Symptoms Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Make an appointment to see your doctor if you notice anything different or unusual about the look and feel of your breasts.
The symptoms of breast cancer include:
- a new lump or thickening in your breast or armpit
- a change in size, shape or feel of your breast
- skin changes in the breast such as puckering, dimpling, a rash or redness of the skin
- fluid leaking from the nipple in a woman who isnt pregnant or breast feeding
- changes in the position of nipple
Venous Lymph Node Transfer And Lymphatic Grafting
If you have lymphedema from a previous surgery, Sylvesters expert surgeons can prevent or provide relief from the debilitating condition caused when cancerous lymph nodes in the armpit must be removed during surgery, disrupting the normal flow of lymphatic fluid out of the arm. With nowhere to go, the fluid backs up in the tissues of the limb, causing painful swelling. In vascularized lymph node transfer, lymph nodes and their blood supply are transferred into regions where lymph nodes have been dissected to restore normal drainage.
Hormone Receptor Status Influences Breast Cancer Survival Rates
The hormone receptor status of a breast tumour is not usually included in formal discussions of prognosis.
Each breast tumour will potentially have a different hormone receptor status. When a breast cancer tumour tests positive for the hormones estrogen and progesterone, it implies two things:-
Therefore, due to improvements in treatments, overall survival rates will be higher for hormone receptor positive breast tumors than for those that are hormone negative.
Don’t Miss: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Treatment
Special Types Of Invasive Breast Cancers
Some invasive breast cancers have special features or develop in different ways that affect their treatment and outlook. These cancers are less common but can be more serious than other types of breast cancer.
Inflammatory breast cancer is an uncommon type of invasive breast cancer. It accounts for about 1% to 5% of all breast cancers.
Continue Learning About Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
Also Check: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
Certain Breast Cancer Subtypes Have A Better Statistical Prognosis
In general, tubular, mucinous and medullary breast carcinomas have a better prognosis than the other sub-types.
The table below gives a very general approximation of the survival rates that may be associated with the different breast cancer subtypes.
However, please bear in mind that these figures are a rough generalization only and survival will always be determined by the individual characteristics of each breast cancer and each patient.
Nonetheless, the relative aggressiveness of the different breast cancer subtypes can be interpreted from the table.
and is almost always near 100% curable.)
| breast cancer sub-type | |
| Inflammatory breast carcinoma | 65% 35% |
Why Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Going To Be Higher Than The Most Up
It is important to remember that the breast cancer survival rates that are listed on this page are, in reality, going to be higher.
This is because the breast cancer survival rates data is gathered from a large number of people with the disease over a 5 year period. Hence, even the most up-to-date statistics are still going to be a little out of date.
Thus, with the ongoing improvements and advancements in breast cancer screening, research, early detection and advanced tailored treatment, the outcomes at present will be even better than the statistics listed here.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rates
How Is Noninvasive Breast Cancer Treated
The standard treatment for DCIS is surgery. In most cases, women can opt for lumpectomy, which is breast-conserving surgery. It only removes the area with the cancer and some healthy tissue surrounding it. Radiation therapy is usually necessary after to decrease the risk of the cancer returning. Sometimes, doctors recommend mastectomy, which removes the entire breast. This may be the best choice if the DCIS is large or there are multiple spots within the breast.
Your preference also plays a role in the extent of surgery. A second opinion can help you make this decision. The process can give you another point of view or verify what you have already heard. In either case, you will be making an informed decision, which can increase your confidence.
Hormone therapy will be a treatment option for hormone receptor-positive tumors. Your pathology report will tell your doctor whether or not this treatment is appropriate.
LCIS does not require treatment, but it does increase your risk of breast cancer in the future. Your doctor may recommend additional screening exams, estrogen blocking, or preventive mastectomy.
Diagnosing Invasive Breast Cancer
In many people the cancer is found during breast screening.
Its important that you see your GP if you have any symptoms. They may refer you to a specialist breast clinic. At the breast clinic the doctor or specialist nurse takes your medical history and examines your breasts. They also feel for any swollen lymph nodes under your arms and at the base of your neck.
You may have some or all of the following tests:
- a mammogram
- an ultrasound
- a biopsy a small sample of cells or tissue is taken from your breast and looked at under a microscope
Changes seen on the mammogram or ultrasound could be due to cancer, so you may have a biopsy of the breast. You might also have an ultrasound of the lymph nodes under your arm. You may also have lymph node biopsies if they look abnormal.
You should get your results within 1 or 2 weeks at a follow up appointment.
- drugs that help prevent or slow down bone thinning or bone damage
- a combination of these treatments
You may have surgery to your armpit called a sentinel lymph node biopsy. This means having about 3-5 lymph nodes removed. Sometimes surgeons have to remove more lymph nodes. Your doctor will let you know whether you need this.
You might have chemotherapy or hormone therapy before surgery called neoadjuvant therapy. The aim is to shrink the cancer down. This means that some people may be able to have breast conserving surgery, who might have needed removal of the breast .
Don’t Miss: What Is Hr Positive Breast Cancer
When To Contact A Doctor
When a person should consult a doctor depends on various factors.
A person may not notice any symptoms or signs of cancer. In these cases, a doctor may discover it during a routine blood test or examination.
A person should contact a doctor if they:
- develop any unexplained symptoms that do not go away
- notice any spots on their skin
- notice a lump on their breast
Once a person has received a diagnosis of noninvasive cancer, they should work with a doctor to develop a plan of action.
Strategies may include scheduled follow-up visits to check the progress of treatment or of the cancer itself. The doctor will determine how often they want to see a person.
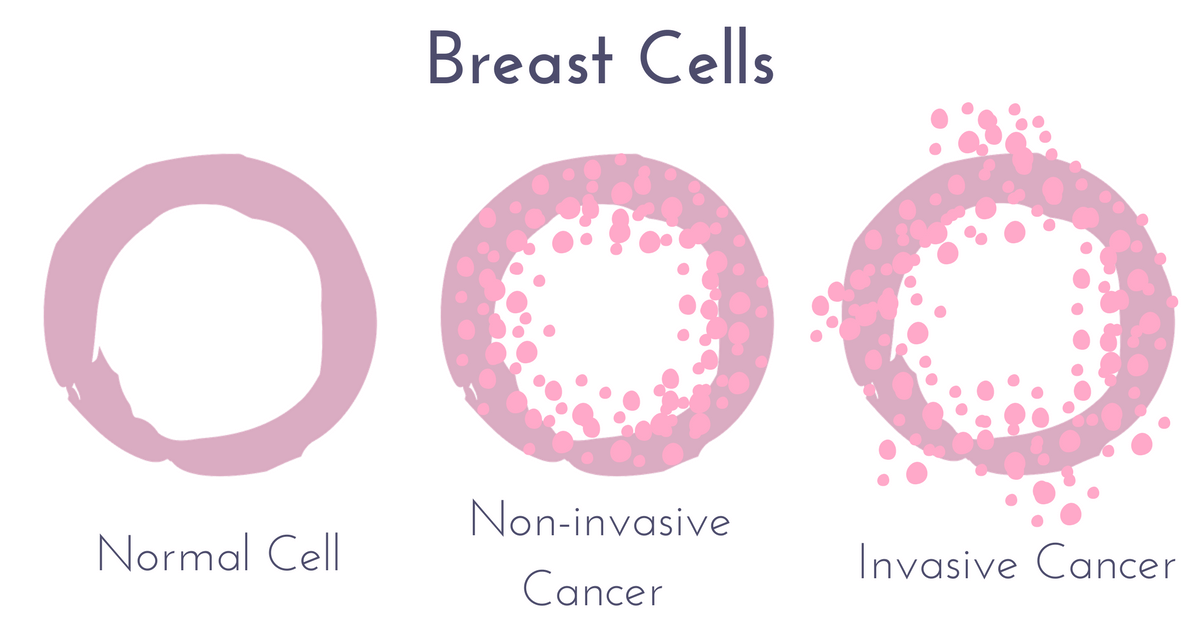
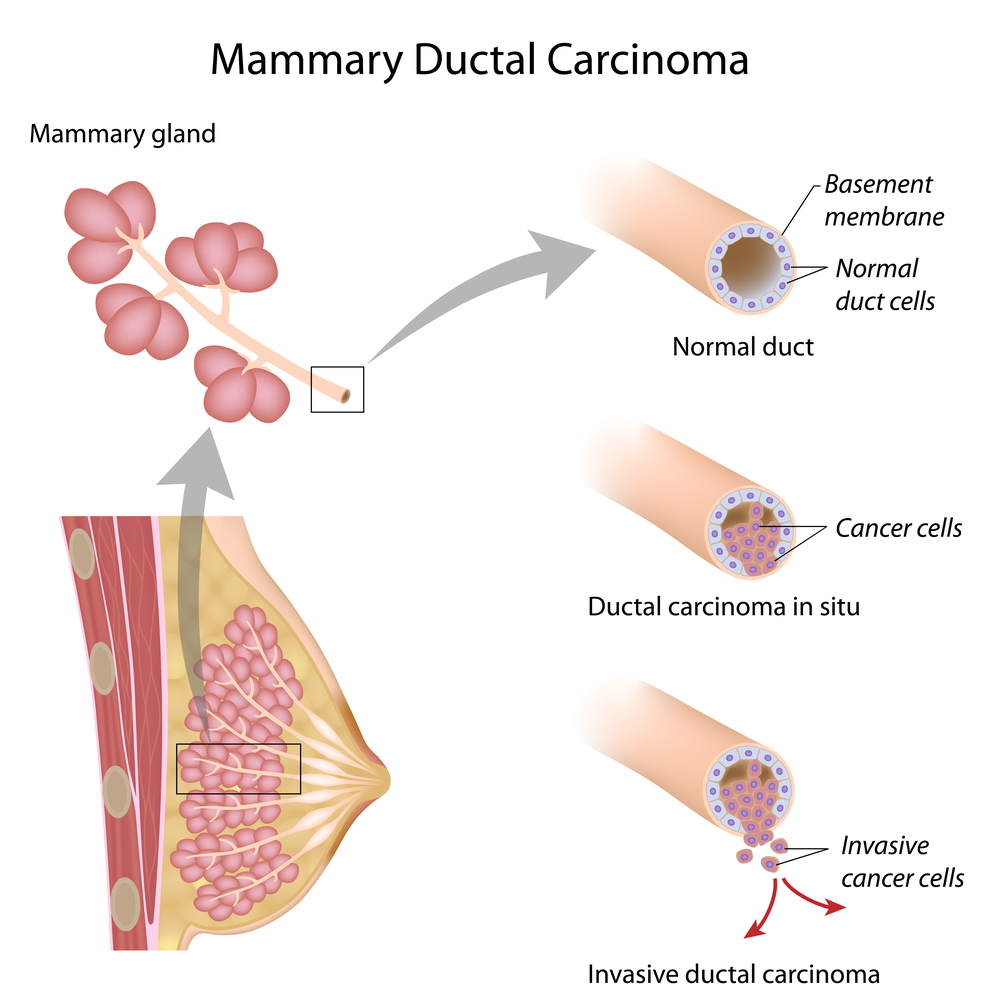
Carcinoma In Situ Vs Invasive Carcinoma
In contrast to carcinoma, or invasive cancer, carcinoma in situ has not yet invaded the basement membrane, and there is no stromal invasion. Other than thisthe fact that the cells have not yet broken through the supporting structure from which they beganthe cells appear the same as invasive cancer cells would appear under the microscope.
Also Check: Can Getting Hit In Your Breast Cause Cancer
Stage Of Cancer Carcinoma In Situ And Additional Terms
A common question is, “What stage of cancer is carcinoma in situ?” Carcinoma in situ is referred to as stage 0 cancer. At this stage, cancer is considered non-invasive. Stage 1 cancers and beyond are considered invasive, meaning that even if low, there is a potential they could spread. Other terms that may be used in defining the same thing as carcinoma in situ or stage 0 cancer include:
- Non-infiltrating
- Intra-epithelial
Sentinel Node Biopsy And Mastectomy For Dcis
A sentinel node biopsy is a procedure used to check whether or not invasive breast cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area . The surgeon removes 1-5 nodes.
Having a sentinel node biopsy during a mastectomy helps some people with DCIS avoid an axillary dissection. Once a mastectomy has been done, a person cant have a sentinel node biopsy.
If it turns out theres invasive breast cancer in the tissue removed during the mastectomy, a sentinel node biopsy will have already been done.
If a sentinel node biopsy wasnt done and invasive breast cancer is found, an axillary dissection may be needed. An axillary dissection removes more axillary lymph nodes than a sentinel node biopsy. Because it disrupts more of the normal tissue in the underarm area, axillary dissection is more likely to affect arm function and cause lymphedema.
So, even though a sentinel node biopsy may not be needed with DCIS, most people who have a mastectomy for DCIS will have a sentinel node biopsy done at the same time.
Don’t Miss: Baking Soda And Breast Cancer
How Is Stage 0 Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Contact your physician if you have a lump or other changes to your breasts. Discuss your family history of cancer and ask how often you should be screened.
Stage 0 breast cancer is often found during mammogram screening. Following a suspicious mammogram, your doctor may order a diagnostic mammogram or another imaging test, such as an ultrasound.
If theres still some question about the suspicious area, youll need a biopsy. Biopsy is the only way to diagnose cancer. For this, the doctor will use a needle to remove a tissue sample. A pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope and provide a report to your doctor.
The pathology report will say whether there are atypical cells present and, if so, how aggressive they may be.
Treatment Of Breast Cancer By Stage
This information is based on AJCC Staging systems prior to 2018 which were primarily based on tumor size and lymph node status. Since the updated staging system for breast cancer now also includes estrogen receptor , progesterone receptor , and HER2 status, the stages may be higher or lower than previous staging systems. Whether or not treatment strategies will change with this new staging system are yet to be determined. You should discuss your stage and treatment options with your physician.
The stage of your breast cancer is an important factor in making decisions about your treatment options. In general, the more the breast cancer has spread, the more treatment you will likely need. But other factors can also be important, such as:
- If the cancer cells contain hormone receptors
- If the cancer cells have large amounts of the HER2 protein
- Your overall health and personal preferences
- If you have gone through menopause or not
- How fast the cancer is growing
Talk with your doctor about how these factors can affect your treatment options.
Stage 0 means that the cancer is limited to the inside of the milk duct and is non-invasive. Treatment for this non-invasive breast tumor is often different from the treatment of invasive breast cancer.
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a stage 0 breast tumor.
Recommended Reading: Will My Breast Cancer Come Back
What Is The Prognosis Of Patients With Inflammatory Breast Cancer
The prognosis, or likely outcome, for a patient diagnosed with cancer is often viewed as the chance that the cancer will be treated successfully and that the patient will recover completely. Many factors can influence a cancer patients prognosis, including the type and location of the cancer, the stage of the disease, the patients age and overall general health, and the extent to which the patients disease responds to treatment.
Because inflammatory breast cancer usually develops quickly and spreads aggressively to other parts of the body, women diagnosed with this disease, in general, do not survive as long as women diagnosed with other types of breast cancer.
It is important to keep in mind, however, that survival statistics are based on large numbers of patients and that an individual womans prognosis could be better or worse, depending on her tumor characteristics and medical history. Women who have inflammatory breast cancer are encouraged to talk with their doctor about their prognosis, given their particular situation.
Ongoing research, especially at the molecular level, will increase our understanding of how inflammatory breast cancer begins and progresses. This knowledge should enable the development of new treatments and more accurate prognoses for women diagnosed with this disease. It is important, therefore, that women who are diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer talk with their doctor about the option of participating in a clinical trial.
What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and very aggressive disease in which cancer cells block lymph vessels in the skin of the breast. This type of breast cancer is called inflammatory because the breast often looks swollen and red, or inflamed.
Inflammatory breast cancer is rare, accounting for 1 to 5 percent of all breast cancers diagnosed in the United States. Most inflammatory breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas, which means they developed from cells that line the milk ducts of the breast and then spread beyond the ducts.
Inflammatory breast cancer progresses rapidly, often in a matter of weeks or months. At diagnosis, inflammatory breast cancer is either stage III or IV disease, depending on whether cancer cells have spread only to nearby lymph nodes or to other tissues as well.
Additional features of inflammatory breast cancer include the following:
- Compared with other types of breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer tends to be diagnosed at younger ages.
- Inflammatory breast cancer is more common and diagnosed at younger ages in African American women than in white women.
- Inflammatory breast tumors are frequently hormone receptor negative, which means they cannot be treated with hormone therapies, such as tamoxifen, that interfere with the growth of cancer cells fueled by estrogen.
- Inflammatory breast cancer is more common in obese women than in women of normal weight.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Coping With A Diagnosis Of Dcis
Being told you have DCIS can be a difficult and worrying time. Everyone reacts differently to their diagnosis and have their own way of coping.
Although DCIS is an early form of breast cancer with a very good prognosis, people understandably may feel very anxious and frightened by the diagnosis. People can often struggle to come to terms with being offered treatments such as a mastectomy, at the same time as being told their DCIS may never do them any harm.
Some people are reluctant to say theyre anxious about a diagnosis of DCIS because they worry others will see it as less important than other types of breast cancer. Because of this they might feel less able to ask for support. But there are people who can support you so dont be afraid to ask for help if you need it. By letting other people know how you feel, particularly your family and friends, they can be more supportive.
Some people find it helpful to discuss their feelings and concerns with their breast care nurse or specialist. If youd like to talk through your feelings and concerns in more depth over a period of time, a counsellor or psychologist may be more appropriate. Your breast care nurse, specialist or GP can arrange this.
Find out more about coping emotionally with breast cancer.
If you want to talk you can also call our Helpline on 0808 800 6000.
Can I Avoid Radiation After My Lumpectomy
Most women will benefit from radiation to reduce the risk of a local recurrence of their cancer in that breast. For years, we have been trying to identify which women are at lower risk of recurrence after a lumpectomy and can avoid radiation. It is important to state that the standard of care treatment generally includes radiation after a lumpectomy. There may be a few exceptions that may allow you to avoid radiation. If you are over 70 years old and have a favorable type of DCIS you may consider a lumpectomy only, with close mammographic follow up with your breast surgeon. Make sure to ask your breast surgeon and radiation oncologist if the risks vs. benefits favor radiation or just close observation without radiation.
Read Also: Can You Get Rid Of Breast Cancer
Difficult Decisions For Patients
Toro de Stefani is one of 60,000 U.S. women diagnosed with DCIS each year. Each must decide on a treatment option.
Current guidelines that recommend lumpectomy and radiation are causing concerns that the condition may be overtreated, since most cases never become invasive.
This gives medical professionals enormous uncertainty about how to advise women on an individual basis, says Thompson, professor of Surgery at MD Anderson. And therefore, historically the treatments have ranged from active surveillance on one end of the pectrum all the way to mastectomies on the other.
Thompson says DCIS diagnoses have increased as breast imaging has become more accurate and frequent. The National Institutes of Health estimates that by 2020, more than 1 million women in the U.S. will be living with a DCIS diagnosis, compared to 500,000 in 2005.
Before mammograms became common, many women had the condition for years without being aware of it, because it grows so slowly and causes no symptoms.
Perhaps, surprisingly, given that breast screening has been around for three or four decades, were only now really coming to grips with the fact that we often diagnose some conditions like DCIS as breast cancer even though theyre not conventional, invasive breast cancers, Thompson says.
Hes participating in three DCIS research studies that he hopes will make treatment decisions easier.