M Categories For Breast Cancer
M followed by a 0 or 1 indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs — for example, the lungs, liver, or bones.
M0: No distant spread is found on x-rays or by physical exam.
cM0: Small numbers of cancer cells are found in blood or bone marrow , or tiny areas of cancer spread are found in lymph nodes away from the underarm, collarbone, or internal mammary areas.
M1: Cancer has spread to distant organs .
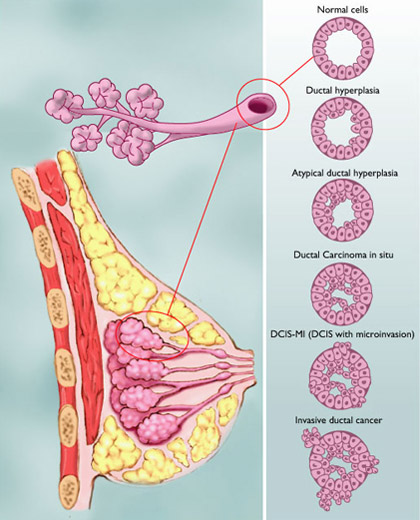
How Is Invasive Mammary Carcinoma Diagnosed
Same Day Results
At the Johns Hopkins Breast Center, our breast specialists understand how quickly patients want results from a biopsy or scan if there is a suspicion of breast cancer. We follow strict guidelines for biopsies and pathology reports. Most of our patients will receive diagnosis immediately following their biopsy procedure, and a pathology confirmation within 24 hours.
Learn more about the steps of diagnosis, including:
- Digital mammography
- Pathology
What Is Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
LCIS, like DCIS, is another type of in situ breast cancer. A doctor would detect it through a biopsy.
Researchers are unsure if LCIS is a type of pre-cancer as it rarely transforms into an invasive cancer. However, people with LCIS have a higher risk of developing breast cancer in the future.
Doctors tend to find LCIS after conducting a biopsy for another reason, as it does not usually show up on mammograms and is rarer than DCIS.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Radiation Therapy For Idc
Radiation therapy directs high-energy rays at the breast, chest area, under the arm, and/or the collarbone area to destroy any cancer cells that may be left behind after surgery. This treatment also reduces the risk of recurrence .
Radiation therapy is most often recommended after surgeries that conserve healthy breast tissue, such as lumpectomy and partial mastectomy. Radiation therapy may be recommended after mastectomy as well, especially if the tumor was large and/or the lymph nodes were involved.
Like surgery, radiation is considered a local treatment because it treats just the tumor and surrounding area.
There are different ways of giving radiation therapy, including:
Researchers are studying partial-breast radiation for use after lumpectomy to see how the benefits compare to the current standard of radiation to the whole breast. Because this technique is still under investigation, it is not yet widely available.
You and your doctor can work together to determine what form of radiation therapy is best for you.
How A Breast Cancers Stage Is Determined
Your pathology report will include information that is used to calculate the stage of the breast cancer that is, whether it is limited to one area in the breast, or it has spread to healthy tissues inside the breast or to other parts of the body. Your doctor will begin to determine this during surgery to remove the cancer and look at one or more of the underarm lymph nodes, which is where breast cancer tends to travel first. He or she also may order additional blood tests or imaging tests if there is reason to believe the cancer might have spread beyond the breast.
The breast cancer staging system, called the TNM system, is overseen by the American Joint Committee on Cancer . The AJCC is a group of cancer experts who oversee how cancer is classified and communicated. This is to ensure that all doctors and treatment facilities are describing cancer in a uniform way so that the treatment results of all people can be compared and understood.
In the past, stage number was calculated based on just three clinical characteristics, T, N, and M:
- the size of the cancer tumor and whether or not it has grown into nearby tissue
- whether cancer is in the lymph nodes
- whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the breast
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M give more details about each characteristic. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Jump to more detailed information about the TNM system.
Jump to a specific breast cancer stage to learn more:
Recommended Reading: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Causes Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Unfortunately, doctors have yet to figure out the exact cause of invasive ductal carcinoma. When you get this type of cancer, it means something damaged your cells’ DNA and caused it to change. The result is that the cells grow abnormally and uncontrollably in your breast tissue.
Doctors are still looking for genetic and environmental factors that damage the DNA. They have determined that caffeine, deodorant, microwaves and cell phone use do not lead to this type of cancer.
Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Affected By Tumor Grade
Breast cancer grade refers to the size and shape of the malignant breast cancer cells. If the breast cancer cells look very different than normal breast tissue cells, and somewhat random in appearance, they are called poorly differentiated and described as high grade.
There are three main breast cancer grades and these are as follows:-
- Grade 1: The cancer cells are well differentiated and look the most like normal cells. These type of cancers tend to be slow-growing.
- Grade 2: These cancer cells are moderately differentiated. This means that the cells look less like normal cells and tend to grow faster.
- Grade 3: Poorly differentiated cells do not appear like normal cells at all and tend to be very fast growing. Hence, the affect on prognosis.
Microscopic Images of Ductal cell carcinoma in Situ Grades 1, 2 and 3
Higher grade breast cancers tend to have a poorer prognosis.
You will be able to find the Grade of your tumor on your pathology report.
Read Also: Baking Soda And Honey For Cancer
Side Effects And Complications
All treatments have some side effects that range from mild to severe. Most clear up when treatment ends, but there can be some lasting complications.
Its important to tell your oncologist about all symptoms, even if they seem minor. Your healthcare team will work with you to ease side effects and deal with complications.
How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Diagnosed
Same Day Results
At the Johns Hopkins Breast Center, we know how quickly patients want results from a biopsy or scan if there is a suspicion of breast cancer. We follow strict guidelines for biopsies and pathology reports. Most of our patients will receive the probability of cancer immediately following their biopsy procedure and a pathology confirmation within 24 hours.
Learn more about the steps of diagnosis, including:
- Digital mammography
- Biologic targeted therapy
Also Check: Does Getting Hit In The Breast Cause Cancer
What Is The Significance Of The Stage Of The Tumor
The stage of a cancer is a measurement of the extent of the tumor and its spread. The standard staging system for breast cancer uses a system known as TNM, where:
- T stands for the main tumor
- N stands for spread to nearby lymph nodes
- M stands for metastasis
If the stage is based on removal of the cancer with surgery and review by the pathologist, the letter p may appear before the T and N letters.
The T category is based on the size of the tumor and whether or not it has spread to the skin over the breast or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast. Since the entire tumor must be removed to learn the T category, this information is not given for needle biopsies.
The N category indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are affected. Higher numbers after the N indicate more lymph node involvement by cancer. If no nearby lymph nodes were removed to be checked for cancer spread, the report may list the N category as NX, where the letter X is used to mean that the information is not available .
The M category is usually based on the results of lab and imaging tests, and is not part of the pathology report from breast cancer surgery. In a pathology report, the M category is often left off or listed as MX .
T Categories For Breast Cancer
T followed by a number from 0 to 4 describes the main tumor’s size and if it has spread to the skin or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast.
TX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed.
T0: No evidence of primary tumor.
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
T1 : Tumor is 2 cm or less across.
T2: Tumor is more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm across.
T3: Tumor is more than 5 cm across.
T4 : Tumor of any size growing into the chest wall or skin. This includes inflammatory breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Anne Hathaway Breast
What Is Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Stage IV is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. It has spread to nearby lymph nodes and to distant parts of the body beyond the breast. This means it possibly involves your organs such as the lungs, liver, or brain or your bones.
Breast cancer may be stage IV when it is first diagnosed, or it can be a recurrence of a previous breast cancer that has spread.
Examples Using The Full Staging System

Because there are so many factors that go into stage grouping for breast cancer, it’s not possible to describe here every combination that might be included in each stage. The many different possible combinations mean that two women who have the same stage of breast cancer might have different factors that make up their stage.
Here are 3 examples of how all of the factors listed above are used to determine the pathologic breast cancer stage:
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Talk With Others Who Understand
MyBCTeam is the social network for people with breast cancer and their loved ones. On MyBCTeam, more than 53,000 members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their stories with others who understand life with breast cancer.
Are you living with invasive ductal carcinoma? Share your experiences in the comments below, or start a conversation by posting on MyBCTeam.
Tests And Procedures To Diagnose Idc
Its hard to diagnose this condition alone. It requires a combination of procedures, examinations and specific testing.
- Breast mammography- this is an X-ray test to view the breast. The result of this shows finger-like projections and this projections shows invasion of the cancer cells.
- Ultrasound- also views additional tissues in the breast that affected by the cancer cells.
- Breast Physical Examination- note for any swelling, redness, scaliness or any unusual changes in the breast.
- Biopsy- this test will require some abnormal tissues to be taken out and do pathological test. There are two kinds of this biopsy:
- Core Need Biopsy- a large needle is inserted to the breast to extract samples from the breast and leaves a small scar in the breast. It has two types:
- Excisional biopsy- removes the entire suspiciously abnormal mass or lumps in the breast.
- Incisional biopsy- only small abnormal tissues is removed from the breast.
- Fine needle aspiration- a hollow and small needle is inserted in the breast and extract abnormal tissues. This procedure doesnt leave a scar in the breast.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the breast- it uses magnetic and radio waves thru a computer screen to view tissue of the breast. A dye is usually inserted to clearly view the abnormalities in the breast.
Don’t Miss: Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer Curable
Less Commonly Occurring Breast Cancer
Medullary carcinoma: Medullary carcinoma is an invasive breast cancer that forms a distinct boundary between tumor tissue and normal tissue. Only 5% of breast cancers are medullary carcinoma.
Mutinous carcinoma: Also called colloid carcinoma, mutinous carcinoma is a rare breast cancer formed by the mucus-producing cancer cells. Women with mutinous carcinoma generally have a better prognosis than women with more common types of invasive carcinoma.
Tubular carcinoma: Tubular carcinomas are a special type of infiltrating breast carcinoma. Women with tubular carcinoma generally have a better prognosis than women with more common types of invasive carcinoma. Tubular carcinomas account for around 2% of breast cancer diagnoses.
Immunohistochemistry Determines Between Invasive And In
Though somewhat rare, physicians who specialize in breast cancer diagnosis will tell you that it is quite possible for a breast carcinoma to present with both in situ and infiltrative characteristics. A mix.
An infiltrative ductal carcinoma with a central necrosis will so closely mimic a DCIS with central comedo necrosis that the initial morphological evaluation might well mislabel the lesion as high grade comedo DCIS.
In order to determine the true extent and potential threat of the breast carcinoma, one has to perform additional biopsies and imaging studies from various locations. Also, doctors must pay very close attention to the immunohistochemical analysis of the biopsy specimen.
There are certain proteins present in an infiltrating ductal carcinoma that are distinct from comedo breast carcinoma in situ. The key feature is an assessment of the myoepithelial lining of the duct. So, myoepithelial cell involvement tends to be indicative of an infiltrative or pre-invasive status for breast cancer.
Immunohistochemical evidence for either a deficient or absent basement membrane and myoepithelial cell layer will generally confirm a diagnosis of infiltrative breast carcinoma with central necrosis, rather than a comedo type DCIS.
You May Like: Baking Soda For Breast Cancer
Infiltrating/invasive Lobular Breast Carcinoma
Infiltrating lobular carcinoma usually appears as a subtle thickening in the upper-outer breast quadrant.
As the name suggests, these tumours originate mostly in the breast lobules rather than the lining of the breast ducts.
Invasive lobular cancer is a less common type of breast cancer than invasive ductal cancer. This cancer accounts for about 10% of all invasive breast cancer cases.
Prognosis for infiltrating and invasive lobular breast carcinomas will naturally be influenced by tumor size, grade, stage and hormone receptor status..
However, lobular breast cancers, when positive for estrogen and progesterone receptors, tend to respond very well to hormone therapy.
The overall breast cancer survival rates for infiltrating lobular carcinoma, when matched by stage, are a little higher than for ductal carcinoma for the first 5 years.
Survival rates range from about 77% to 93%, but on average, the 5-year survival rate was estimated at about 90%.
90%2010
Invasive Ductal Cancer With Central Necrosis
Necrosis refers to the debris left behind when cells die. In the context of a suspected breast cancer tumor doctors usually consider necrosis as an indicator of a more aggressive breast carcinoma.
It is quite common to see cell necrosis in mature invasive breast cancers. However, in the case of central necrosis, when the necrosis collects in a central location doctors commonly associate this with comedo DCIS or comedo carcinoma and notinfiltrative breast cancer.
Also Check: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
Less Common Invasive Breast Cancers
- Inflammatory breast cancer is an aggressive form of locally advanced breast cancer. Its called inflammatory breast cancer because the main warning signs are swelling and redness in the breast.
With inflammatory breast cancer, warning signs tend to arise within weeks or months. With other breast cancers, warning signs may not occur for years.
- Paget disease of the breast is a cancer in the skin of the nipple or in the skin closely surrounding the nipple. Its usually found with an underlying breast cancer.
- Metaplastic breast cancers tend to be larger and have a higher tumor grade than more common breast cancers. Metaplastic breast cancers can be hard to diagnose because the tumor cells can look very different from the tumor cells of more common breast cancers.
Stage Ia & Ib Treatment Options

Stage I describes invasive breast cancer . Stage I is divided into subcategories known as IA and IB.
In general, stage IA describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- the tumor measures up to 2 centimeters and
- the cancer has not spread outside the breast no lymph nodes are involved
In general, stage IB describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- there is no tumor in the breast instead, small groups of cancer cells larger than 0.2 millimeter but not larger than 2 mm are found in the lymph nodes or
- there is a tumor in the breast that is no larger than 2 cm, and there are small groups of cancer cells larger than 0.2 mm but not larger than 2 mm in the lymph nodes
Still, if the cancer is estrogen-receptor-positive or progesterone-receptor-positive, it is likely to be classified as stage IA.
Don’t Miss: Anne Hathaway Breast Cancer
Stage Iia & Iib Treatment Options
Stage II is divided into subcategories known as IIA and IIB.
In general, stage IIA describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- no tumor can be found in the breast, but cancer is found in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or in the lymph nodes near the breast bone or
- the tumor measures 2 centimeters or smaller and has spread to the axillary lymph nodes or
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but not larger than 5 cm and has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes
Still, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- has not spread to the lymph nodes or parts of the body away from the breast
it will likely be classified as stage IB.
Similarly, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- has not spread to the lymph nodes
- has an Oncotype DX Recurrence Score of 9
it will likely be classified as stage IA.
In general, stage IIB describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but no larger than 5 cm small groups of breast cancer cells larger than 0.2 mm but not larger than 2 mm are found in the lymph nodes or
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but no larger than 5 cm cancer has spread to 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or to lymph nodes near the breastbone or
- the tumor is larger than 5 cm but has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes
Still, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- cancer is found in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes