Breast Cancer Is An Issue That Affects Us All
- Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women in Canada and the second leading cause of cancer deaths in Canadian women.
- An estimated 26,300 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer every year in Canada, and 5,000 women will die from it.
- In Quebec, an estimated 6,000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer yearly, and 1,350 women die from it.
- Women aged 50 to 69 have the highest rate of breast cancer. Among the women between the ages of 20 and 49 that ave been diagnosed with cancer, 18% of them have breast cancer. It is actually the leading cause of cancer deaths in this age group.
In Canada, it is also estimated that 210 men will be diagnosed with breast cancer each year and 60 will die from it. Learn more about male breast cancer here.
These statistics indicate that if these trends continue:
- 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer in her lifetime.
- 1 in 31 women will die of breast cancer.
Scenario : The Cure Model
We consider a cohort of 45,647 women with a survival of 72.4% at 20 years. Assume that a new treatment prevents 30% of all deaths . In this simulation, we randomly removed 30% of deaths from the cohort and assumed that these women were alive at 20 years. We assume further that the time to death of women who are not cured is the same as in the absence of treatments. The three curves representing the survival experience of the untreated and treated women are presented in Fig. ac.
a Impact of 30% reduction in deaths on annual mortality rates, ER-positive patients in SEER. b Impact of 30% reduction in deaths on actuarial survival, ER-positive patients in SEER. c Impact of 30% reduction in deaths on time to death, ER-positive patients in SEER
How Many People Survive Breast Cancer
- Almost nine in ten of women survive breast cancer for five years or more.
- Breast cancer survival is improving and has doubled in the past 40 years in the UK due to a combination of improvements in treatment and care, earlier detection through screening and a focus on targets, including faster diagnosis.
- An estimated 600,000 people are alive in the UK after a diagnosis of breast cancer. This is predicted to rise to 1.2 million in 2030.
For many the overwhelming emotional and physical effects of the disease can be long-lasting.
Every year around 11,500women and 85 men die from breast cancer in the UK thats nearly 1,000 deaths each month, 31 each day or one every 45 minutes.
Breast cancer is the fourth most common cause of cancer death in the UK.
Breast cancer is a leading cause of death in women under 50 in the UK.
Also Check: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Us Cancer Statistics Data Visualizations Tool
The Data Visualizations tool makes it easy for anyone to explore and use the latest official federal government cancer data from United States Cancer Statistics. It includes the latest cancer data covering the U.S. population.
See how the rates of new breast cancers or breast cancer deaths changed over time for the entire United States and individual states.Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Cure Versus Progression Delay: Models
For the following hypothetical scenarios, we consider the basic model to recapitulate the survival experience of 45,647 ER-positive breast cancer patients diagnosed in the SEER database between 1990 and 1995 and then introduce two theoretical treatments. In this database, the actuarial 20-year breast cancer mortality was 72.4%. By simulation, we can evaluate how the effects of cytotoxic and cytostatic treatments are expected to influence the shape of the mortality curves. To illuminate the two models in terms of expected survival patterns, we have simulated cohorts of 91,294 women under the two scenarios.
Read Also: Anne Hathaway Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Mortality By Sex And Uk Country
Breast cancer is the 4th most common cause of cancer death in the UK, accounting for 7% of all cancer deaths .
In females in the UK, breast cancer is the 2nd most common cause of cancer death . In males in the UK, it is not among the 20 most common causes of cancer death .
99% of breast cancer deaths in the UK are in females, and 1% are in males .
Breast cancer mortality rates rates) are similar to the UK average in all the UK constituent countries.
For breast cancer mortality and incidence rates do not vary between the UK constituent nations.
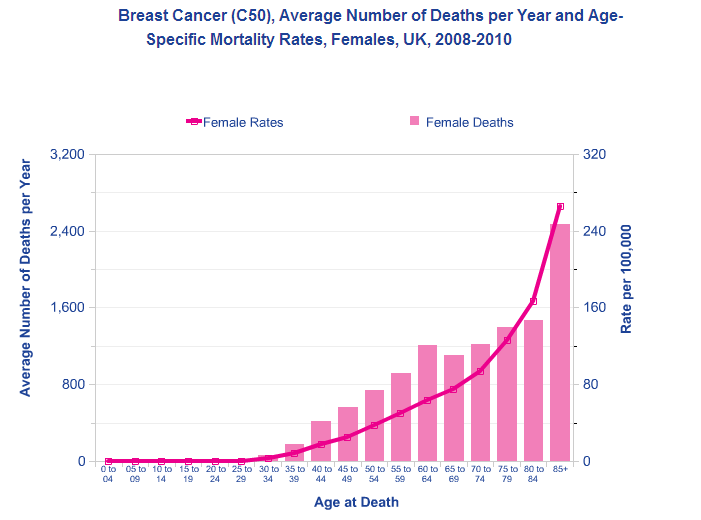
Breast Cancer , Number of Deaths, Crude and European Age-Standardised Mortality Rates per 100,000 Population, UK, 2018
Lifetime Risk Of Developing Or Dying From Cancer
The lifetime risk of developing or dying from cancer refers to the chance a person has, over the course of his or her lifetime , of being diagnosed with or dying from cancer. These risk estimates are one way to measure of how widespread cancer is in the United States.
The following tables list lifetime risks of developing and dying from certain cancers for men and women in the US. The information is from the National Cancer Institutes Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results database, and is based on incidence and mortality data for the United States from 2014 through 2016, the most recent years for which data are available.
The risk is expressed both in terms of a percentage and as odds.
- For example, the risk that a man will develop cancer pf the pancreas during his lifetime is 1.66%. This means he has about 1 chance in 60 of developing pancreatic cancer .
- Put another way, 1 out of every 60 men in the United States will develop pancreatic cancer during his lifetime.
These numbers are average risks for the overall US population. Your risk may be higher or lower than these numbers, depending on your particular risk factors.
You May Like: What Are The Side Effects Of Radiation After Breast Cancer
Scenario : The Progression Model
We now consider a drug that does not cure patients but doubles the time to death for each patient. We have given the drug to a cohort of 45,647 women with the same inherent mortality risk as the untreated cohort in scenario 1. The net benefit in terms of survival at 20 years is from 72.4 to 79% . The three curves are presented in Fig. ac. The intervention doubled the time to death for individual patients this resulted in an increase in the mean time to death from 6.3 to 9.2 years . These curves are notable in that a profound impact on delaying the time to death has a relatively modest impact on mortality i.e. if we double the life expectancy of each patient in the study, we improve actuarial survival at 20 years from 72.4 to 79.9%. This is equivalent to curing 30% of the patients.
a Impact of doubling time to death on annual hazard rates, ER-positive patients in SEER. b Impact of doubling time to death on actuarial survival, ER-positive patients in SEER. c Impact of doubling time to death on time to death, ER-positive patients in SEER
Breast Cancer Survival Rates By Stage And Age
The relative 5-year survival rate for breast cancer is 91%. This means that those who have breast cancer are, on average, 91% as likely as those who dont have the disease to live for at least 5 years after their diagnosis. The survival rate is an estimate across the population, and an individuals chance of survival is dependent on their specific characteristics and the nature of the tumour, such as the stage of the breast cancer at diagnosis, the age, gender and the subtype of the breast cancer .
The 5-year survival rate for Stage 1 breast cancer is, on average, 100% and Stage 2 is 95%. For locally advanced cancers the survival rate is 81%, while the 5-year survival rate for Stage 4 is significantly lower at 32%.
The 5-year survival rate also differs depending on the age group. For those aged over 85, the 5-year survival rate is 75%, while for those between 40 and 44 years of age it is 93%.
While the 5-year survival rate post-diagnosis is 91%, the survival rate 10 years after diagnosis of breast cancer is 86%.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Physician Trust Versus A More Generalized Distrust
How could these results be? The authors note that attempts to increase physician trust as a strategy to reduce mistrust in the healthcare system have had results ranging from zero to very modest, which makes sense if patients view the two issues as separate. I like to make an analogy to Congress. Voters routinely express extreme distrust of Congress, but most voters actually like their own representative. Similarly, its not hard to envision how most patients might actually like and trust their own doctors, while simultaneously having a great deal of mistrust for the health care system as a whole.
As the authors note:
So what to do?
The authors note that improving trust in the healthcare system will require more than just trying to build trust in patients physicians, noting:
If ordinary businesses can learn to increase trust in their brands, why not the same with health care institutions? Dean says.
Breast Cancer Mortality Over Time
Breast cancer mortality rates in the U.S. increased slowly from 1975 through the 1980s .
From 1989-2018 , breast cancer mortality decreased by 41 percent due to improved breast cancer treatment and early detection . Since 1989, about 403,200 breast cancer deaths in U.S. women have been avoided .
Breast cancer mortality in women decreased by about one percent per year from 2014-2018 . Different breast cancer mortality trends may have been seen in some groups of women.
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Type 3
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
There are many different signs and symptoms of breast cancer, so regularly checking your breasts for anything different or new is important.
The earlier breast cancer is diagnosed, the better the chance of successful treatment. Getting to know what your breasts look and feel like normally means its easier to spot any unusual changes and check them with your doctor. Common breast cancer signs and symptoms include:
- A lump or swelling in the breast, upper chest or armpit. You might feel the lump, but not see it.
- Changes in the size or shape of the breast
- A change in skin texture i.e. puckering or dimpling of the skin
- A change in the colour of the breast – the breast may look red or inflamed
- Rash, crusting or changes to the nipple
- Any unusual discharge from either nipple
Almost half of women in the UK do not check their breasts regularly for potential signs of breast cancer.
According to a YouGov survey commissioned by Breast Cancer Now, one in 10 women have never checked their breasts for new or unusual changes. Meanwhile, a fifth of women check their breasts once every six months or less, while 13% do this once a year or less.
Asked what stops or prevents them from checking their breasts more regularly, almost half of women said they forget. This is concerning when most cases of the disease are detected because women have spotted new or unusual changes to their breasts.
Some factors are outside our control, including:
Global Breast Cancer Statistics

- Breast cancer is the most common cancer worldwide.
- In 2020, there were 2.3 million women diagnosed with breast cancer and 685,000 deaths globally with breast cancer surpassing lung cancer as the most commonly diagnosed cancer.
- As of the end of 2020, there were 7.8 million women alive who were diagnosed with breast cancer over the past five years.
Don’t Miss: Triple Negative Breast Cancer Brca
Take Action To Change Young Adult Breast Cancer Statistics
When all young adults affected by breast cancer work together, we can raise awareness, improve our representation in research and make each other stronger. We are dedicated to these goals, working to turn our unique challenges into opportunities for shared success. Join the movement! Become an advocate for young women with breast cancer.
Screening For Breast Cancer
Women aged between 50 and 74 are invited to access free screening mammograms every two years via the BreastScreen Australia Program.
Women aged 40-49 and 75 and over are also eligible to receive free mammograms, however they do not receive an invitation to attend.
It is recommended that women with a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer, aged between 40 and 49 or over 75 discuss options with their GP, or contact BreastScreen Australia on 13 20 50.
Don’t Miss: How To Detect Breast Cancer Early
Why Do Some Women Refuse Treatments For Their Breast Cancer
Adjuvant therapy after surgery, such as chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and radiation therapy, has contributed to a 39% decrease in breast cancer mortality since 1989. Unfortunately, a significant number of women decline evidence-based adjuvant therapy. A recent study suggests that distrust of the medical system plays a significant role in such refusal.
I write about alternative cancer treatments a lot, in particular the lack of evidence for such practices, many of which are at best pseudoscientific and at worst pure mystical nonsense. The reason, of course, is simple. Im a breast cancer surgeon, and I hate seeing people who might be saved from death due to cancer falling prey to treatments that demonstrably lessen their chances of survival, either by leading patients to reject effective treatment in favor of ineffective or even harmful treatments or, at the very least, to delay effective treatment until the patient realizes that the quackery chosen isnt preventing the growth and spread of his or her tumor. This can sometimes take a long time. Ive seen women with breast cancer whose breasts were basically eaten away until there was nothing left but an ulcerated mass on their chestmore than that, a bleeding, rotting, malodorous ulcerated mass. Yes, its an ugly picture, but Ive seen it all too many times.
Incidence Rate For All Invasive Breast Cancer *
- For all invasive BC: Declined from 1999-2003 stable since 2003
- Rates increased rapidly between 1980-87 due largely to greater use of mammography screening, leading to increased detection of breast cancers too small to be felt. This inflates the incidence rate because tumors are being detected 1 to 3 years earlier.
- Rates stabilized/slowed in 1990s.
- There was a sharp decrease in 2002-2003 due to decreased use of menopausal hormones.
- Since 2003 rates have been stable. However, the population has been increasing.
- For non invasive DCIS rates rose rapidly during 80s and 90s, due to mammography screening. Since 1999 incidence of in situ cases have stabilized among women 50 and older, but continue to increase in young women.
* includes initial diagnosis of Stage IV only, not metastatic recurrences
Recommended Reading: What Is Hr Positive Breast Cancer
Patient Refusal Of Adjuvant Therapy: A Question Of Trust
Earlier this month a number of news stories and press releases appeared about a study published in late September by investigators at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Columbia University, and Massachusetts General Hospital looking at trustor, more specifically, a lack of trustas a key motivator in women refusing adjuvant therapy recommendations and opting for discordant care i.e., care that doesnt conform to evidence-based care recommended by the patients physicians. Its an issue that hasnt been studied as well as it should be, as the authors, Lorraine T. Dean, Shadiya L. Moss, Anne Marie McCarthy, and Katrina Armstrong point out in the introduction:
To this end, the authors used Pennsylvania and Florida cancer registries, using data from a population from a study originally intended to assess the differences in breast cancer women associated with race. The inclusion criteria for the study included localized invasive breast cancer, age under 65 at the time of diagnosis, residency in either Pennsylvania or Florida at the time of diagnosis, and diagnosis between January 1, 2005 and December 31, 2007. Exclusion criteria included patients over 65, cognitive impairment, inability to speak English or Spanish, and metastatic disease at presentation. The overall response rate was very good for surveys of this type, 61%.
The authors found:
Breast Cancer Mortality Rates Worldwide
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer mortality among women in most countries in the world .
Its estimated more than 680,000 breast cancer deaths occurred worldwide in 2020 .
Rates of breast cancer mortality vary around the world
Breast cancer is the most common cause of cancer mortality among women in developing countries .
Breast cancer is the second most common cause of cancer mortality among women in developed countries .
Read Also: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Reduce The Female Breast Cancer Death Rate C04
Objective added to your list.
Objective removed from your list.
Objective added to your list.
Objective removed from your list.
19.4 breast cancer deaths per 100,000 females
Target:
Baseline:19.7 breast cancer deaths per 100,000 females occurred in 2018
Reduce the female breast cancer death rate