Emma D Wrenn And Kevin J Cheung
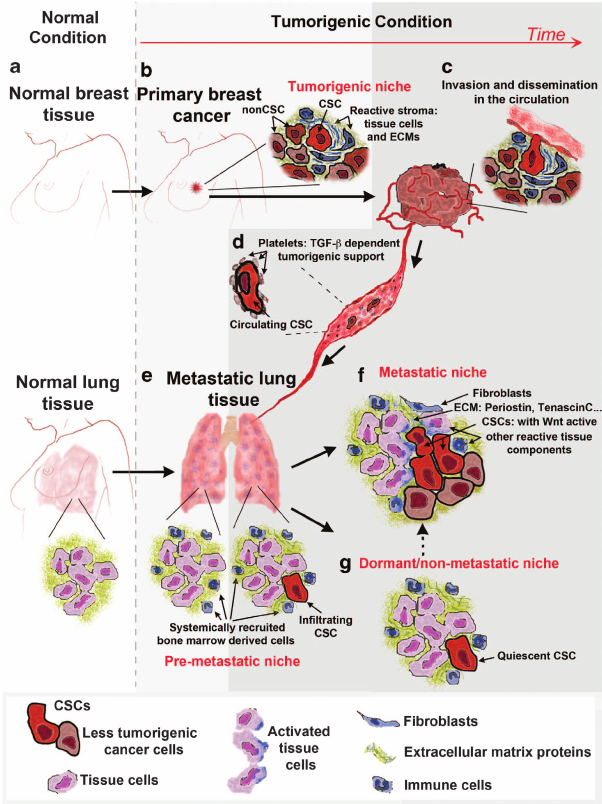
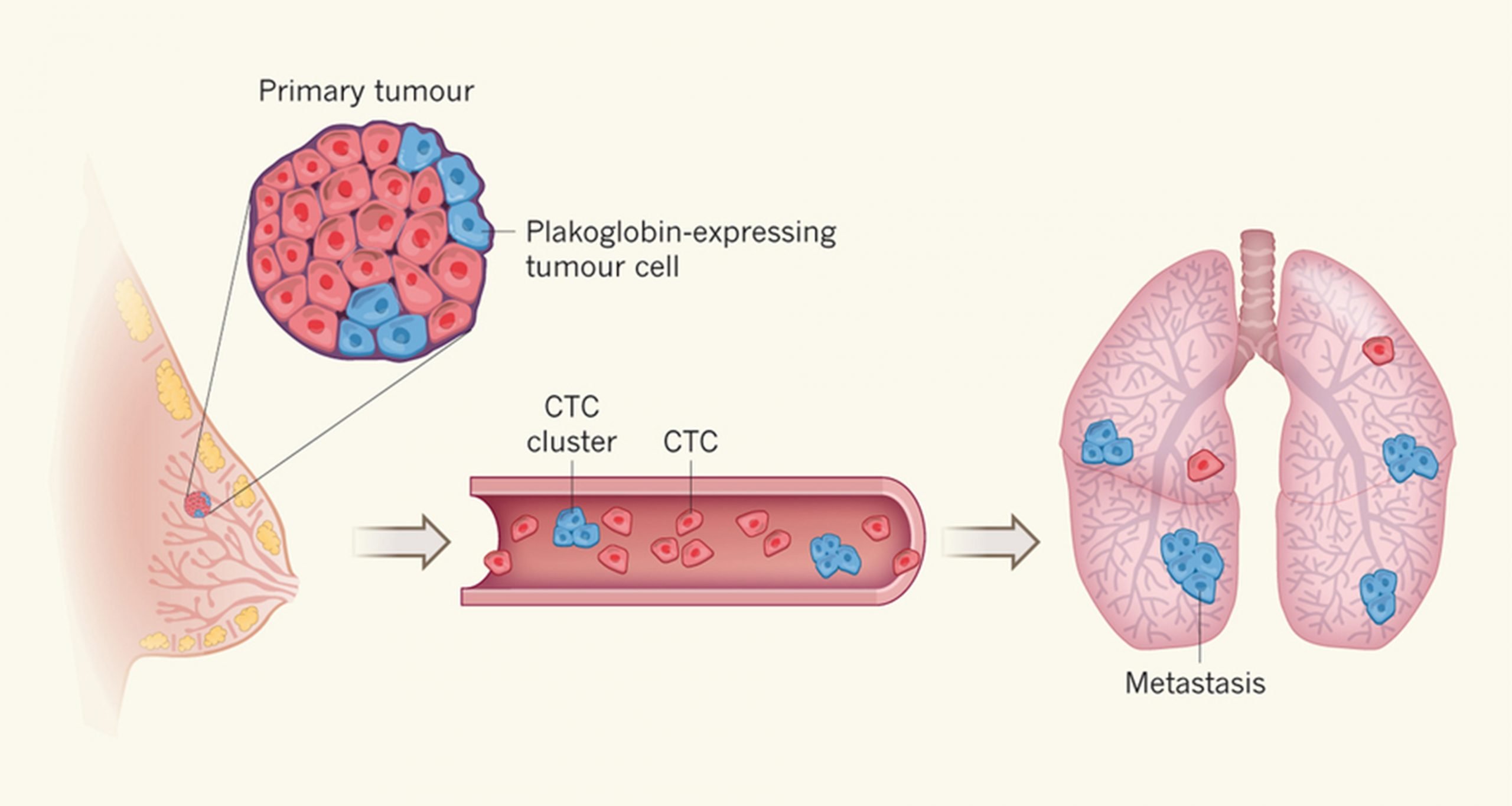
A large number of tumor cells reaching distant sites will die and never grow into a clinically detectable metastasis . Disseminated tumor cells encounter inhospitable stromal matrices, cell types, and paracrine signals different from their organ of origin. In addition, they are actively eliminated by immune cells, such as natural killer and T-cells. Diverse mechanisms have been described that enable tumor cells to overcome these barriers: entry into a stem cell-like state, epithelial-to-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-to-epithelial transitions, genetic mutation, and co-option of the native microenvironment for example . Here, we focus on an emerging mechanism by which cancer cells increase their chance of successmetastasizing as cohesive clusters of cells, also known as collective metastasis.
Fig. 2
Clusters resist programmed cell death. Tumor cell clusters have increased survival at metastatic sites through several mechanisms including depletion of reactive oxygen species, resistance to NK cell killing, and pro-survival signals transduced downstream of cellcell adhesion
Alternative And Complementary Therapies
Some patients with metastatic breast cancer opt to try alternative therapies that are claimed to achieve healing effects similar to scientifically-tested medical approaches, but lack scientific evidence to support those claims. Approaches that are considered alternative therapies when applied to cancer treatment include vitamin therapies, homeopathic treatments, extreme diets, chiropractic treatment and acupuncture.
Some alternative treatments are harmful or even life-threatening. Amygdalin, an extract derived from apricot kernels, exposes the patient to cyanide. Bee venom can cause a life-threatening allergic reaction. Severe dietary restrictions such as Macrobiotic diets can disrupt the bodyâs metabolism and cause dangerous weight loss. People should be aware that foods, vitamins, and other treatments may interfere with the effectiveness of surgery, chemotherapy or radiation. It is essential that patients work with their doctors and openly discuss possible effects of any treatment they are considering. Alternative and complementary therapies are not regulated by the U.S. federal government and may lack quality controls.
How Is Metastatic Breast Cancer Diagnosed
If you have symptoms of metastatic breast cancer, your provider may recommend tests including:
- Blood tests, including complete blood count and comprehensive metabolic panel.
- Imaging studies, including MRI, CT, bone scan and PET.
- Bronchoscopy, which uses a scope to look inside your lungs this can be done if there is a concerning spot in the lungs.
- Biopsy to remove tissue from a suspicious area and analyze it.
- A tap to remove fluid from an area with symptoms. For example, pleural tap removes fluid from the lung area. Spinal tap removes fluid from the spinal cord area.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Symptom Checker
Additional Tools For Diagnosing Advanced Breast Cancer
The additional tools below are often used specifically for diagnosing advanced cancer:
Sentinel lymph node biopsy: This procedure removes sentinel lymph node cells during surgery for examination. When breast cancer spreads, it often heads first to the lymph nodes.
Chest X-ray: This detailed image of the chest may help doctors see whether cancer has spread to the bones.
Computed tomography scan: Also known as a CAT scan, this procedure takes detailed pictures of internal areas of the body using a computer linked to an X-ray machine. A dye may be used to help the organs show up more clearly in the images.
Bone scan: This procedure looks for bone metastasis, or cancer cells that have spread to the bone. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the blood, then detected with a scanner.
Positron emission tomography scan: A PET scan is a detailed imaging tool that uses a radioactive drug, known as a tracer, to search for cancer cells within your body.
What To Expect When Taking Keytruda
Keytruda is given as a 30-minute infusion, every 3 or 6 weeks, depending on the dose given at each infusion. The Keytruda infusion is given before the chemotherapy infusion. If you are receiving Keytruda for metastatic or unresectable locally advanced triple-negative breast cancer, you may continue treatment with Keytruda and chemotherapy for up to 2 years, unless the cancer grows or you develop unacceptable side effects.
Women who are pregnant or planning to get pregnant should not be given Keytruda. Keytruda can cause embryo death and birth defects. Its important that you dont get pregnant while youre getting Keytruda you must use effective birth control.
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Breast Cancer Mayo Clinic
Phase Iii Keynote 355 Trial
The much anticipated KEYNOTE-355 trial was presented at the inaugural virtual ASCO annual meeting in June 2020. This trial investigated pembrolizumab/chemo vs chemo in patients with treatment-naïve, metastatic TNBC. Patients were excluded if they had active brain metastases or recurrence of disease < 6 mo prior to primary treatment. PD-L1 was assessed with the IHC 22C3 pharmDx CPS assay in a central laboratory. The primary outcome measure was pre-defined as OS and PFS in the PD-L1 positive population and the ITT population. In this trial, a hierarchial statistical testing method involved statistical testing of OS and PFS in the CPS > 10 group initially, followed by CPS > 1 and then the ITT population. The trial included 566 patients in the chemotherapy/IO arm vs 281 in the chemotherapy arm. In patients with a CPS score of 10 or greater, the median PFS favoured pembrolizumab with a PFS of 9.6 mo vs 5.6 mo . In patients with a CPS score of 1 or greater, the median PFS favoured the pembrolizumab arm with a PFS of 7.6 mo vs 5.6 mo . This was not statistically significant. This was similar to the ITT population where the PFS was 7.5 mo in the pembrolizumab arm and 5.6 mo in the placebo arm . OS data is awaited. This progression free survival improvement led to accelerated FDA approval for pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy in the first-line setting in November of 2020.
Also Check: Can Biting Breasts Cause Cancer
Regulatory Factors Of The Rankl Pathway
RANKL clearly holds the key to the osteolytic process. In fact, a new drug, denosumab , a fully human monoclonal antibody to RANKL, has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of postmenopausal women with high risk of osteoporotic fractures, and is under priority review for patients with bone metastases. Osteoblasts and bone stromal cells can respond to a variety of substances that upregulate RANKL. PTH/PTHrP, TNF-, prostaglandins , IL-1, IL-11, FGF-2, and IGF-1 have been reported to increase RANKL production. Cells of the immune system, T cells and dendritic cells can also express RANKL. In this context, RANKL increases in the presence of inflammatory agents from infectious organisms, such as lipopolysaccharide, CpGpDNA and viral double-stranded DNA . Several of these RANKL inducers merit further discussion with respect to metastatic breast cancer-induced osteolysis.
Recommended Reading: What To Expect During Chemo For Breast Cancer
What Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the breast tissues. Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers that affect women and is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in women. Men can also develop breast cancer, however, less than 1% of breast cancers are diagnosed in men.
Cancers are a unique group of diseases caused by genetic mutations, which make certain types of cells turn abnormal and grow out of control. Most types of cancers grow into masses of tissue known as tumors. Cancer spreads when tumor cells break off from the primary tumor, migrate to other parts of the body and start growing.
How Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer Diagnosed
The first step might be a mammogram to evaluate a suspicious mass or lump in your breast. Based on what they learn, healthcare providers might perform a biopsy to remove breast tissue. Then they examine the tissues cells to determine the cancer subtype. Identifying the cancer subtype is part of the staging process, which is when providers decide how to treat your cancer.
Sometimes providers use the following tests before treatment to check on your tumors size and whether it has spread, or after treatment to monitor response to treatment:
Recommended Reading: Stage 4 Breast Cancer Symptoms Treatments
What Treatments Are Available For Brain Metastases
The treatment array includes radiation, surgery, and chemotherapy. The size and number of metastases will determine treatment. Chemotherapy is challenging because of the blood brain barrier, which protects the brain by blocking entry of bacteria and toxins, but it also prevents entry of most chemotherapies. Clinical researchers are testing promising new drugs and studying ways to penetrate the blood brain barrier.
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Genetics
One of the leading causes of triple-negative is a womans genetic makeup, specifically the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are genes that are supposed to produce tumor suppressant proteins in the body.
In the case of triple-negative breast cancer, 10% to 15% of Caucasians with triple-negative breast cancer have a BRCA1 gene mutation, while 35% of African Americans with triple-negative breast cancer have a BRCA1 gene mutation.
For a while the BRCA1 gene was the only gene known for increasing the risk of triple-negative breast cancer.
These genes, if defected can increase their risk of getting any type of breast cancer by 20% as well as elevating the chances that their breast cancer diagnosis be triple negative breast cancers .
Recommended Reading: Estrace Breast Cancer
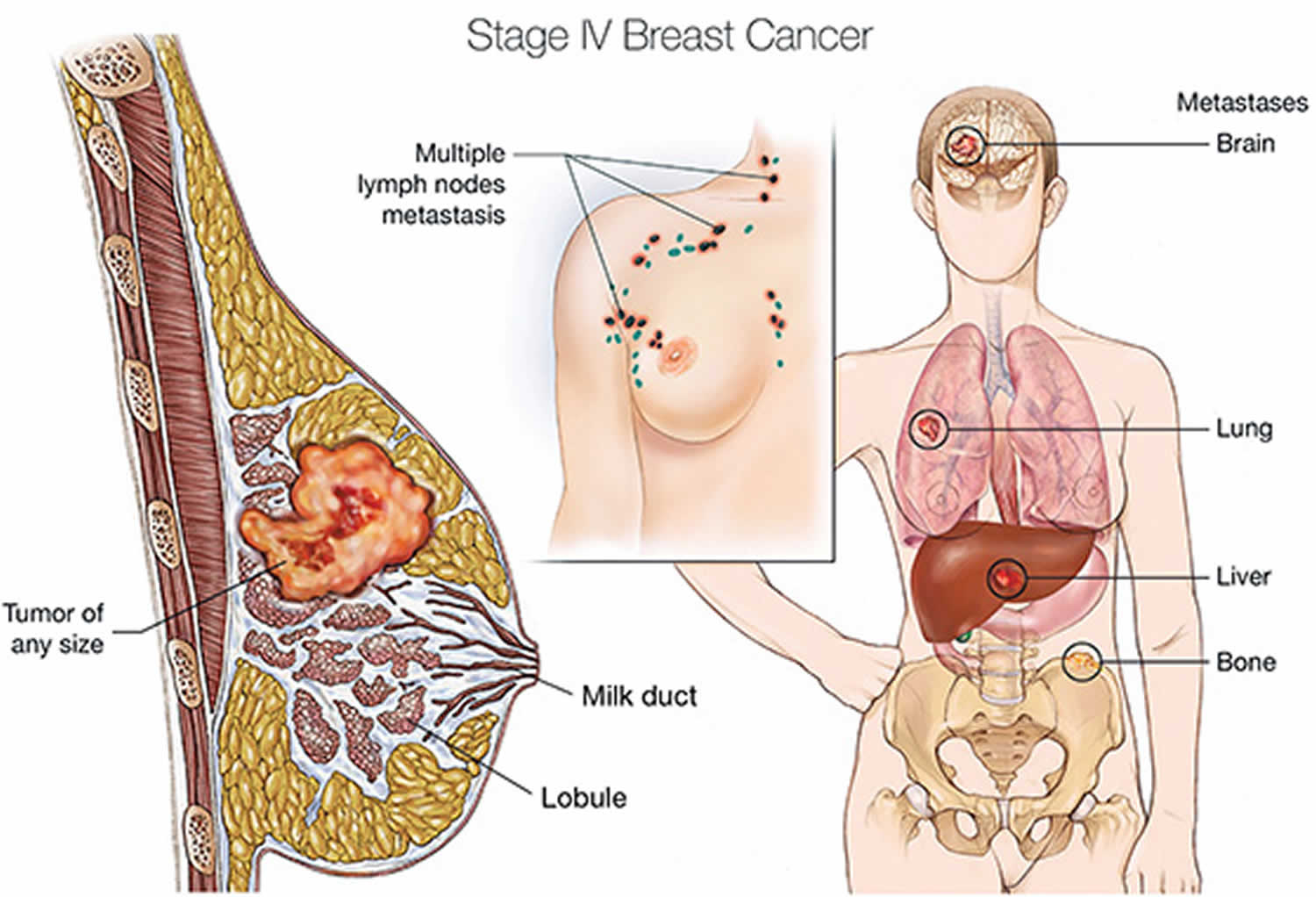
Where Does Breast Cancer Usually Spread
Breast cancer can spread, or metastasize, to bones, the brain, the liver, and the lungs. Metastasis to each vital organ has a unique set of symptoms. Breast cancer that has spread to bones can cause pain and fractures. Spread to the brain, it can cause headache, dizziness, and seizures. Spread to the lungs, it can cause shortness of breath. Spread to the liver, it can cause jaundice or yellowing of the skin and swelling of the abdomen.
How Do Breast Cancers Start
The human body is made of countless cells that reproduce, by splitting, to replace or repair other cells. New cells usually work like their parent cells. Sometimes, however, a new cell has an error. Not all cells with errors are bad some are harmless, or benign. Others, however, reproduce rapidly and harm healthy cells. The offensive cells are said to be malignant because they dont function like healthy parent cells.
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Stage 4 Breast Cancer
What Happens When Breast Cancer Spreads To The Brain
When breast cancer spreads to the brain, symptoms may include headaches, seizures, nausea and vomiting, disturbances in vision, and changed behavior. Increased risk for metastases to the brain include being a younger patient having four or more positive lymph nodes having poorly differentiated tumors having HER2 positive tumors or triple negative tumors and already having lung or liver metastases.
Metastatic Breast Cancer Symptoms And Diagnosis
The symptoms of metastatic breast cancer can vary greatly depending on the location of the cancer. This section covers the symptoms of breast cancer that has spread to the bone, lung, brain, and liver, and the tests used to diagnose metastatic breast cancer.
Bone Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisThe most common symptom of breast cancer that has spread to the bone is a sudden, noticeable new pain. Breast cancer can spread to any bone, but most often spreads to the ribs, spine, pelvis, or the long bones in the arms and legs. Learn more.
Lung Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisWhen breast cancer moves into the lung, it often doesnt cause symptoms. If a lung metastasis does cause symptoms, they may include pain or discomfort in the lung, shortness of breath, persistent cough, and others. Learn more.
Brain Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisSymptoms of breast cancer that has spread to the brain can include headache, changes in speech or vision, memory problems, and others. Learn more.
Liver Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisWhen breast cancer spreads to the liver, it often doesnt cause symptoms. If a liver metastasis does cause symptoms, they can include pain or discomfort in the mid-section, fatigue and weakness, weight loss or poor appetite, fever, and others. Learn more.
Read Also: Stage Four Breast Cancer Symptoms
Combination Therapy And Precision Medicine
Because of the intratumor complexity and the plasticity of metastases, it is expected that many of the targeted agents will show limited efficacies when applied singly and do not outperform the current standard-of-care in clinical trials. An emerging concept to overcome these issues is combination therapy, which combines multiple drugs and aims to inhibit multiple molecular targets simultaneously. Because effective first-line treatments exist for ER+ and HER2+ breast tumors, the primary focus of combination therapy in these two subtypes is to overcome acquired resistance and to achieve enduring treatment efficacies from anti-ER and anti-HER2 therapies. Resistance to hormonal therapy can occur through multiple mechanisms, including reactivation of the ER pathway through ER mutation, ER protein modifications, or modulation of the ER genome-wide binding, upregulation of RTKs, such as EGFR, ERBB2, IGF1R, and FGFR, and activation of the PI3K survival signaling, or activation of CDKs and cell proliferation via other upstream pathways. Resistance to anti-HER2 therapy typically leads to reactivation of the PI3K signaling, either through upregulation of the ERBB2 partners EGFR/ERBB3, loss of PTEN, or mutation of the PI3K pathway components. Thus, the inhibitors of these molecular targets are promising candidates to be included in the combination therapy .
What Causes Metastatic Breast Cancer
Breast cancer treatments are intended to eliminate any cancer cells that may remain after surgery. Potential treatments include radiation, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
In some cases, some cancer cells survive these treatments. These cancer cells may break away from the original tumor. These cells then make their way to other parts of the body via the circulatory or lymphatic systems.
Once the cells settle somewhere in the body, they have the potential to form a new tumor. This can happen quickly or develop years after initial treatment.
Several tests are used to confirm a diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer. These include:
- MRI
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Final Stage Symptoms
S David Nathanson And Michael Detmar
The scientifically based management of breast cancer is dependent upon an understanding of the natural history of the disease. Initially only direct treatment of the diseased breast was possible, and surgery played a predominant role well into the middle of the twentieth century . Treatment by radical mastectomy was offered as an all or nothing response the practitioner could do a drastic operation with the hope that all the cancer had been removed. Patients and their families to this day ask the surgeon whether he/she got it all. Until fairly recently that also meant removing all the lymph nodes in the axilla, even when the tumor had not spread to those nodes, exposing the patient to an uncomfortable series of postoperative complications, including severe lymphedema of the arm.
The procedures and processes that played out in the imagination of physicians treating patients with BC were based upon a mechanical/anatomic understanding of metastasis. In a sense, everything in the metastatic process could be related to tubes, namely, blood vessels and lymphatics, and their connections in the breast, axilla, and the systemic circulation tumor cells traveled through these vessels to other parts of the body where they might invade the end organ, such as the lung, liver, bone or brain, forming metastases. Once vital organs had succumbed to these invasive tumors the patient would eventually die of the disease.
Can Liver Metastases Be Treated And If So How
One option, if there is disease restricted to the liver, is stereotactic radiation, which goes directly to the cancer cells. Ablation is another option, although rarely used, and it uses coldness, heat, or electrical currents to destroy the tumor. Chemotherapy, is the standard, and most common way that liver metastases are managed.
Read Also: Her2 Breast Cancer Symptoms
Can You Do Anything To Prevent Or Slow The Spread Of Breast Cancer
Like any type of cancer, there are factors that can put you at higher risk. For breast cancer, these include things like smoking, unhealthy diet, lack of exercise and not performing monthly self-breast exams. Its also important to make sure and get your annual mammogram for breast cancer screening.
Other risk factors can include using hormone-based prescriptions, how many children youve had in the past, getting older and at what age you got your period and went through menopause.
In some instances, you cant necessarily prevent breast cancer, but you can sometimes slow it down, stop it from spreading or reduce the size of the tumor, says Dr. Roesch. You can do this by taking your medications as directed, following through with treatments, going to your appointments and being involved in your cancer care.
Youre in control of taking your medication correctly, eating a healthy diet, participating in an exercise program and managing stress. All of these things can contribute to a stronger physical body and better mental attitude both of which can have a positive impact on your breast cancer diagnosis.
Read Also: Can Birth Control Cause Breast Cancer
Can Breast Cancer Recur At The Same Site
Yes, it can recur locally or regionally. Symptoms of a local recurrence are a new lump, a firm area, pulling or swelling at the site, redness, change in the shape of the nipple, and thickening near the scar. Symptoms of regional recurrence, which includes the underarm lymph nodes and upper chest area on the same side as the initial cancer, are a lump, swelling, or numbness of the arm, pain, and problems swallowing. These symptoms warrant prompt reporting to your physician.
Also Check: Breast Pain During Chemo
Stages Of Breast Cancer
The stage of breast cancer is based on the size and location of the tumor, as well as whether the cancer has spread beyond the part of the breast in which it originated. To determine the stage of breast cancer, healthcare professionals use a scale of stage 0 to stage 4.
Stage 0 breast cancers are isolated in one part of the breast, such as a duct or lobule, and show no sign of spreading into other tissue.
Stage 1 is typically localized, although further local growth or spread may cause the cancer to move into stage 2.
In stage 3, the cancer may be larger and has affected the lymph system. Stage 4 cancer has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes, and into other organs and tissues of the body.
In addition to stages, breast cancers are given grades based on the size, shape, and activity of the cells in the tumor. A higher-grade cancer means a greater percentage of cells look and act abnormal, or they no longer resemble normal, healthy cells.
On a scale of 1 to 3, with 3 being the most serious, TNBC is often labeled grade 3.
You May Like: Do Breast Cancer Tumors Hurt