What Are The Chances Of Breast Cancer Recurring
Despite huge advancements in breast cancer screening, early detection and treatment, a percentage of breast cancers will recur and spread to distant sites.
Although at the moment, it is almost impossible to say which cancers will recur and at what time period from diagnosis, there are a few factors that are known to increase the risk for recurrence.
These risk factors include:-
- Lymph node involvement and number of lymph nodes affected at the time of diagnosis
- Tumor Size at the time of diagnosis
- A subtype of Breast Cancer and hormonal receptor Status
- The time span from the initial diagnosis to recurrence of breast cancer
Metastatic Breast Cancer Statistics
1 in 8 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer in the US and 1 in 3 of those will become metastatic. African American women are 40% more likely to die from breast cancer than Caucasian women.
Men get breast cancer too. All people, male and female, are born with some breast cells and tissue. Even though males do not develop milk-producing breasts, a mans breast cells and tissue can still develop cancer. Male breast cancer is rare. Less than one percent of all breast cancer cases develop in men, and only one in a thousand men will be diagnosed with breast cancer and only about 2% will metastasize.
In 2019, its estimated that among U.S. women and men there will be 268,600 new cases of advanced breast cancer and 41,760 breast cancer deaths. Of those deaths, it is estimated that 97-99% of those will be from metastatic breast cancer. Men get breast cancer too. It is estimated that there will be 2670 new male breast cancer diagnosis in 2019 and 500 of those will die due to metastatic breast cancer.
Immunogenic Potential Of Tnbc
The tumour microenvironment plays an important role in defining the interaction of our immune system with tumours. In TNBC, the TME is characterized by higher levels of vascular endothelial like growth factor , tumour infiltrating lymphocytes and tumour associated macrophages in contrast to other types of breast cancer. Additionally, there is a high level of expression of TILs in patients with TNBC. These have been shown to be a useful prognostic indicator across malignancies. TNBC has been shown to have consistently elevated TILs in contrast to other subtypes and TILs have been shown to be associated with improved survival. Ibrahim et al found that patients with lymphocyte-predominant breast cancer had a 40% pathological complete response rate compared to 7% of those patients without. High TILS are more frequent in TNBC compared to HER2-positive and luminal tumours and are associated with improved disease free survival and OS in early stage breast cancer. This is consistent with findings in other malignancies demonstrating the important role of the immune system in cancer biology and prognostication. All of these features demonstrate that the TME of TNBC is highly immunogenic.
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Early Stage Clinical Trials
In a proof of concept study published in the Lancet, authors investigated olaparib in patients with advanced metastatic breast cancer with germline BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations. They investigated two doses of olaparib at 400 mg BD and 100 mg BD. Approximately half of patients in this study had TNBC with the remainder having other histological subtypes. Patients were heavily pretreated with a median of 3 prior chemotherapy regimens and platinum sensitivity was not needed for trial enrolment. Overall response rates were impressive in this heavily pre-treated population at 41% in the group receiving the higher dose and 22% in the group receiving the lower dose.
Kaufman et al investigated olaparib further in a large phase 2 basket trial with 298 patients in a single-arm study. Patients with any advanced solid-organ malignancy were included if they harboured a gBRCA mutation. In the breast cohort, patients may have received multiple lines of treatment and there was no requirement for platinum sensitivity. Response rates were modest with only 8 of 62 patients responding in this unselected population.
Cryoablation For Metastatic Breast Cancer

Cryoablation may be an option to treat small, isolated metastatic breast cancer tumors in women who arent good candidates for surgery. Guided by imaging , cryoablation inserts a special freezing probe through the skin and to the tumor to be treated. Once the tip of the probe is in the right spot inside the tumor core, pressurized argon gas is injected through the probe into the tumor, freezing and destroying the cancerous tissue. Cryoablation techniques may vary from one cancer treatment facility to another. Cryoablation is more common in cases where the breast cancer is being well-controlled by systemic treatments such as chemotherapy and hormonal therapy.
Donât Miss: What Age Should You Get Checked For Breast Cancer
Don’t Miss: Estrace Breast Cancer
Is Tumour Dormancy The Sole Explanation For Recurrence
In pondering the mechanisms of metastatic relapse among breast cancer patients, one obvious question is whether early recurrence is simply the consequence of direct metastatic outgrowth, whereas late relapses reflect a period of tumour dormancy. To address this query, it is imperative to consider how long it takes for a single cancer cell to grow into a clinically detectable metastasis. Pioneering measurements of breast tumour volume doubling time carried out by radiographic analysis on more than 800 women concluded that it takes ~12 years on average for a single cell with a 10-µm diameter to reach a clinically detectable mass of 1cm,, and that metastases can have a TVDT up to twofold higher than their matched primary tumours. However, these initial analyses focused on a small number of samples, without taking into account the vast heterogeneity among breast tumours or the effect that adjuvant therapies might have on their growth rate, as the subjects in this study were untreated.
Fig. 3: The puzzling timing of metastatic relapse in breast cancer patients.
How Can I Take Care Of Myself While Living With Metastatic Breast Cancer
Living with metastatic breast cancer can be challenging. Your care team can help provide physical and emotional support. Talk to them about how you can:
- Eat the most nutritious diet for your needs.
- Exercise regularly.
- Get emotional support, including finding support groups.
- Reach out for help from friends, family and loved ones.
- Find mental health services.
- Find complementary therapies.
You May Like: Estrogen Dominant Breast Cancer
In Situ Breast Carcinoma Incidence
- There are around 8,300 new breast carcinoma in situ cases in the UK every year, that’s 23 every day .
- In females in the UK, breast carcinoma in situ accounted for around 8,300 new cancer cases every year .
- In males in the UK, breast carcinoma in situ accounted for around 30 new cancer cases every year in 2016-2018.
- Incidence rates for breast carcinoma in situ in the UK are highest in people aged 65 to 69 .
- Each year around a tenth of all new breast carcinoma in situ cases in the UK are diagnosed in people aged 75 and over .
- Since the early 1990s, breast carcinoma in situ incidence rates have tripled in the UK. Rates in females have around tripled , and rates in males have around doubled .
- Over the last decade, breast carcinoma in situ incidence rates have increased by almost a third in the UK. Rates in females have increased by around a third , and rates in males have remained stable .
- Most in situ breast carcinomas are intraductal.
- In situ breast carcinoma is more common in White females than in Asian or Black females.
- Breast carcinoma in situ incidence rates in England in females are 28% lower in the most deprived quintile compared with the least, and in males are similar in the most deprived quintile compared with the least .
- Around 910 cases of breast carcinoma in situ each year in England in females are linked with lower deprivation.
- An estimated 63,800 women who had previously been diagnosed with in situ breast carcinoma were alive in the UK at the end of 2010.
What Is Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer is not a specific type of breast cancer. Its the most advanced stage of breast cancer.
Metastatic breast cancer is breast cancer that has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes to other parts of the body .
Although metastatic breast cancer has spread to another part of the body, its still breast cancer and treated as breast cancer.
For example, breast cancer that has spread to the bones is still breast cancer . So, its treated with breast cancer drugs, rather than treatments for a cancer that began in the bones.
Learn what Komen is doing to help people with metastatic breast cancer.
Also Check: Stage 3 Lymph Nodes Cancer
Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment And Planning
After a diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer, its helpful to take all the time you need to gather information and make decisions about your treatment. Learn about the medical specialists that may be involved in your care, treatment options, genetic testing, taking a break from treatment, and more.
SurgeryDoctors sometimes recommend surgery for metastatic breast cancer in order, for example, to prevent broken bones or cancer cell blockages in the liver. Learn more.
ChemotherapyChemotherapy is used in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer to damage or destroy the cancer cells as much as possible. Learn more.
Radiation TherapyYour doctor may suggest radiation therapy if youre having symptoms for reasons such as easing pain and controlling the cancer in a specific area. Learn more.
Hormonal TherapyHormonal therapy medicines are used to help shrink or slow the growth of hormone-receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Learn more.
Targeted TherapyTargeted therapies target specific characteristics of cancer cells, such as a protein that allows the cancer cells to grow in a rapid or abnormal way. Learn more.
Local Treatments for Distant Areas of MetastasisLocal treatments are directed specifically to the new locations of the breast cancer such as the bones or liver. These treatments may be recommended if, for example, the metastatic breast cancer is causing pain. Learn more.
Are New Treatments For Metastatic Cancer Being Developed
Yes. Researchers are now studying new ways to kill or stop the growth of primary cancer cells and metastatic cancer cells. One new area of research includes ways to boost the strength of the immune response against tumors.
Regulatory T-cells and RANKL proteins may play a role in breast cancer metastasisRecent breast cancer research suggests that the bodys regulatory T cells, which are an integral part of the immune response system, may play a key role in metastasis.
It is speculated that the T cells produce a protein which seems to accelerate the spread of breast cancer cells to other areas of the body. The inflammatory protein RANKL seems to influence the T-cells ability to spread cancer cells to distant areas of the body.
It is believed that by interfering with RANKLs ability to interact with the T-cells, the early metastasis of breast cancer cells can be significantly inhibited
You May Like: Mayo Clinic Breast Cancer Symptoms
How Do Breast Cancer Cells Spread Around The Body
Breast cancer cells travel through the body like any other cancer cells. Firstly, cancer cells can invade neighbouring healthy tissue. Following this, the cancer cells then invade local lymph nodes or blood vessels.
When breast cancer spreads to the axillary lymph nodes this is still a relatively early stage of metastasis, and potentially curable.
The cancer cells will typically travel through the lymphatic system or blood vessels to other distant parts of the body.
The Extrinsic Effect Of Targeted Therapy
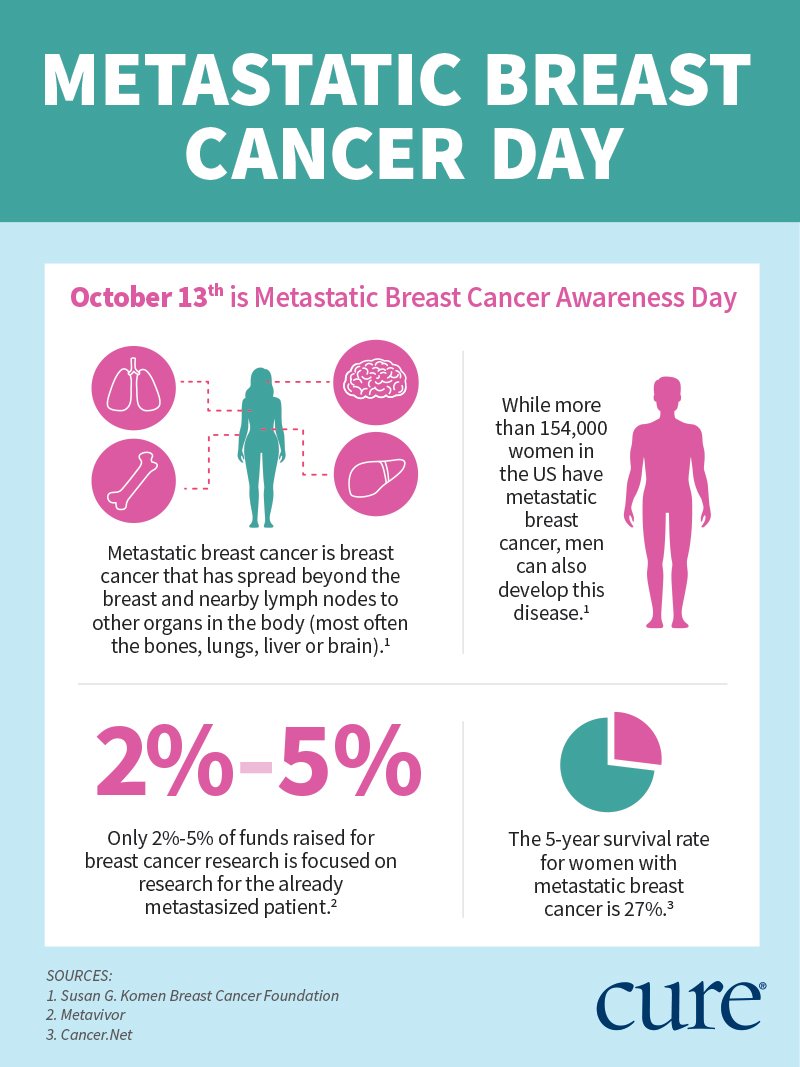
Fig. 4: The effects of cell-extrinsic and cell-intrinsic determinants in dictating breast cancer outcomes.
Part I The journey of a breast cancer patient from the development of undetectable disease and its clinical discovery , through its surgical removal and adjuvant ET , to metastatic relapse and death . The presence of tumour lesions across the body is indicated by starsthe smaller referring to the clinically undetectable ones , the bigger ones to the clinically detectable ones . Part II The development of an HR+ breast tumour lesion in the breast , comprising a mixture of ER+/PR+ and ER/PR cells . DTC escape from the primary site can occur early and/or late during tumorigenesis , although the HR phenotype of DTCs at these stages is often unclear. Bones, lungs and liver are represented as common secondary sites for breast cancer metastases, albeit the sequential patterns of DTC spread among these organs are still elusive . Targeted treatment for HR+ breast cancer patients relies on adjuvant ET. Several mechanisms of ET resistance cytostasis, ESR1 mutations and HR function regulationcontribute to DTC outgrowth. DTC disseminated tumour cell, ER oestrogen receptor, ET endocrine therapy, HR hormone receptor, PR progesterone receptor. Figure created with BioRender.com.
Read Also: Treatment For Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Myth #: If Youre Diagnosed With Metastatic Breast Cancer You Did Something Wrong Or Didnt Get The Right Treatment The First Time
When some people hear stage IV breast cancer, they assume something must have been missed along the way to let the cancer get that far. There is a misconception that breast cancer always develops in orderly steps from stages I to II, III, and then IV and that theres plenty of time to catch it early. People with MBC can face misguided assumptions that they must have skipped mammograms or self-exams, or they didnt control risk factors such as not exercising enough, watching their weight, or eating healthy. But a person can do everything right and still get MBC. Although regular screenings increase the odds of diagnosing breast cancer at an earlier stage, they cant guarantee it.
Another major misconception: If youre diagnosed with metastatic cancer after being treated for an early-stage breast cancer, you must have chosen the wrong treatment regimen or it wasnt aggressive enough. But between 20% and 30% of people with an earlier-stage breast cancer will eventually go on to develop MBC and theres often no good explanation as to why. And it can happen to anyone. Treatments can reduce the risk of recurrence, but they cant eliminate it.
As Illimae of Houston notes: that a stage IV diagnosis equals negligence on the part of the patient. In my case, it had spread before I ever felt a lump. I felt it Saturday and saw my doc on Monday, I ignored nothing, sometimes it just happens that fast.
Also Check: What Is Hr Positive Breast Cancer
What Is Seer Data
SEER is part of the National Cancer Institute and stands for Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program, a premier source for cancer statistics in the United States.
The SEER program collects information on incidence, prevalence and survival from specific geographic areas representing 28 percent of the US population and compiles reports on all of these plus cancer mortality for the entire country. For more information, click HERE.
Recommended Reading: 3a Breast Cancer
Clinical Manifestations Of Stage 4
The main classification signs of breast cancer stage 4 are its spread to remote organs or lymph nodes. The size of the tumor at this stage is no longer important moreover, it may no longer be detected at the primary site.
It is the metastases that most often develop in the liver, lungs, and bones that give information about the development of the oncological process. They are painful and cause vivid symptoms. Metastases in the liver give jaundice and increase abdominal size. Metastases in the lungs give shortness of breath, and in the bones severe pain and frequent fractures.
- severe intoxication
Genomic Features Of Tnbc
Triple negative breast cancer is characterised by the absence of expression of ER/PR/HER2. Almost 20 years ago breast cancer was classified using gene expression profiling into four main subtypes Luminal A , Luminal B , HER2-overexpressing and basal-like. Although basal-like broadly corresponds to TNBC, the terms are not synomonous. In one study, 70% of TNBC belonged to the basal subtype and 76% of basal-type tumours would be classified as TNBC. A small proportion of basal-like tumours express ER or express HER2.
Importantly, basal-like tumours express cytokeratins such as CK5/6, cadherin as well as epidermal like growth factor . Contrary to previous doctrine, it appears that basal-like tumours do not arise from normal breast tissue but instead arise from luminal progenitor cells.
Read Also: Treatment For Breast Cancer Stage 3
Lineage Tracing In Metastasis Models
The quantitative lineage-tracing strategies have proven to be successful in resolving cell fates in normal epithelial tissues either using tissue âspecific or stem-cell-specific transgenes. To conduct an inducible lineage-tracing experiment two components must be engineered into the mouse genome: a switch and a reporter. The switch is commonly a drug-regulated form of the bacterial enzyme Cre-recombinase. This enzyme recognizes specific sequences, called LoxP sites. Proteins that are capable of enhancing the identification of labeled cells or a specific population in unlabelled cells are encoded by the reporter transgenes. After harvesting all the ten mouse mammary glands from the transgenic mice, single cell suspension is usually made and transplanted either in tail vein of non transgenic recipient mice or in cleared fat pad of non-transgenic mice repopulating the mammary fat pad. These cells are then followed in the blood stream, lungs, bone marrow and liver to look for the favorable site of metastasis.these transgenic cells can be traced according to their special features of either fluorescence or induced by placing the recipients on doxycycline food.
Breast Cancer Subtypes Hormonal And Her2 Status And Survival Rates
Many research studies over the years have shown that Estrogen-positive breast cancers have better survival rates than all of the Estrogen-negative subtypes.
Progesterone-positive breast cancer also appears to have improved survival rates in comparison to progesterone-negative cases.
A recent research study combines hormone receptivity, HER2 status and stage and found some interesting results:-
For ER+ sub-types survival rates were significantly better than all other subtypes. For example, at stage 1b,
ER+ PR+ HER2- 5-year survival rates were 98.6%ER+ PR- HER2+ 5-year survival rates were 97.3%
The subtype triple negative breast cancer had the worst survival rates over all three stages. At stage I the 5-year survival rate was 92.9% and at stage III 48.9%.
Don’t Miss: Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer Survival