Treating Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the tumor is large or growing into nearby tissues , or the cancer has spread to many nearby lymph nodes.
If you have inflammatory breast cancer: Stage III cancers also include some inflammatory breast cancers that have not spread beyond nearby lymph nodes. Treatment of these cancers can be slightly different from the treatment of other stage III breast cancers. You can find more details in our section about treatment for inflammatory breast cancer.
There are two main approaches to treating stage III breast cancer:
Treatments For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
The following are treatment options for ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma. Doctors consider stage 2A to be early stage breast cancer. Stage 2B is considered to be locally advanced breast cancer. Your healthcare team will suggest treatments based on your needs and work with you to develop a treatment plan.
M Categories For Breast Cancer
M followed by a 0 or 1 indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs for example, the lungs, liver, or bones.
M0: No distant spread is found on x-rays or by physical exam.
cM0: Small numbers of cancer cells are found in blood or bone marrow , or tiny areas of cancer spread are found in lymph nodes away from the underarm, collarbone, or internal mammary areas.
M1: Cancer has spread to distant organs .
Dont Miss: Does Breast Cancer Go Away
Read Also: How Many People Are Diagnosed With Breast Cancer Per Year
The Number Staging System
Breast cancer can also be divided into four number stages. We have put these into a table to make them easier to understand. You can .
This information is about stage 1 to 3 breast cancer.
Stage 1 breast cancer is when the cancer is 2cm or smaller. There may be no cancer cells in the lymph nodes in the armpit or tiny numbers of cancer cells are found. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast, but cancer cells have spread to lymph nodes in the armpit.
Stage 2 breast cancer is when the cancer is up to or bigger than 5cm. It may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes under the arm. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast. But cancer cells have spread to 1 to 3 lymph nodes in the armpit or near the breast bone.
Stage 3 breast cancer is sometimes called locally advanced breast cancer. The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit and sometimes to other lymph nodes nearby. It may have spread to the skin of the breast or to the chest muscle. The skin may be red, swollen or have broken down. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast or is small but has spread to 4 to 9 lymph nodes in the armpit.
Stage 4 breast cancer is also called secondary or metastatic breast cancer. This is when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones, the liver or lungs. We have separate information about secondary breast cancer.
Treatments For Breast Cancer

If you have breast cancer, your healthcare team will create a treatment plan just for you. It will be based on your health and specific information about the cancer. When deciding which treatments to offer for ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma, your healthcare team will consider:
- the stage
- if you have reached menopause
- the hormone receptor status of the cancer
- the HER2 status of the cancer
- the risk that the cancer will come back, or recur
- your overall health
Read Also: What Age Could You Get Breast Cancer
Talk To Your Doctor To Find Out What Your Breast Cancer Stage Is And How It Is Used To Plan The Best Treatment For You
After surgery, your doctor will receive a that describes the size and location of the primary tumor, the spread of cancer to nearby lymph nodes, tumor grade, and whether certain biomarkers are present. The pathology report and other test results are used to determine your breast cancer stage.
You are likely to have many questions. Ask your doctor to explain how staging is used to decide the best options to treat your cancer and whether there are that might be right for you.
The treatment of breast cancer depends partly on the stage of the disease.
How Much Do Tamoxifen And Raloxifene Lower The Risk Of Breast Cancer
Multiple studies have shown that both tamoxifen and raloxifene can reduce the risk of developing estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in healthy postmenopausal women who are at high risk of developing the disease. Tamoxifen lowered the risk by 50 percent. Raloxifene lowered the risk by 38 percent. Overall, the combined results of these studies showed that taking tamoxifen or raloxifene daily for five years reduced the risk of developing breast cancer by at least one-third. In one trial directly comparing tamoxifen with raloxifene, raloxifene was found to be slightly less effective than tamoxifen for preventing breast cancer.
Both tamoxifen and raloxifene have been approved for use to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in women at high risk of the disease. Tamoxifen is approved for use in both premenopausal women and postmenopausal women . Raloxifene is approved for use only in postmenopausal women.
Less common but more serious side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include blood clots to the lungs or legs. Other serious side effects of tamoxifen are an increased risk for cataracts and endometrial cancers. Other common, less serious shared side effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene include hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.
You May Like: How Many People Survive Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cellsform In The Tissues Of The Breast
The is made up of and . Each breast has 15 to 20 sections calledlobes. Each lobe has many smaller sections called . Lobules end in dozens of tiny bulbs thatcan make milk. The lobes, lobules, and bulbs are linked by thin tubes calledducts.
Anatomy of the female breast. The nipple and areola are shown on the outside of the breast. The lymph nodes, lobes, lobules, ducts, and other parts of the inside of the breast are also shown.
Each breast also has and . The lymph vessels carry an almost colorless, watery called . Lymphvessels carry lymph between . Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures found throughout the body. They lymph and store that help fight and disease. Groups of lymph nodes are found near the breast in the , above the, and in the chest.
The most common type of is , which begins in the of the ducts. that begins in thelobes or lobules is called and is more often found in bothbreasts than are other types of breast cancer. is an uncommon type ofbreast cancer in which the breast is warm, red, and swollen.
See the following summaries for more information about breast cancer:
Can Exercise Help Reduce My Risk Of Developing Breast Cancer
Exercise is a big part of a healthy lifestyle. It can also be a useful way to reduce your risk of developing breast cancer in your postmenopausal years. Women often gain weight and body fat during menopause. People with higher amounts of body fat can be at a higher risk of breast cancer. However, by reducing your body fat through exercise, you may be able to lower your risk of developing breast cancer.
The general recommendation for regular exercise is about 150 minutes each week. This would mean that you work out for about 30 minutes, five days each week. However, doubling the amount of weekly exercise to 300 minutes can greatly benefit postmenopausal women. The longer duration of exercise allows for you to burn more fat and improve your heart and lung function.
The type of exercise you do can vary the main goal is get your heart rate up as you exercise. Its recommended that your heart rate is raised about 65 to 75% of your maximum heart rate during exercise. You can figure out your maximum heart rate by subtracting your current age from 220. If you are 65, for example, your maximum heart rate is 155.
Aerobic exercise is a great way to improve your heart and lung function, as well as burn fat. Some aerobic exercises you can try include:
- Walking.
- Dancing.
- Hiking.
Remember, there are many benefits to working more exercise into your weekly routine. Some benefits of aerobic exercise can include:
You May Like: What To Say To Breast Cancer Patient
Tucatinib Neratinib And Lapatinib
The tyrosine-kinase inhibitors FDA-approved for metastatic breast cancer treatment are:
- Tucatinib
- Neratinib
- Lapatinib
Tyrosine-kinase inhibitors are a class of drugs that target enzymes important for cell functions . These drugs can block tyrosine-kinase enzymes at many points along the cancer growth pathway.
A tyrosine-kinase inhibitor in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy can be used to treat HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. This combination may give women with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer more time before the cancer spreads compared to treatment with trastuzumab and chemotherapy alone .
Adding the tyrosine-kinase inhibitor tucatinib to treatment with trastuzumab and chemotherapy may also increase overall survival in women with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer who were treated with trastuzumab in the past .
Neratinib is also used to treat HER2-positive early breast cancer.
Tucatinib, neratinib and lapatinib are pills.
Learn about neratinib and treatment of early breast cancer.
Tucatinib, neratinib and lapatinib and brain metastases
Many drug therapies cannot pass through the blood to the brain . So, they cant treat breast cancer that has spread to the brain.
However, tucatinib, neratinib and lapatinib can pass through the blood-brain barrier and may be used to treat some metastatic breast cancers that have spread to the brain.
How The Breast Cancer Staging Process Starts
The breast cancer staging process begins with diagnostic testing. Depending on previous screening results, if any breast cancer symptoms are present, and other factors, your doctor may recommend one of the following tests:
- Diagnostic mammogram A mammogram involves using an X-ray to take photos of your breast tissue at different angles. To do this, your breasts are gently compressed between two plates so the X-ray can be taken.
- Ultrasound An ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that bounces soundwaves of your breast tissue to create a picture of the inside of your breast.
- MRI An MRI is another non-invasive imaging test that uses radio waves and a magnetic field to create an image of your breast tissue. This can help doctors determine the size and placement of tumors.
- Biopsy A biopsy removes small masses and growths from your breast so they can be examined under a microscope by a pathologist and determine if theyre cancerous.
If cancer is detected, a CT scan may be ordered to look for any distant metastasis or local invasion to other organs. And youll likely be connected with a breast surgeon right away, either through a nurse navigator or your doctor.
Don’t Miss: Is Breast Cancer Internal Cancer
What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
The most common types of breast cancer are:
- Infiltrating ductal carcinoma. This cancer starts in the milk ducts of the breast. It then breaks through the wall of the duct and invades the surrounding tissue in the breast. This is the most common form of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of cases.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ is ductal carcinoma in its earliest stage, or precancerous . In situ refers to the fact that the cancer hasn’t spread beyond its point of origin. In this case, the disease is confined to the milk ducts and has not invaded nearby breast tissue. If untreated, ductal carcinoma in situ may become invasive cancer. It is almost always curable.
- Infiltrating lobular carcinoma. This cancer begins in the lobules of the breast where breast milk is produced, but has spread to surrounding tissues in the breast. It accounts for 10 to 15% of breast cancers. This cancer can be more difficult to diagnose with mammograms.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ is a marker for cancer that is only in the lobules of the breast. It isn’t a true cancer, but serves as a marker for the increased risk of developing breast cancer later, possibly in both or either breasts. Thus, it is important for women with lobular carcinoma in situ to have regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
Does A Benign Breast Condition Mean That I Have A Higher Risk Of Getting Breast Cancer
Benign breast conditions rarely increase your risk of breast cancer. Some women have biopsies that show a condition called hyperplasia . This condition increases your risk only slightly.
When the biopsy shows hyperplasia and abnormal cells, which is a condition called atypical hyperplasia, your risk of breast cancer increases somewhat more. Atypical hyperplasia occurs in about 5% of benign breast biopsies.
Also Check: What Are The Common Signs Of Breast Cancer
The Tnm Staging System
The TNM staging system gives the complete stage of the cancer:
- T describes the size of the tumour.
- N describes whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes;and which nodes are involved. For example, N0 means no lymph nodes are affected. N1 means there are cancer cells in 1 to 3 of the lymph nodes.
- M describes whether the cancer has spread to another part of the body. For example, M0 means the cancer has not spread to other parts of the body.
Sometimes the final TNM staging may not be certain until after surgery to remove the cancer.
Treatment Of Breast Cancer Stages I
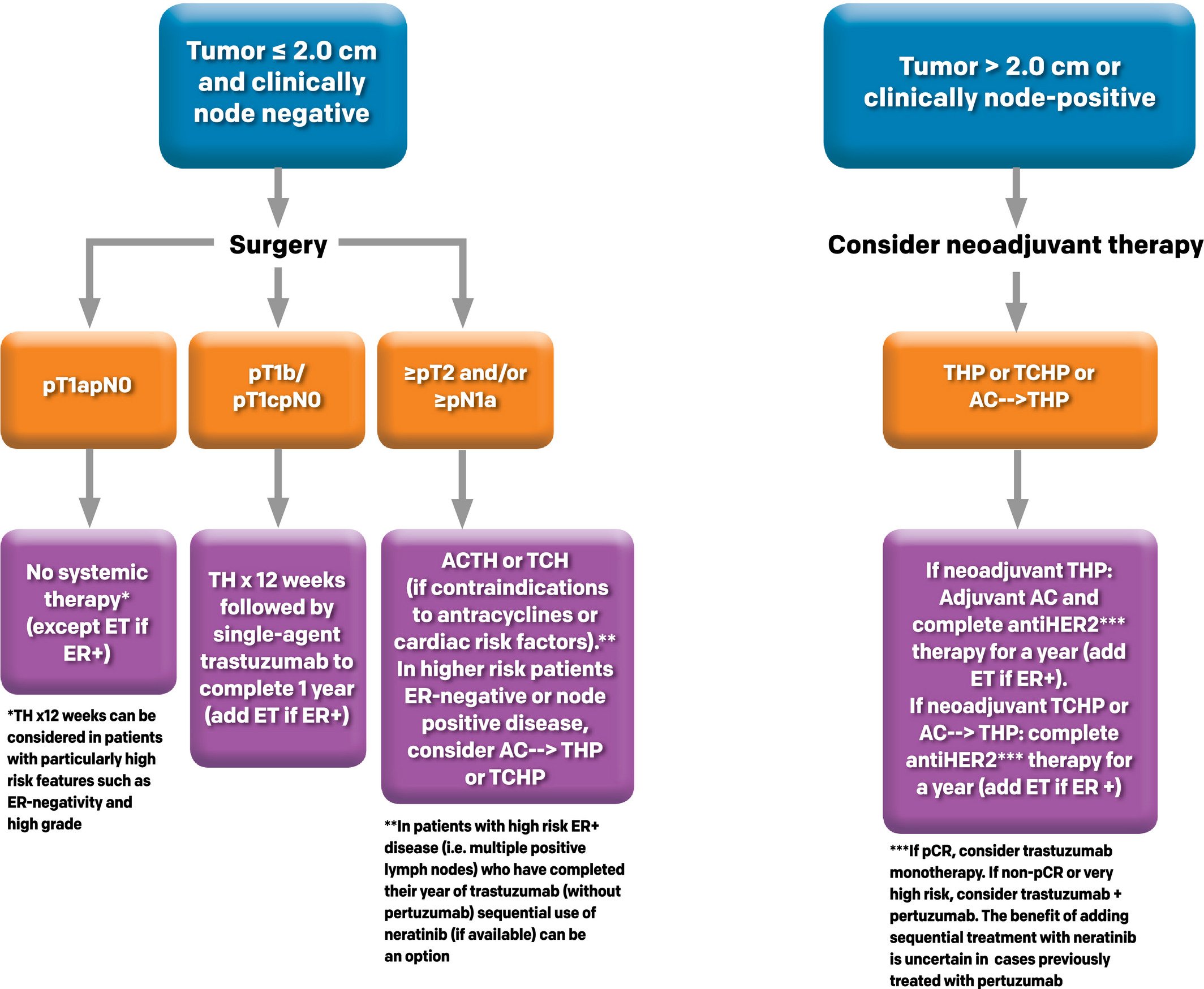
The stage of your breast cancer is an important factor in making decisions about your treatment.;
Most women with breast cancer in stages I, II, or III are treated with surgery, often followed by radiation therapy. Many women also get some kind of drug therapy. In general, the more the breast cancer has spread, the more treatment you will likely need.;But your treatment options are affected by your personal preferences and other information about your breast cancer, such as:
- If the cancer cells contain hormone receptors. That is, if the cancer is estrogen receptor -positive or progesterone receptor -positive.
- If the cancer cells have large amounts of the HER2 protein
- How fast the cancer is growing
- Your overall health
- If you have gone through menopause or not
Talk with your doctor about how these factors can affect your treatment options.
Don’t Miss: What Happens When Breast Cancer Spreads
Six Types Of Standard Treatment Are Used:
Surgery
Most patients with breast cancer have to remove the cancer.
is the removal of the during surgery. The sentinel lymph node is the first in a group of lymph nodes to receive from the . It is the first lymph node the cancer is likely to spread to from the primary tumor. A substance and/or blue is near the . The substance or dye flows through the lymph to the lymph nodes. The first lymph node to receive the substance or dye is removed. A views the under a to look for cancer . If cancer cells are not found, it may not be necessary to remove more lymph nodes. Sometimes, a sentinel lymph node is found in more than one group of nodes. After the sentinel lymph node biopsy, the removes the tumor using or . If cancer cells were found, more lymph nodes will be removed through a separate . This is called a .
Types of surgery include the following:
may be given before surgery to remove the tumor. When given before surgery, chemotherapy will shrink the tumor and reduce the amount of tissue that needs to be removed during surgery. Treatment given before surgery is called preoperative therapy or .
After the doctor removes all the cancer that can be seen atthe time of the surgery, some patients may be given ,chemotherapy, , or after surgery, to kill any cancer cells that are left. Treatment given after the surgery, tolower the risk that the cancer will come back, is called or .
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
Treatment For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
The most common type of treatment for stage 2 breast cancer is surgery.
Surgery
In most cases, treatment involves removing the cancer.
A person with stage 2A or 2B breast cancer may undergo a lumpectomy or mastectomy. The doctors and the individual can decide based on the size and location of the tumor.
Combination therapy
A doctor may recommend a combination of radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy to people with stage 2A or 2B breast cancer.
The subcategories for stage 3 breast cancer are 3A, 3B, and 3C.
3A breast cancer is an invasive breast cancer where:
- There is no tumor in the breast, or a tumor of any size is growing alongside cancer found in four to nine axillary lymph nodes or the lymph nodes by the breastbone.
- A person has a tumor greater than 5 cm, as well as clusters of breast cancer cells in the lymph nodes that are between 0.22 mm in diameter.
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm, and cancer has also spread to one to three axillary lymph nodes or the lymph nodes near the breastbone.
Stage 3B breast cancer is invasive breast cancer where:
- A tumor of any size has spread into the chest wall or skin of the breast, causing swelling or an ulcer to develop. It could also have spread to up to nine axillary lymph nodes or may have spread to lymph nodes by the breastbone.
If cancer spreads to the skin of the breast, a person may have inflammatory cancer.
Symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer include:
Stage 3C breast cancer is an invasive breast cancer where:
Don’t Miss: Can Breast Cancer Develop In One Year
The Grading System Is Used To Describe How Quickly A Breast Tumor Is Likely To Grow And Spread
The system describes a tumor based on how abnormal the cancer cells and tissue look under a microscope and how quickly the cancer cells are likely to grow and spread. cancer cells look more like normal cells and tend to grow and spread more slowly than cancer cells. To describe how abnormal the cancer cells and tissue are, the pathologist will assess the following three features:
- How much of the tumor tissue has normal breast ducts.
- The size and shape of the in the tumor cells.
- How many dividing cells are present, which is a measure of how fast the tumor cells are growing and dividing.
For each feature, the pathologist assigns a score of 1 to 3; a score of 1 means the cells and tumor tissue look the most like normal cells and tissue, and a score of 3 means the cells and tissue look the most abnormal. The scores for each feature are added together to get a total score between 3 and 9.
Three grades are possible:
- Total score of 3 to 5: G1 .
- Total score of 6 to 7: G2 .
- Total score of 8 to 9: G3 .