How Is Cancer In Lymph Nodes Found
Normal lymph nodes are tiny and can be hard to find, but when theres infection, inflammation, or cancer, the nodes can get larger. Those near the bodys surface often get big enough to feel with your fingers, and some can even be seen. But if there are only a few cancer cells in a lymph node, it may look and feel normal. Lymph nodes deep in the body cannot be felt or seen. So doctors may use scans or other imaging tests to look for enlarged nodes that are deep in the body. Often, enlarged lymph nodes near a cancer are assumed to contain cancer.
The only way to know whether there is cancer in a lymph node is to do a biopsy. Doctors may remove lymph nodes or take samples of one or more nodes using needles. The tissue thats removed is looked at under the microscope by a pathologist to find out if there are cancer cells in it. The pathologist prepares a report, which details what was found. If a node has cancer in it, the report describes what it looks like and how much was seen.
When a surgeon operates to remove a primary cancer, they may remove one or more of the nearby lymph nodes as well. Removal of one lymph node is considered a biopsy, but when many lymph nodes are removed, its called lymph node dissection. When cancer has spread to lymph nodes, theres a higher risk that the cancer might come back after surgery. This information helps the doctor decide whether more treatment, like chemo, immunotherapy, targeted therapy or radiation, might be needed after surgery.
What Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the breast tissues. Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers that affect women and is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in women. Men can also develop breast cancer, however, less than 1% of breast cancers are diagnosed in men.
Cancers are a unique group of diseases caused by genetic mutations, which make certain types of cells turn abnormal and grow out of control. Most types of cancers grow into masses of tissue known as tumors. Cancer spreads when tumor cells break off from the primary tumor, migrate to other parts of the body and start growing.
Will The Treatments Be Any Different To Common Breast Cancer
Breast cancer that has not invaded the lymph nodes will usually be treated with:
- Surgery
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy
This is known as “localized breast cancer.” Your surgeon may opt to remove all of the surrounding lymph nodes “axillary lymph node dissection,” to prevent the spread of any cancer cells after surgery and treatment is completed. This will give you more chance for a cure and higher survival rate.
If breast cancer is “regionally advanced” and found in the lymph nodes, the above treatments will be done along with added treatments to stall cancer growth in the lymph nodes and any cancer cells that have spread. These additional treatments may include:
1. Endocrine Therapy
If your breast tumor is “hormone receptor positive” or receptive to estrogen, an estrogen blocking medication will be given. In these types of tumors, estrogen can make the cancer grow faster. Your doctor may also choose to do a hysterectomy and remove the ovaries to prevent further estrogen production in the body. Using these estrogen blocking medications can either stop or slow the growth of breast cancer tumors. Your doctor may also advise you to not use any estrogen containing or estrogen like substances.
2. Targeted Therapy
Read Also: How Would I Know If I Have Breast Cancer
What Is Stage Ii Breast Cancer
Stage II describes cancer that is in a limited region of the breast but has grown larger. It reflects how many lymph nodes may contain cancer cells. This stage is divided into two subcategories.
Stage IIA is based on one of the following:
- Either there is no tumor in the breast or there is a breast tumor up to 20 millimeters , plus cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, but cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage IIB is based on one of these criteria:
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, along with cancer that has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
- A tumor in the breast is larger than 50 millimeters, but cancer has not spread to any lymph nodes.
Lymph Nodes: An Early Warning Sign Of Cancer
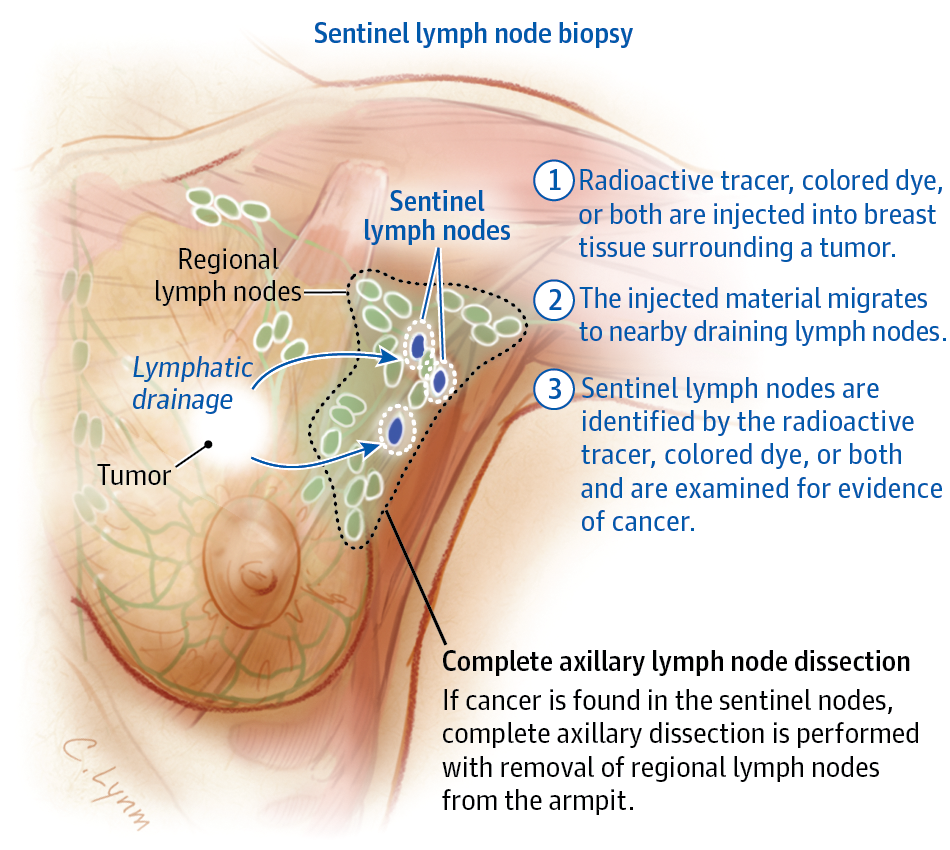
Categories:Cancer Screening,Lymphomas
Lymph nodes are part of your immune system, and they let you know when your body is fighting an infection by becoming enlarged or sensitive to the touch. They also function as an early warning system for some types of cancer, including lymphoma, leukemia, and breast cancer.
Also Check: What To Say To Someone Diagnosed With Breast Cancer
Lymph Node Status And Breast Cancer Treatment
The biopsy results will show how many lymph nodes were removed and how many were involved . This is referred to as lymph node status.
If the breast cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes, the status is referred to as node-negative. If the report indicates that cancer is present in the lymph nodes, the status is referred to as node-positive. Positive results also mean that the cancer may have already or could possibly spread to other organs, such as the bones, liver, lungs, and brain – further tests are required to make this determination.
The results of the report also indicate how much cancer is in each node. Cancer cells can range from small and few in number to large and many in number. This information may be reported as:
- Microscopic , which means only a few cancer cells are in the node and that a microscope is needed to find them.
- Gross , which means there is a lot of cancer in the node and that it can be seen or felt without the use of a microscope.
- Extracapsular extension, which means the cancer has spread outside the wall of the node.
Diagnosing Symptoms Related To Lymph Nodes
When touching an affected area, swollen lymph nodes may feel soft and round, like lumps the size of a pea, peanut or grape. If theyre painful when touched, that may be a sign of inflammation. Since lymph nodes appear in parallelas, for instance, on both sides of the neckyou can feel lymph glands on both sides to see whether they are a normal size on one side and enlarged on the other, which may be a sign of infection.
In determining a diagnosis, its important for doctors to look at other symptoms or factors. Swollen lymph nodes near the ear may indicate an ear infection, for instance. Swollen glands in the neck area near the collarbone, combined with a sore throat and cough, may be a sign of an upper respiratory infection. When multiple regions of lymph nodes are swollen, it may indicate a body-wide disease that needs immediate attention.
Besides reviewing your medical history, doctors may use some of the following methods to diagnose the cause of swollen lymph nodes:
- Physical examination, feeling with fingers the nodes in the affected area to check their size and whether they feel hard, tender or warm
- Lab tests, including blood tests to check for suspected underlying conditions
Recommended Reading: What Is Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer
Genomic Test For Prediction Of Nodal Response To Treatment
A genomic test was developed at the MD Anderson Cancer Center to predict pathologic response to sequential taxane-anthracycline-based chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment. This test was evaluated in a validation cohort, and the predicted sensitivity to chemotherapy in 28% of patients was associated with a pathologic response in 56% and significantly improved distant relapse-free survival . Of particular interest was a significantly higher probability of negative pathologic nodal status after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients whose breast cancer was predicted to be sensitive to chemotherapy.
Overall, in a cohort of 153 patients, 65 were clinically node-negative before treatment, of which 69% had a pathologic node-negative status after completion of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In addition, 44% of clinically node-positive patients at initial diagnosis converted to a pN0 status after completion of neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Fig. 1
Prediction test development.
This prospective study would enable us to determine the combined accuracy of genomic prediction of tumoral chemosensitivity and SLNB after neoadjuvant chemotherapy to identify which patients could safely undergo conservative surgical management of their regional lymph nodes.
What Does It Mean If Theres Cancer In My Lymph Node
If cancer is found in one or more lymph nodes, it could mean that more tests are needed to know how far the cancer has spread. This information is used to determine the stage of your cancer and the best treatment options.
For more information on staging, see Cancer Staging, or find your cancer type for more detailed information.
Read Also: Does All Breast Cancer Require Surgery
Cancer In Nearby Lymph Nodes
Sometimes cancer is found in lymph nodes that are near to where the cancer started. For example, breast cancer cells may travel to lymph nodes in the armpit or above the collar bone .
If a surgeon removes a primary cancer, they often remove some of the nearby lymph nodes. The lymph nodes are examined to see if there are any cancer cells in them.
The risk of the cancer coming back may be higher if the nearby lymph nodes contain cancer cells. Your doctors may suggest you have more treatment after surgery to reduce the risk.
Cancer in lymph nodes that are further away is called secondary cancer. Cancer found in nearby lymph nodes is usually treated differently to cancer in lymph nodes that are further away from the primary cancer.
More Information About The Tnm Staging System
The T category describes the original tumor:
- TX means the tumor can’t be assessed.
- T0 means there isn’t any evidence of the primary tumor.
- Tis means the cancer is “in situ” .
- T1, T2, T3, T4: These numbers are based on the size of the tumor and the extent to which it has grown into neighboring breast tissue. The higher the T number, the larger the tumor and/or the more it may have grown into the breast tissue.
The N category describes whether or not the cancer has reached nearby lymph nodes:
- NX means the nearby lymph nodes can’t be assessed, for example, if they were previously removed.
- N0 means nearby lymph nodes do not contain cancer.
- N1, N2, N3: These numbers are based on the number of lymph nodes involved and how much cancer is found in them. The higher the N number, the greater the extent of the lymph node involvement.
The M category tells whether or not there is evidence that the cancer has traveled to other parts of the body:
- MX means metastasis can’t be assessed.
- M0 means there is no distant metastasis.
- M1 means that distant metastasis is present.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Breast Cancer
What Does Cancer In A Lymph Node Mean
Cancer in your lymph nodes may point to lymphoma or another blood cancer, or may be a cancer that has spread from another site.
Based on the source of the cancer cells and how far away that is from the swollen nodes, your doctor will recommend a treatment plan. It could include surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, or a combination of treatments.
How Fast Breast Cancer Grows
People may wonder about growth or doubling time when considering how long to wait to begin treatment. This growth is also very important to understand if you have a lump and have been advised to simply observe it over time.
Unless your healthcare provider is extremely confident that a lump is benign, it should be evaluated right away rather than waiting.
In general, the growth of breast cancer can be quite variable, but several studies provide at least an estimate of what may be happening.
You May Like: How Young Can You Get Breast Cancer
If Your Breast Cancer Has Spread
Even if your breast cancer has spread to other parts of your body, it does not necessarily mean its not treatable. If the cancer cannot be removed, the goal of treatment is to improve symptoms, improve quality of life and extend survival.
Some women live with breast cancer for several years as they learn to adjust and accept that theyll be on treatment for an indefinite period of time, explains Dr. Roesch. Your cancer team will help you learn and cope with what you can expect on this journey.
Understanding Your Cancer And Treatment
Not all breast cancers are alike. Someone elses experience with their treatment may be completely different from yours. Understanding your type and stage can help make sense of your doctors recommendations. This may help you feel better about your treatment choices.
A big part of cancer treatment is the relationship between you and your oncology team. Here are some things youll want to know about early on so youre well informed about your specific type of breast cancer:
Oncologists meet with cancer patients every day and its their job to see you as a whole person. Express your wants and needs. Rest assured that no question is too insignificant to ask.
Don’t Miss: Does Stress Cause Breast Cancer
Symptoms Of Secondary Cancer In The Lymph Nodes
The most common symptom of cancer in the lymph nodes is that 1 or more lymph nodes become swollen or feel hard. But if there are only a small number of cancer cells in the lymph nodes, you may not notice any changes.
If the swollen lymph nodes are deep inside the chest or tummy, the lymph nodes cannot be seen or felt. Often there are no symptoms. But sometimes swollen lymph nodes may press on nearby organs or structures. This can cause symptoms. For example, lymph nodes pressing on the lungs may cause breathlessness.
If lymph nodes press on the blood vessels, they can slow the flow of blood through the vessels. This can cause the area to become swollen and can sometimes lead to a blood clot forming.
Symptoms of a blood clot include:
- pain, redness or swelling in a leg or arm
- breathlessness
How Is A Local Recurrence After Lumpectomy Diagnosed
After a diagnosis of early stage breast cancer, any remaining breast tissue should be evaluated annually with scans .
Most local recurrences within the breast after lumpectomy are detected on routine annual breast imaging, which usually takes the form of mammography and ultrasound, and on occasions MRI.
If you have a local recurrence or new primary breast cancer, you may find symptoms similar to an initial breast cancer. This includes:
- A new lump in the breast, armpit area or around the collarbone
- A change in breast size or shape
- Changes to the nipple, such as sores or crusting, an ulcer or inverted nipple
- Clear or bloody nipple discharge
- Changes to the skin including redness, puckering or dimpling
- Breast tenderness or pain
Once a local recurrence has been diagnosed, we do tests to see whether there are signs of cancer elsewhere in the body. These may include a chest X-ray, CT scan, bone scan or PET scan, and blood tests , then we have to figure out how best to treat the tumour in the breast. Usually in these cases we do a mastectomy, as the prior less drastic surgery and radiation didnt take care of it.
You May Like: Can You Have Breast Cancer At 21
How Does Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
Cancer can spread from where it started to other parts of the body.
When cancer cells break away from a tumor, they can travel to other areas through either the bloodstream or the lymph system. If they travel through the lymph system, the cancer cells may end up in lymph nodes. Most of the escaped cancer cells die or are killed before they can start growing somewhere else. But one or two might settle in a new area, begin to grow, and form new tumors. This spread of cancer to a new part of the body is called metastasis.
In order for cancer cells to spread to new parts of the body, they have to go through several changes. They must become able to break away from the original tumor and attach to the outside wall of a lymph or blood vessel. Then they must move through the vessel wall to flow with the blood or lymph to a new organ or lymph node.
When cancer does spread to lymph nodes, it usually spreads to nodes near the tumor itself. These are the nodes that have been doing most of the work to filter out or kill the cancer cells.
A Swollen Arm Or Hand
You are at risk of long term swelling in your hand and arm after surgery to remove your lymph nodes in the armpit. This is swelling caused by lymph fluid that can’t drain away. It can happen any time after surgery and radiotherapy to your armpit.
Not everyone will get this and it is less likely to happen if you only have a few nodes removed. But it is very important to speak to your specialist nurse or surgeon if you think your arm or hand may be swollen.
Unfortunately, once you have lymphoedema it cant be cured. But early treatment can help to control it. Your nurse will talk to you about ways of preventing lymphoedema.
Also Check: Can Getting Hit In Your Breast Cause Cancer
Where In The Body Does Breast Cancer Spread
In theory, breast cancer can spread to any part of the body, but it most commonly spreads to the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones and sometimes the brain. Keep in mind though, that even if your breast cancer spreads to other areas of your body, its still considered breast cancer. For example, if breast cancer spreads to your lungs, it does not mean that you now have lung cancer too.
If your breast cancer has moved to other parts of your body, you might experience symptoms relating to the area it has spread to, but not always.
Here Dr. Roesch explains how metastatic breast cancer can affect different parts of the body: