast cancer genes can help you and your care team decide if this option is right for you.
What Can You Tell Me About Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stages
Staging describes how advanced your cancer is, based on the location, size and how far it has spread. There are five stages of ductal carcinoma:
- Stage 0: The cancer is localized to your milk ducts. This stage is also known as non-invasive ductal carcinoma in situ.
- Stage 1: The cancer has spread outside of your milk ducts to the breast tissue, but it hasnt spread to your lymph nodes. In some cases, the cancer may have spread to your lymph nodes, but not to your surrounding breast tissue.
- Stage 2: The tumor is small and has spread to one to three of your lymph nodes. Or, the tumor is larger, but hasnt spread to any of your lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: The cancer has often spread to more than three of your lymph nodes or is causing inflammation of most of your breast skin, but hasnt spread to other areas of your body.
- Stage 4: The cancer has spread to your other organs, which may include your bones, liver, lungs, brain, chest wall or distant lymph nodes.
Recommended Reading: Grade 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Are Metastatic And Invasive Cancers Diagnosed
You should report persistent symptoms to your doctor, especially if youve previously been treated for cancer.
Theres no single test that can determine whether you have invasive cancer or metastatic cancer. Diagnosis usually requires a series of tests.
Tumors may be seen on imaging tests like:
- ultrasounds
- bone scans
- positron emission tomography scans
Blood tests can provide some information but cant say for certain if you have cancer or what type it may be.
If a tumor is found, a biopsy must be done. Following a biopsy, a pathologist will analyze the cells to determine what type they are. This analysis will help explain whether its primary or metastatic cancer.
In some cases, even though a metastatic tumor is discovered, the primary cancer cant be found. That may be because the original tumor is too small to visualize on diagnostic studies.
Whether its early-stage invasive cancer or metastatic disease, youll need to work closely with your doctor. Your oncology team will offer recommendations about potential treatments based on your test results.
Your doctor may also be able to give you information about clinical trials for people with metastatic cancer.
How Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer Different From Other Types Of Breast Cancer
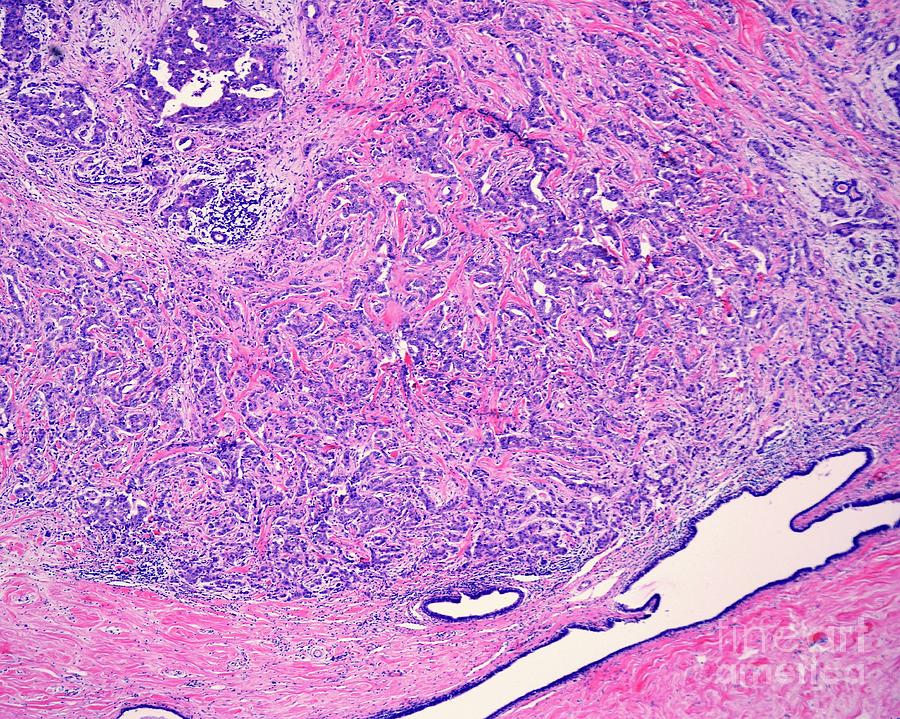
Triple negative breast cancer is different from other types of breast cancer because it does not have any of the three receptors commonly found on breast cancer cells:
If you have triple negative breast cancer, you may notice that your treatment is slightly different from that offered to other people with breast cancer.
People with oestrogen and/or progesterone receptor positive breast cancer will usually take tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor as part of their treatment. People with HER2 positive breast cancer will usually take a drug called Herceptin. These drugs are not effective against triple negative breast cancer.
You May Like: Her2 Breast Cancer Symptoms
Cancer Cure And All Clear
Many people who have cancer want to know if theyre cured. You may hear words like cure and all clear in the media.
Cured means theres no chance of the breast cancer coming back. However, its not possible to be sure that breast cancer will never come back. Treatment for breast cancer will be successful for most people, and the risk of recurrence gets less as time goes on. Recurrence, unfortunately, can happen even many years after treatment, so no one can say with certainty that youre definitely cured.
All clear, or in remission which is another term you may have heard used, means theres no obvious sign of cancer at the moment.
If your breast cancer has spread to other parts of your body this will affect your prognosis. Secondary breast cancer can be treated, sometimes for many years, but not cured. Find out more about secondary breast cancer.
In order to be as clear as possible, your treatment team is more likely to talk about your chances of survival over a period of time or the possibility of remaining free of breast cancer in the future.
Why Are Receptors Important
Receptors are tiny proteins on the surface of the cells that act like light switches that can turn on and off cancer cell growth. The Estrogen receptor , Progesterone receptor and HER2 receptor results are incredibly important for you to know and understand. There are great treatments available for all combinations of cancer receptor types. This information is critical in guiding you to therapies that may be needed before or after surgery, such as chemotherapy or hormonal therapy. You should try to understand this aspect of your cancer care from the outset. Take our lesson on My Tumor Receptors to learn the essentials.
Recommended Reading: Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer Survival
Oncogene Expression May Negatively Affect Breast Cancer Outcome
A relatively new addition to the discussion of breast cancer survival statistics and prognosis is oncogene expression.
An oncogene is a tiny fragment of genetic material which is carried in a chromosome and can cause normal cells to become malignant.
The oncogene HER-2, in particular, has been linked to more aggressive breast cancers.
Around one-third of all breast tumours produce the HER-2 oncogene, and these patients tend to have higher rates of recurrence and lower overall breast cancer survival rates.
According to a 2013 Canadian scientific study, the overall 5-year survival rate of HER-2 positive breast cancer is 88.6%. Furthermore, the relapse-free survival rate for 5 years is 79.4%.
Recommended Reading: What Are Common Treatments For Breast Cancer
Side Effects And Complications
All treatments have some side effects that range from mild to severe. Most clear up when treatment ends, but there can be some lasting complications.
Its important to tell your oncologist about all symptoms, even if they seem minor. Your healthcare team will work with you to ease side effects and deal with complications.
Also Check: Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer Curable
Treatment For Invasive Breast Cancer
Treatment for invasive breast cancer usually involves some combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy and/or HER2-targeted therapy.
The order of therapies and the specific treatments depend on the cancer stage and the characteristics of the tumor .
Learn more about treatment.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
You may want to ask your provider:
- What type of breast cancer recurrence do I have?
- Has the cancer spread outside the breast?
- What stage is the breast cancer?
- What is the best treatment for this type of breast cancer?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Most breast cancer recurrences respond well to treatments. You may be able to try new drugs or combination therapies in development in clinical trials. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option based on your unique situation.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/24/2021.
References
Also Check: Red Mill Baking Soda Cancer
Causes And Risk Factors
The underlying causes of IDC are not fully known. Scientists continue to study what makes a person more or less likely to develop breast cancer. There are some risk factors you can change and some you cannot.
Researchers think certain hormonal, environmental, and lifestyle factors increase a persons risk for breast cancer. Smoking, birth control pills and hormone replacement, obesity, lack of exercise, and prior radiation to the chest have been associated with higher cancer risk. Other times, people develop breast cancer without such known risk factors.
There are some breast cancer risk factors that are not changeable. They are things you are born with or inherit from your parents. This includes:
- Being female – breast cancer is more common in women
- Being older – breast cancer risk increases with age
- Certain breast cancer genes – breast cancer gene 1 and breast cancer gene 2 are inherited tumor suppressor genes that are inherited.
- A family history of breast cancer
Your healthcare provider should review both kinds of risk factors with you and help you make decisions about your health choices and cancer screening.
Concluding Remarks And Future Directions

In this review, we have cited evidence that myoepithelial cells in both mice and human mammary glands originate from a suprabasal cell type within the luminal epithelial compartment within the adult breast. Furthermore, we discuss observations that normal myoepithelial cells are critical for correct polarity of luminal epithelial cells, most likely via production of laminin-1. On the other hand, the myoepithelial cells present in tumors have many traits in common with normal myoepithelial cells, but show either complete absence or reduced expression of laminin-1 and are thus unable to induce the polarization of luminal epithelial cells.
In summary, although much remains to be learned, the role of myoepithelial cells as possible tumor suppressors may include their function as a guardian of ânormalcy,â being a paracrine inhibitor of invasion in early breast cancer as well as a target for differentiation therapy by inducing malignant cancer cells to differentiate along the myoepithelial pathway to a less devastating cell type.
Recommended Reading: Define Stage 3 Cancer
Symptoms Of Invasive & Noninvasive Breast Cancer
Mammogram screenings usually find both invasive and noninvasive breast cancers before symptoms develop. If symptoms develop, they may include:
- Breast lump
- Change in size, shape, or appearance of the breast or nipple
- Thickening or hardening of the breast
- Skin changes on the breast or nipple
- Swelling of part or all of the breast
- Inverted nipple or nipple discharge that isnt breast milk
Symptoms Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Make an appointment to see your doctor if you notice anything different or unusual about the look and feel of your breasts.
The symptoms of breast cancer include:
- a new lump or thickening in your breast or armpit
- a change in size, shape or feel of your breast
- skin changes in the breast such as puckering, dimpling, a rash or redness of the skin
- fluid leaking from the nipple in a woman who isnt pregnant or breast feeding
- changes in the position of nipple
Don’t Miss: Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer Terminal
What Is The Survival Rate For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Survival rates are a way to discuss the prognosis and outlook of a cancer diagnosis. The number most frequently mentioned is 5-year survival. Many patients live much longer, and some die earlier from causes other than breast cancer. With a constant change and improvement in therapies, these numbers also change. Current 5-year survival statistics are based on patients who were diagnosed at least 5 years ago and may have received different therapies than are available today.
Below are the statistics from the National Cancer Instituteâs SEER database for survival of all patients with breast cancer, by tumor stage:
| Stage |
|---|
Additional Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma:
There are four types of invasive ductal carcinoma that are less common:
- Medullary Ductal Carcinoma This type of cancer is rare and only three to five percent of breast cancers are diagnosed as medullary ductal carcinoma. The tumor usually shows up on a mammogram and it does not always feel like a lump rather it can feel like a spongy change of breast tissue.
- Mucinous Ductal Carcinoma This occurs when cancer cells within the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma carries a better prognosis than more common types of IDCs.
- Papillary Carcinoma This is a very good prognosis breast cancer that primarily occur in women over the age of 60.
- Tubular Ductal Carcinoma This is a rare diagnosis of IDC, making up only two percent of diagnoses of breast cancer. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
Show me more…
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Testing For Her2 Status
There are several tests used to find out if breast cancer is HER2-positive. How your results appear in the report will depend on the test you have. Two of the most common tests are:
- IHC test: The IHC test uses a chemical dye to stain the HER2 proteins. The IHC gives a score of 0 to 3+ that measures the amount of HER2 proteins on the surface of cells in a breast cancer tissue sample. If the score is 0 to 1+, its considered HER2-negative. If the score is 2+, itâs considered borderline. A score of 3+ is considered HER2-positive. If the IHC test results are borderline, its likely that a FISH test will be done on a sample of the cancer tissue to determine if the cancer is HER2-positive.
- FISH test: The FISH test uses special labels that attach to the HER2 proteins. The special labels have chemicals added to them so they change color and glow in the dark when they attach to the HER2 proteins. This test is the most accurate, but it is more expensive and takes longer to return results. This is why an IHC test is usually the first test done to see if a cancer is HER2-positive. With the FISH test, you get a score of either positive or negative .
Itâs important to know which HER2 test you had. Generally, only cancers that test IHC 3+ or FISH positive respond to the medicines that target HER2-positive breast cancers. An IHC 2+ test result is called borderline. If you have an IHC 2+ result, ask to have the tissue retested with the FISH test.
What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer
As its name suggests, inflammatory breast cancer often causes the breast to become red, swollen, and inflamed. Some women with IBC also notice thickened or discolored breast skin with tiny dimples, puckers, or ridges that make it look like an orange peel. While the symptoms may sound like an infection, the real culprit is cancer that is blocking lymphatic vessels in the skin and breast tissue, causing a buildup of fluid and, in some cases, pain, discoloration, and sudden swelling of the breast. Also called inflammatory breast carcinoma or locally advanced breast cancer, IBC can spread quickly, making prompt diagnosis and treatment essential.
Read Also: Stage 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Tnbc Subtyping And Treatment Regimens
In 2011, Lehmann et al. performed gene expression profiling of tumor samples from 587 TNBC patients and divided TNBC into six subtypes: basal-like 1 , basal-like 2 , mesenchymal , mesenchymal stem-like , immunomodulatory , and luminal androgen receptor . They also performed gene profiling and compared existing TNBC breast cancer cell lines, classifying them into six different subtypes, thus providing an accurate cell model for clinical treatment of TNBC .
Table 1 Genomic TNBC subtypes and assignment of TNBC cell lines to subtypes
Diagnosis Of Invasive & Noninvasive Breast Cancer
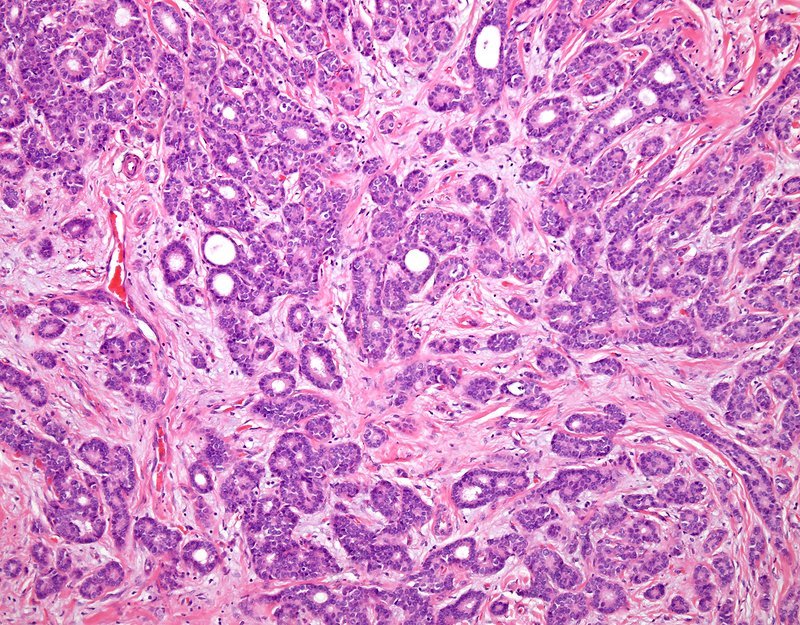
For a suspicious mammogram or breast exam, your doctor will likely recommend a biopsy to take a sample of cells. In most cases, the sample will tell your doctor about the type and grade of cancer and whether or not the cancer cells are positive for the HER-2 and hormone receptor proteins. This information guides your treatment plan.
Read Also: Stage 4 Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment