Life Style And Dietary Cause
Sedentary life style, high dietary intake of fat obesity particularly in postmenopausal women may cause breast cancer. The use of alcohol is also another one cause of breast cancer. The risk increases with the amount of alcohol consumed. Women who consume two to five alcoholic beverages per day have a risk about one and a half times that of nondrinkers for the development of breast cancer.
Dilemmas Of Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Indeed, there are many serious and personal questions involving stage IV breast cancer. So, overall survival is less likely, and gains from intensive breast cancer treatment are unfortunately rather modest. A serious consideration is, therefore, quality of life during the course of treatment.
These decisions tend to be a dynamic process, based on individual cases, between patients and physicians. Respect needs to be given to the expectations for treatment, the status of the disease and the patient wishes.
Tnm System For Breast Cancer
Doctors also group cancers by the letters T, N, or M. Each of those letters tells you something about your cancer.
âTâ stands for tumor, or the lump of cancer found in the breast itself. The higher the number assigned after it, the bigger or wider the mass.
âNâ stands for nodes, as in lymph nodes. These small filters are found throughout the body, and they’re especially dense in and around the breast. They’re meant to catch cancer cells before they travel to other parts of the body. Here, too, a number tells you whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many.
âMâ stands for metastasis. The cancer has spread beyond the breast and lymph nodes.
Also Check: Stage 1b Breast Cancer Prognosis
Can Exercise Help Reduce My Risk Of Developing Breast Cancer
Exercise is a big part of a healthy lifestyle. It can also be a useful way to reduce your risk of developing breast cancer in your postmenopausal years. Women often gain weight and body fat during menopause. People with higher amounts of body fat can be at a higher risk of breast cancer. However, by reducing your body fat through exercise, you may be able to lower your risk of developing breast cancer.
The general recommendation for regular exercise is about 150 minutes each week. This would mean that you work out for about 30 minutes, five days each week. However, doubling the amount of weekly exercise to 300 minutes can greatly benefit postmenopausal women. The longer duration of exercise allows for you to burn more fat and improve your heart and lung function.
The type of exercise you do can vary the main goal is get your heart rate up as you exercise. Its recommended that your heart rate is raised about 65 to 75% of your maximum heart rate during exercise. You can figure out your maximum heart rate by subtracting your current age from 220. If you are 65, for example, your maximum heart rate is 155.
Aerobic exercise is a great way to improve your heart and lung function, as well as burn fat. Some aerobic exercises you can try include:
- Walking.
- Dancing.
- Hiking.
Remember, there are many benefits to working more exercise into your weekly routine. Some benefits of aerobic exercise can include:
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:

Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
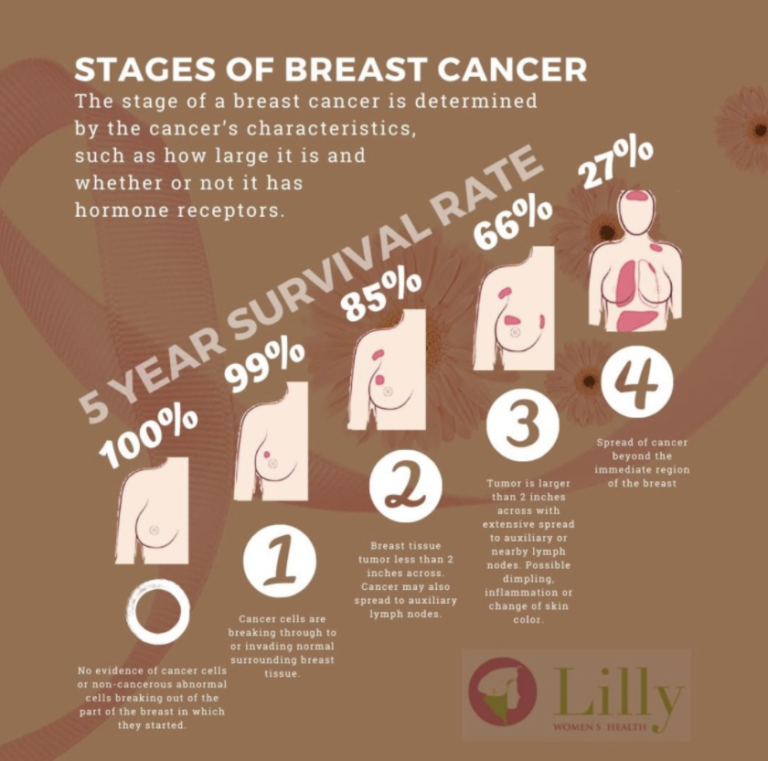
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
You May Like: Stage 3a Cancer
Grading Invasive Breast Cancer Cells
Three features of the invasive breast cancer cell are studied and each is given a score. The scores are then added to get a number between 3 and 9 that is used to get a grade of 1, 2, or 3, which is noted on your pathology report. Sometimes the terms well differentiated, moderately differentiated, and poorly differentiated are used to describe the grade instead of numbers:
- Grade 1 or well differentiated . The cells are slower-growing, and look more like normal breast cells.
- Grade 2 or moderately differentiated . The cells are growing at a speed of and look like cells somewhere between grades 1 and 3.
- Grade 3 or poorly differentiated . The cancer cells look very different from normal cells and will probably grow and spread faster.
Our information about pathology reports can help you understand details about your breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Staging: What You Need To Know
When youve first been diagnosed with breast cancer, a big question on your mind will likely be: How bad is it? Doctors determine how advanced cancer is through the diagnosis and staging process, labeling your cancer with a stage between 0 and 4.
The higher the stage, the more advanced the cancer is. Treatment options will typically be more aggressive for more advanced cancers, and prognosis, or outlook, is worse.
Verywell / Jessica Olah
Breast cancers are uncontrolled growths that develop in and around the breast tissue. More advanced cancers have likely also spread to other tissues.
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers in females. More than 280,000 females are diagnosed with breast cancer each year in the United States. Thankfully, about 90% of females diagnosed with breast cancer are still alive five years later.
When first diagnosed with cancer, youll undergo testing and analysis. Doctors will use those results, along with guidelines set out by the American Joint Committee on Cancer , to determine cancers stage.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Whats The Risk Of Recurrence
Everyone who has had breast cancer has some risk of recurrence, but its typically low.
In general, the more time that goes by, the lower the risk of recurrence. Cancer is most likely to recur in the first two years after treatment, and once people get to five years of living cancer-free after treatment, its considered to be a significant milestone to be celebrated. Recurrence after that five year markrare, but possibleis called late recurrence.
Theres still so much that is unknown about cancer recurrence, but researchers have found some patterns in recent years that point to clues about why it happens. These factors might be linked to a higher risk of breast cancer recurrence:
- Having high blood sugar
- Not eating enough fruits and vegetables
- Having had a surgical site infection after your surgery
Certain characteristics of your original cancer also might mean a higher risk of recurrence, such as:
- A tumor of more than five centimeters across
- Cancer cells that are HER2-positive
- Cancer cells that are triple negative
- Cancer cells in four or more axillary lymph nodes at the time of surgery
- Cancer cells in the chest muscles or breast skin
You might be at higher risk for late recurrence if you had:
- A tumor of more than two centimeters
- A high number of affected lymph nodes
- A hormone receptor-positive cancer
Also Check: Can Breast Cancer Spread To Bones
Pathophysiology Of Breast Cancer Metastasis To The Bone
BC spread is a complex multistep process. It begins with the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of locally invasive carcinoma cells which then enter the lumina of blood vessels, a process called intravasation . Once in the systemic circulation, these circulating tumour cells must survive a variety of stress factors in order to reach the bone marrow, namely the stress imposed by matrix detachment , the shear forces, and the predation by cells of the innate immune system . To evade these threats, CTCs form relatively large emboli via interactions with blood platelets . However, the majority become trapped in capillary beds during its first passage through the circulation . Nevertheless, some CTCs may avoid this rapid trapping because of their plasticity or chance passage through arteriovenous shunts . Eventually, some CTCs become lodged in the microvasculature of distant organs and initiate intraluminal growth, rupturing the walls of surrounding vessels, and placing cells in direct contact with the parenchyma of a specific organ . Also, CTCs may be able to extravasate from the vessels lumina into the stromal microenvironment by penetrating the endothelial cell and pericyte layers .
Read Also: Treatment For Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Grade 3 Breast Cancer
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma: The Most Common Kind
The most common form of breast cancer is invasive ductal carcinoma , sometimes also called infiltrating ductal carcinoma. About 80 percent of all new breast cancer cases in women, and nearly all breast cancer in men, are IDC. The risk of IDC also increases as people grow older.
IDC starts in the ducts just as DCIS does, but the cancer then grows beyond the ducts and invades, or infiltrates, the fatty tissue surrounding the ducts. Without treatment, the cancer continues to metastasize, or spread, into the lymph nodes and bloodstream.
The options available to treat IDC depend on the type of breast cancer it is, what mutations it does or does not have, how aggressive it is, and other factors. One of the most important of those other factors is the cancer stage.
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
- the skin
Recommended Reading: Vernon Johnston Baking Soda
Why Were New Measures Added To The Staging System
The new measures give information on the biology of the tumor that affects prognosis. Adding these measures improved staging.
For example, with breast cancer, a large tumor may have a better prognosis than a small tumor, based on biological measures. In the same way, a small tumor may have a worse prognosis than a large tumor based on these measures.
Frequently Occurring Breast Cancer
Lobular carcinoma in situ : The term, in situ, refers to cancer that has not spread past the area where it initially developed. LCIS is a sharp increase in the number of cells within the milk glands of the breast.
Ductal carcinoma in situ : DCIS, the most common type of non-invasive breast cancer, is confined to the ducts of the breast. For example, ductal comedocarcinoma.
Typical Structure associated with ductal carcinoma
Recommended Reading: How Bad Is Stage 3 Cancer
What Should A Person With Stage 0 Or Stage 1 Breast Cancer Expect Regarding Treatment
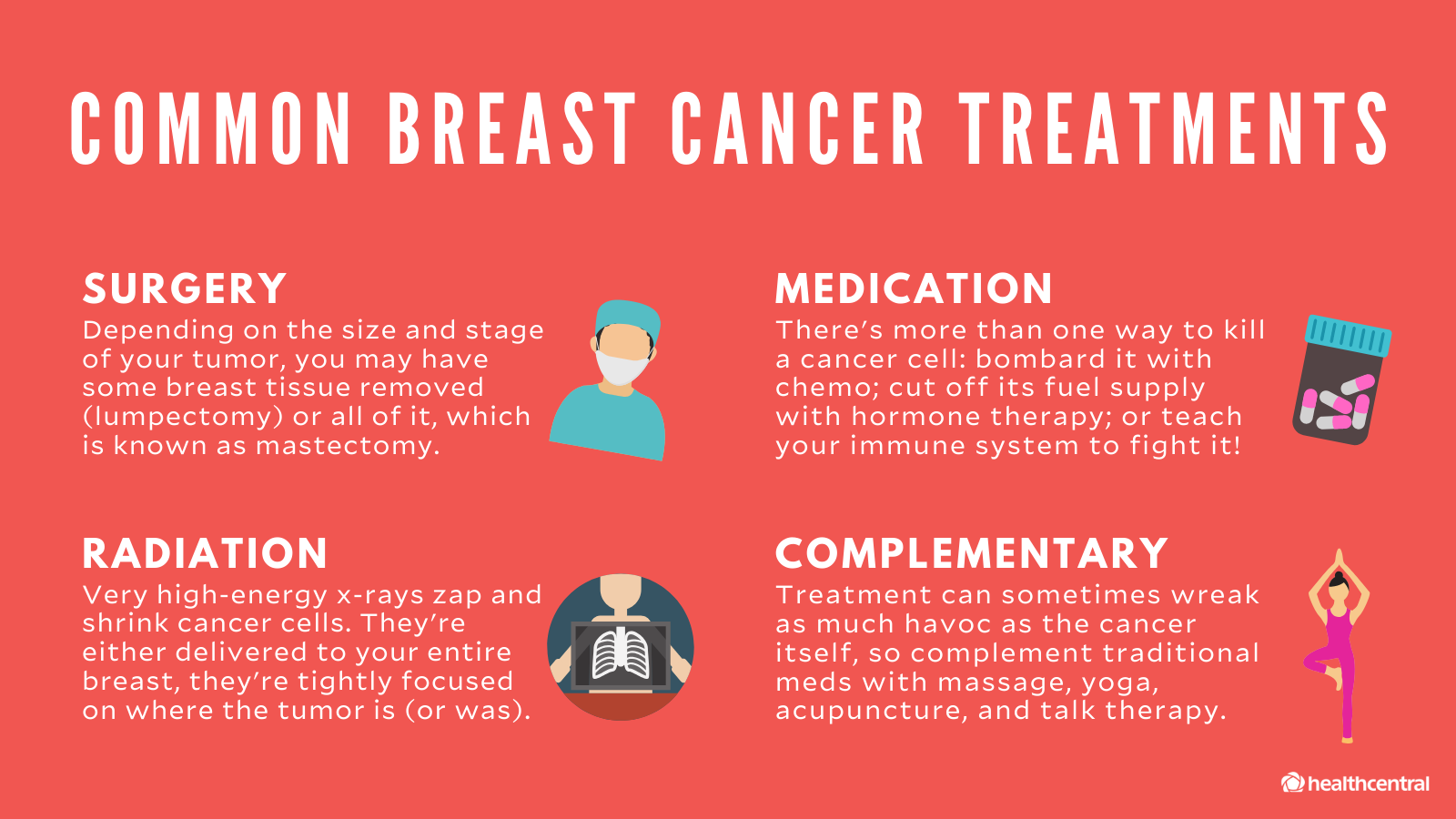
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered non-invasive, it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors. Like stage 0, Chemotherapy is often not necessary for earlier stages of cancer.
Material on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
Less Commonly Occurring Breast Cancer
Medullary carcinoma: Medullary carcinoma is an invasive breast cancer that forms a distinct boundary between tumor tissue and normal tissue. Only 5% of breast cancers are medullary carcinoma.
Mutinous carcinoma: Also called colloid carcinoma, mutinous carcinoma is a rare breast cancer formed by the mucus-producing cancer cells. Women with mutinous carcinoma generally have a better prognosis than women with more common types of invasive carcinoma.
Tubular carcinoma: Tubular carcinomas are a special type of infiltrating breast carcinoma. Women with tubular carcinoma generally have a better prognosis than women with more common types of invasive carcinoma. Tubular carcinomas account for around 2% of breast cancer diagnoses.
Don’t Miss: Stage 2 Triple Positive Breast Cancer
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stages
Invasive ductal carcinoma stages provide physicians with a uniform way to describe how far a patients cancer may have spread beyond its original location in a milk duct. This information can be helpful when evaluating treatment options, but it is not a prognostic indicator in and of itself. Many factors can influence a patients outcome, so the best source of information for understanding a breast cancer prognosis is always a physician who is familiar with the patients case.
In general, breast cancer stages are established based on three key variables: the size of a tumor, the extent of lymph node involvement and whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. This information may be obtained through a combination of clinical examinations, imaging studies, blood tests, lymph node removal and tissue samples . If, based on the initial test results, a physician believes that the cancer may have spread to other parts of the body, further testing may be ordered, such as a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or liver function test.
Invasive ductal carcinoma is usually described through a numeric scale ranging from 1 to 4 . Specifically, the invasive ductal carcinoma stages are:
If youd like to learn more about invasive ductal carcinoma stages and treatment options, call or complete a new patient registration form online.
- BROWSE
Additional Markers For Breast Cancer Staging
Additional markers specific to breast cancer will further define your stage, which may be helpful in choosing targeted treatments to fight the cancer.
- ER: The cancer has an estrogen receptor. Estrogen is a hormone, and some cancers have receptors that respond to estrogen.
- PR: The cancer has a progesterone receptor. Progesterone is also a hormone.
- HER2: The cancer makes the protein HER2 .
- G: Grade of cancer refers to how different the cells look from normal. Grade 1 indicates that the cells look fairly normal, while grade 2 cells are growing a little faster, and grade 3 cells look markedly different than normal breast tissue.
These markers, along with the TNM measurements, define your stage.
A cancer recurrence refers to cancer that returns in the same breast, and it requires new staging. This new stage is marked by an R at the end to indicate restaging. If it develops in the other breast, its considered a new cancer.
Don’t Miss: Mayo Clinic Breast Cancer Stages
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 cancer means the breast cancer has extended to beyond the immediate region of the tumor and may have invaded nearby lymph nodes and muscles, but has not spread to distant organs. Although this stage is considered to be advanced, there are a growing number of effective treatment options.
This stage is divided into three groups: Stage 3A, Stage 3B, and Stage 3C. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and surrounding tissue.
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 breast cancer is divided into three groups:
- Stage 3A
- Stage 3C
Stage 3A can mean:
No cancer is seen in the breast, but cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast measures up to 5cm and cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is larger than 5cm, and cancer is found in up to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone.
Stage 3B means the cancer in the breast can be any size and has spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall. Cancer is found in up to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breast bone.
Stage 3C means the cancer in the breast can be any size, may have spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall and cancer is found in 10 or more lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone, or to nodes above or below the collarbone.
You May Like: First Stage Breast Cancer Symptoms
What Can I Expect While Living With Metastatic Breast Cancer
Your care team will monitor you every few months to check if the cancer is responding to treatment, and also to see if you are having any side effects. The process of restaging the cancer includes:
- History/physical exam.
- Blood tests.
- Imaging tests, including CTs and bone scan or PET scan.
Before your scans or tests, its normal to feel anxiety. It may help to bring a friend or family member to the appointment with you.
Read Also: What Chemo Drugs Are Used For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Prognostic Impact Of Tumor
It has been previously reported that tumor-specific expression of the rate-limiting enzyme, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutharyl-coenzyme A reductase , in the mevalonate pathway is associated with more favorable tumor parameters in breast cancer. In the present study, it is examined the prognostic value of HMG–CoAR expression in a large cohort of primary breast cancer patients with long-term follow up.
Don’t Miss: Effects Of Breast Cancer On A Person