Screening Guidelines For Women At Average Breast Cancer Risk
MSK doctors recommend the following for women at average risk* of breast cancer:
- Women between the ages of 25 and 40 should have anannual clinical breast examination.
- Women 40 and older should have an annual mammogram in addition to anannual clinical breast examination.
- Ultrasound may be recommended for women with dense breast tissue.
- All women should consider performing a monthly self breast exam beginning at age 20 and become familiar with their breasts so they are better able to notice changes.
Can Breast Cancer In Younger Women Be Prevented
For women with a family history that is suggestive of a hereditary predisposition for breast cancer, a referral for genetic counseling may be appropriate. Identifying such genetic conditions will allow for a more personalized discussion on screening and preventive treatment options. For example, screening in BRCA mutation carriers begins at the age of 25.
Measures that all women can take to reduce breast cancer risk include:
- Achieving and maintaining ideal body weight
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Getting regular exercise
- Breastfeeding
That being said, if breast cancer does develop, early detection and prompt treatment can significantly increase a woman’s chances of survival. More than 90% of women whose breast cancer is found in an early stage will survive.
Young women should be counseled on breast awareness and to report any breast changes to their healthcare provider. These changes can include:
Stay Away From Tobacco
There is no safe form of tobacco. If you smoke cigarettes or use other types of tobacco products, it’s best to stop. It’s also important to stay away from tobacco smoke . Both using tobacco products and being exposed to tobacco smoke can cause cancer as well as many other health problems. If you don’t use tobacco products, you can help others by encouraging the people around you to quit. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 for help, or see;How to Quit Smoking or Smokeless Tobacco;to learn more about quitting.
Also Check: Does Breast Cancer Make You Lose Hair
For Women Who Have Had Mantle Radiation:
- a clinical breast exam every six months beginning at the time of your radiation treatment
- an annual mammogram starting eight years after your radiation treatment
- possible annual breast MRI
All women at above-average breast cancer risk should speak with their doctor about additional screening tests, perform a monthly self breast exam, and become familiar with their breasts so they are better able to notice changes.
MSK offers a comprehensive program for women at increased breast cancer risk, including regular breast exams and imaging. It allows any developments to be identified and dealt with right away.
How Common Is It
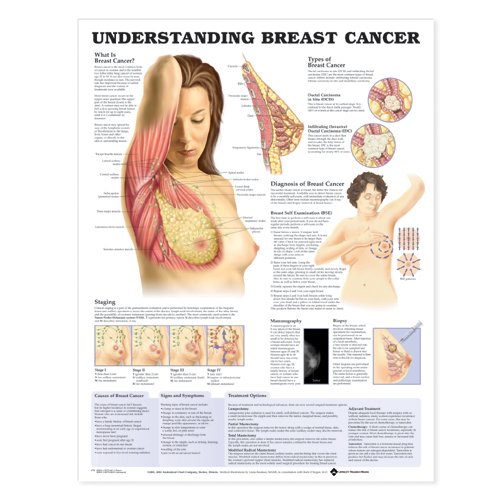
Breast cancer isnt common in women under 40.
A womans risk of breast cancer throughout her 30s is just 1 in 227, or about 0.4 percent. By age 40 to 50, the risk is roughly 1 in 68, or about 1.5 percent. From age 60 to 70, the chance increases to 1 in 28, or 3.6 percent.
Out of all types of cancer, though, breast cancer is the most common among U.S. women. A womans risk of developing breast cancer during her lifetime is about 12 percent.
Read Also: How Many People Survive Breast Cancer
Don’t Miss: Is Breast Cancer Hard Or Soft Lump
Who Should Get Screened
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force suggest that females aged 5074 years who are at average risk of developing breast cancer should go for screening every 2 years.
Those aged 4049 years, particularly those with a higher risk of breast cancer, should speak to their doctor about the risks and benefits of undergoing regular screening.
Doctors tend to use a mammogram to screen people for breast cancer. A mammogram is a breast X-ray that can help detect breast cancer early on, before it starts to produce symptoms.
Other exams available for people at a higher risk of breast cancer include:
There are both risks and benefits associated with regularly screening for breast cancer. Many people conclude that the benefits outweigh the risks, but getting screened is a personal decision.
The risks of screening for breast cancer include:
- False positives: A false positive occurs when a test result falsely suggests that a person has cancer. False positives can prompt additional tests, which may cause anxiety and can be expensive and time consuming.
- Overtreatment: Some cancers are benign and do not go on to cause symptoms or other problems. Treating these types of cancers is called overtreatment, and it can lead to unnecessary side effects, expense, and anxiety.
- False negatives: A false negative occurs when a test result misses the presence of a cancer. False negatives can delay diagnosis and treatment.
Taking Charge: Who Gets Breast Cancer
There are no rules about who gets this disease. The two most significant risk factors are being a woman, and increasing age. However, there are other factors that may increase your risk, and some that may lower it.
The development of breast cancer may be influenced by factors that affect the levels of female hormones that circulate in your body throughout life. These factors include the age when you began your menstrual period, the number of times you have been pregnant, your age at first pregnancy, whether you have breastfed your children, and your level of physical activity.
Recommended Reading: What Stage Is Grade 3 Breast Cancer
What Are The Breast Cancer Symptoms I Need To Look Out For
People of all ages should be familiar with the normal look and feel of their breasts. If you notice any of the following changes please see your doctor immediately:
- a lump, lumpiness or thickening of the breast
- changes in the skin of a breast, such as puckering, dimpling or a rash
- persistent or unusual breast pain
- a change in the shape or size of a breast
- discharge from a nipple, a nipple rash or a change in its shape.
How Can I Detect My Breast Cancer Early
The best way for young women to find breast cancer early is to be breast self-aware. Become familiar with your breasts: their shape, size and what they feel like. Learn what is normal for you. Sometimes your breasts may change throughout your monthly cycle. If you are pregnant or nursing, your breasts will change even more dramatically. If you find anything unusual, see your doctor immediately and insist on a diagnosis. In general, women should have a yearly clinical breast examination by a doctor beginning at age 20 and start having annual mammograms beginning at age 45.
Recommended Reading: What To Say To Someone Diagnosed With Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer And Birth Control
Some research has shown that taking hormonal birth control slightly increases the risk of breast cancer. However, once you stop using hormonal birth control, risk levels eventually return to normal.
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center also notes that the overall cancer risk for teens remains low, even though using hormonal birth control minimally increases the risk of developing cancer.
If you use hormonal birth control and youre concerned about your cancer risk, please discuss your options with your doctor before stopping your birth control.
According to research, including a , use of oral contraceptives increases the risk of early onset breast cancer in people under 25 years old who have a BRCA gene mutation.
Doctors should exercise caution before recommending oral contraceptives to someone in this group.
That said, an increased breast cancer risk is just one of many factors to consider before deciding on the right birth control method.
Teens going through the earlier stages of puberty may notice lumps near their nipples. Tenderness and soreness are also possible. These occur during normal breast development and arent a cause of concern on their own.
Your period can also cause tenderness and soreness in the breasts.
General Considerations For Screening
The goal of screening for cancer is to detect preclinical disease in healthy, asymptomatic patients to prevent adverse outcomes, improve survival, and avoid the need for more intensive treatments. Screening tests have both benefits and adverse consequences .
Breast self-examination, breast self-awareness, clinical breast examination, and mammography all have been used alone or in combination to screen for breast cancer. In general, more intensive screening detects more disease. Screening intensity can be increased by combining multiple screening methods, extending screening over a wider age range, or repeating the screening test more frequently. However, more frequent use of the same screening test typically is associated with diminishing returns and an increased rate of screening-related harms. Determining the appropriate combination of screening methods, the age to start screening, the age to stop screening, and how frequently to repeat the screening tests require finding the appropriate balance of benefits and harms. Determining this balance can be difficult because some issues, particularly the importance of harms, are subjective and valued differently from patient to patient. This balance can depend on other factors, particularly the characteristics of the screening tests in different populations and at different ages.
Recommended Reading: Will I Need Chemo For Breast Cancer
Why Do People Get Breast Cancer
Any woman can get breast cancer, but these things can make some women more likely to get it:
- Family history: A woman whose mother, sister, aunt, or daughter has had breast cancer is more likely to get it.
- Age: As women get older, they are more at risk for breast cancer. Teens as well as women in their twenties and thirties are less likely to get breast cancer.
- Diet and lifestyle choices: Women who smoke, eat high-fat diets, drink alcohol, and don’t get enough exercise may be more at risk for developing breast cancer.
What Are The Symptoms
The most common symptoms of breast cancer in men are
- A lump or swelling in the breast.
- Redness or flaky skin in the breast.
- Irritation or dimpling of breast skin.
- Nipple discharge.
- Pulling in of the nipple or pain in the nipple area.
These symptoms can happen with other conditions that are not cancer. If you have any symptoms that worry you, see your doctor right away.
Read Also: Do Hormones Cause Breast Cancer
Benefits Of Mammographic Screening
The ACS systematic review also examined the effect of screening mammography on life expectancy. Although the review concluded that there was high-quality evidence that mammographic screening increases life expectancy by decreasing breast cancer mortality, the authors were not able to estimate the size of the increase 23.
How Old Do You Have To Be To Get Breast Cancer
A woman has a 12% absolute risk for developing breast cancer in her lifetime, but a womans personal cancer risk changes throughout her life. Breast cancer risk increases with age; the two biggest factors for developing breast cancer are getting older and being a woman. Breast cancer doesnt just affect older women, however.
Recommended Reading: Which Type Of Breast Cancer Has The Poorest Prognosis
What Can I Do To Reduce My Risk
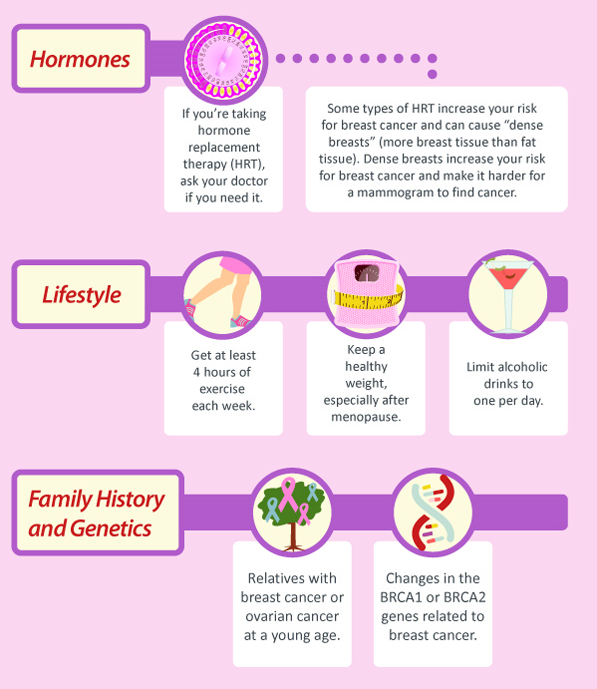
If several members of your family have had breast or ovarian cancer, or one of your family members has a known BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, share this information with your doctor. Your doctor may refer you for genetic counseling. In men, mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes can increase the risk of breast cancer, high-grade prostate cancer, and pancreatic cancer.
If genetic testing shows that you have a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation, your doctor will explain what you should do to find cancer early, if you get it.
All men can lower their risk by keeping a healthy weight and exercising regularly.
Types Of Breast Lumps That Teens Can Get
The most common type of breast cancer found in teens is secretory adenocarcinoma. This is generally a slow growing, nonaggressive cancer.
Though theres little chance of this type of cancer spreading to other parts of the body, spread to local lymph nodes has been noted in a few cases.
Most breast lumps in teenage girls are fibroadenomas, which are noncancerous. An overgrowth of connective tissue in the breast causes fibroadenomas.
The lump is usually hard and rubbery, and you can move it around with your fingers. Fibroadenomas account for 91 percent of all solid breast masses in girls younger than 19 years old.
Other less common breast lumps in teens include cysts, which are noncancerous fluid-filled sacs.
Banging or injuring breast tissue, possibly during a fall or while playing sports, can also cause lumps.
If you feel anything unusual in your breast, see your doctor. They will ask:
- about your familys medical history
- when you discovered the lump
- if theres nipple discharge
- if the lump hurts
If anything looks or feels suspicious, your doctor will have you undergo an ultrasound. This test uses sound waves to see into your breasts. It can help determine whether a lump is solid, which is an indication of cancer.
If its fluid-filled, that will most likely indicate a cyst. Your doctor may also insert a fine needle into the lump to draw out tissue and test it for cancer.
Read Also: What To Eat During Breast Cancer Treatment
Patient Characteristics With Reference To Age At Diagnosis
Clinical factors and tumor characteristics of the six age groups are shown in Table;. Distant metastasis at the time of diagnosis was more common with increasing age. There was considerably more missing data for the oldest age category concerning axillary lymph node status. It was more common for older women to have been regarded as unsuitable for surgery, and it was also less common for these women to have undergone an axillary dissection.
Table 1 Distribution of age at diagnosis in relation to patient characteristics, tumor characteristics, and surgical treatment
Guidelines For Genetic Testing For Breast Cancer
About 10% of breast cancers are related to inheritance of damaged genes. BRCA1 and BRCA2 are the genes most frequently implicated, but there are many other genes, such as PALB2, ATM, and CHEK2, that need to be considered as well.; Genetic testing usually starts with a family member who has already developed a breast or ovarian cancer.; If this individual is positive for a mutation then all of the other family members can be tested for the same mutation to determine who is high risk and who is not.; If no one in the family is known to carry a mutation then the test is considered non-informative.; That means the test was unable to tell us which relatives in the family are high risk. ;People who have inherited a damaged gene are at increased risk for breast and other cancers.; The risk may be as high as 80% depending on the specific gene and family history.;Guidelines for determining whether an individual should get genetic testing or not are constantly evolving. General criteria include:
- Someone in your family is known to carry a mutated gene
- Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry
- You were diagnosed with breast cancer before age 50
- A man in your family has been diagnosed with breast cancer
- You were diagnosed with ovarian cancer
- There are multiple breast cancers on one side of your family
- Cancer was diagnosed in both breasts
Also Check: Can Breast Cancer Develop In One Year
Your Personal History Of Breast Cancer
If youve been diagnosed with breast cancer in the past, you are more likely to develop a new cancer in the other breast or in another part of the same breast. This is not considered a recurrence but a new breast cancer.
What to do: Follow your cancer teams instructions on monitoring to stay on top of this risk. Ask your doctor whether you should see a genetic counselor.
Personal History Of Breast Disease
Females who have previously had breast cancer are at risk of developing a second breast cancer, either in the other breast or in a different part of the same breast. This is not the same as the first cancer returning.
Having a personal history of certain noncancerous breast conditions can also increase a persons risk of breast cancer. This can include conditions such as atypical hyperplasia, lobular carcinoma in situ, and ductal carcinoma in situ.
People with a history of breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer should ask their doctors about .
Recommended Reading: Why Do Chemo Before Breast Cancer Surgery
What Is The Youngest Age At Which You Can Get Breast Cancer
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Can I Screen With Ultrasound Instead
An ultrasound scan is also not a reliable stand-alone method of breast screening in young women. Its a useful targeted diagnostic tool for adding extra information when investigating a known abnormality, but its not accurate enough for generally scanning the breast and screening for cancer.
Lifestyle factors
You can reduce your lifetime risk of breast cancer by adopting healthy lifestyle choices while you are still young.
- Be active. Regular exercise is associated with a decrease in the lifetime risk of breast cancer. Read the World Health Organisations exercise recommendations.
- Maintain a healthy body weight. Women who are overweight or obese have a higher risk of breast cancer after menopause so its important to adopt healthy eating patterns early in life. Eat plenty of fruit and vegetables and stay away from junk food or make it only an occasional treat.
- Limit alcohol. Alcoholic drinks raise the levels of oestrogen in the body and contribute to breast cancer risk.
Also Check: How Likely Am I To Get Breast Cancer