The Grading System Is Used To Describe How Quickly A Breast Tumor Is Likely To Grow And Spread
The grading system describes a tumor based on how abnormal the cancer cells and tissue look under a microscope and how quickly the cancer cells are likely to grow and spread. Low-grade cancer cells look more like normal cells and tend to grow and spread more slowly than high-grade cancer cells. To describe how abnormal the cancer cells and tissue are, the pathologist will assess the following three features:
- How much of the tumor tissue has normal breast ducts.
- The size and shape of the nuclei in the tumor cells.
- How many dividing cells are present, which is a measure of how fast the tumor cells are growing and dividing.
For each feature, the pathologist assigns a score of 1 to 3 a score of 1 means the cells and tumor tissue look the most like normal cells and tissue, and a score of 3 means the cells and tissue look the most abnormal. The scores for each feature are added together to get a total score between 3 and 9.
Three grades are possible:
- Total score of 3 to 5: G1 .
- Total score of 6 to 7: G2 .
- Total score of 8 to 9: G3 .
The ‘look Good Feel Better’ Program
The American Cancer Society has teamed up with the Personal Care Products Council and the National Cosmetology Association to create “Look Good Feel Better.” This program teaches beauty techniques that can boost your appearance and how you feel about yourself after your cancer treatment.
For more information, call 800-395-LOOK, or go to the website.
Show Sources
Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can have a number of symptoms, but the first noticeable symptom is usually a lump or area of thickened breast tissue.
Most breast lumps aren’t cancerous, but it’s always best to have them checked by your doctor. You should also see your GP if you notice any of the following:
- a change in the size or shape of one or both breasts
- discharge from either of your nipples
- a lump or swelling in either of your armpits
- dimpling on the skin of your breasts
- a rash on or around your nipple
- a change in the appearance of your nipple, such as becoming sunken into your breast
Breast pain alone isn’t a symptom of breast cancer.
Learn more about the symptoms of breast cancer
After examining your breasts, your GP may refer you to a specialist breast cancer clinic for further tests. This might include a mammography or a biopsy.
Read more about breast screening and how breast cancer is diagnosed
Read Also: How Often Is Chemo Given For Breast Cancer
Ajcc Pathological Prognostic Stage Groups
The Pathological Prognostic Stage applies to patients with invasive breast cancer initially treated with surgery. It includes all information used for clinical staging, surgical findings, and pathological findings following surgery to remove the tumor. Pathological Prognostic Stage is not used for patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy before surgery to remove the tumor.
References
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options

The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
- The stage of the cancer .
- The type of breast cancer.
- Estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor levels in the tumor tissue.
- Human epidermal growth factor type 2 receptor levels in the tumor tissue.
- Whether the tumor tissue is triple negative .
- How fast the tumor is growing.
- How likely the tumor is to recur .
- A womans age, general health, and menopausal status .
- Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has recurred .
Don’t Miss: Stage Iii Cancer
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Whether you are thinking about treatment, getting treatment, or not being treated at all, you can still get supportive care to help with pain or other symptoms. Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help.
The American Cancer Society also has programs and services including rides to treatment, lodging, and more to help you get through treatment. Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists.
How Does Trastuzumab Deruxtecan Work
Trastuzumab attaches to the HER2 proteins, and can stop the cancer cells growing, the website breastcancernow.org explained. It also helps the bodys immune system destroy cancer cells. When the trastuzumab attaches to the cancer proteins, it delivers deruxtecan directly into the breast cancer cells to kill them.
Also Check: Mayo Clinic Breast Cancer Stages
Can Other Drugs Interfere With Hormone Therapy
Certain drugs, including several commonly prescribed antidepressants , inhibit an enzyme called CYP2D6. This enzyme plays a critical role in the body’s use of tamoxifen because CYP2D6 metabolizes, or breaks down, tamoxifen into molecules, or metabolites, that are much more active than tamoxifen itself.
The possibility that SSRIs might, by inhibiting CYP2D6, slow the metabolism of tamoxifen and reduce its effectiveness is a concern given that as many as one-fourth of breast cancer patients experience clinical depression and may be treated with SSRIs. In addition, SSRIs are sometimes used to treat hot flashes caused by hormone therapy.
Many experts suggest that patients who are taking antidepressants along with tamoxifen should discuss treatment options with their doctors, such as switching from an SSRI that is a potent inhibitor of CYP2D6, such as paroxetine hydrochloride , to one that is a weaker inhibitor, such as sertraline or citalopram , or to an antidepressant that does not inhibit CYP2D6, such as venlafaxine . Or doctors may suggest that their postmenopausal patients take an aromatase inhibitor instead of tamoxifen.
Other medications that inhibit CYP2D6 include the following:
- Quinidine, which is used to treat abnormal heart rhythms
How Can I Protect Myself From Breast Cancer
Follow these three steps for early detection:
- Get a mammogram. The American Cancer Society recommends having a baseline mammogram at age 35, and a screening mammogram every year after age 40. Mammograms are an important part of your health history. Recently, the US Preventive Services Task Force came out with new recommendations regarding when and how often one should have mammograms. These include starting at age 50 and having them every two years. We do not agree with this, but we are in agreement with the American Cancer Society and have not changed our guidelines, which recommend yearly mammograms starting at age 40.
- Examine your breasts each month after age 20. You will become familiar with the contours and feel of your breasts and will be more alert to changes.
- Have your breast examined by a healthcare provider at least once every three years after age 20, and every year after age 40. Clinical breast exams can detect lumps that may not be detected by mammogram.
Recommended Reading: Anne Hathaway Boob Size
What Is The Prognosis After Recurrence
Many patients with a recurrence of breast cancer can be successfully treated, often with methods other than radiation if radiation was used in the initial treatment. For patients treated initially for invasive breast cancer, five percent to 10 percent will be found to have distant metastases at the time of discovery of the breast recurrence. The same proportion will have recurrences that are too extensive to be operated on. While in these cases the patient’s disease can often be managed over a period of years, the goals of treatment change from obtaining a cure to preventing further progression or managing symptoms. Five-year cure rates for patients with relapse after breast conservation therapy are approximately 60 percent to 75 percent if the relapse is confined to the breast and a mastectomy is then performed.
For patients treated initially for DCIS, about one-half of recurrences are invasive and one-half noninvasive DCIS. Long-term control rates following recurrence after initial breast conservation therapy have been high, often over 90 percent.
Who Gets Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women other than skin cancer. Increasing age is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer, with 66% of breast cancer patients being diagnosed after the age of 55.
In the US, breast cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death in women after lung cancer, and it’s the leading cause of cancer death among women ages 35 to 54. Only 5 to 10% of breast cancers occur in women with a clearly defined genetic predisposition for the disease. The majority of breast cancer cases are “sporadic, meaning there is no definitive gene mutation.
Also Check: Her2 Breast Cancer Symptoms
Breast Cancer Is Sometimes Caused By Inherited Gene Mutations
The genes in cells carry the hereditary information that is received from a persons parents. Hereditary breast cancer makes up about 5% to 10% of all breast cancer. Some mutated genes related to breast cancer are more common in certain ethnic groups.
Women who have certain gene mutations, such as a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, have an increased risk of breast cancer. These women also have an increased risk of ovarian cancer, and may have an increased risk of other cancers. Men who have a mutated gene related to breast cancer also have an increased risk of breast cancer. For more information, see the PDQ summary onMale Breast Cancer Treatment.
There are tests that can detect mutated genes. Thesegenetic tests are sometimes done for members of families with a high risk of cancer. See the PDQ summary on Genetics of Breast and Gynecologic Cancers for more information.
Treatment Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
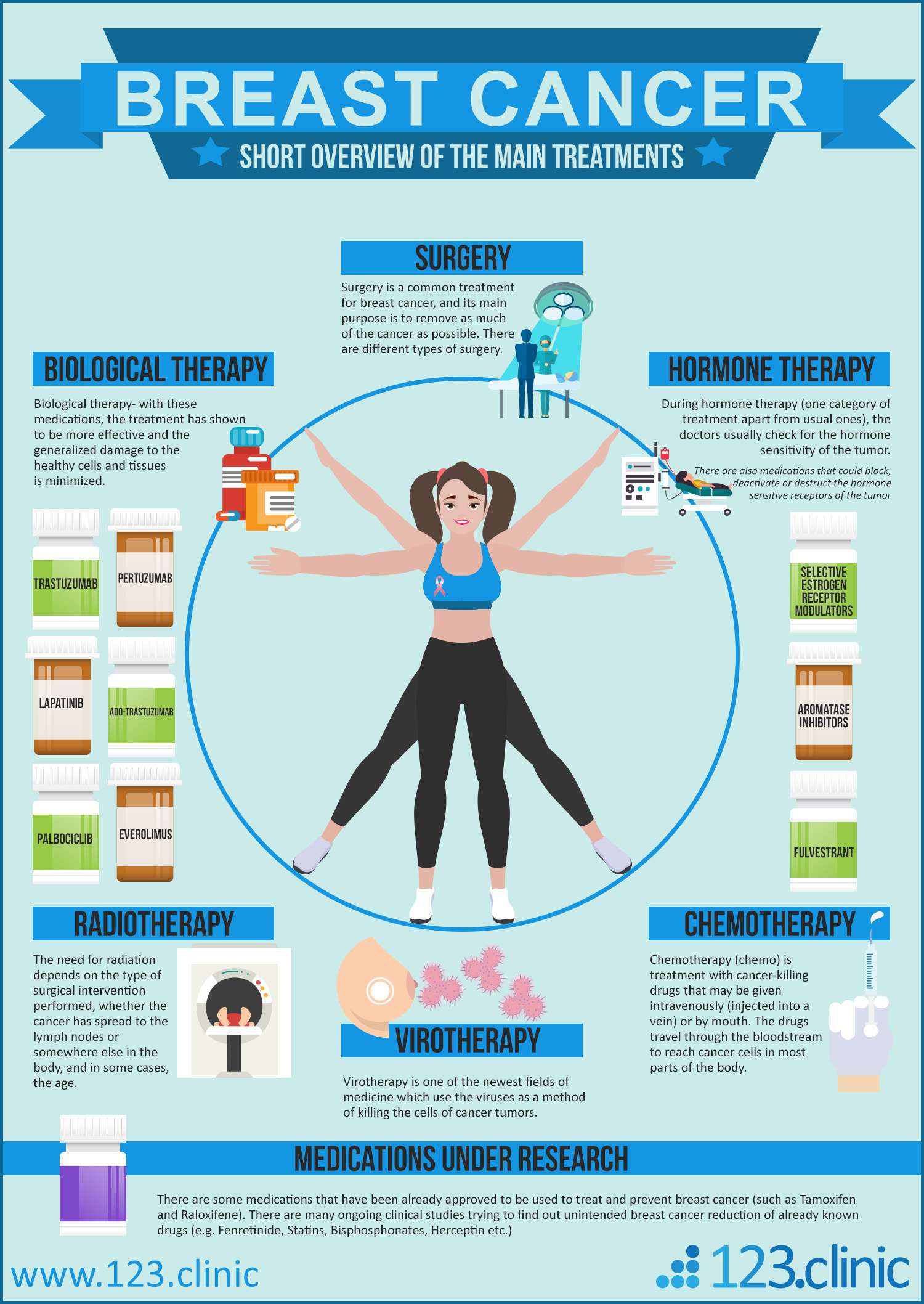
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment options for metastaticbreast cancer may include the following:
Hormone therapy
In postmenopausal women who have just been diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer that is hormone receptor positive or if the hormone receptor status is not known, treatment may include:
- A clinical trial of high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant.
- Clinical trials testing new anticancer drugs, new drug combinations, and new ways of giving treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Don’t Miss: Stage Iii A Cancer
Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Stage 4 means the breast cancer has spread to other organs or areas of the body, such as the brain, bones, lung and/or liver. In these cases, your team may recommend a systemic therapy such as hormone therapy or chemotherapy, or targeted drugs such as those that block HER2, immunotherapy or some combination of all these options.
Your treatment plan may also include surgery and/or radiation. While this diagnosis may be scary, its important to know that your cancer care team has more tools to treat stage 4 breast cancer than ever before. Make sure to discuss all the options with your doctor.
Does A Benign Breast Condition Mean That I Have A Higher Risk Of Getting Breast Cancer
Benign breast conditions rarely increase your risk of breast cancer. Some women have biopsies that show a condition called hyperplasia . This condition increases your risk only slightly.
When the biopsy shows hyperplasia and abnormal cells, which is a condition called atypical hyperplasia, your risk of breast cancer increases somewhat more. Atypical hyperplasia occurs in about 5% of benign breast biopsies.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Stage 3 Symptoms
Side Effects And Complications
All treatments have some side effects that range from mild to severe. Most clear up when treatment ends, but there can be some lasting complications.
Its important to tell your oncologist about all symptoms, even if they seem minor. Your healthcare team will work with you to ease side effects and deal with complications.
What Are The Cosmetic Results Of Breast Conservation Therapy
Eighty percent to 90 percent of women treated with modern surgery and radiotherapy techniques have excellent or good cosmetic results that is, little or no change in the treated breast in size, shape, texture or appearance compared with what it was like before treatment.
Patients with large breasts seem to have greater shrinkage of the breast after radiation therapy than do patients with smaller breasts. However, this problem usually can be overcome with the use of higher x-ray energies or with IMRT. Partial breast radiation using brachytherapy can also be considered if the patient has a small early-stage tumor. This treatment is still undergoing clinical investigation. Certain single institution studies on brachytherapy and intraoperative radiation have shown some promising results. You would need to discuss this with your doctor before or shortly after surgery to determine if you qualify for partial breast radiation.
Recommended Reading: Hormone Therapy For Breast Cancer Stage 4
Stage 0 Breast Cancer
Stage 0 is the lowest-risk breast cancer stage. In this stage, breast cancer is detected before it spreads from the milk duct. Ductal carcinoma in situ is an example of stage 0 breast cancer.
Treatment may include surgery to remove the breast cancer, possibly followed by radiation or hormonal therapy if the cancer is hormone receptor-positive. Hormonal therapy may include tamoxifen or a type of drug known as an aromatase inhibitor, which is taken for five years after surgery to lower the risk of the breast cancer recurring.
The surgeon may remove just the tumor, via breast conservation surgery, or the entire breast, if the cancer is large or has been detected in several spots in the milk ducts.
Ajcc Anatomic And Prognostic Stage Groups
There are three stage group tables for invasive cancer:
- Anatomic Stage Group. The Anatomic Stage Group table is used in regions of the world where tumor grading and/or biomarker testing for ER, PR, and HER2 are not routinely available.
- Clinical Prognostic Stage Group. The Clinical Prognostic Stage Group table is used for all patients in the United States. Patients who have neoadjuvant therapy as their initial treatment should have the clinical prognostic stage and the observed degree of response to treatment recorded, but these patients are not assigned a pathological prognostic stage.
- Pathological Prognostic Stage Group. The Pathological Prognostic Stage Group table is used for all patients in the United States who have surgery as initial treatment and have pathological T and N information reported.
In the United States, cancer registries and clinicians must use the Clinical and Pathological Prognostic Stage Group tables for reporting. It is expected that testing is performed for grade, HER2, ER, and PR status and that results are reported for all cases of invasive cancer in the United States.
AJCC Anatomic Stage Groups
AJCC Prognostic Stage Groups
The Clinical Prognostic Stage is used for clinical classification and staging of patients in the United States with invasive breast cancer. It uses TNM information based on the patients history, physical examination, imaging results , and biopsies.
You May Like: Estrogen Induced Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Breast
The breast is made up of lobes and ducts. Each breast has 15 to 20 sections called lobes. Each lobe has many smaller sections called lobules. Lobules end in dozens of tiny bulbs that can make milk. The lobes, lobules, and bulbs are linked by thin tubes called ducts.
Each breast also has blood vessels and lymph vessels. The lymph vessels carry an almost colorless, watery fluid called lymph. Lymph vessels carry lymph between lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures found throughout the body. They filter lymph and store white blood cells that help fightinfection and disease. Groups of lymph nodes are found near the breast in theaxilla , above thecollarbone, and in the chest.
The most common type of breast cancer is ductal carcinoma, which begins in the cells of the ducts. Cancer that begins in the lobes or lobules is called lobular carcinoma and is more often found in both breasts than are other types of breast cancer. Inflammatory breast cancer is an uncommon type of breast cancer in which the breast is warm, red, and swollen.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information about breast cancer: