Symptoms Of Metastatic Cancer
Metastatic cancer does not always cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, what they are like and how often you have them will depend on the size and location of the metastatic tumors. Some common signs of metastatic cancer include:
- pain and fractures, when cancer has spread to the bone
- headache, seizures, or dizziness, when cancer has spread to the brain
- shortness of breath, when cancer has spread to the lung
- jaundice or swelling in the belly, when cancer has spread to the liver
What Should A Person With Stage 0 Or Stage 1 Breast Cancer Expect Regarding Treatment
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered non-invasive, it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors. Like stage 0, Chemotherapy is often not necessary for earlier stages of cancer.
Material on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
When Do People Get A Metastatic Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Metastatic breast cancer can occur at different points:
- De novo metastatic breast cancer: About 6% of women and 9% of men have metastatic breast cancer when theyre first diagnosed with breast cancer.
- Distant recurrence: Most commonly, metastatic breast cancer is diagnosed after the original breast cancer treatment. A recurrence refers to the cancer coming back and spreading to a different part of the body, which can happen even years after the original diagnosis and treatment.
Also Check: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
How Does Cancer Spread Or Metastasize
The spread of cancer usually happens through one or more of the following steps:
- Cancer cells invade nearby healthy cells. When the healthy cell is taken over, it too can replicate more abnormal cells.
- Cancer cells penetrate into the circulatory or lymph system. Cancer cells travel through the walls of nearby lymph vessels or blood vessels.
- Migration through circulation. Cancer cells are carried by the lymph system and the bloodstream to other parts of the body.
- Cancer cells lodge in capillaries. Cancer cells stop moving as they are lodged in capillaries at a distant location and divide and migrate into the surrounding tissue.
- New small tumors grow. Cancer cells form small tumors at the new location
When Metastatic Cancer Can No Longer Be Controlled
If you have been told your cancer can no longer be controlled, you and your loved ones may want to discuss end-of-life care. Whether or not you choose to continue treatment to shrink the cancer or control its growth, you can always receive palliative care to control the symptoms of cancer and the side effects of treatment. Information on coping with and planning for end-of-life care is available in the Advanced Cancer section of this site.
Also Check: Why Is Left Breast Cancer More Common
Symptoms Of Metastasis May Vary Depending On Where The Cancer Has Spread To
Here are some symptoms that vary by locations commonly associated with breast cancer metastasis.
Metastasis in the bone may cause:
- Severe, progressive pain
- Bones that are more easily fractured or broken
Metastasis to the brain may cause:
- Persistent, progressively worsening headache or pressure to the head
- Vision disturbances
- Behavioral changes or personality changes
Metastasis to the liver may cause:
- Jaundice
- Abnormally high enzymes in the liver
- Abdominal pain, appetite loss, nausea, and vomiting
Metastasis to the lungs may cause:
- Chronic cough or inability to get a full breath
- Abnormal chest X-ray
- Chest pain
- Other nonspecific systemic symptoms of metastatic breast cancer can include fatigue, weight loss, and poor appetite, but its important to remember these can also be caused by medication or depression.
If you notice these symptoms, be sure you talk with your physician. They could be important for getting the treatment you need.
Interested in learning more? i3Health is hosting an upcoming webinar Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Applying Treatment Advances to Personalized Care. Learn more here.
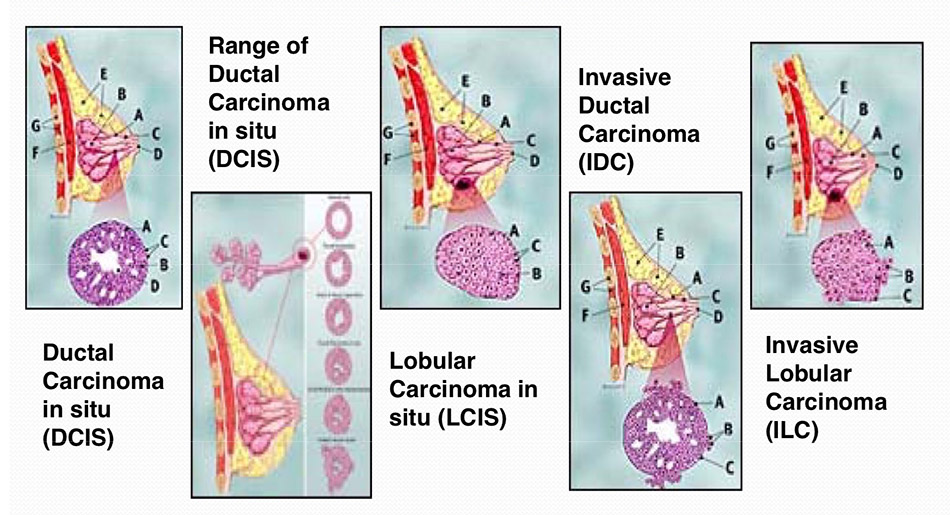
Is Metastatic Breast Cancer An Invasive Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer is considered an invasive cancer, which means it invades or spreads to other parts of the body. Invasive cancer may be found in breast tissue surrounding a tumor or in more distant parts of the body like the brain.
Noninvasive cancer tends to stay in the area where it originated. Ductal carcinoma in situ is the most common type of noninvasive breast cancer. This cancer develops and typically stays in the milk ducts.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Local Or Regional Treatments For Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Although systemic drugs are the main treatment for stage IV breast cancer, local and regional treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy, or regional chemotherapy are sometimes used as well. These can help treat breast cancer in a specific part of the body, but they are very unlikely to get rid of all of the cancer. These treatments are more likely to be used to help prevent or treat symptoms or complications from the cancer.
Radiation therapy and/or surgery may also be used in certain situations, such as:
- When the breast tumor is causing an open wound in the breast
- To treat a small number of metastases in a certain area, such as the brain
- To help prevent bone fractures
- When an area of cancer spread is pressing on the spinal cord
- To treat a blood vessel blockage in the liver
- To provide relief of pain or other symptoms
In some cases, regional chemo may be useful as well.
If your doctor recommends such local or regional treatments, it is important that you understand their goalwhether it is to try to cure the cancer or to prevent or treat symptoms.
Can Stage 4 Breast Cancer Go Into Remission
Stage 4 breast cancer can go into remission, meaning that it isnt detected in imaging or other tests. Pathological complete remission indicates a lack of cancer cells in tissues removed after surgery or biopsy.
But its rare to take tissue samples while treating stage 4 breast cancer. This could mean that although treatment has been effective, it hasnt completely destroyed the cancer.
Advances in stage 4 breast cancer treatments are helping to increase the length of remission.
Don’t Miss: What Does Triple Negative Mean For Breast Cancer
Treatment For Metastatic Cancer
There are treatments for most types of metastatic cancer. Often, the goal of treating metastatic cancer is to control it by stopping or slowing its growth. Some people can live for years with metastatic cancer that is well controlled. Other treatments may improve the quality of life by relieving symptoms. This type of care is called palliative care. It can be given at any point during treatment for cancer.
The treatment that you may have depends on your type of primary cancer, where it has spread, treatments youve had in the past, and your general health. To learn about treatment options, including clinical trials, find your type of cancer among the PDQ® Cancer Information Summaries for Adult Treatment and Pediatric Treatment.
Study Population And Sampling
The medical records of patients with histologically diagnosed non-metastatic breast cancer from January 1997 to December 2012 were reviewed. NMBC included early breast cancer and locally advanced breast cancer cases .
Inclusion criteria: Patients who had complete remission after primary treatment with curative intent. Complete remission was defined as absence of symptoms and signs of breast cancer, associated normalization of radiological and biochemical indices after treatment.
Exclusion criteria: Patients whose medical records did not meet up to 90% of the information required for the study.
Read Also: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Metavivor Announces Grant Awards For Metastatic Breast Cancer Research
METAvivor Research and Support announces 23 new grant awards for metastatic breast cancer research totaling $3,650,000. Metavivor is one of the few organizations that continued a research award program during this year of the Covid-19 pandemic. The grants hold promise for future treatments and therapies that will have a significant and positive impact for those living with metastatic breast cancer. Continue
Systemic Treatments For Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Treatment often continues until the cancer starts growing again or until side effects become unacceptable. If this happens, other drugs might be tried. The types of drugs used for stage IV breast cancer depend on the hormone receptor status and the HER2 status of the cancer:
Hormone receptor-positive cancers
Women with hormone receptor-positive cancers are often treated first with hormone therapy . This may be combined with a targeted drug such as a CDK4/6 inhibitor, everolimus or a PI3K inhibitor.
Women who havent yet gone through menopause are often treated with tamoxifen or with medicines that keep the ovaries from making hormones along with other drugs. Because hormone therapy can take months to work, chemo is often the first treatment for patients with serious problems from their cancer spread, such as breathing problems.
Hormone receptor-negative cancers
Chemo is the main treatment for women with hormone receptor-negative cancers, because hormone therapy isnt helpful for these cancers.
HER2-positive cancers
Trastuzumab may help women with HER2-positive cancers live longer if its given along with chemo or with other medications such as hormonal therapy or other anti-HER2 drugs. Pertuzumab , another targeted drug, might be added as well. Other options might include targeted drugs such as lapatinib or ado-trastuzumab emtansine .
HER2-negative cancers in women with a BRCA gene mutation
HER2-negative breast cancers in women with a PIK3CA mutation
Read Also: Anne Hathaway Breast Implants
Why Does Metastatic Breast Cancer Happen
Most often, metastatic cancer occurs because treatment didnt destroy all the cancer cells. Sometimes, a few cells remain dormant, or are hidden and undetectable. Then, for reasons providers dont fully understand, the cells begin to grow and spread again.
De novo metastatic breast cancer means that at the time of initial diagnosis, the breast cancer has already spread to other parts of the body. In the absence of treatment, the cancer spreads.
There is nothing you can do to keep breast cancer from metastasizing. And metastatic breast cancer doesnt happen because of something you did.
Immunogenic Potential Of Tnbc
The tumour microenvironment plays an important role in defining the interaction of our immune system with tumours. In TNBC, the TME is characterized by higher levels of vascular endothelial like growth factor , tumour infiltrating lymphocytes and tumour associated macrophages in contrast to other types of breast cancer. Additionally, there is a high level of expression of TILs in patients with TNBC. These have been shown to be a useful prognostic indicator across malignancies. TNBC has been shown to have consistently elevated TILs in contrast to other subtypes and TILs have been shown to be associated with improved survival. Ibrahim et al found that patients with lymphocyte-predominant breast cancer had a 40% pathological complete response rate compared to 7% of those patients without. High TILS are more frequent in TNBC compared to HER2-positive and luminal tumours and are associated with improved disease free survival and OS in early stage breast cancer. This is consistent with findings in other malignancies demonstrating the important role of the immune system in cancer biology and prognostication. All of these features demonstrate that the TME of TNBC is highly immunogenic.
You May Like: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Looking For More Of An Introduction
If you would like more of an introduction, explore these related items. Please note that these links will take you to other sections on Cancer.Net:
- ASCO AnswersFact Sheet: Read a 1-page fact sheet that offers an introduction to metastatic breast cancer. This free fact sheet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
- ASCO AnswersGuide:Get this free 52-page booklet that helps you better understand breast cancer. The booklet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
- Cancer.Net Patient Education Video: View a short video led by an ASCO expert in metastatic breast cancer that provides basic information and areas of research.
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer and stage 4 metastatic breast cancer are the same thing. Cancer stage refers to how advanced or widespread cancer is in the body. Oncologists, or cancer specialists, use cancer stage to guide important treatment decisions. Your doctor will determine the cancer stage at the time of your initial breast cancer diagnosis. However, breast cancer metastasis can occur years after an original diagnosis.
Read Also: Can Getting Hit In Your Breast Cause Cancer
Key Differences Between Invasive And Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer isnt a specific type of breast cancer, but is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. Both invasive and metastatic breast cancer have spread beyond the exact point where they started. Invasive breast cancers may have spread within the breast only, or to nearby lymph nodes or tissues, or may have spread to distant body parts. All metastatic breast cancers have spread outside of the breast and nearby lymph nodes to distant body parts. If a cancer is only invasive within the breast, its usually easier for doctors to treat than metastatic disease.
Continued
Cellular And Tumour Mass Dormancy
Two different models of tumour dormancycellular and tumour mass dormancyhave been proposed. Cellular dormancy refers to the presence of solitary or small cell clusters of DTCs that exist in a G0/G1 growth-arrested state and result from quiescence, senescence or differentiation. An inability to properly adhere to the ECM,, reduced signalling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase /AKT pathway and a low ratio of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase to the stress-induced kinase p38, are some of the plethoras of predominantly cell-intrinsic mechanisms that have been reported to induce cellular dormancy. On the other hand, escape from cellular dormancy has been shown to occur upon increased matrix stiffness through TGF1 expression, following the release of neutrophil extracellular traps by inflammatory neutrophils, and as a result of aberrant activation of the adhesion protein vascular cell adhesion protein 1 in indolent breast DTCs lodged in the bone marrow via engaging 41-expressing osteoclasts.
Don’t Miss: How To Donate To Breast Cancer Charity
How Is Breast Cancer Staged
Breast cancer stages indicate how advanced or widespread cancer is in the body. Cancer specialists determine cancer stage at the time of diagnosis. If cancer spreads after the original diagnosis, the stage number may change. These factors determine breast cancer stage:
-
Tumor size and grade, including whether the tumor has grown into nearby tissue. Tumor grade indicates how abnormal the cancer cells look.
-
Lymph node involvement, or the presence of cancer cells in lymph nodes.
-
Metastasis, or cancer spread outside of the breast.
-
Hormone receptor status, or whether cancer cells are more likely to grow in response to estrogen or progesterone hormones.
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 , a gene that contributes to breast cancer.
-
Oncotype DX score, findings from a gene test that gauge cancer cells responsiveness to certain treatments.
Advanced Cancer That Progresses During Treatment
Treatment for advanced breast cancer can often shrink the cancer or slow its growth , but after a time, it tends to stop working. Further treatment options at this point depend on several factors, including previous treatments, where the cancer is located, and a woman’s age, general health, and desire to continue getting treatment.
You May Like: Don Harrington Breast Cancer Center
Can Earlier Detection Of Recurrence Improve Breast Cancer Outcomes
The risk of metastatic relapse weighs heavily on the minds of patients, physicians and caregivers for years, sometimes decades, after treatment of the primary tumour is complete. Nearly 17 million cancer survivors are living in the United States, 3.9 million of whom are breast cancer survivors, and repeated monitoring for cancer recurrence in these individuals presents a significant challenge to healthcare delivery systems. For breast cancer patients, current American Society of Clinical Oncology and National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines limit follow-up care to mammography, medical history and physical exam, stating that in the absence of clinical signs and symptoms suggestive of recurrent disease, there is no indication for laboratory or imaging studies for metastases screening., Despite these guidelines, however, many patients receive high-cost imaging analysis and tumour marker blood tests during routine follow-up exams, exposing them to radiation and increasing healthcare costs.,,, So, what has led to the current precarious balance between the desire to detect recurrence early and clinical guidelines that limit the use of diagnostic tests?
Table 1 Exploiting tumour dormancy as a window of therapeutic opportunity to target MRD.
Combination Therapies With Taxanes
A number of combination therapies have been studied for the treatment of MBC, and several taxane combinations are highlighted by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network as preferred regimens, including doxorubicin with docetaxel or CrEL-paclitaxel, capecitabine with docetaxel, and gemcitabine with CrEL-paclitaxel. The NCCN guidelines go on to state that although combination chemotherapy often produces higher response rates and longer disease-free intervals in comparison with single agents, these regimens are associated with increased toxicity and do not lead to significant improvements in OS. Administering single agents sequentially reduces the likelihood for dose reductions. Thus, the NCCN panel states that there is little compelling evidence that combination chemotherapy is superior to sequential single agents.
Recommended Reading: Can Asbestos Cause Breast Cancer
Phase Iii Impassion 131
The IMpassion-131 study investigated if nab-paclitaxel could be replaced with paclitaxel in combination with atezolizumab in the first-line setting of advanced TNBC. Inclusion criteria were identical to the IMpassion130 trial, but the primary endpoint pertained to investigator-assessed PFS/OS tested first in the PD-L1 positive population. Patients were randomised in a 2:1 ratio to atezolizumab/paclitaxel vs placebo/paclitaxel . In the PD-L1 positive population, there was no significant improvement in the atezolizumab arm with a PFS of 6 mo compared to 5.7 in the placebo arm . There were also no significant differences in PFS in the overall population . In an interim OS analysis, there was no significant differences in OS in the PD-L1 population or the ITT population . The trend towards an improvement in OS was somewhat of a concern for investigators and the medical oncology community. Further analysis demonstrated that patients in both arm had an equivalent exposure to paclitaxel. The reasons for this trend however remain unclear. Speculation includes the potential immune mitigating effects of dexamethasone usage for paclitaxel treatment. This trial resulted in an FDA alert warning against the use of paclitaxel in combination with atezolizumab in TNBC. No new safety signals emerged.