What To Expect When The Catheter Is Removed
Once you finish treatment with LDR or HDR implants, the catheter will be removed. Here are some things to expect:
- You will get medicine for pain before the catheter or applicator is removed.
- The area where the catheter or applicator was might be tender for a few months.
- There is no radiation in your body after the catheter or applicator is removed. It is safe for people to be near you-even young children and pregnant women.
For a week or two, you may need to limit activities that take a lot of effort. Ask your doctor what kinds of activities are safe for you and which ones you should avoid.
Also Check: Estrogen Related Cancer
What Is The Prognosis After Recurrence
Many patients with a recurrence of breast cancer can be successfully treated, often with methods other than radiation if radiation was used in the initial treatment. For patients treated initially for invasive breast cancer, five percent to 10 percent will be found to have distant metastases at the time of discovery of the breast recurrence. The same proportion will have recurrences that are too extensive to be operated on. While in these cases the patients disease can often be managed over a period of years, the goals of treatment change from obtaining a cure to preventing further progression or managing symptoms. Five-year cure rates for patients with relapse after breast conservation therapy are approximately 60 percent to 75 percent if the relapse is confined to the breast and a mastectomy is then performed.
For patients treated initially for DCIS, about one-half of recurrences are invasive and one-half noninvasive DCIS. Long-term control rates following recurrence after initial breast conservation therapy have been high, often over 90 percent.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Advanced Stage Symptoms
What Are The Different Kinds Of Radiation Therapy
Most radiation therapy is administered by a radiation oncologist at a radiation center and usually begins three to four weeks after surgery. The radiation is used to destroy undetectable cancer cells and reduce the risk of cancer recurring in the affected breast.
There are two main kinds of radiation therapy that may be considered, and some people have both.
- External Beam Breast Cancer Radiation
- Internal Breast Cancer Radiation
Keep in mind that the course of treatment you decide is something you should discuss with your radiation oncologist in order to ensure that it is as effective as possible.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
In general, cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Palliative care focuses on improving how you feel during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after a cancer diagnosis. People who receive palliative care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, and report that they are more satisfied with treatment.
Palliative treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies. You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the cancer, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
-
Music therapy, meditation, stress management, and yoga for reducing anxiety and stress.
-
Meditation, relaxation, yoga, massage, and music therapy for depression and to improve other mood problems.
-
Meditation and yoga to improve general quality of life.
-
Acupressure and acupuncture to help with nausea and vomiting from chemotherapy.
How Are Photon And Proton Beam Therapies Different From Each Other
Although both photon and proton therapies are forms of radiation therapy, there are 2 main differences.a) The type of particle that is aimed at the tumor: Photons such as X-rays are delivered as waves which do not have any charge. They pass through the body and release energy all along the way. A proton is an invisibly-small positively-charged particle. How deeply a proton travels into the body depends on the speed of the proton when it leaves the machine. 15
b) The effect of radiation on cells surrounding the tumor: The energy in photon beams gets absorbed gradually as the beams pass through tissues. Because of this, they cause damage to the tissues they pass through as they travel towards the targeted tumor. If the remaining energy of the beam is not fully absorbed by the tumor, a photon beam can continue to pass through and damage or kill more healthy cells until it exits the patients body.15
Protons release their energy all at once. They do not damage cells they pass through until they release their energy in a single burst. The distance that a proton travels before it releases its energy is determined by how fast it is moving. Proton beams are delivered at speeds that cause almost all of the energy to be released inside the tumor. Because all the radiation energy is targeted at the tumor, little energy is released into the tissues beyond the tumor. This saves the surrounding tissue from any damage.16
Dont Miss: Stage 3 B Cancer
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Breast Cancer Take To Develop
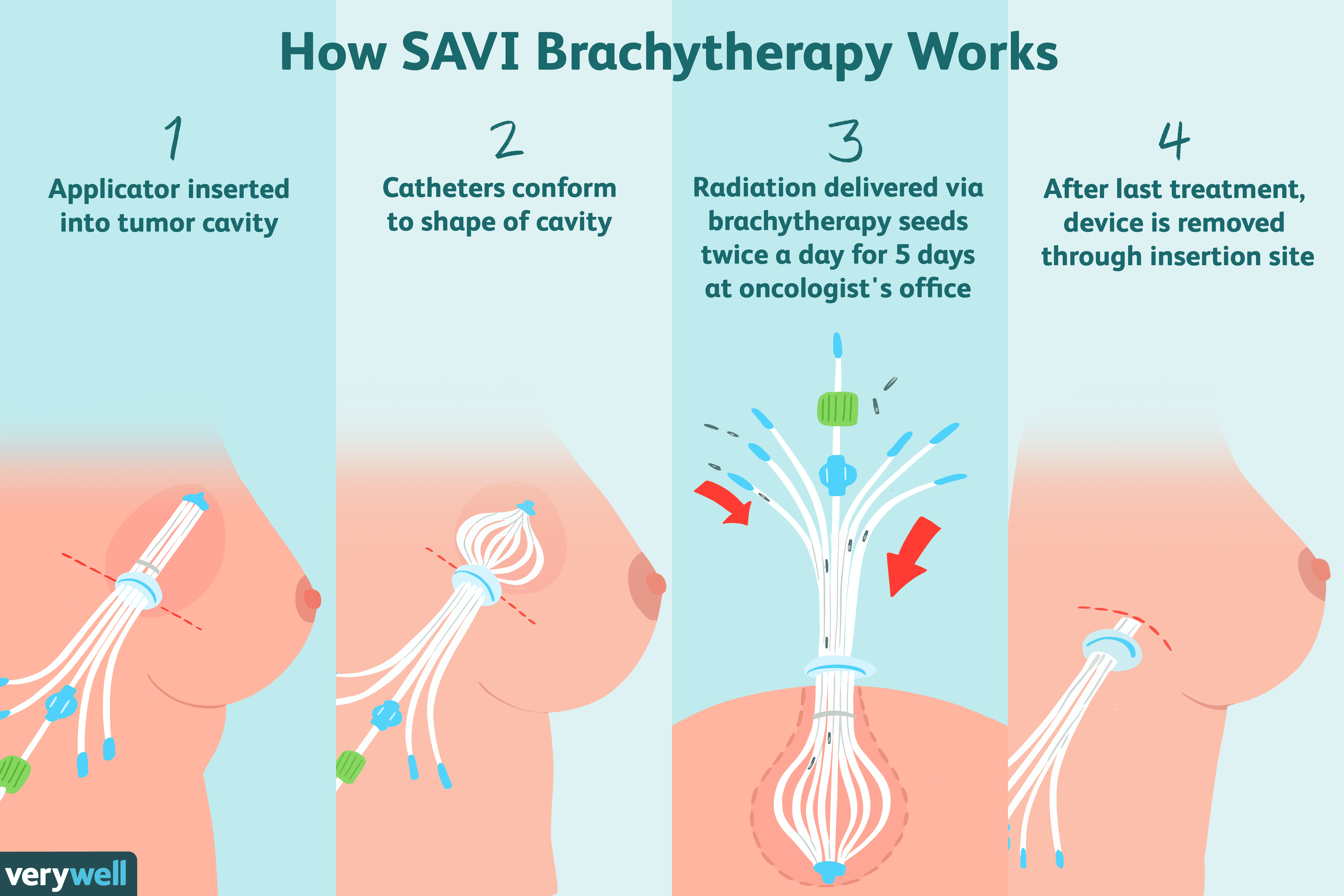
Brachytherapy Delivered Via Implantable Device
The doctor places a device inside the breast at the time of the surgery or shortly thereafter which carries targeted radiation to the tissue where the cancer originally grew . This type of radiation may take only one treatment delivered in the operating room or may take 5-7 days given on an outpatient basis in the radiation therapy department.In nearly all cases, the appropriate method is determined by the radiation oncologist based on the location and size of the tumor.
Problems Moving Your Arm And Shoulder
Radiotherapy might make it harder to move your arm and shoulder. This can affect your activities and work. It usually improves when the treatment finishes. Your nurse or physiotherapist can give you exercises to help.
Its important to continue the arm exercise you were shown after your surgery. This will make it easier for you to lift your arm to the correct position during radiotherapy. It can also help stop your arm and shoulder from becoming stiff.
Dont Miss: How Long Can You Live Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Recommended Reading: How Fast Can Breast Cancer Grow
What Types Of Radiation Treatments Are Recommended For Breast Cancer
There are two primary types of radiation used to treat breast cancer.
External beam radiation
This type of radiation is administered via a machine. A technician will carefully calibrate the device to target the area of the body affected by cancer. This could be the whole breast, the lymph nodes, the chest wall, or another location your oncologist may choose to target.
External beam radiation is the most common type of radiation used in the treatment of breast cancer. Many patients with breast cancer undergo external beam radiation after initial surgery to remove cancerous tissues. The radiation can help destroy any remaining cancer cells and prevent cancer from returning.
These treatments usually last between two and ten weeks.
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is also known as internal radiation. Instead of using a machine to deliver the radiation externally, the oncologist places a catheter directly into or near the tissue affected by cancer. Then, radiation pellets are inserted into the catheter, exposing the affected area to radiation for a short amount of time. The pellets are then removed while the catheter remains in place for the subsequent treatment.
Brachytherapy typically happens twice a day for five days, but the timeline can vary depending on your oncologist’s recommendations. Once the final treatment is complete, medical staff will remove the catheter.
How Do I Prepare For Breast Cancer Radiation Therapy
Radiation treatment requires preparation on the part of you and your medical team. Thats because radiation dosages must be precisely targeted to maximize their curative effect while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. This is particularly critical with external-beam radiation. Planning may involve:
- Radiation simulation: During a simulation procedure, your physician will mark your body to improve positioning for the radiation session. If youre undergoing brachytherapy, your medical team may also insert marker pellets in the tumor bed to guide introduction of the radioactive isotopes.
- Planning scans: Your physician will take CT scans of your breast and chest cavity.
This preparatory work enables your physician to select the type and dosage of radiation best suited to treating your cancer.
Also Check: Hormone Therapy For Breast Cancer Stage 4
Who Is Most Vulnerable To The Health Effects Of Ionizing Radiation
- Everyone should be aware of the potential health hazards of ionizing radiation, but some women are more vulnerable than others to its health effects. Women carrying the BRCA1 mutation have deficits in many cell processes and a heightened sensitivity to the effects of radiation exposures. These women are more likely to develop breast cancer and may be especially susceptible to the cancer-inducing effects of exposure to ionizing.,,,This is especially true if women began exposures, including from mammography, at age 30 or earlier.
- The detrimental risks from mammography might also be heightened in older women, whose breast epithelial cells have gone through several decades of cell division. Cells derived from older womens breast tissue were more sensitive to the DNA-damaging effects of low-energy radiation, increasing the likelihood of later conversion to cancerous cells.
- However, a recent laboratory study in rats indicates that having given birth and lactating the young was protective against development of breast cancersespecially ER+/PR+ tumorsin animals that had been exposed to radiation before puberty. This protective effect was not found if the animals had been exposed to the radiation as young adults.
When Is Radiation Therapy Used In Breast Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is used to treat breast cancer in the following circumstances:
- Radiation after lumpectomy: A lumpectomy is the surgical removal of a breast tumor and the surrounding tissue. It is an important procedure in breast-conserving surgery . Radiation therapy is used in conjunction with surgery to kill any leftover cancer cells in the adjacent tissue, to reduce the possibility of the diseases resurgence at a later date.
- Radiation after mastectomy: A mastectomy is the surgical removal of the entire breast, due to the size of the tumor or the spreading nature of the cancer. Radiation is used to check the possible reappearance of cancer in the lymph nodes.
- Radiation for locally advanced breast cancer: Some tumors cannot be removed by surgery. Radiation is a primary therapy in these situations.
- Radiation for metastatic breast cancer: Radiation can also be used to shrink metastasizing tumors that are an ongoing source of pain.
- Proton therapy: Proton-beam therapy replaces X-rays with protons as the radiation agent. Proton beams release energy in narrower intervals, which means that, in theory, they can be focused more completely on cancer cells than X-rays.
You May Like: Metastatic Breast Cancer Stage 3
Breast Cancer: Types Of Treatment
Have questions about breast cancer? Ask here.
ON THIS PAGE: You will learn about the different types of treatments doctors use for people with breast cancer. Use the menu to see other pages.
This section explains the types of treatments that are the standard of care for early-stage and locally advanced breast cancer. Standard of care means the best treatments known. When making treatment plan decisions, you are strongly encouraged to consider clinical trials as an option. A clinical trial is a research study that tests a new approach to treatment. Doctors want to learn whether the new treatment is safe, effective, and possibly better than the standard treatment. Clinical trials can test a new drug and how often it should be given, a new combination of standard treatments, or new doses of standard drugs or other treatments. Some clinical trials also test giving less treatment than what is usually done as the standard of care. Clinical trials are an option to consider for treatment and care for all stages of cancer. Your doctor can help you consider all your treatment options. Learn more about clinical trials in the About Clinical Trials and Latest Research sections of this guide.
Side Effects Of Radiation For Breast Cancer
Radiation treatments today are very precise, resulting in little harm to surrounding skin or healthy tissues. Many women tolerate radiation therapy to the breast very well and report few lasting side effects.
That said, after a few weeks of radiation, patients may experience:
- a sunburn-like condition on the skin
- changes in the color of the skin
- swelling and heaviness in the breast
- fatigue
Our radiation oncologists will explain in detail what to expect and when side effects are likely to appear. They can also prescribe a topical cream to minimize any changes in the skin. The fatigue women experience during treatment varies greatly, but in general women can remain active in all of their normal daily activities. Most women are able to continue working throughout the course of their care.
Other side effects can appear months or years after treatment has ended. These are called late effects.
Late effects of breast cancer radiation are not common but may include:
- inflammation in the lung, especially for women who have also received chemotherapy
- injury to the heart when there is significant heart exposure
- lymphedema in the arm, especially when radiation therapy is given after lymph node dissection
You May Like: Does Getting Hit In The Breast Cause Cancer
What Are The Physical Side Effects
Receiving the radiation will not be painful. Side effects vary from person to person and depend on the site being treated. The most common side effects in the treatment of breast cancer are:
- Fatigue
- Skin changes
- Uncomfortable sensations in the treated breast
Please talk to your doctor or nurse if you have concerns about side effects before you begin treatment or if you have questions about managing your side effects during treatment.
You May Like: Can Asbestos Cause Breast Cancer
Radiation For Metastatic Breast Cancer
For women with breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, radiation can be used to help with symptoms in the affected area. Radiation is particularly useful for cancer that has spread to the bone and is causing pain. Radiation can help relieve pain in approximately 80 percent of women.
Read Also: Breast Cancer Type 3
When Is Radiation Used To Treat Breast Cancer
People with breast cancer can be broadly divided into two groups:
- Those with local or regional cancer limited to the breast and area lymph nodes.
- Those with metastatic disease that has spread to other organs .
If you have local/regional cancer, radiation therapy is often used after surgery to reduce the chance of breast cancer recurrence . If you need chemotherapy as well, the radiation is typically given after chemotherapy is completed.
The type of surgery that you have determines how your radiation therapy is given. Surgery for breast cancer is most often either a lumpectomy or a mastectomy.
- Lumpectomy involves removing the part of the breast with the tumor while sparing the remainder of the breast.
- Mastectomy involves the removal of the entire breast tissue on one side, often with the removal of the lymph nodes under the arm .
Whole Breast Radiation After Lumpectomy
Patient lying “supine” for breast radiation treatment.
In some cases after a lumpectomy, radiation will also be given to the lymph nodes under the arm . This depends on whether or not there was cancer found in the lymph nodes. Ask your radiation oncologist whether you need radiation to the axillary lymph nodes.
Partial Breast Radiation After Lumpectomy
Chest Wall and Lymph Node Radiation After Mastectomy
- The tumor size.
Is The Radiation From Cell Phones Harmful
Cell phones emit radiation in the radiofrequency region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Second-, third-, and fourth-generation cell phones emit radiofrequency in the frequency range of 0.72.7 GHz. Fifth-generation cell phones are anticipated to use the frequency spectrum up to 80 GHz.
These frequencies all fall in the nonionizing range of the spectrum, which is low frequency and low energy. The energy is too low to damage DNA. By contrast, ionizing radiation, which includes x-rays, radon, and cosmic rays, is high frequency and high energy. Energy from ionizing radiation can damage DNA. DNA damage can cause changes to genes that may increase the risk of cancer.
The NCI fact sheet Electromagnetic Fields and Cancer lists sources of radiofrequency radiation. More information about ionizing radiation can be found on the Radiation page.
The human body does absorb energy from devices that emit radiofrequency radiation. The only consistently recognized biological effect of radiofrequency radiation absorption in humans that the general public might encounter is heating to the area of the body where a cell phone is held . However, that heating is not sufficient to measurably increase body temperature. There are no other clearly established dangerous health effects on the human body from radiofrequency radiation.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 3 Breast Cancer
How We Protect Breast Cancer Patients Hearts During Radiation Therapy
Many breast cancer patients undergo radiation therapy as part of their treatment. While radiation therapy often comes with side effects, such as skin irritation and fatigue, patients with left-sided breast cancer have an added concern: potential for heart disease.
Years ago, researchers discovered that many patients who underwent radiation therapy to the left breast later developed heart conditions, including pericardial disease, conduction abnormalities, coronary artery disease, congestive heart disease, heart valve disease and even sudden cardiac death. Scientists linked these problems to the hearts exposure to radiation during treatment. Thats why MD Anderson now takes extra precautions to protect patients hearts during radiation therapy. Our goal is to offer state-of-the-art radiation therapy for breast cancer without increasing the risk of long-term heart issues.
How we protect the heart during radiation therapy
Here are four methods that we use at MD Anderson to reduce the risk of radiation-induced heart disease.
Multi-leaf collimation: Our linear accelerator machines are equipped with a special shield to protect the heart from radiation exposure. This shield has multiple leafs that can move independently in and out of the path of the radiation beam to allow the radiation to target cancer cells while protecting nearby healthy tissue.
How we determine the best method for you
Focus on a healthy lifestyle