Examples Using The Full Staging System
Because there are so many factors that go into stage grouping for breast cancer, it’s not possible to describe here every combination that might be included in each stage. The many different possible combinations mean that two women who have the same stage of breast cancer might have different factors that make up their stage.
Here are 3 examples of how all of the factors listed above are used to determine the pathologic breast cancer stage:
What Is Secondary Breast Cancer
Secondary breast cancer is when cancer cells from a cancer that started in the breast spread to other parts of the body. The cancer that started in the breast is called primary breast cancer.Secondary breast cancer is also called advanced breast cancer or metastatic breast cancer. The most common places for breast cancer to spread to are the:
Rarely, breast cancer may spread to other parts of the body, such as the bone marrow, ovaries or lining of the tummy which is called the peritoneum.
Breast cancer can spread to different parts of the body. This does not mean it will go to all these places.
Related Stories & Media
Also Check: Estrogen Negative Progesterone Positive Breast Cancer
Whats The Difference Between Metastatic And Recurring Breast Cancer
Recurrent cancer is cancer that comes back after your initial treatment. This can happen when treatment doesnt completely destroy all of the cancer cells in a tumor. As time passes, these remaining cancer cells can begin to grow into detectable tumors.
Like metastasis, recurrence can happen with almost every type of cancer. As well see below, some types of recurrent cancer can happen distantly and therefore also fall under the umbrella of metastatic cancer.
Breast cancer may recur locally, regionally, or distantly:
- Local recurring breast cancer occurs when a new tumor develops in the breast that was originally affected. If the breast has been removed, the tumor may grow in the chest wall or nearby skin.
- Regional recurring breast cancer happens in the same region as the original cancer. In the case of breast cancer, this may be the lymph nodes above the collarbone or in the armpit.
- Distant recurring breast cancer happens when cancer cells travel to a different part of the body. This new location is far away from the original cancer. When cancer recurs distantly, its considered metastatic cancer.
, the most common metastasis locations for breast cancer are the:
The frequency that breast cancer metastasizes to each of these sites can vary based off of the population studied. A in Scientific Reports included a group of 4,932 people with metastatic breast cancer. Researchers determined the metastatic site for each person and found that:
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Get Free Breast Cancer Screening
Stages Of Breast Cancer: Stage Iiic
Stage IIIc breast cancers basically involve tumors of any size with significant metastases to:-
- the lymph nodes behind the sternum
- lymph nodes under the arm
- the lymph nodes above or below the collarbone
The extent and depth of lymph node involvement make these patients unsuitable candidates for surgical treatment as a primary mode of therapy. Chemotherapy is the treatment of choice for women with stage IIIb and IIIc breast cancers.
However, up to 70% of patients with stage III breast cancers who have chemotherapy remain alive and disease-free after 7 years.
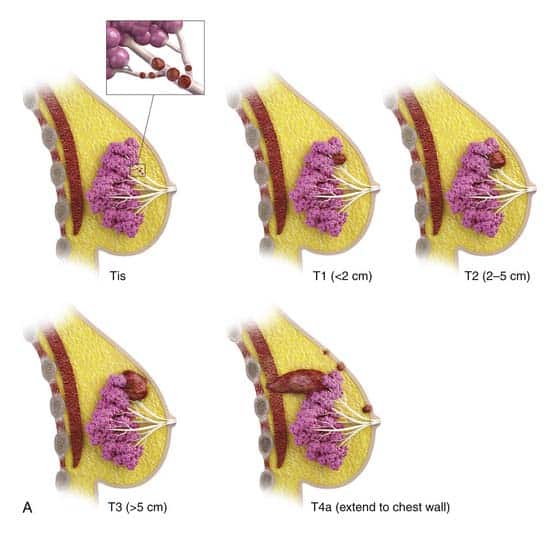
What Is Stage Ii Breast Cancer
Stage II describes cancer that is in a limited region of the breast but has grown larger. It reflects how many lymph nodes may contain cancer cells. This stage is divided into two subcategories.
Stage IIA is based on one of the following:
- Either there is no tumor in the breast or there is a breast tumor up to 20 millimeters , plus cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, but cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage IIB is based on one of these criteria:
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, along with cancer that has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
- A tumor in the breast is larger than 50 millimeters, but cancer has not spread to any lymph nodes.
You May Like: Can You Live With Stage 4 Breast Cancer
How Breast Cancer Spreads And Recurs
Breast cancer is frightening enough without the fear that it could travel to other parts of the body. Metastasis is the term for the spread of cancer. About 250,000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer and roughly 40,000 will die from the disease each year. When breast cancer is diagnosed in the early stages, many women go on to live cancer-free lives.
Yet for others, the disease is metastatic at the time of diagnosis or later recurs. It’s thought that metastatic disease is responsible for around 66% of the deaths related to breast cancer. How does breast cancer spread or recur?
How Many Lymph Nodes Does Stage 3c Cancer Affect
At this point, it has also spread into your breastbone or skin and affects up to nine lymph nodes. In stage 3C, the cancer may have spread to over 10 lymph nodes even if no tumor is present. The lymph nodes affected may be near your collarbone, underarm, or breastbone. Treatment options at stage 3 include:
You May Like: When Is Breast Cancer Awareness Day
Phase Iii Keynote 355 Trial
The much anticipated KEYNOTE-355 trial was presented at the inaugural virtual ASCO annual meeting in June 2020. This trial investigated pembrolizumab/chemo vs chemo in patients with treatment-naïve, metastatic TNBC. Patients were excluded if they had active brain metastases or recurrence of disease < 6 mo prior to primary treatment. PD-L1 was assessed with the IHC 22C3 pharmDx CPS assay in a central laboratory. The primary outcome measure was pre-defined as OS and PFS in the PD-L1 positive population and the ITT population. In this trial, a hierarchial statistical testing method involved statistical testing of OS and PFS in the CPS > 10 group initially, followed by CPS > 1 and then the ITT population. The trial included 566 patients in the chemotherapy/IO arm vs 281 in the chemotherapy arm. In patients with a CPS score of 10 or greater, the median PFS favoured pembrolizumab with a PFS of 9.6 mo vs 5.6 mo . In patients with a CPS score of 1 or greater, the median PFS favoured the pembrolizumab arm with a PFS of 7.6 mo vs 5.6 mo . This was not statistically significant. This was similar to the ITT population where the PFS was 7.5 mo in the pembrolizumab arm and 5.6 mo in the placebo arm . OS data is awaited. This progression free survival improvement led to accelerated FDA approval for pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy in the first-line setting in November of 2020.
Read Also: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Metastatic Breast Cancer Symptoms And Diagnosis
The symptoms of metastatic breast cancer can vary greatly depending on the location of the cancer. This section covers the symptoms of breast cancer that has spread to the bone, lung, brain, and liver, and the tests used to diagnose metastatic breast cancer.
Bone Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisThe most common symptom of breast cancer that has spread to the bone is a sudden, noticeable new pain. Breast cancer can spread to any bone, but most often spreads to the ribs, spine, pelvis, or the long bones in the arms and legs. Learn more.
Lung Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisWhen breast cancer moves into the lung, it often doesnt cause symptoms. If a lung metastasis does cause symptoms, they may include pain or discomfort in the lung, shortness of breath, persistent cough, and others. Learn more.
Brain Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisSymptoms of breast cancer that has spread to the brain can include headache, changes in speech or vision, memory problems, and others. Learn more.
Liver Metastasis: Symptoms and DiagnosisWhen breast cancer spreads to the liver, it often doesnt cause symptoms. If a liver metastasis does cause symptoms, they can include pain or discomfort in the mid-section, fatigue and weakness, weight loss or poor appetite, fever, and others. Learn more.
Don’t Miss: How Dangerous Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for breast cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the breast.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the breast to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
Dont Miss: Lymphatic Cancer Stage 3
What Can I Do To Reduce My Risk
If several members of your family have had breast or ovarian cancer, or one of your family members has a known BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, share this information with your doctor. Your doctor may refer you for genetic counseling. In men, mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes can increase the risk of breast cancer, high-grade prostate cancer, and pancreatic cancer.
If genetic testing shows that you have a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation, your doctor will explain what you should do to find cancer early, if you get it.
All men can lower their risk by keeping a healthy weight and exercising regularly.
As a neurosurgeon, Don knew everything in life and in surgery is all risk versus benefit. After discovering his family history of breast cancer, he took responsibility for his own health by getting tested and later having an elective mastectomy.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Side Effects Of Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
Breast Cancers Survival Is Influenced By Tumor Grade
Grade identifies the size and shape of the malignant breast cancer cells. At the event the breast cancer cells look very different than normal breast tissue cells, and random in appearance, they can be called, that was badly differentiated and described as âhigh gradeâ. Higher level breast cancer cells tend to really have a poorer prognosis.
Dont Miss: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Symptoms Of Metastatic Cancer
Metastatic cancer does not always cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, what they are like and how often you have them will depend on the size and location of the metastatic tumors. Some common signs of metastatic cancer include:
- pain and fractures, when cancer has spread to the bone
- headache, seizures, or dizziness, when cancer has spread to the brain
- shortness of breath, when cancer has spread to the lung
- jaundice or swelling in the belly, when cancer has spread to the liver
Read Also: Red Mill Baking Soda Cancer
Recommended Reading: Triple-negative Breast Cancer Symptoms
What Are The Symptoms
The most common symptoms of breast cancer in men are
- A lump or swelling in the breast.
- Redness or flaky skin in the breast.
- Irritation or dimpling of breast skin.
- Nipple discharge.
- Pulling in of the nipple or pain in the nipple area.
These symptoms can happen with other conditions that are not cancer. If you have any symptoms or changes, see your doctor right away.
What Factors Affect The Growth Of Breast Cancer Cells
A number of factors, such as age or having a history of hormone replacement therapy, can influence the growth rate of breast cancer cells. This is important when thinking about whether a breast cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or other organs, or has not spread at all. The type of breast cancer also matters because some can spread more quickly and do so with tumors that are still relatively small.
You May Like: Has Anne Hathaway Had Breast Cancer
How Having Metastatic From The Start Might Influence Treatment
There are some advantages for women diagnosed with de novo metastatic breast cancer compared to women who have progressed following an early breast cancer. The main advantage is that their cancer is treatment naïve, meaning it has not previously been exposed to any anti-cancer treatments and is therefore likely to be more responsive to treatment. There have been some reports of small numbers of women who may even be cured from metastatic breast cancer in this circumstance. In addition, there are more treatment options available than for those who have received previous treatment for early breast cancer who may have already used up some of their options.
The one positive was that my oncologist said that he more or less had an open book of treatments that he could offer me.
Another positive that women sometimes describe is that they can feel the cancer in their breast getting smaller once treatments starts. Mammograms and breast ultrasounds may be used as a way of checking that the cancer in the breast is responding to treatment. Many women find this reassuring, knowing that the treatment they are having is working for them.
What Is Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer is not a specific type of breast cancer. Its the most advanced stage of breast cancer.
Metastatic breast cancer is breast cancer that has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes to other parts of the body .
Although metastatic breast cancer has spread to another part of the body, its still breast cancer and treated as breast cancer.
For example, breast cancer that has spread to the bones is still breast cancer . So, its treated with breast cancer drugs, rather than treatments for a cancer that began in the bones.
Learn what Komen is doing to help people with metastatic breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: Can Stage 1 Breast Cancer Metastasis
How Does Cancer Start
Cancer begins when a normal breast cell undergoes a number of mutations in genes that control the growth of the cell. These mutations may occur over a long period of time, even decades, before a cancer cell forms. A cancer cell must divide on average 30 times before it forms a mass that can be felt in the breast.
What Is Metastatic Cancer
Metastatic cancer is cancer thats spread to a different part of the body than where it originated. You may also see metastatic cancer referred to as stage 4 cancer.
In some cases, the cancer may have already spread by the time of initial diagnosis. Other times, the cancer may spread after the initial treatment. For example, a person who has been treated for early-stage breast cancer may later be diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer.
Metastasis can occur with almost every type of cancer and is considered advanced-stage cancer. Cancer metastasis may occur months to years after initial breast cancer treatment.
Theres also a type of metastatic cancer called oligometastatic cancer. This is where theres only a few small areas of metastatic cancer. Because this type of metastatic cancer is only found in a few locations, researchers hope it will be
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Research And Treatment Impact Factor
What To Expect When Taking Keytruda
Keytruda is given as a 30-minute infusion, every 3 or 6 weeks, depending on the dose given at each infusion. The Keytruda infusion is given before the chemotherapy infusion. If you are receiving Keytruda for metastatic or unresectable locally advanced triple-negative breast cancer, you may continue treatment with Keytruda and chemotherapy for up to 2 years, unless the cancer grows or you develop unacceptable side effects.
Women who are pregnant or planning to get pregnant should not be given Keytruda. Keytruda can cause embryo death and birth defects. Its important that you dont get pregnant while youre getting Keytruda you must use effective birth control.
Noninvasive Or Preinvasive Breast Cancers

Noninvasive cancers remain confined to the primary site of development, but are always treated, because it is not possible to know if they will become invasive or not. Noninvasive breast cancers include:
- Ductal carcinoma in situ : Abnormal cells in the milk duct
- Lobular carcinoma in situ : Abnormal cells in the lobules
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Aggressive Breast Cancer
Concluding Remarks On Current And Future Perspectives On Tnbc Metastasis Therapy
Due to their molecular heterogeneity, there are no drugs that can target the entire spectrum of TNBC tumors and each subtype is vulnerable to specific therapeutic approaches. Despite the lack of FDA-approved targeted therapies for TNBC to date, ongoing clinical trials are assessing the efficacy of single or combinatorial approaches that tackle different TNBC molecular alterations. Up to 20% of TNBC have been associated with germ-line mutations in BRCA1 . TNBC tumors with loss of function of BRCA1 or BRCA2 are sensitive to poly polymerase inhibitors and alkylating agents that induce DNA double-strand breaks . Olaparib has been the most successful PARP inhibitor against BRCA-mutated TNBC, inducing partial responses in 54% of patients when administered as a single agent and an overall response rate of 88% when combined with carboplatin . Anti-androgens as well as FGFR inhibitors have been tested in clinical trials against TNBCs that are androgen receptor-positive or harbor FGFR amplification, respectively . Gamma-secretase inhibitors that block the NOTCH pathway are currently in clinical trials for TNBC patients with upregulated NOTCH signaling . All together clinical trials have shown that each agent alone provides small or no benefit in TNBC patients suggesting that further effort is needed to discover novel targets of TNBC and to identify each patients molecular profile that will lead to a more individualized treatment.