Breast Cancer Cell Growth
Cancer begins when there are genetic changes, called mutations, in a normal breast cell. These changes happen in genes that control the growth of the cell. These changes may occur over a long period of time, even decades, before a cancer cell forms.
These tumor cells multiply and divide exponentially, meaning that one cell becomes two, two cells become four, and so on. That’s why a tumor size will increase more rapidly, the larger it becomes.
That said, not all cells are dividing at the same time. The cancer’s growth can change at different stages as a tumor forms. Compared with many types of cancer, breast cancer has a “low growth fraction.” This means that the proportion of cancer cells that are in an active cell cycle is low.
Some tumors, such as lymphomas and some leukemias, have much higher growth fractions. They may be active for a much shorter period of time before they are detected, even in children.
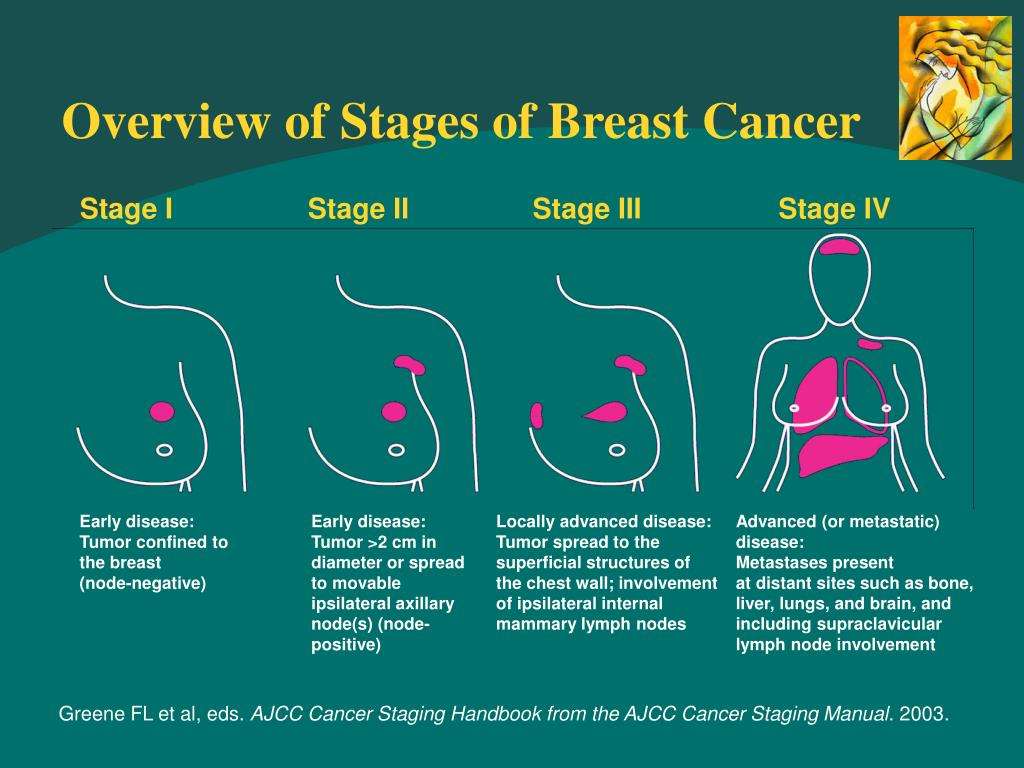
Stages Of Breast Cancer
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how much cancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is often called the extent of cancer. Information from tests is used to find out the size of the tumour, what part of the breast has cancer, whether the cancer has spread from where it first started and where the cancer has spread. Your healthcare team uses the stage to plan treatment and estimate the outcome .
The most common staging system for breast cancer is the TNM system. For breast cancer there are 5 stages stage 0 followed by stages 1 to 4. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I, II, III and IV. Generally, the higher the stage number, the more the cancer has spread. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about staging.
When describing the stage of breast cancer, sometimes doctors group them as follows:
In situ breast cancer The cancer cells are only in the duct or lobule where they started and have not grown into nearby breast tissue . It is stage 0.
Early stage breast cancer The tumour is smaller than 5 cm and the cancer has not spread to more than 3 lymph nodes. It includes stages 1A, 1B and 2A.
Locally advanced breast cancer The tumour is larger than 5 cm. The cancer may have spread to the skin, the muscles of the chest wall or more than 3 lymph nodes. It includes stages 2B, 3A, 3B and 3C. Inflammatory breast cancer is also considered locally advanced breast cancer.
Find out more about .
Appearance Of Cancer Cells
The appearance, or differentiation, of the cancer cells is another factor in cancer staging. Doctors grade cancer cells according to how similar they appear to noncancerous cells under a microscope.
Healthcare professionals classify cancer cells that are close to resembling healthy cells as being low grade or well differentiated. These cancers typically grow more slowly.
High grade, or poorly differentiated, cancer cells appear very different from normal cells and tend to grow faster.
After assessing the different characteristics of the breast cancer, doctors use the information to determine its overall stage from 04.
Here is an overview of each breast cancer stage :
- Stage 0: This cancer is noninvasive and is only present inside the milk duct. This stage includes ductal carcinoma in situ.
- Stage 1: These are small tumors that either have not spread to the lymph nodes or have only affected a small area of the sentinel lymph node.
- Stage 2: These are larger tumors that have spread to some nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: These tumors are large or growing into surrounding tissues, such as breast skin, muscle, and lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: These are tumors that started in the breast but have spread to other parts of the body.
When recommending treatment options for breast cancer, a doctor will take into account:
Treatment options can include:
Early detection and diagnosis of breast cancer can significantly improve a persons outlook.
- lymph node involvement
Read Also: Stage 2 Triple Positive Breast Cancer
What Happens After The Local Breast Cancer Treatment
Following local breast cancer treatment, the treatment team will determine the likelihood that the cancer will recur outside the breast. This team usually includes a medical oncologist, a specialist trained in using medicines to treat breast cancer. The medical oncologist, who works with the surgeon, may advise the use of the drugs like tamoxifen or anastrozole or possibly chemotherapy. These treatments are used in addition to, but not in place of, local breast cancer treatment with surgery and/or radiation therapy.
After treatment for breast cancer, it is especially important for a woman to continue to do a monthly breast examination. Regular examinations will help you detect local recurrences. Early signs of recurrence can be noted in the incision area itself, the opposite breast, the axilla , or supraclavicular region .
Maintaining your follow-up schedule with your physician is also necessary so problems can be detected when treatment can be most effective. Your health care provider will also be able to answer any questions you may have about breast self-examination after the following procedures.
What Is Staging For Cancer
Staging is the process of learning how much cancer is in your body and where it is. Tests like biopsies, CTs and MRIs are done to help stage your cancer. Your providers need to know about your cancer and your health so that they can plan the best treatment for you.
Staging looks at the size of the tumor and where it is, and if it has spread to other organs. The staging system for breast cancer is called the TNM system, as described by the American Joint Committee on Cancer. It has three parts:
- T-describes the size/location/extent of the “primary” tumor in the breast.
- N-describes if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M-describes if the cancer has spread to other organs .
Your healthcare provider will use the results of the tests you had to determine your TNM result and combine these to get a stage from 0 to IV.
You May Like: Side Effects Of Chemo For Breast Cancer
What Should A Person With Stage 0 Or Stage 1 Breast Cancer Expect Regarding Treatment
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered non-invasive, it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors. Like stage 0, Chemotherapy is often not necessary for earlier stages of cancer.
Material on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
How Is Early/moderate Stage Breast Cancer Treated
Treatment for breast cancer depends on many factors, like your cancer stage, age, overall health, and testing results. If you have early or moderate stage breast cancer, your treatment may be different than someone who has advanced breast cancer. Your treatment may include some or all of the following:
Recommended Reading: 3b Cancer
Trust Your Care To Us
No matter which stage your breast cancer falls under, the team of experts at Regional Cancer Care Associates wont let you fight alone. Once we determine the stage of your cancer, we will collaborate with our on-site oncologists, plastic surgeons and other specialists to devise an effective course of treatment. To learn more, contact us today.
The Breast Cancer Stages: From 0 To 4
The stage of your cancer will appear on your pathology report, a report that details the size, shape and look of the cancer cells under a microscope. . Most cancers, including invasive breast cancer, have four stages.
Stage 0 is abnormal cells that have not spread beyond the ducts or lobules of the breast, such as DCIS or LCIS, respectively.
Stage I cancer is invasive and spreading beyond where it started.
In Stage IA, the cancer is 2 cm or smaller and has not spread into the lymph nodes or outside of the breast.
In Stage IB, small clumps of cancer cells ranging from 0.2 to 2 mm exist in the lymph nodes. There may not be a tumor in the breast, but if there is, it measures no bigger than 2 cm.
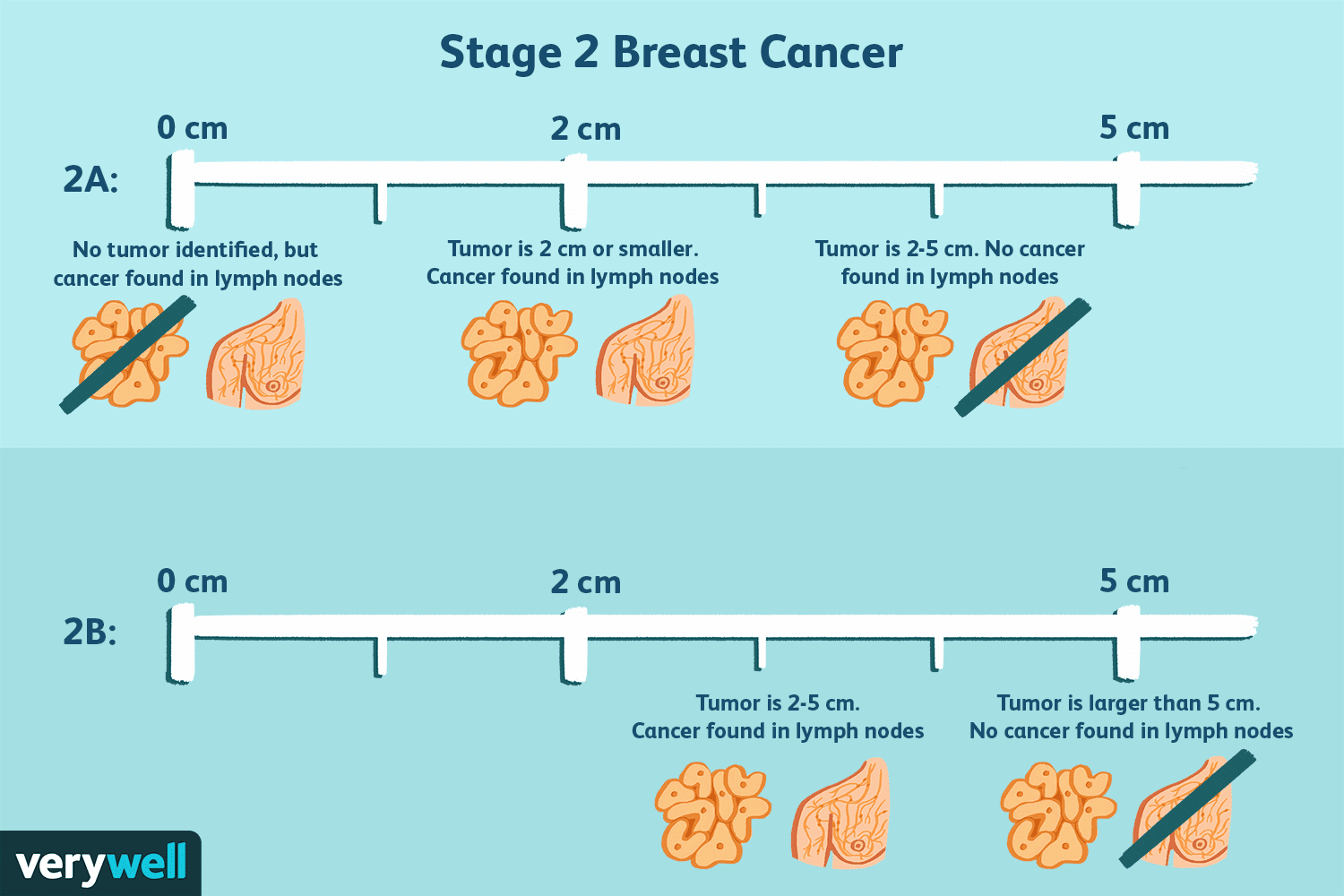
Stage II cancer also has two subcategories. Stage IIA describes a cancer that has spread to 1 to 3 lymph nodes under your arms with or without a tumor up to 2 cm large in the breast, or the breast tumor measures 2 to 5 cm without cancer cells in the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage IIB refers to a tumor between 2 and 5 cm along with cancer in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or lymph nodes near the breastbone, or the tumor is larger than 5 cm when no cancer cells exist in the axillary lymph nodes.
In Stage IIIB, the tumor has reached the skin of your breast and/or your chest wall and up to 9 lymph nodes under your arms or near your breastbone.
Inflammatory breast cancer is automatically Stage IIIB or a later stage.
Stage IIIC involves three behaviors of the cancer:
Also Check: Stage 3c Breast Cancer
Grading For Breast Cancer
Tumour grading describes how active the cells are and how quickly the tumour is likely to grow. To determine tumour grade, a pathologist will study the tumour tissue removed during a biopsy under a microscope.
- Grade 1 Cancer cells look a little different to normal cells. These tumours are usually slow-growing.
- Grade 2 Cancer cells do not look like normal cells. They tend to grow faster than grade 1 cancer cells.
- Grade 3 Cancers cells look very different from normal cells. They tend to grow and spread rapidly.
The breast cancers grade is used to help predict your likely outcome and determine which treatments are likely to be the most effective.
How Do Tamoxifen Raloxifene Anastrozole And Exemestane Reduce The Risk Of Breast Cancer
If you are at increased risk for developing breast cancer, four medications tamoxifen , raloxifene , anastrozole , and exemestane may help reduce your risk of developing this disease. These medications act only to reduce the risk of a specific type of breast cancer called estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. This type of breast cancer accounts for about two-thirds of all breast cancers.
Tamoxifen and raloxifene are in a class of drugs called selective estrogen receptor modulators . These drugs work by blocking the effects of estrogen in breast tissue by attaching to estrogen receptors in breast cells. Because SERMs bind to receptors, estrogen is blocked from binding. Estrogen is the fuel that makes most breast cancer cells grow. Blocking estrogen prevents estrogen from triggering the development of estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer.
Anastrozole and exemestane are in a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors . These drugs work by blocking the production of estrogen. Aromatase inhibitors do this by blocking the activity of an enzyme called aromatase, which is needed to make estrogen.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Symptoms Mayo Clinic
Supporting Someone With Breast Cancer
If youre reading this because theres a breast cancer survivor in your life, youre already being supportive.
Maybe you dont know what to say or fear saying the wrong thing. Say something anyway. Dont let breast cancer go unmentioned. The best thing you can do now is to be there and let them lead the way.
People with breast cancer may feel obligated to act with confidence and have a positive attitude. That may mask whats really going on. Let them know they can be real with you, then listen without judgment.
Offer to help in a concrete way. Can you prepare a meal? Do some chores? Share a movie night? Let them know what youre willing to do. But take them at their word. If they dont want help, dont push it. Just making the offer lets them know you care.
The end of treatment is not the end of the experience. There are many adjustments ahead. Some things may never return to the way they were, but change isnt always a bad thing.
N Categories For Breast Cancer
N followed by a number from 0 to 3 indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are involved.
Lymph node staging for breast cancer is based on how the nodes look under the microscope, and has changed as technology has gotten better. Newer methods have made it possible to find smaller and smaller groups of cancer cells, but experts haven’t been sure how much these tiny deposits of cancer cells influence outlook.
Its not yet clear how much cancer in the lymph node is needed to see a change in outlook or treatment. This is still being studied, but for now, a deposit of cancer cells must contain at least 200 cells or be at least 0.2 mm across for it to change the N stage. An area of cancer spread that is smaller than 0.2 mm doesn’t change the stage, but is recorded with abbreviations that indicate the type of special test used to find the spread.
If the area of cancer spread is at least 0.2 mm , but still not larger than 2 mm, it is called a micrometastasis . Micrometastases are counted only if there aren’t any larger areas of cancer spread. Areas of cancer spread larger than 2 mm are known to influence outlook and do change the N stage. These larger areas are sometimes called macrometastases, but are more often just called metastases.
NX: Nearby lymph nodes cannot be assessed .
N0: Cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes.
N1c: Both N1a and N1b apply.
N3: Any of the following:
N3a: either:
N3b: either:
Read Also: Did Anne Hathaway Have Cancer In Real Life
Why Were New Measures Added To The Staging System
The new measures give information on the biology of the tumor that affects prognosis. Adding these measures improved staging.
For example, with breast cancer, a large tumor may have a better prognosis than a small tumor, based on biological measures. In the same way, a small tumor may have a worse prognosis than a large tumor based on these measures.
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Factors That Affect Growth Rate
A number of studies have identified other factors that affect the rate of growth of a breast cancer. These include:
- The type of cancer: Inflammatory breast cancer tends to grow much more quickly than other types of breast cancer.
- Age at diagnosis: Breast cancers in young women tend to grow more rapidly than breast cancers in older women. They also have a higher tumor grade.
- Menopausal state: Breast tumors often grow more rapidly in women before menopause than they do in postmenopausal women. This is likely due to estrogen in the body.
- Receptor status: Triple negative cancers, in general, grow more rapidly than estrogen receptor-positive tumors. Triple positive tumors also grow more rapidly.
- Estrogen treatment: Women who used hormone replacement therapy after menopause had, in general, more rapid growth rate of breast tumors.
- Ki-67 index: This measures a specific tumor marker. A higher index means a faster doubling time.
- Tumor grade: This describes what the cells look like. A higher tumor grade indicates a faster doubling time.
Tumor Size And Breast Cancer Staging
Doctors determine the stage of cancer as part of their diagnosis. To confirm the breast cancer stage, they assess several different factors, including tumor size.
Doctors use multiple tests and examinations to evaluate the specific characteristics of a persons breast cancer. They use this information to assign values to the TNM staging system, where:
- T refers to the size of the main, or primary, tumor.
- N refers to whether cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- M refers to whether the cancer is metastatic, which means if it has spread to distant parts of the body.
The overall stages of cancer range from 0 to 4. Stage 0 means the breast cancer is at a very early stage and has not yet spread. Stage 4 refers to late stage breast cancer, in which it has spread to other parts of the body.
While every persons breast cancer is different, its stage generally indicates an individuals treatment options and outlook.
People with early stage breast cancer are likely to have smaller tumors that doctors can easily treat. Larger tumors tend to indicate later stage breast cancer, which may be more difficult to treat.
Doctors measure the size of the primary breast cancer tumor at its widest point. They usually give the size in millimeters or centimeters .
According to the , doctors use the following system to grade tumor size:
Tumor size is just one of several factors that doctors consider when determining the stage of a persons breast cancer. Other factors include the below.
Also Check: Grade 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Fast Breast Cancer Grows
One main reason for why people ask about how fast breast cancer grows, or its doubling time, is when they consider how long to wait to begin treatment. This growth rate also is important to understand if you have a lump and have been advised to simply observe it over time.
In general, the growth of breast cancer can be quite variable, but several studies provide at least an estimate of what may be happening.
Unless your healthcare provider is extremely confident that a lump is benign, it should be evaluated right away rather than waiting.