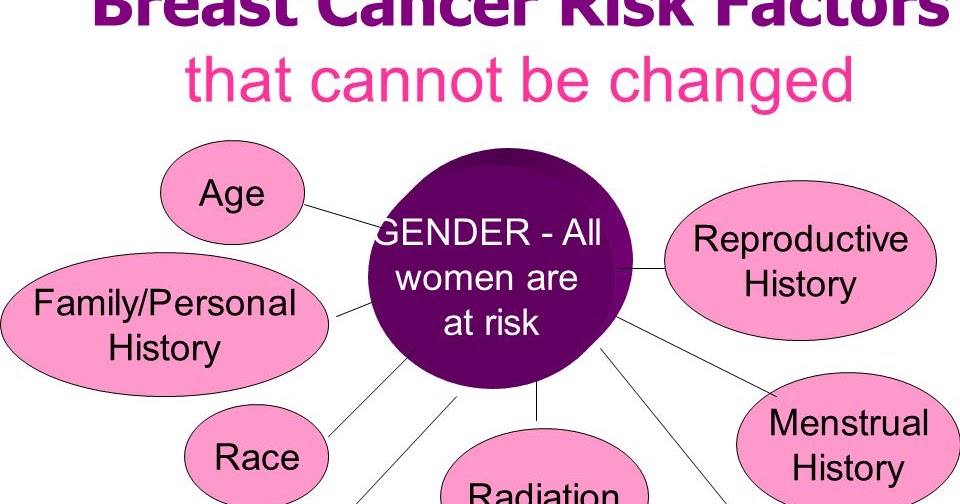
What Factors Put You At High Risk For Breast Cancer
Doctors consider several factors to determine if youre at a high risk of breast cancer. All of these factors, except for pregnancy history and radiation exposure, are things you cannot change:
- Family history: If youve had one or more close relatives, such as parents, siblings, or children with breast cancer, your risk increases.
- Genetics: Having inherited gene mutations that are associated with family cancer syndromes, particularly those in BRCA1 or BRCA2, significantly boost your risk of developing breast cancer.
- Age: The risk of breast cancer goes up as you get older.
- Personal history: A personal history of certain breast conditions raises your breast cancer risk. These include:
Remember that theres no standardized way to determine breast cancer risk. While breast cancer risk assessment tools are important in helping to estimate risk, they typically dont take all of the factors above into account.
Breast Cancer: Risk Factors Symptoms When You Should Get Screened And More
Your Health staff
Apart from skin cancer, breast cancer is the most common type of cancer found in American women, according to the Centers for Disease Control. When it is detected early, breast cancer has a good chance of being treated successfully. That is why its important to understand the risk factors, signs and symptoms, and when and how to get screened.
Taking Charge: Who Gets Breast Cancer
There are no rules about who gets this disease. The two most significant risk factors are being a woman, and increasing age. However, there are other factors that may increase your risk, and some that may lower it.
The development of breast cancer may be influenced by factors that affect the levels of female hormones that circulate in your body throughout life. These factors include the age when you began your menstrual period, the number of times you have been pregnant, your age at first pregnancy, whether you have breastfed your children, and your level of physical activity.
Don’t Miss: Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer Curable
Light Exposure At Night
The results of several studies suggest that women who work at night factory workers, doctors, nurses, and police officers, for example have a higher risk of breast cancer compared to women who work during the day. Other research suggests that women who live in areas with high levels of external light at night have a higher risk of breast cancer.
High Risk Group #: Having Lcis

LCIS, or Lobular Carcinoma in Situ, is the most dangerous benign breast condition of them all, which develops because of abnormal proliferation of cells within breast lobules .
This growth is known to somehow remain static within the breast lobule for long periods of time until one day it breaks out, invades the surrounding structures, and thus, gives rise to lobular or ductal breast cancer.
In fact, the risk of developing breast cancer in those suffering from LCIS is so high that most breast cancer forums have a separate section for this condition to help these women combat the fear of developing breast cancer for the rest of their lives.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Does Pregnancy Affect The Risk Of Other Cancers
Research has shown the following with regard to pregnancy and the risk of other cancers:
- Women who have had a full-term pregnancy have reduced risks of ovarian and endometrial cancers. Furthermore, the risks of these cancers decline with each additional full-term pregnancy.
- Pregnancy also plays a role in an extremely rare type of tumor called a gestational trophoblastic tumor. In this type of tumor, which starts in the uterus, cancer cells grow in the tissues that are formed following conception.
- There is some evidence that pregnancy-related factors may affect the risk of other cancer types, but these relationships have not been as well studied as those for breast and gynecologic cancers. The associations require further study to clarify the exact relationships.
As in the development of breast cancer, exposures to hormones are thought to explain the role of pregnancy in the development of ovarian, endometrial, and other cancers. Changes in the levels of hormones during pregnancy may contribute to the variation in risk of these tumors after pregnancy .
Screening For Women At Above
For women who have an above-average breast cancer risk but aren’t exactly at high risk somewhere around 15 to 20 percent lifetime risk, for example the ACS guidelines note there’s not enough evidence to make a screening recommendation.
It’s women who fall into this “middle ground” of risk that are challenging in terms of recommendations, Garber says.
“We have to walk a fine line, because there’s worry that we’re overdiagnosing women who have cancers that would not be dangerous, and that are very slowly growing, Garber says. And you don’t want to overtreat people.” But she acknowledges that some cancers will be missed following these guidelines.
Don’t Miss: Anne Hathaway Breast Implants
Understanding Your Risk For Breast Cancer
Breast cancer has become the most commonly diagnosed cancer globally as of 2021, accounting for 12% of all new annual cancer cases worldwide, according to the World Health Organization.
One in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime. The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2021, there will be 281,550 new cases of invasive breast cancer diagnosed in women in the United States, along with 49,290 new cases of noninvasive breast cancer.
While all women are at risk for breast cancer, some may be at a higher risk. Understanding your personal risk can provide crucial information and help determine next steps about screenings and ways to help reduce your risk.
High Risk Group #: Genetic Mutations
Scientists have identified many genes whose mutations lead to breast cancer. But the most important ones on the list are the BRCA1 and BRCA 2 genes.
Why? Because 45 – 65% women who have this genetic mutation are known to develop breast cancer.
And though genetic mutations and family history of breast cancer account for only 13% of all cases diagnosed, it is still a significant risk factor for those women who have multiple breast cancer sufferers in their family or have a mother, sister, or first cousin who were diagnosed with it quite early in life.
Read Also: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Previous Breast Cancer Or Lump
If you have previously had breast cancer or early non-invasive cancer cell changes in breast ducts, you have a higher risk of developing it again, either in your other breast or in the same breast.
A benign breast lump does not mean you have breast cancer, but certain types of breast lumps may slightly increase your risk of developing cancer.
Some benign changes in your breast tissue, such as cells growing abnormally in ducts , or abnormal cells inside your breast lobes , can make getting breast cancer more likely.
Family History And Breast Cancer Risk
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women, affecting one in eight throughout their lifetimes. A family history of the disease does increase your risk, but by how much depends on who in your family had breast cancer.
Here’s a general sense of how family history affects a woman’s risk of breast cancer:
| Family History of Breast Cancer | Your Breast Cancer Risk |
|---|---|
| First-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child | 24 percent |
| Third-degree relative | 16 percent |
Prostate cancer in male relatives also increases your risk of breast cancer, but the percent increase is not known.
Breast cancer or prostate cancer in younger relatives raises your risk more than having older relatives with these conditions.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Screening For Women At Average Risk
Although screening guidelines for women at average risk vary by organization, they are more similar now than they were in the past, Garber says.
The American Cancer Society advises women ages 45-54 to get mammograms annually, and women ages 55 and older to get them once every other year, with the option of continuing annual screening. For average-risk women ages 40-44, the ACS recommends offering the option of annual mammograms.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends starting regular mammography after a woman turns 50, and then only once every other year.
Reproductive History Estrogen Is The Main Hormone Associated With Breast Cancer Estrogen Affects The Growth Of Breast Cells Experts Believe That It Plays An Important Role In The Growth Of Breast Cancer Cells As Well The Type Of Exposure And How Long Cells Are Exposed To Estrogen Affects The Chances That Breast Cancer Will Develop
Early menarche
The start of menstruation is called menarche. Early menarche is when menstruation starts at an early age . Starting your period early means that your cells are exposed to estrogen and other hormones for a greater amount of time. This increases the risk of breast cancer.
Late menopause
Menopause occurs as the ovaries stop making hormones and the level of hormones in the body drops. This causes a woman to stop menstruating. If you enter menopause at a later age , it means that your cells are exposed to estrogen and other hormones for a greater amount of time. This increases the risk for breast cancer. Likewise, menopause at a younger age decreases the length of time breast tissue is exposed to estrogen and other hormones. Early menopause is linked with a lower risk of breast cancer.
Late pregnancy or no pregnancies
Pregnancy interrupts the exposure of breast cells to circulating estrogen. It also lowers the total number of menstrual cycles a woman has in her lifetime.
Women who have their first full-term pregnancy after the age of 30 have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer than women who have at least one full-term pregnancy at an earlier age. Becoming pregnant at an early age reduces breast cancer risk.
The more children a woman has, the greater the protection against breast cancer. Not becoming pregnant at all increases the risk for breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
High Risk Group #: Those Who Are Undergoing Combination Hormone Replacement Therapy
Women going through menopause often undergo hormone-replacement therapy to restore the level of female sex hormones in their body, thus reducing the intense problems that accompany menopause.
Unfortunately, studies have shown that those who undergo combination hormone therapy with estrogen and progestin are at a significantly high risk of developing breast cancer if they continue taking the treatment for more than 5 years.
Reducing Your Breast Cancer Risk
We can help to reduce our breast cancer risk by eating healthily, maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, and drinking alcohol in moderation. Visit out page about breast cancer prevention for more information. Unfortunately there is little we can do about some of the other risks, apart from be aware of them. But you can be aware of breast changes to look out for. You can watch our video on how to check your breasts here. It is important to attend for breast screening tests with BreastCheck when you are invited.
Don’t Miss: How To Remove Breast Cancer Naturally
Is Abortion Linked To Breast Cancer Risk
A few retrospective studies reported in the mid-1990s suggested that induced abortion was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. However, these studies had important design limitations that could have affected the results. A key limitation was their reliance on self-reporting of medical history information by the study participants, which can introduce bias. Prospective studies, which are more rigorous in design and unaffected by such bias, have consistently shown no association between induced abortion and breast cancer risk . Moreover, in 2009, the Committee on Gynecologic Practice of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists concluded that more rigorous recent studies demonstrate no causal relationship between induced abortion and a subsequent increase in breast cancer risk . Major findings from these studies include:
- Women who have had an induced abortion have the same risk of breast cancer as other women.
- Women who have had a spontaneous abortion have the same risk of breast cancer as other women.
- Cancers other than breast cancer also appear to be unrelated to a history of induced or spontaneous abortion.
Environmental And Lifestyle Risk Factors
- Lack of Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle with little physical activity can increase your risk for breast cancer.
- Poor Diet: A diet high in saturated fat and lacking fruits and vegetables can increase your risk for breast cancer.
- Being Overweight or Obese: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk for breast cancer. Your risk is increased if you have already gone through menopause.
- Drinking Alcohol: Frequent consumption of alcohol can increase your risk for breast cancer. The more alcohol you consume, the greater the risk.
- Radiation to the Chest: Having radiation therapy to the chest before the age of 30 can increase your risk for breast cancer.
- Combined Hormone Replacement Therapy : Taking combined hormone replacement therapy, as prescribed for menopause, can increase your risk for breast cancer and increases the risk that the cancer will be detected at a more advanced stage.
Also Check: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Using The Oral Contraceptive Pill
A number of studies suggest a womans breast cancer risk is increased while she is taking the oral contraceptive pill and for up to 10 years after stopping it. For most young women in their 20s and 30s the increase in risk is small, but for older women and those with other strong risk factors the risk may be greater.
When You Can’t Find Your Family History
While many women already know if their mother, sister, or daughter have had breast cancer, you might not have this information.
If your close family members passed away at a young age, if some of them didn’t have access to health care , if you were adopted, or if members of your family have been otherwise separated, you might not know which illnesses run in your family.
While family history is important information, breast cancer screenings are the most important tools for early detection, whether or not you have a family history of the disease.
Read Also: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Does Your Family Health History Put You At Risk
Collect your family health history of breast, ovarian, and other cancers and share this information with your doctor. You can inherit BRCA and other mutations from your mother or your father, so be sure to include information from both sides of your family. Include your close relatives: parents, sisters, brothers, children, grandparents, aunts, uncles, nieces, nephews, and grandchildren. If you have had breast, ovarian, or other cancers, make sure that your family members know about your diagnosis.
Tell your doctor if you have a personal or family health history of any of the following:
- Breast cancer, especially at a younger age
- Triple-negative breast cancer at age 60 or younger in women
- Cancer in both breasts
- Breast cancer in a male relative
- Ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Metastatic or high grade prostate cancer
- Breast, ovarian, pancreatic, or high grade prostate cancer among multiple blood relatives
- Ashkenazi or Eastern European Jewish ancestry
- A known BRCA mutation in the family
You can use the My Family Health Portrait tool to collect your family health history information and share this information with your doctor and other family members. Update your family health history information on a regular basis and let your doctor know if any new cases of breast or ovarian cancer occur.
What Is High Risk

“There’s not one definition of high risk,” acknowledges Judy Garber, MD, chair of the Breast Cancer Research Foundation’s scientific advisory board and director of the Center for Cancer Genetics and Prevention at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston.
“I’m afraid the field has not come to the place where they can say ‘okay, here is the cut-off for medium. Here is the cut-off for high,'” Dr. Garber says.
What some professionals can agree on is that if your lifetime risk of breast cancer exceeds 20 percent, you are considered high risk because you are eligible for annual screening with magnetic resonance imaging .
Read Also: Can Getting Hit In Your Breast Cause Cancer
Hormone Therapy After Menopause
Hormone therapy with estrogen has been used for many years to help relieve symptoms of menopause and help prevent osteoporosis . This treatment goes by many names, such as post-menopausal hormone therapy , hormone replacement therapy , and menopausal hormone therapy .
There are 2 main types of hormone therapy. For women who still have a uterus , doctors generally prescribe estrogen and progesterone . Progesterone is needed because estrogen alone can increase the risk of cancer of the uterus. For women whove had a hysterectomy , estrogen alone can be used. This is known as estrogen replacement therapy or just estrogen therapy .
Combined hormone therapy : Use of combined hormone therapy after menopause increases the risk of breast cancer. This increase in risk is typically seen after about 4 years of use. Combined HT also increases the likelihood that the cancer may be found at a more advanced stage.
The increased risk from combined HT appears to apply mainly to current and recent users. A womans breast cancer risk seems to go back down within 5 years of stopping treatment.
Estrogen therapy : Studies of the use of estrogen alone after menopause have had mixed results, with some finding a slightly higher risk and some finding no increase. If ET does increase the risk of breast cancer, it is not by much.
To learn more, see Menopausal Hormone Therapy and Cancer Risk.