How Does Breast Cancer Spread
Breast cancer can invade and grow into the tissue surrounding the breast or it can travel to other parts of the body and form a new tumor there. Nearly all types of cancer have the ability to spread , but whether or not it will spread is often linked to what type of breast cancer you have.
Breast cancer can spread in three ways:
Every cancer is different, but the type of breast cancer you have typically plays a role in how aggressive or slow moving it is and where its most likely to spread, says Dr. Roesch.
Emma D Wrenn And Kevin J Cheung
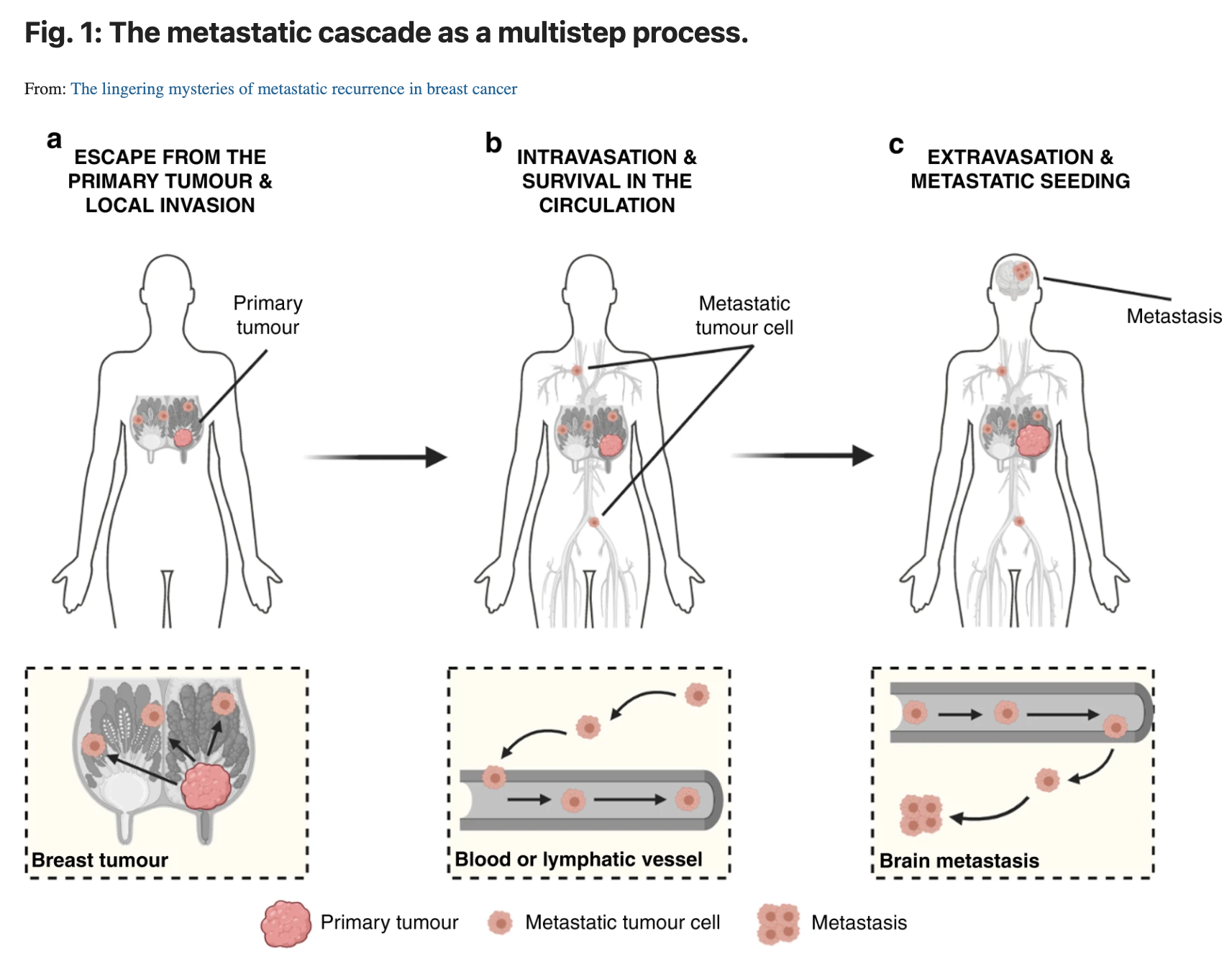
A large number of tumor cells reaching distant sites will die and never grow into a clinically detectable metastasis . Disseminated tumor cells encounter inhospitable stromal matrices, cell types, and paracrine signals different from their organ of origin. In addition, they are actively eliminated by immune cells, such as natural killer and T-cells. Diverse mechanisms have been described that enable tumor cells to overcome these barriers: entry into a stem cell-like state, epithelial-to-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-to-epithelial transitions, genetic mutation, and co-option of the native microenvironment for example . Here, we focus on an emerging mechanism by which cancer cells increase their chance of successmetastasizing as cohesive clusters of cells, also known as collective metastasis.
Fig. 2
Clusters resist programmed cell death. Tumor cell clusters have increased survival at metastatic sites through several mechanisms including depletion of reactive oxygen species, resistance to NK cell killing, and pro-survival signals transduced downstream of cellcell adhesion
What Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Metastatic Breast Cancer
If youve been diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer, ask your provider:
- What are my treatment options?
- What is my prognosis?
- What side effects can I expect?
- Will complementary therapy help me feel better?
- What if I want to stop treatment?
- How can I feel my best during treatment?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Metastatic breast cancer is advanced breast cancer. Providers classify it as stage 4 breast cancer. It happens when cancer cells, often left behind after previous breast cancer treatment, start to spread to other parts of the body. While there is no cure for metastatic breast cancer, treatment can prolong your life and help you feel better. There are many medications available, so if one treatment isnt working, your care team can try a different approach. If you notice any symptoms or dont feel your best, especially if youve undergone breast cancer treatment in the past, talk to your healthcare provider.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 04/14/2021.
References
Also Check: What Age Does Breast Cancer Occur
Symptoms Of Metastasis May Vary Depending On Where The Cancer Has Spread To
Here are some symptoms that vary by locations commonly associated with breast cancer metastasis.
Metastasis in the bone may cause:
- Severe, progressive pain
- Bones that are more easily fractured or broken
Metastasis to the brain may cause:
- Persistent, progressively worsening headache or pressure to the head
- Vision disturbances
- Behavioral changes or personality changes
Metastasis to the liver may cause:
- Jaundice
- Abnormally high enzymes in the liver
- Abdominal pain, appetite loss, nausea, and vomiting
Metastasis to the lungs may cause:
- Chronic cough or inability to get a full breath
- Abnormal chest X-ray
- Chest pain
- Other nonspecific systemic symptoms of metastatic breast cancer can include fatigue, weight loss, and poor appetite, but its important to remember these can also be caused by medication or depression.
If you notice these symptoms, be sure you talk with your physician. They could be important for getting the treatment you need.
Interested in learning more? i3Health is hosting an upcoming webinar Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Applying Treatment Advances to Personalized Care. Learn more here.
Breast Cancer Is A Heterogeneous Disease

Based on the presence or absence of the oestrogen receptor and progesterone receptor , and the expression and amplification of the human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 , breast cancer can be divided into three clinical subtypes: hormone-receptor -positive , HER2-positive and triple-negative ., In the United States, 71% of breast cancers are HR+, 17% are HER2+ and 12% are TN. Following the discovery of five intrinsic molecular subgroups of the disease based on a 50-gene expression classifier luminal A, luminal B, HER2-enriched, basal-like and normal-likeit became apparent that a large degree of unappreciated molecular heterogeneity exists across and within each subtype of breast cancer. While TN and HER2+ patients often present with basal-like and HER2-enriched cancers, respectively, HR+ women are usually diagnosed with luminal A or luminal B tumours. However, despite sharing some common traits, luminal A cancers are generally ER+, PR high and Ki67 low, resulting in low-grade, slow-proliferating neoplasms, whereas luminal B tumours are typically ER+, PR variable and Ki67 variable, translating into more aggressive cancers with a higher proliferative rate.
Read Also: What Type Of Breast Cancer Is Genetic
Metastatic Ovarian Cancer Symptoms
When ovarian cancer is in the early stages, cancer cells are only located within the pelvis. A persons symptoms may include pain in their pelvis or abdomen, bloating, and bladder symptoms such as needing to urinate often.
As ovarian cancer spreads to other areas, additional symptoms may appear. If cancer has metastasized to organs in the abdomen, a person may experience nausea, vomiting, constipation, back pain, and swelling in the abdomen from ascites .
Other symptoms may depend on the exact location of the cancer:
- Liver Abdominal swelling or jaundice
- Lung Shortness of breath
- Brain Headache, dizziness, or seizures
- Bones Pain or fractures
- Breast Mass in breast or underarm area
If you have been diagnosed with ovarian cancer and are noticing health changes in another part of your body, talk to your oncologist.
Whats The Difference Between Metastatic And Recurring Breast Cancer
Recurrent cancer is cancer that comes back after your initial treatment. This can happen when treatment doesnt completely destroy all of the cancer cells in a tumor. As time passes, these remaining cancer cells can begin to grow into detectable tumors.
Like metastasis, recurrence can happen with almost every type of cancer. As well see below, some types of recurrent cancer can happen distantly and therefore also fall under the umbrella of metastatic cancer.
Breast cancer may recur locally, regionally, or distantly:
- Local recurring breast cancer occurs when a new tumor develops in the breast that was originally affected. If the breast has been removed, the tumor may grow in the chest wall or nearby skin.
- Regional recurring breast cancer happens in the same region as the original cancer. In the case of breast cancer, this may be the lymph nodes above the collarbone or in the armpit.
- Distant recurring breast cancer happens when cancer cells travel to a different part of the body. This new location is far away from the original cancer. When cancer recurs distantly, its considered metastatic cancer.
, the most common metastasis locations for breast cancer are the:
- bones
- liver
- brain
The frequency that breast cancer metastasizes to each of these sites can vary based off of the population studied. A in Scientific Reports included a group of 4,932 people with metastatic breast cancer. Researchers determined the metastatic site for each person and found that:
Recommended Reading: Who Gets Metastatic Breast Cancer
Treating Metastatic Breast Cancer
If you receive a diagnosis of breast cancer thats spread to your colon, your doctor will likely order additional tests to see whether the cancer has spread to other parts of your body.
Once you know exactly whats going on, you and your doctor can discuss the best options for treatment. This may include one or more of the following therapies.
The Wide Window Of Relapse In Breast Cancer
In contrast with other solid tumours in which metastatic recurrence can occur within a few weeks or a few years following diagnosis, breast cancer is characterised by a wide window of relapse, spanning months to decades after surgery. The basis of this peculiar pattern of recurrence is still elusive, but is likely to be linked to the aforementioned molecular differences underlying each subgroup, with basal-like and HER2-enriched patients experiencing early relapses , as opposed to patients with luminal cancers characterised by a more favourable prognosis.,, Nonetheless, patients with luminal B tumours tend to have shorter survival times than luminal A patients. In addition to the contribution of the molecular subtype of the primary tumour, the risk and timing of recurrence is also influenced by other tumour-related factors that constitute the pillars of the TNM classification system: tumour size and spread , regional lymph node involvement and the presence of distant metastasis . Based on the premise that the chance of survival is intimately linked to the anatomic extent of the disease, the TNM staging system stratifies cancer patients at diagnosis into four stageswith patients with Stage I disease having a much better prognosis as opposed to patients with Stage IV diseasethus representing the gold standard tool for prognostication.
Recommended Reading: Is Breast Cancer Curable At Stage 3
Don’t Miss: What Fruit Is Good For Breast Cancer
What Are Metastatic And Recurrent Breast Cancer
Breast cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow out of control in one or both breasts.
- Metastatic breast cancer means that cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Recurrent breast cancer means that cancer has come back in or near the original site or in another part of the body.
For most women who have had breast cancer, their greatest fear is that the cancer will come back or spread. Finding out that this has happened can turn your world upside down. But there is hope. Some recurrent breast cancers can be successfully treated. Other recurrent breast cancers and metastatic breast cancer usually can’t be cured. But with treatment, some women live for many years.
Progression During Hormone Therapy
For hormone receptor-positive cancers that were being treated with hormone therapy, switching to another type of hormone therapy sometimes helps. For example, if either letrozole or anastrozole were given, using exemestane, possibly with everolimus , may be an option. Another option might be using fulvestrant or a different aromatase inhibitor, along with a CDK inhibitor. If the cancer has a PIK3CA mutation and has grown while being treated with an aromatase inhibitor, fulvestrant with alpelisib might be considered. If the cancer is no longer responding to any hormone drugs, chemotherapy immunotherapy, or PARP inhibitors might be options depending on specific features of the cancer or any gene changes that might be present.
Don’t Miss: How To Examine Your Breast For Cancer
Where Does Breast Cancer Metastasize To
Sometimes, breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body. This does not always happen, but when it does, it is known as metastatic breast cancer.
Metastatic breast cancer is treated differently than localized breast cancer. As a result, oncologists typically check for evidence of metastasis during the diagnostic/staging process. Additionally, breast cancer can spread after a patient has been diagnosed. To watch for potential signs of metastasis, patients are typically scheduled for frequent imaging scans during and after treatment.
Can Earlier Detection Of Recurrence Improve Breast Cancer Outcomes
The risk of metastatic relapse weighs heavily on the minds of patients, physicians and caregivers for years, sometimes decades, after treatment of the primary tumour is complete. Nearly 17 million cancer survivors are living in the United States, 3.9 million of whom are breast cancer survivors, and repeated monitoring for cancer recurrence in these individuals presents a significant challenge to healthcare delivery systems. For breast cancer patients, current American Society of Clinical Oncology and National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines limit follow-up care to mammography, medical history and physical exam, stating that in the absence of clinical signs and symptoms suggestive of recurrent disease, there is no indication for laboratory or imaging studies for metastases screening., Despite these guidelines, however, many patients receive high-cost imaging analysis and tumour marker blood tests during routine follow-up exams, exposing them to radiation and increasing healthcare costs.,,, So, what has led to the current precarious balance between the desire to detect recurrence early and clinical guidelines that limit the use of diagnostic tests?
Table 1 Exploiting tumour dormancy as a window of therapeutic opportunity to target MRD.
Also Check: What Happens When Breast Cancer Spreads To The Lungs
Talking To Family And Friends About Metastatic Breast Cancer
Telling your loved ones about a recurrence of breast cancer may be more difficult than it was telling them about the original diagnosis. If this is a first diagnosis and its metastatic, telling friends and family can also be extremely challenging. You may be concerned about upsetting your family and friends or worried about how they will react. Even after youve shared the news, you may find it difficult to communicate openly at times. Sometimes its uncomfortable to ask for help, answer questions about how youre doing, or tell well-meaning relatives and friends that you need some time and space for yourself.
The most important thing to keep in mind is that youre always in control of the conversation. Its entirely up to you how much information you want to share.
Advanced Cancer That Progresses During Treatment
Treatment for advanced breast cancer can often shrink the cancer or slow its growth , but after a time, it tends to stop working. Further treatment options at this point depend on several factors, including previous treatments, where the cancer is located, a woman’s menopause status, general health, desire to continue getting treatment, and whether the hormone receptor status and HER2 status have changed on the cancer cells.
Read Also: How To Support Breast Cancer
What You Need To Know
- Metastatic breast cancer is serious, but the diagnosis does not always mean the end of life.
- The most common place for breast cancer to spread is to the bones. The liver and the lungs are other areas where breast cancer can metastasize.
- In about 15% of cases, metastatic breast cancer can be detected at the time of diagnosis. It can affect people who had breast cancer without seeking treatments, patients with aggressive breast cancer types and those with breast cancer not detected by screening.
Signs That Breast Cancer Has Spread To The Bone
Most aches and pains arent cancer, stresses Huston. But its important to keep an open and honest dialogue with your doctor about any unusual or persistent discomfort you may be having. He or she can determine if getting images is appropriate to rule out bone metastasis. Here are the symptoms of bone metastasis to look out for:
If you report any of the above symptoms to your doctor, he or she may want to do a thorough physical exam, blood tests, and a bone scan to check for bone metastasis. Depending on the results and where or how severe the bone pain is, he or she may also order an X-ray, PET scan, or CT scan. In some cases, a tissue biopsy is also done to confirm the diagnosis.
Also Check: How Often Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed
The Extrinsic Effect Of Targeted Therapy
Fig. 4: The effects of cell-extrinsic and cell-intrinsic determinants in dictating breast cancer outcomes.
Part I The journey of a breast cancer patient from the development of undetectable disease and its clinical discovery , through its surgical removal and adjuvant ET , to metastatic relapse and death . The presence of tumour lesions across the body is indicated by starsthe smaller referring to the clinically undetectable ones , the bigger ones to the clinically detectable ones . Part II The development of an HR+ breast tumour lesion in the breast , comprising a mixture of ER+/PR+ and ER/PR cells . DTC escape from the primary site can occur early and/or late during tumorigenesis , although the HR phenotype of DTCs at these stages is often unclear. Bones, lungs and liver are represented as common secondary sites for breast cancer metastases, albeit the sequential patterns of DTC spread among these organs are still elusive . Targeted treatment for HR+ breast cancer patients relies on adjuvant ET. Several mechanisms of ET resistance cytostasis, ESR1 mutations and HR function regulationcontribute to DTC outgrowth. DTC disseminated tumour cell, ER oestrogen receptor, ET endocrine therapy, HR hormone receptor, PR progesterone receptor. Figure created with BioRender.com.
Where Can Breast Cancer Spread
The most common places for breast cancer to spread to are the lymph nodes, bone, liver, lungs and brain. The symptoms you may experience will depend on where in the body the cancer has spread to. You might not have all of the symptoms mentioned here.
Remember other conditions can cause these symptoms. They don’t necessarily mean that you have cancer that has spread. But if you have symptoms that you are worried about, discuss them with your GP, cancer specialist, or breast care nurse so that you can be checked.
Also Check: Can Breast Cancer Return After Mastectomy
How Do Breast Cancers Spread
Cancer cells break away from the primary tumor, entering the bloodstream or the lymphatic system. As large vessels narrow, cancer cells stop traveling and lodge themselves in a new area. Then they begin dividing and moving into surrounding tissue. The cancer cells take over the new area, crowding out healthy cells and forming a new tumor. Cancer cells are insidious because the new tumor can set up its own network of blood vessels to obtain nutrients for growth and further spread.
Association Of Clinicopathologic Factors And The Sites Of Distant Relapse
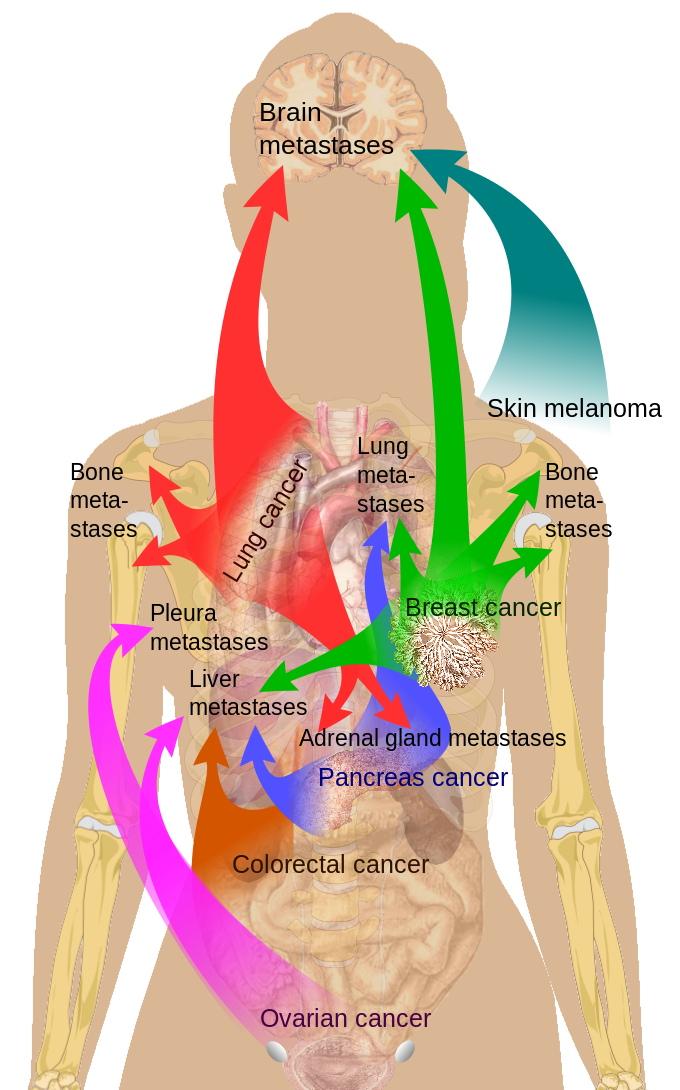
The association of the five most common sites with clinicopathologic factors was examined, including the patients age at diagnosis, race, tumor type, and histologic grade. None of these variables was significantly associated with metastasis to bone, liver, lung, or pleura, while the age at diagnosis had a significant negative impact for CNS relapse by univariate analysis and multivariate analysis . Furthermore, a high histologic grade was significantly correlated to CNS metastasis by univariate analysis, although it was not an independent factor by multivariate analysis.
Recommended Reading: Do Phytoestrogens Cause Breast Cancer