Should I Be Tested For Genetic Mutations
At-risk families can take blood tests to look for mutations in these genes.
You may want to discuss genetic testing with your doctor if:
- You have two or more blood relatives â mother, sister, aunt, cousin, or daughter â with premenopausal breast cancer or ovarian cancer diagnosed at any age.
- You were diagnosed with breast cancer, especially before menopause, and have a blood relative with breast or ovarian cancer.
- You were diagnosed with ovarian cancer and you have blood relatives who have had ovarian or breast cancer.
- A male in your family has or had breast cancer.
- You or a family member has been diagnosed with bilateral breast cancer .
- You were diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer before the age of 60.
- You are related to someone who has a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation.
- You are of Ashkenazi Jewish descent and have had breast or ovarian cancer or have blood relatives who have had breast or ovarian cancer.
- You may also want to consider testing if you are a Black woman. Black women are just as likely to have hereditary breast cancer mutations as white women, but tend not to get tested as frequently, putting you at a higher risk of the cancer going undetected.
How Common Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in the United States, except for skin cancers. It is about 30% of all new female cancers each year.
The American Cancer Society’s estimates for breast cancer in the United States for 2022 are:
- About 287,850 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed in women.
- About 51,400 new cases of ductal carcinoma in situ will be diagnosed.
- About 43,250 women will die from breast cancer.
Breast cancer mainly occurs in middle-aged and older women. The median age at the time of breast cancer diagnosis is 62. This means half of the women who developed breast cancer are 62 years of age or younger when they are diagnosed. A very small number of women diagnosed with breast cancer are younger than 45.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
There are many different signs and symptoms of breast cancer, so regularly checking your breasts for anything different or new is important.
The earlier breast cancer is diagnosed, the better the chance of successful treatment. Getting to know what your breasts look and feel like normally means its easier to spot any unusual changes and check them with your doctor. Common breast cancer signs and symptoms include:
- A lump or swelling in the breast, upper chest or armpit. You might feel the lump, but not see it.
- Changes in the size or shape of the breast
- A change in skin texture i.e. puckering or dimpling of the skin
- A change in the colour of the breast – the breast may look red or inflamed
- Rash, crusting or changes to the nipple
- Any unusual discharge from either nipple
Over a third of women in the UK do not check their breasts regularly for potential signs of breast cancer.
According to a YouGov survey commissioned by Breast Cancer Now, a third of those who do check their breasts for possible signs and symptoms dont feel confident that they would notice a change.
Asked what stops or prevents them from checking their breasts more regularly, over half forgetting to check, over a third not being in the habit of checking, a fifth not feeling confident in checking their breasts, not knowing how to check , not knowing what to look for and being worried about finding a new or unusual change .
Some factors are outside our control, including:
Read Also: How Do I Self Check For Breast Cancer
How Common Is Breast Cancer Five Facts You Need To Know
When it comes to staying proactive about breast cancer, education is the first step. Its important to know the risks factors so that you can stay on top of your health.
#1: Breast Cancer Becomes More Common With Age
According to the most recent SEER results from the National Cancer Institute, this is how a womans breast cancer risk changes by decade:
- Age 30 1 in 227
- Age 40 1 in 68
- Age 50 1 in 42
- Age 60 1 in 28
- Age 70 1 in 26
Its important to receive check-ups such as mammograms with your doctor at regular intervals to keep up with any changes in breast tissue.
#2: Breast Cancer is More Common with Certain Genetic Factors
Chances are, you know someone who has developed breast cancer. In fact, 3.1 million women in the U.S. alone have a history of breast cancer. If a close family member has been diagnosed with breast cancer, its important to be aware of your genetic risk factors.
For example, your chance of getting breast cancer nearly doubles if you have a sister, daughter, or mother who has been diagnosed. According to the latest research, mutations in certain genes like the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes can increase your chances significantly. Women with the BRCA1 gene have around a 72percent chance of developing cancer, while those with the BRCA2 gene have a 69percent lifetime risk.
#3: Breast Cancer Affects Men, Too
#4: Certain Lifestyle Factors Increase Risk
#5: Breast Cancer is as Common as Ever But Survival Rates are Increasing
Genetic Testing For Breast Cancer Genes
Genetic tests can tell you if you have an inherited gene mutation for breast cancer. You can have a test that looks for an individual gene abnormality or a larger panel test that examines several genes at one time. Experts usually recommend gene testing if you have breast cancer or strong risk factors, such as a family history of hereditary cancers. Talk to your doctor if youâd like to learn more about genetic testing.
Also Check: Metastatic Breast Cancer To Lungs
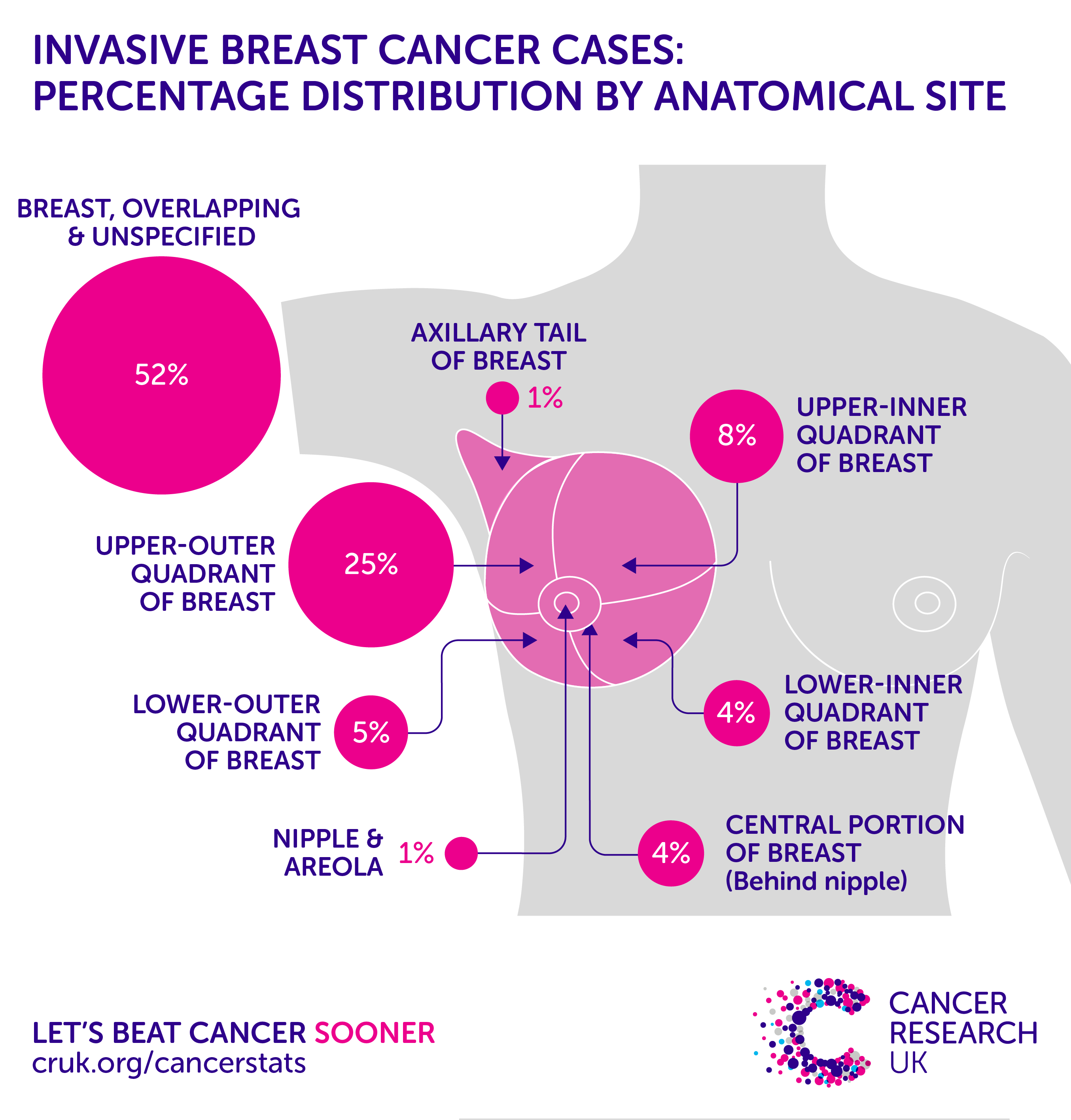
Where Breast Cancer Starts
Breast cancers can start from different parts of the breast. The breast is an organ that sits on top of the upper ribs and chest muscles. There is a left and right breast and each one has mainly glands, ducts, and fatty tissue. In women, the breast makes and delivers milk to feed newborns and infants. The amount of fatty tissue in the breast determines the size of each breast.
The breast has different parts:
- Lobules are the glands that make breast milk. Cancers that start here are called lobular cancers.
- Ducts are small canals that come out from the lobules and carry the milk to the nipple. This is the most common place for breast cancer to start. Cancers that start here are called ductal cancers.
- The nipple is the opening in the skin of the breast where the ducts come together and turn into larger ducts so the milk can leave the breast. The nipple is surrounded by slightly darker thicker skin called the areola. A less common type of breast cancer called Paget disease of the breast can start in the nipple.
- The fat and connective tissue surround the ducts and lobules and help keep them in place. A less common type of breast cancer called phyllodes tumor can start in the stroma.
- Blood vessels and lymph vessels are also found in each breast. Angiosarcoma is a less common type of breast cancer that can start in the lining of these vessels. The lymph system is described below.
To learn more, see Types of Breast Cancer.
Checking For Ductal Breast Cancer In Lymph Nodes
The goal of invasive ductal carcinoma treatment is to get the cancer out of the breast. But we also may need to remove lymph nodes if the cancer has spread there, Wright explains.
Your lymph nodes are part of your immune system. Lymph fluid from the breast drains into the axillary lymph nodes. The number and location of axillary lymph nodes may be different from person to person.
A sentinel lymph node biopsy is a test that can help your doctor determine if removing lymph nodes may be part of your cancer surgery.
The sentinel lymph node is where cancer from invasive ductal carcinoma is likely to show up first. Your doctor can identify the sentinel lymph node by injecting dye into the breast and seeing which node takes up the dye first: This is the sentinel. A sample of tissue from this node can reveal if cancer has spread there.
If theres no cancer in the sentinel node, the other nodes are OK and dont need to be removed, says Wright. If theres a small amount of cancer present, well leave nodes in place and treat the area with radiation or use chemotherapy.
If we see a lot of cancer in the lymph nodes or if four or more lymph nodes are affected, we perform an axillary lymph node dissection: surgery to remove the nodes.
You May Like: Ca 125 Breast Cancer Blood Test
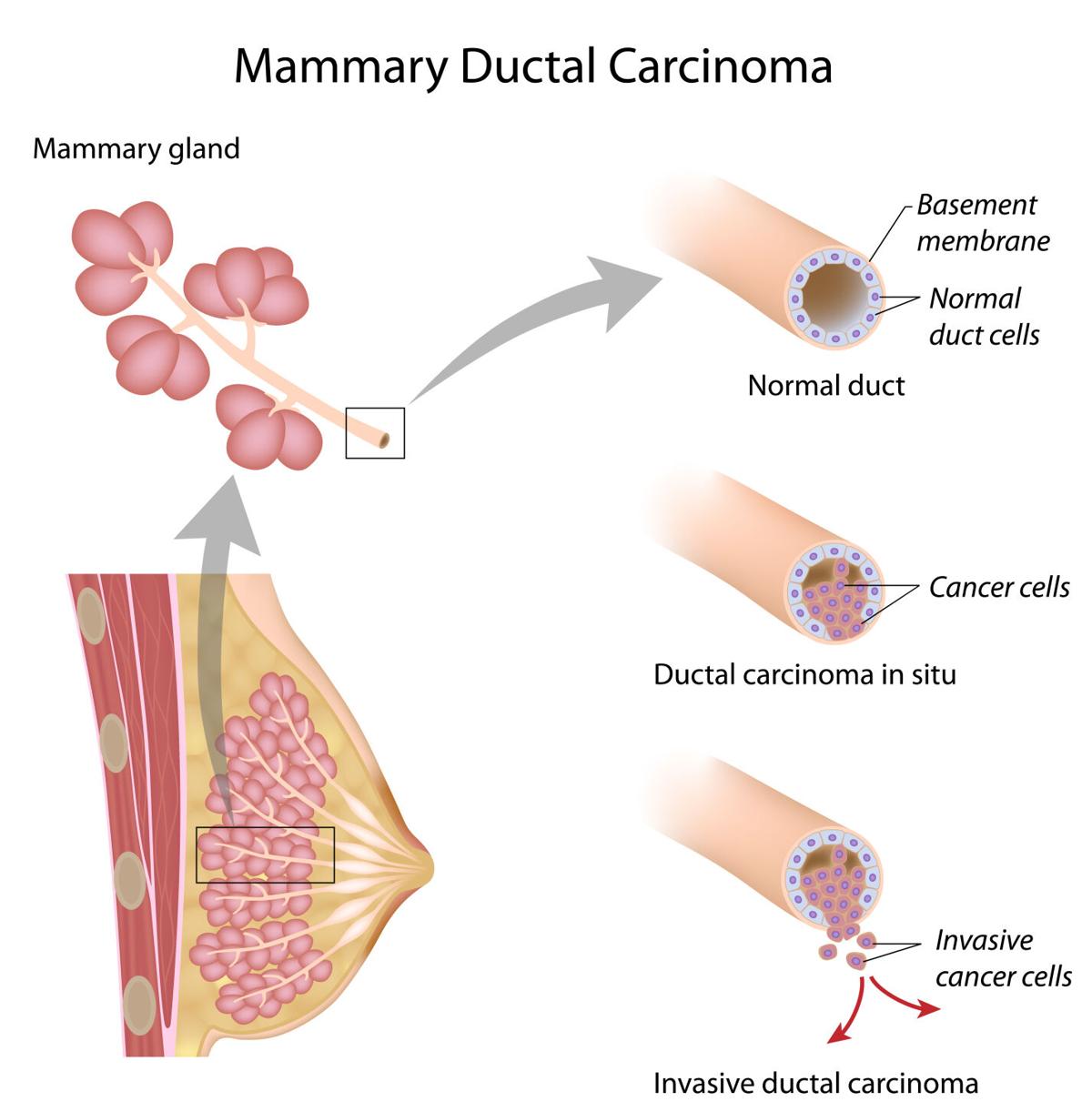
Noninvasive Types Of Breast Cancer
In situ breast cancer cells are non-invasive and remain in a particular location of the breast, without spreading to surrounding tissue, lobules or ducts.
Breast cancer that does not spread beyond the milk ducts or lobules is known as in situ. The two types of in situ cancers are ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma.
Ductal carcinoma in situ
About 20 percent of newly diagnosed breast cancers are classified as DCIS, according to the ACS. DCIS starts out as a mass that grows in a milk duct, which carries milk from the lobules, or glands, to the nipple. A DCIS hasnt spread to other parts of the body. Over time, chances increase for the mass to break through the ductal walls into the surrounding tissue and fat of the breast. With advances in diagnostics and treatments, however, most patients treated for DCIS, also called stage 0 breast cancer, have positive outcomes.
Lobular carcinoma in situ
An LCIS is technically not considered cancer, but rather a change in the breast. In the breast are tens of thousands of tiny clusters of lobules to produce breast milk. Cells that resemble cancer cells may grow inside these lobules. LCIS tends to remain there and not spread. However, having LCIS puts you at an increased risk for invasive breast cancer, so your care team may want to monitor you in order to promptly address any changes.
Breast cancer treatment: The care you need is one call away
Breast Cancer: What Are The Stages
The staging process for cancer involves determining the severity of the disease by examining how much cancer is present and where it has spread. Factors like tumor size and whether it has spread to lymph nodes or other body parts are the basis of this process.
Your doctor can carry out staging either before or after surgery. Staging before surgery is a clinical stage, while staging conducted after surgery is called the pathologic stage.
Here are the different stages of breast cancer:
You May Like: How Do They Do Radiation For Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Breast cancer survival rates vary widely based on many factors.
Two of the most important factors are the type of cancer you have and the stage of the cancer at the time you receive a diagnosis. Other factors that may play a role include:
shows theres a higher mortality rate in People of Color with breast cancer diagnoses compared with white people. One reason for this may be healthcare disparities.
The good news is breast cancer survival rates are improving.
According to the ACS , in 1975, the 5-year survival rate for breast cancer in women was 75.2 percent. But for women diagnosed between 2008 and 2014, it was 90.6 percent.
The 5-year survival rates for breast cancer differ depending on the stage at diagnosis. They range from 99 percent for localized early stage cancers to 27 percent for advanced metastatic cancers.
Breast Cancer Incidence By Sex And Uk Country
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases .
In females in the UK, breast cancer is the most common cancer . In males in the UK, it is not among the 20 most common cancers .
99% of breast cancer cases in the UK are in females, and 1% are in males.
Breast cancer incidence rates rate ) for persons are similar to the UK average in all the UK constituent countries.
Breast Cancer , Average Number of New Cases Per Year, Crude and European Age-Standardised Incidence Rates per 100,000 Population, UK, 2016-2018
You May Like: How To Self Test For Breast Cancer
Fact : Men Get Breast Cancer Too A Mans Lifetime Risk Of Breast Cancer Is About 1 In 1000
Many people do not realise that men have breast tissue and that they can develop breast cancer. But breast cancer is less common in men because their breast duct cells are less developed than those of women and because they normally have lower levels of female hormones that affect the growth of breast cells.
Where Does Cancer Spread To First
In metastasis, cancer cells break away from where they first formed and form new tumors in other parts of the body.Where Cancer Spreads.Cancer TypeMain Sites of MetastasisBladderBone, liver, lungBreastBone, brain, liver, lungColonLiver, lung, peritoneumKidneyAdrenal gland, bone, brain, liver, lung9 more rowsNov 10, 2020
Also Check: Can An Oval Breast Mass Be Cancer
Living With Breast Cancer
Being diagnosed with breast cancer can affect daily life in many ways, depending on what stage it’s at and the treatment you will have.
How people cope with the diagnosis and treatment varies from person to person. There are several forms of support available, if you need it.
Forms of support may include:
- family and friends, who can be a powerful support system
- communicating with other people in the same situation
- finding out as much as possible about your condition
- not trying to do too much or overexerting yourself
- making time for yourself
Find out more about living with breast cancer.
What Is A Normal Breast
No breast is typical. What is normal for you may not be normal for another woman. Most women say their breasts feel lumpy or uneven. The way your breasts look and feel can be affected by getting your period, having children, losing or gaining weight, and taking certain medications. Breasts also tend to change as you age. For more information, see the National Cancer Institutes Breast Changes and Conditions.
Recommended Reading: Free Bras For Breast Cancer Survivors
Kinds Of Breast Cancer
The most common kinds of breast cancer are
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells begin in the ducts and then grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells begin in the lobules and then spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
There are several other less common kinds of breast cancer, such as Pagets disease, medullary, mucinous, and inflammatory breast cancer.
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a breast disease that may lead to invasive breast cancer. The cancer cells are only in the lining of the ducts, and have not spread to other tissues in the breast.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
We take your privacy seriously. You can review and change the way we collect information below.
What You Can Do: Self
When it comes to breast cancer, early detection makes a significant difference. There are several steps you can take to detect breast changes, and also some breast care services you should seek to stay proactive.
- Know signs & symptoms. Though not everyone who gets breast cancer experiences any signs or symptoms, its important to follow-up with any changes in nipple discharge, breast pain or sensation, or changes in the texture or appearance of breasts.
- Self-exams. Its extremely important to perform a monthly breast self-exam. In fact, for 40 percent of cancers that are diagnosed, treatment was sought because a woman felt a lump during a self-exam.
- Clinical breast exam. Though its important to do a monthly exam at home, its also pivotal to get an annual clinical breast exam from a health professional. A doctor or nurse might notice something that went undetected during a home exam.
- Mammogram. With a specialized x-ray called a mammogram, your breast health team can detect abnormalities in breast tissue. The National Breast Cancer Foundation recommends that women who are 40 or older should have mammograms every one or two years. For younger women, you should talk to your doctor about any genetic or lifestyle factors to come up with a personalized mammogram plan.
Read Also: What To Do If Diagnosed With Breast Cancer
What Do Lumps In My Breast Mean
Many conditions can cause lumps in the breast, including cancer. But most breast lumps are caused by other medical conditions. The two most common causes of breast lumps are fibrocystic breast condition and cysts. Fibrocystic condition causes noncancerous changes in the breast that can make them lumpy, tender, and sore. Cysts are small fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the breast.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
We take your privacy seriously. You can review and change the way we collect information below.
These cookies allow us to count visits and traffic sources so we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to know which pages are the most and least popular and see how visitors move around the site. All information these cookies collect is aggregated and therefore anonymous. If you do not allow these cookies we will not know when you have visited our site, and will not be able to monitor its performance.