How Can A Person Who Has Inherited A Harmful Brca1 Or Brca2 Gene Variant Reduce Their Risk Of Cancer
Several options are available for reducing cancer risk in individuals who have inherited a harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 variant. These include enhanced screening, risk-reducing surgery , and chemoprevention.
Enhanced screening. Some women who test positive for harmful BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants may choose to start breast cancer screening at younger ages, have more frequent screening than is recommended for women with an average risk of breast cancer, or have screening with magnetic resonance imaging in addition to mammography.
No effective ovarian cancer screening methods are known. Some groups recommend transvaginal ultrasound, blood tests for the CA-125 antigen , and clinical examinations for ovarian cancer screening in women with harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants. However, none of these methods appear to detect ovarian tumors at an early enough stage to improve long-term survival .
The benefits of screening men who carry harmful variants in BRCA1 or BRCA2 for breast and other cancers are not known. Some expert groups recommend that such men undergo regular annual clinical breast exams starting at age 35 . The National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend that men with harmful germline variants in BRCA1 or BRCA2 consider having a discussion with their doctor about prostate-specific antigen testing for prostate cancer screening starting at age 40 .
What Are The Screening Options For Hboc
Screening is the use of different tests to find specific types of cancer before signs and symptoms appear. It is important to talk with your health care team about the following screening options, as each person is different:
Screening for women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation
-
Monthly breast self-examinations, beginning at age 18
-
Clinical breast examinations performed twice a year by a health care team or nurse, beginning at age 25
-
Yearly magnetic resonance imaging scans of both breasts, between ages 25 and 29.
-
Yearly mammogram and breast MRI, between ages 30 and 75.
-
Pelvic examination, trans-vaginal ultrasound, and CA-125 blood test every 6 months, beginning at age 30 to 35. It should be noted, however, that screening is not yet able to find most early ovarian cancers.
-
Consideration of prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy, between ages 35 and 40, and once a woman is done giving birth to children
Screening for men with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation
Screening options may change over time as new methods are developed and more is learned about HBOC. Talk with your health care team about appropriate screening tests for you.
Learn more about what to expect when having common tests, procedures, and scans.
Are Harmful Variants In Brca1 And Brca2 More Common In Certain Racial/ethnic Populations Than Others
Yes. The likelihood of carrying an inherited mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2 varies across specific population groups. While the prevalence in the general population is about 0.2%0.3% , about 2.0% of people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent carry a harmful variant in one of these two genes and the variants are usually one of three specific variants, called founder mutations. Other populations, such as Norwegian, Dutch, and Icelandic peoples, also have founder mutations .
Different racial/ethnic and geographic populations also tend to carry different variants in these genes. For instance, African Americans have BRCA1 variants that are not seen in other racial/ethnic groups in the United States . Most people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent in the United States who carry a BRCA variant have one of three specific variants . In the Icelandic population, a different variant in BRCA1 is common among those who inherit a mutation in BRCA1.
Read Also: What Is Mbc Breast Cancer
Read Also: Can Nipple Piercing Cause Cancer
What To Think About
Genetic counselling before and after a BRCA test can help you understand the benefits, risks, and possible outcomes of testing.
- To find doctors who do gene tests and counselling, contact your local chapter of the Canadian Cancer Society at www.cancer.ca.
- To find a genetic counsellor near you, contact the contact the Canadian Association of Genetic Counsellors at www.cagc-accg.ca.
- Breast Cancer Risk: Should I Have a BRCA Gene Test?
Read Also: Are Breast Cancer Lumps Hard Or Soft
Can Hboc Be Avoided

There are options available for people with HBOC who are interested in having a child and reducing that childs risk of this hereditary syndrome. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis is a medical procedure done along with in-vitro fertilization . It allows people who carry a specific known genetic mutation to reduce the likelihood that their children will inherit the condition. For PGD, a womans eggs are removed and fertilized in a laboratory. When the embryos reach a certain size, 1 cell is removed and tested for the specific hereditary condition. The parents can then choose to transfer the embryos that do not have the mutation. PGD has been used for over 2 decades for several hereditary cancer syndromes. However, it is a complex procedure with financial, physical, and emotional factors to consider before starting. For more information, talk with an assisted reproduction specialist at a fertility clinic.
Don’t Miss: Estrogen Positive Her2 Negative Breast Cancer
Genetic Testing Facilities And Costs
You can get a genetic test in your doctors office to see if you have inherited an abnormal BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2 gene mutation. The doctor takes a blood or saliva sample and sends it to a commercial laboratory, or sometimes a research testing facility. During testing, the genes are separated from the rest of the DNA and scanned for abnormalities.
Whether the genetic test is handled by a research testing facility depends on the type of test and the specific genes being tested. Research laboratories tend to perform free and anonymous tests. But research laboratories may provide limited results or require multiple family members to participate. It also may take many months or years for test results to be ready, if they are ever made available at all.
In the United States, several laboratories conduct commercial BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2 testing, including Myriad Genetic Laboratories, Ambry Genetics, and GeneDx. These facilities report results in two to four weeks.
The most common causes of hereditary breast cancer are BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. But abnormalities in other genes also have been associated with breast cancer risk.
Although many insurance plans cover genetic testing, its smart to confirm whether your insurance plan does.
What Are The Genetic Mutations Linked To Breast Cancer
Mutations of genes are like spelling errors in the genetic code of a gene. Those who have a gene mutation may be at higher than average risk for developing certain cancers. A genetic mutation that increases the risk of breast cancer is present in some families.
BRCA 1& 2
BRCA1 and BRCA2 are the most common genetic mutations that cause breast cancer. These are short for breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 and breast cancer susceptibility gene 2. The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are found in every person.
The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are responsible for the repair of certain types of DNA errors that may happen each time a human cell makes a copy of itself. If the gene does not have a mutation, the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes help ensure the stability of a cells genetic material, or DNA, and help stop uncontrolled cell growth.
Mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 have been linked to an increased risk for multiple types of cancer, most notably breast and ovarian cancer. Having an inherited mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2 does not mean a person is guaranteed to develop cancer, but the chances are much higher than for someone who does not have a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation. People who inherit a harmful mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2 have a lifetime risk of developing breast cancer of 50-80%, compared to 13% for an average person without the mutation.
Other Genes Linked to Breast Cancer
People can inherit these mutations from their parents, or mutations can happen during a persons lifetime.
Also Check: Triple Positive Breast Cancer Stage 4
When To Get Tested
When your personal or family history suggests the presence of a harmful BRCA mutation, such as you or someone in your family has had breast cancer before the age of 50 or ovarian cancer at any age, is a male with breast cancer, or when a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation has been identified in a family member
Does Someone Who Inherits A Cancer Susceptibility Variant Always Get Cancer
No. Even if a cancer susceptibility variant is present in a family, it does not necessarily mean that everyone who inherits the variant will develop cancer. Several factors influence whether a given person with the variant will actually develop cancer. One is the penetrance of the variant. When not all people who carry a variant go on to develop the disease associated with that variant, it is said to have incomplete or reduced penetrance. Hereditary cancer syndromes can also vary in their expressivitythat is, people who inherit the variant may vary in the extent to which they show signs and symptoms of the syndrome, including the development of associated cancers. Lifestyle factors and environmental risks can also influence disease expression.
Also Check: What Is Stage 3b Breast Cancer
Who Should Have Brca Testing
The BRCA gene test is offered only to people who are likely to have an inherited mutation, based on personal or family history, or who have specific types of breast cancer. The BRCA gene test isnt routinely performed on women at average risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
At Elite Womens Health, it is our goal to offer personalized healthcare to each of our patients. Our providers will examine your personal and family cancer history and if your family history indicates you are at higher risk for carrying the BRCA mutations, we will refer you to Courtney Miller, our Womens Health Nurse Practitioner. Courtney will sit down with you and have an in-depth discussion on the benefits and risks of BRCA testing and assess if this test if the right one for you.
Should I Be Tested For Genetic Mutations
At-risk families can take blood tests to look for mutations in these genes.
You may want to discuss genetic testing with your doctor if:
- You have two or more blood relatives — mother, sister, aunt, cousin, or daughter — with premenopausal breast cancer or ovarian cancer diagnosed at any age.
- You were diagnosed with breast cancer, especially before menopause, and have a blood relative with breast or ovarian cancer.
- You were diagnosed with ovarian cancer and you have blood relatives who have had ovarian or breast cancer.
- A male in your family has or had breast cancer.
- You or a family member has been diagnosed with bilateral breast cancer .
- You were diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer before the age of 60.
- You are related to someone who has a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation.
- You are of Ashkenazi Jewish descent and have had breast or ovarian cancer or have blood relatives who have had breast or ovarian cancer.
Also Check: Treatment For Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast
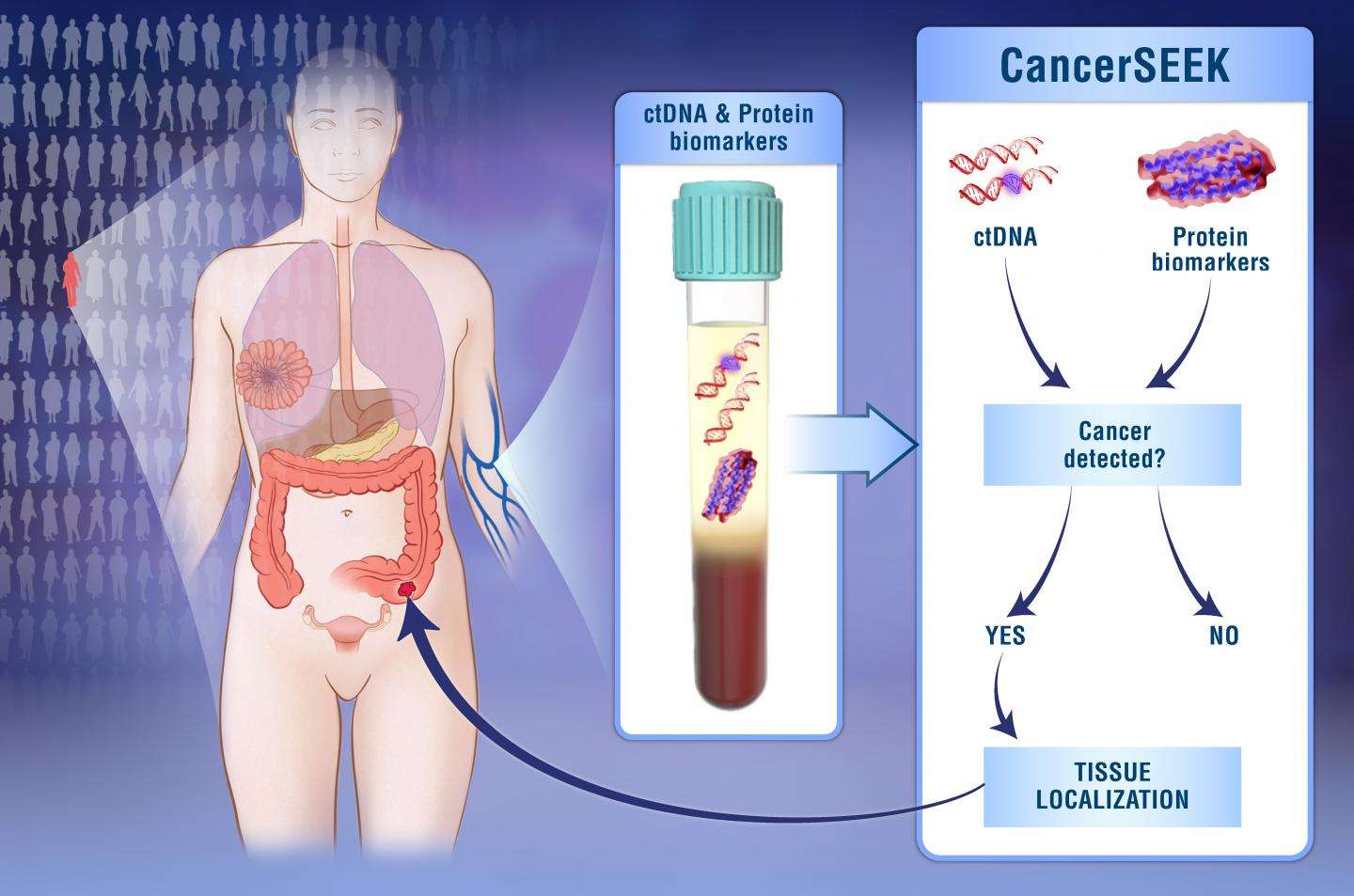
Report: New Blood Test For Early Detection Of 8 Major Cancer Typeswhat Does This Mean For You
You may have heard the recent hype about a new study in which a blood test was used for the early detection of 8 major cancer types. What does the study really mean and, more importantly, when will it impact you?
Our Rivkin Scientific Advisory Council, a group of scientific and clinical experts in the field of ovarian cancer, have provided insight on the new study. Here is their summary and commentary on the new report:
A study published in Science last week reported the development of a test called CancerSEEK to see if the researchers could detect several types of solid tumors at early stages. The researchers analyzed blood from patients with ovarian, liver, stomach, esophageal, pancreatic, colorectal, lung and breast cancer. They tested for mutations in genes known to promote cancer in the cell-free DNA DNA from cancer cells that is present in the blood. The researchers also looked at levels of various protein biomarkers, including CA-125, in the blood. They used mutation and biomarker data along with machine learning algorithms to see if they could detect a positive cancer signal and pinpoint the location of the cancer in patients with known cancer. For several of the cancer types, they had promising results. However, as the tests are done in patients with known cancer, it is not clear how well the test would detect cancer in people who are not known to have cancer.
Brit Thompson
How The Test Will Feel
An MRI exam causes no pain. You will need to lie still. Too much movement can blur MRI images and cause errors.
If you are very anxious, you may be given medicine to calm your nerves.
The table may be hard or cold, but you can ask for a blanket or pillow. The machine makes loud thumping and humming noises when turned on. You will likely be given ear plugs to help reduce the noise.
An intercom in the room lets you to speak to someone at any time. Some MRIs have televisions and special headphones to help the time pass.
There is no recovery time, unless you were given a medicine to relax. After an MRI scan, you can return to your normal diet, activity, and medicines unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
Recommended Reading: Estrogen Related Cancer
Why It Is Done
A BRCA gene test is done to find out if you have BRCA gene changes that increase your risk of breast, ovarian, and some other cancers.
You might consider this test if you or your family have certain health problems or risk factors. Examples include having one or more members of your family who’ve had breast, ovarian, prostate, or pancreatic cancer, being diagnosed with breast cancer before age 50, and having an Ashkenazi Jewish heritage.
You may feel better if the test shows that you don’t have a BRCA mutation. If the test shows that you do have a BRCA mutation, you may be able to make some decisions that could reduce your cancer risk.
If you are concerned that you may have a BRCA gene change, talk with your doctor.
What If I Dont Have A Strong Family History
After looking at your family history, the genetic doctor might tell you that its unlikely that you have an inherited faulty gene. In this case, your risk of cancer is the same as other members of the population.
In certain situations, the genetic counsellor might suggest you have regular screening. This is more likely if members of your family have breast or bowel cancer.
You can find out about this in our information about:
Also Check: Breast Cancer Weight Gain Symptom
Are People With Brca Mutations At Risk For Other Cancers
The BRCA mutations’ role in cancer risk is an active area of research. In addition to breast and ovarian cancer, the mutation has been linked to prostate and pancreatic cancer. As of 2015, studies have found that the BRCA mutation is present in 0.5%-4% of prostate cancers and 5%-8% of pancreatic cancers.
However, researchers are still gathering information about how BRCA mutation testing should be incorporated into screening for those cancers. For example, while researchers are finding that men carrying BRCA mutations have an increased risk for prostate cancer, it is still unclear what family or personal history factors should prompt men in the general population to receive BRCA mutation testing. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network does recommend that men carrying BRCA2 mutation begin prostate cancer screening at 40 years old. For pancreatic cancer, there are no data showing that BRCA mutation screening improves cancer survival. There are currently no guidelines for BRCA mutation testing and pancreatic cancer.
Genetic Testing For Breast/ovarian Cancer Risk
It is possible to detect mutations in some cancer predisposing genes. Some mutations may not be detected using current technology.
Genetic testing involves first searching for a gene mutation. The genes most commonly tested are BRCA1 and BRCA2. After genetic counselling, a sample of blood is usually taken from a woman in the family who has developed breast cancer or ovarian cancer. The DNA is searched for a gene fault. This testing may take some months.
If a gene fault is not detected after a mutation search, then testing for the family should be considered as inconclusive. However, if a fault is detected, then other family members can be tested to see if they carry the same gene fault or not. The testing for other family members is known as predictive genetic testing. This is a relatively quick test since the laboratory only has to determine the presence or absence of the family gene mutation in a predictive test.
Genetic testing is offered only through a family cancer clinic. If a woman is referred to a family cancer clinic, the availability, limitations, potential benefits, and possible consequences of genetic testing will be discussed with her.
*In July 2011, National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre amalgamated with Cancer Australia to form a single national agency, Cancer Australia, to provide leadership in cancer control and improve outcomes for Australians affected by cancer.
Don’t Miss: Untreated Breast Cancer Symptoms
Blood Testing For Her2/neu
Sometimes, especially when there is not enough tumor tissue available to perform the test, a blood sample is drawn from the patients arm to collect similar data. This blood test is called a serum HER2/neu test, and it can be used as part of the initial workup upon cancer diagnosis or to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. If initially the level of serum HER2/neu is elevated to more than 15ng/mL and then it falls, the treatment is likely working. However, if the serum level remains elevated, this indicates the treatment is not working. If the serum level declines but then, upon later testing, is elevated once again, this is a sign that the cancer could be recurring.
When all three of the tests come back negative for receptors for hormones and negative for HER2, triple negative breast cancer may be the diagnosis.
Materials on this page courtesy of: