How You Can Play A Part
Given the high prevalence of this disease, talking and generating awareness regarding this topic can really make a difference.
Protect yourself and your loved ones by understanding the early signs and symptoms and the importance of screening.
This is all the more reason to create awareness about breast cancer, not only in the month of October, but year-round.
Together, we can make a huge impact. So, play your part in spreading the word, as well as donating to breast cancer charities and research initiatives that aim to find novel cures for the disease.
Continue Reading
What Is Breast Cancer
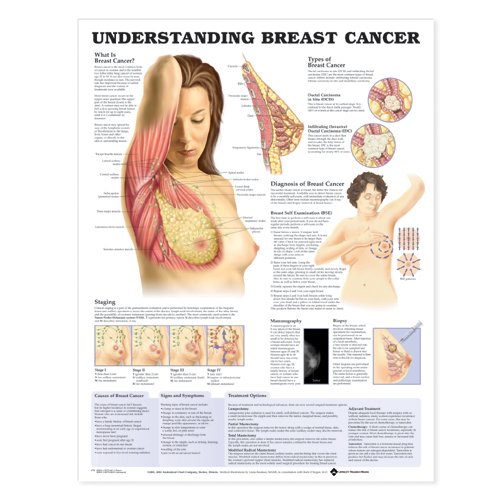
The human body is made of tiny building blocks called cells. Your body creates them, replacing those that die with new ones. Usually, the body creates healthy, normal cells that do just what they’re supposed to do. This includes cells in the breasts, the two rounded areas on the front of the chest.
But if a cell changes into an abnormal, sometimes harmful form, it can divide quickly over and over again without dying, making many, many copies of itself. When this happens, a tumor, abnormal body cells grouped together in the form of a mass or lump, can start to form and grow.
Breast cancer is a kind of tumor that develops in the cells of a person’s breast. You may think that only women can get breast cancer, but because all people have breast tissue, men can get breast cancer as well but this is very rare.
Someone with breast cancer may have cancer cells in just one part of the breast, which might be felt as a lump. The cancer can spread throughout one or both breasts. Sometimes breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, like the bones< , the liver, or elsewhere.
Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can have several symptoms, but the first noticeable symptom is usually a lump or area of thickened breast tissue.
Most breast lumps are not cancerous, but it’s always best to have them checked by a doctor.
You should also see a GP if you notice any of these symptoms:
- a change in the size or shape of one or both breasts
- discharge from either of your nipples, which may be streaked with blood
- a lump or swelling in either of your armpits
- dimpling on the skin of your breasts
- a rash on or around your nipple
- a change in the appearance of your nipple, such as becoming sunken into your breast
Breast pain is not usually a symptom of breast cancer.
Find out more about the symptoms of breast cancer.
Read Also: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Diagnosed During Or After Pregnancy
Being pregnant at the time of diagnosis of breast cancer has been associated with a worse outcome. In one study of 797 such cases, compared with 4,177 non-pregnancy-associated breast cancer controls, women diagnosed while pregnant had larger, more advanced tumors, a greater incidence of receptor-negative tumors, and a higher death rate . A smaller study found no association between pregnancy and increased mortality. In contrast, pregnancy and childbirth following a diagnosis of breast cancer do not increase mortality, and actually may improve survival. One study found that 438 women age < 45 years at diagnosis, who delivered a child 10 or more months following a diagnosis of breast cancer, had a decreased relative risk of death , compared to women who did not bear children following diagnosis. Women who were pregnant at the time they were diagnosed had a mortality rate similar to the latter group. This suggests that childbirth following breast cancer diagnosis does not increase mortality.
Risk Factors To Consider
You may be more likely to get diagnosed with breast cancer at an early age if you have a mother, sister, or another close family member who was diagnosed with breast cancer before age 45.
You may also have a higher risk of diagnosis if you have the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation. The BRCA genes help fix damaged DNA. When theyre altered, the DNA in the cells can change in ways that lead to cancer. Experts link these mutations to an increased risk for breast and ovarian cancers.
Breast cancers that arise from BRCA mutations are more likely to start early and to be more aggressive. Up to 65 percent of women with the BRCA1 mutation, and 45 percent of those with a BRCA2 mutation, will develop breast cancer by age 70.
Treatment with radiation to the chest or breast as a child or teenager can also increase your risk.
Recommended Reading: Tubular Cancer Breast
Guidelines For Genetic Testing For Breast Cancer
About 10% of breast cancers are related to inheritance of damaged genes. BRCA1 and BRCA2 are the genes most frequently implicated, but there are many other genes, such as PALB2, ATM, and CHEK2, that need to be considered as well. Genetic testing usually starts with a family member who has already developed a breast or ovarian cancer. If this individual is positive for a mutation then all of the other family members can be tested for the same mutation to determine who is high risk and who is not. If no one in the family is known to carry a mutation then the test is considered non-informative. That means the test was unable to tell us which relatives in the family are high risk. People who have inherited a damaged gene are at increased risk for breast and other cancers. The risk may be as high as 80% depending on the specific gene and family history. Guidelines for determining whether an individual should get genetic testing or not are constantly evolving. General criteria include:
- Someone in your family is known to carry a mutated gene
- Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry
- You were diagnosed with breast cancer before age 50
- A man in your family has been diagnosed with breast cancer
- You were diagnosed with ovarian cancer
- There are multiple breast cancers on one side of your family
- Cancer was diagnosed in both breasts
Should Women Under Age 40 Get Mammograms
In general, regular mammograms arent recommended for women under 40 years of age, in part because breast tissue tends to be dense, making mammograms less effective.The American Cancer Society recommends women ages 40 to 44 should have a choice to start yearly screening mammograms if they would like. Women ages 45 through 54 should have a mammogram each year and those 55 years and over should continue getting mammograms every 1 to 2 years.. Most experts believe the low risk at that age doesnt justify the exposure to radiation or the cost of mammography. But mammograms may be recommended for younger women with a family history of breast cancer and other risk factors.
Continued
Also Check: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
Women At Higher Risk Of Breast Cancer
Factors that greatly increase breast cancer risk include :
- A BRCA1 or BRCA2 inherited gene mutation
- A personal history of invasive breast cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ
- A personal history of lobular carcinoma in situ or atypical hyperplasia
- Radiation treatment to the chest area between ages 10-30
- Li-Fraumeni, Cowden/PTEN or Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome
- An ATM, BARD1, BRIP1, CDH1, CHEK2, NBN, NF1, PALB2, PTEN, RAD51C, RAD51D, STK11 or TP53 inherited gene mutation
- A greater than 20 percent lifetime risk of invasive breast cancer based mainly on family history
Figure 3.5 below outlines the National Comprehensive Cancer Network breast cancer screening guidelines for women at higher than average risk up to age 75.
The NCCN recommends women older than 75 talk with their health care providers about a breast cancer screening plan thats right for them.
Figure 3.6 below outlines the American Cancer Society breast cancer screening guidelines for women at higher than average risk .
|
Figure 3.5: NCCN breast cancer screening recommendations for women at higher than average risk |
|
Risk factor |
|
Every year starting at age 30 or age recommended by health care provider |
Every year starting at age 30 or age recommended by health care provider |
|
Adapted from ACS materials . |
Can A Woman With Breast Cancer Get Pregnant
For young women, a breast cancer diagnosis also creates uncertainty about having a family. Because cancer treatments can affect ovarian function, specialists with expertise in working with women with cancer can help preserve fertility before treatment begins by freezing eggs or embryos, through a process called cryopreservation. In Connecticut, insurance carriers cover the cost of cryopreservation for men and women under the age of 40 who have cancer.
It also may happen that a young woman is already pregnant when diagnosed with breast cancer, which requires careful conversations between the provider and patient.
Breast cancer is the most common cancer we see in pregnant women, says Dr. Silber. Because pregnancy brings about a variety of changes in the breastand pregnant women arent getting mammogramsit may make the disease harder to diagnose, she notes, but it doesnt mean the prognosis is worse.
In such cases, she explains, Our goal is to do what we can to treat the cancer and protect the pregnancy, adding that there are some types of chemotherapy treatments that can be given during pregnancy to treat breast cancer.
You May Like: Does Breast Tissue Grow Back After Lumpectomy
Screening Guidelines For Women At Average Breast Cancer Risk
MSK doctors recommend the following for women at average risk* of breast cancer:
- Women between the ages of 25 and 40 should have anannual clinical breast examination.
- Women 40 and older should have an annual mammogram in addition to anannual clinical breast examination.
- Ultrasound may be recommended for women with dense breast tissue.
- All women should consider performing a monthly self breast exam beginning at age 20 and become familiar with their breasts so they are better able to notice changes.
Are Women Under 40 At Risk For Breast Cancer
Younger women generally do not consider themselves to be at risk for breast cancer. However, breast cancer can strike at any age: 5% of breast cancer cases occur in women under 40 years of age. All women should be aware of their personal risk factors for breast cancer.
There are several factors that put a woman at higher risk for developing breast cancer, including:
- A personal history of breast cancer or a high risk lesion found by biopsy
- A family history of breast cancer, particularly at an early age
- A family history that is concerning for a genetic syndrome that may put them at a higher risk for breast cancer
- History of radiation therapy to the chest
- A known genetic mutation conferring a high risk for the development of breast cancer
- Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry
Don’t Miss: Did Anne Hathaway Have Cancer
How Can I Detect My Breast Cancer Early
The best way for young women to find breast cancer early is to be breast self-aware. Become familiar with your breasts: their shape, size and what they feel like. Learn what is normal for you. Sometimes your breasts may change throughout your monthly cycle. If you are pregnant or nursing, your breasts will change even more dramatically. If you find anything unusual, see your doctor immediately and insist on a diagnosis. In general, women should have a yearly clinical breast examination by a doctor beginning at age 20 and start having annual mammograms beginning at age 45.
What Is Hereditary Breast And Ovarian Cancer

A diagnosis of Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome is considered when there are multiple cases of breast cancer and/or ovarian cancer on the same side of the family. The chance that a family has HBOC increases in any of these situations:
-
1 or more women are diagnosed at age 45 or younger
-
1 or more women are diagnosed with breast cancer before age 50 with an additional family history of cancer, such as prostate cancer, melanoma, and pancreatic cancer
-
There are breast and/or ovarian cancers in multiple generations on the same side of the family, such as having both a grandmother and an aunt on the fathers side both diagnosed with these cancers
-
A woman is diagnosed with a second breast cancer in the same or the other breast or has both breast and ovarian cancers
-
A male relative is diagnosed with breast cancer
-
There is a history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, and/or pancreatic cancer on the same side of the family
-
Having Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry
Recommended Reading: What Blood Test Can Detect Breast Cancer
Pregnancy Diagnosed During Or After Breast Cancer
Studies of pregnancy after a diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer are retrospective and most are case-controlled investigations. Although one study showed an increased risk for relapse, most other studies show either no difference in recurrence or a decrease in risk of recurrence. Breast cancer survivors and their medical caregivers are advised to fully discuss the risk of recurrence when discussing post-cancer reproductive choices.
Breast Cancer Vs Normal Development
Normal breast development can resemble breast cancer, and it is not possible to tell what is normal and what is not based on a comparison of symptoms.
Normal breast development, however, usually follows a pattern. It begins with nickel-sized lumps under each nipple, and the breasts gradually grow from these lumps.
Breast cancer, in general, is survivable with prompt treatment. This is particularly true of noninvasive breast cancers, and of breast cancers that have not spread to other areas of the body.
Treatments often include chemotherapy, radiation, medication, surgery, or a combination of these.
You May Like: How Fast Does Triple Negative Breast Cancer Grow
Detecting Breast Cancer In Younger Women
While theres no way to predict who will get breast cancer, some factors put women at higher risk at a younger age. Breast cancer risk is higher in women with a family history of breast or ovarian cancers at a young age or who have an Ashkenazi Jewish heritage. Having had radiation therapy in the chest is another important risk to know about.
There are some steps you can take, including discussing your family cancer history with your doctor and taking advantage of genetic testing for BRCA and other genetic mutations, if offered, based on your health and family history.
Through research, we are learning more about cancer, genetics, and risk factors, says Dr. Andrejeva-Wright. Young women should be aware of their family history and keep their doctors updated over time as it changes.
Also, while guidelines no longer call for monthly at-home breast exams, Dr. Andrejeva-Wright urges women of all ages to be breast aware. She advises women to do a breast self-exam at least quarterly and to learn all they can about their risk factors.
Breast awareness entails knowing your family history of breast and other cancers, says Dr. Andrejeva-Wright, It also means knowing any behavioral factors that may increase your risk of developing breast cancer, such as weight gain and alcohol consumption , and doing something about it.
What Are The Signs Of Breast Cancer
A woman who has breast cancer may have no problems, or she may find a painless lump in her breast. If women examine their breasts monthly, they can help find lumps or other changes that a doctor should examine.
Most breast lumps are not cancer, but all lumps should be checked out by a doctor to be sure. Breast lumps that are not cancer may be scar tissue or cysts or they can be due to normal breast changes associated with hormone changes or aging.
Girls who are beginning puberty might notice a lump underneath the nipple when their breasts start developing. Usually, this is a normal. You can ask a parent or your doctor about it to be sure.
P
Don’t Miss: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
How Is Hboc Identified
Mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes can be identified through a blood or saliva test. The usual method of testing, called standard gene sequencing, can find most BRCA mutations. There are other types of mutations called rearrangements, which include deletions or duplications in BRCA1 and BRCA2 that also may cause an increased risk for these cancers. Testing is also available for large rearrangements in BRCA1 and BRCA2.
After initial BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing, additional testing may be recommended if:
- The results were negative, meaning no genetic mutation was detected
- A variant of uncertain significance was detected, which means that there is a genetic change, but it is not known how that change could affect cancer risk
Talk with your health care team and/or a genetic counselor for more information.
Most, but not all, insurance providers, including Medicare and Medicaid, cover the cost of complete BRCA1 and BRCA2 testing. Many genetic specialists offer multigene panels, which may include 6, 20, 40, or more genes depending on your personal and family history. The multigene panel tests may often be done at the same time as BRCA1 and BRCA2 testing. Talk with your genetic counselor for more information on the type of testing you will have and your insurance coverage before testing begins.
Is Family History Of Breast Cancer Important
Yes. While only 5-10% of all women diagnosed with breast cancer have a family history, it is important to know your family’s history of cancer, if any, both on your mother’s side and your father’s side. Women with at least one close family relative should start a screening program with a breast specialist when they are ten years younger than their relative’s age at diagnosis, but usually not before 20 years old.
Recommended Reading: Hr Positive Her2 Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer
Benefits Of Mammographic Screening
The ACS systematic review also examined the effect of screening mammography on life expectancy. Although the review concluded that there was high-quality evidence that mammographic screening increases life expectancy by decreasing breast cancer mortality, the authors were not able to estimate the size of the increase 23.