How Do I Do A Breast Self
If you choose to do one, follow these steps:
In the mirror:
In the shower:
Lying down:
Limited Arm And Shoulder Movement
You might also have limited movement in your arm and shoulder after surgery. This is more common after ALND than SLNB. Your doctor may advise exercises to help keep you from having permanent problems .
Some women notice a rope-like structure that begins under the arm and can extend down toward the elbow. This is sometimes called axillary web syndrome or lymphatic cording. It is more common after ALND than SLNB. Symptoms may not appear for weeks or even months after surgery. It can cause pain and limit movement of the arm and shoulder. This often goes away without treatment, although some women may find physical therapy helpful.
Breast Cancer Screenings In The Us
The United States Preventative Services Task Force recommends American women aged between 50 years old and 74 years old have a mammogram every two years.
Similarly, in the US breast screenings are done via mammogram. However, for those who are at a high risk of getting breast cancer, because of family history or previous health issues, an MRI may be used alongside a mammogram.
Book an appointment at your doctor’s office for your screening. The CBD reports most health insurance companies are required to cover screening mammograms for women. Check your policy and get booked in!
If you’re concerned about any changes to your breasts, contact your doctor for further advice.
For more information about breast cancer and further support see:
You May Like: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Screenings In The Uk
In the UK, women are offered a breast cancer screening when they turn 50 years old until their 71st birthday and are invited every three years. The NHS says if women are over 71 years old, they will no longer receive screening invitations but can still request a breast screening.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE
At woman& home we want to champion women’s health. For relatable, practical, and honest advice on topics that affect women, take a look at our guides to:
The screening involves taking a mammogram of each breast one at a time at different angles. During the screening, your breast will be placed in an X-ray machine and gently compressed with a plate.
You’ll receive your results in a letter to your home address within two weeks. If your screening showed something abnormal, you’ll be invited back for further tests such as an MRI. This does not mean you have cancer, as mammograms aren’t 100% accurate and can show false results.
They can also miss important changes to your breast tissue, which is why even after you’ve had a mammogram, it’s important to check your breasts regularly. For more information about what happens during a mammogram in the UK, visit the NHS website or speak to your doctor.
How Can I Check For Breast Cancer
Dr. Lester recommends two primary ways to check for breast cancer: a monthly self-examination and a yearly mammogram.
Examine your breasts at least once a month in the mirror and by hand. Dr. Lester says, Ladies will know their breasts better than their primary care or gynecologist because only seeing them once a year.
When conducting your self-breast exam, there are six steps to follow:
You should also get a mammogram. According to Dr. Lester, women aged 40 to 44 should have an annual mammogram. He says, If theres a strong family history or youve been found to have a genetic mutation because another family member had breast cancer, you may be getting mammograms every six months.
Dr. Lester says, Well add ultrasound if the radiologist feels its appropriate. Women with dense breast tissue may need an ultrasound to be certain of the diagnosis. For women with a high risk for breast cancer, your doctor may also recommend an annual magnetic resonance imaging test .
You May Like: Breast Cancer Age Of Onset
How Common Is Breast Cancer
After skin cancer, breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in cis women. When it comes to the breast cancer statistics, about 1 in 8 will get breast cancer. Its also the second deadliest type of cancer for cis women. Over 240,000 people are diagnosed with breast cancer each year in the U.S. and 40,000 people die from the disease.
A Cancer Prevention Plan For Women
Finding cancer early improves your chances of successful treatment and long-term survival.
Look for:
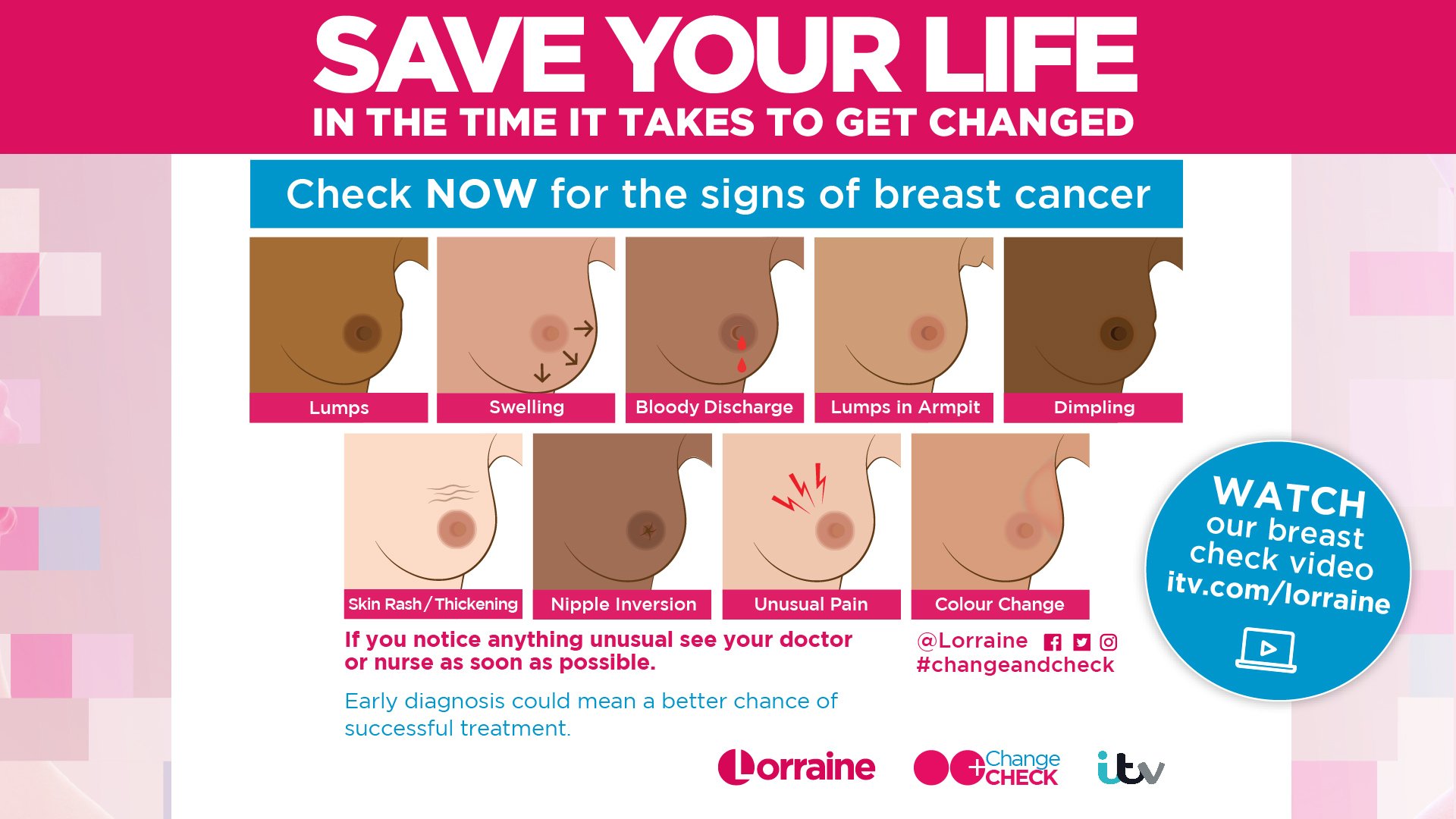
- lumps, sores or ulcers that don’t heal
- unusual changes in your breasts lumps, thickening, unusual discharge, nipples that suddenly turn inwards, changes in shape, colour or unusual pain
- coughs that don’t go away, show blood, or a hoarseness that persists
- weight loss that can’t be explained
- any loss of blood, even a few spots between periods or after they stop
- moles that have changed shape, size or colour, or an inflamed skin sore that hasn’t healed
- blood in a bowel motion
- persistent changes in toilet habits
- persistent abdominal pain or bloating.
Symptoms often relate to more common, less serious health problems. However, if you notice any unusual changes, or symptoms persist, visit your doctor.
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Receptor Testing
When Should I See A Doctor
It is important to remember that most breast changes are not caused by cancer, and the signs and symptoms can be caused by other medical conditions. However, if you have noticed any symptoms or changes in your breasts, it is important that you see your doctor without delay so that the changes can be checked. This may include a physical examination or imaging of your breasts. Early detection gives the best possible chance of survival if you are diagnosed with breast cancer.
It is important to remember that breast awareness does not replace having regular mammograms and other screening tests as recommended by your doctor. Some people diagnosed with breast cancer have signs or symptoms. However, some women have no signs/symptoms and the breast cancer is found during a screening mammogram.
In order to detect breast cancer early, it is recommended that all women between 50-74 years attend regular screening mammograms every two years. These are offered for free by BreastScreen Australia. Women aged 40-49 and 75 years and older are also eligible for free mammograms if they choose to attend. In deciding whether to attend a screening mammogram, women in these age groups can speak with their doctor and should also consider the potential benefits and downsides of screening mammograms for them.
Breast Lumps Or Lumpiness
Many womens breasts feel lumpy. Breast tissue naturally has a bumpy texture.
Some women have lumpier breasts than others. In most cases, this lumpiness is no cause to worry.
If the lumpiness can be felt throughout the breast and feels like your other breast, then its probably normal breast tissue.
Lumps that feel harder or different from the rest of the breast or that feel like a change are a concern and should be checked. This type of lump may be a sign of breast cancer or a benign breast condition .
See a health care provider if you:
- Find a new lump that feels different from the rest of your breast
- Find a new lump that feels different from your other breast
- Feel something thats different from what you felt before
If youre not sure whether you should have a lump checked, see your provider.
It may be helpful to download and print Susan G. Komen®s Questions to Ask Your Doctor If You Find a Lump or Change in Your Breast resource and take it with you to your doctor appointment. Theres plenty of space to write down the answers to these questions, which you can refer to later.
There are other Questions to Ask Your Doctor resources on many different breast cancer topics you may wish to download.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate Of Breast Cancer Stage 4
British Columbia Specific Information
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women in British Columbia. Breast cancer can occur in men as well, but it is not as common. Tests and treatments for breast cancer vary from person to person, and are based on individual circumstances. Certain factors such as your age, family history, or a previous breast cancer diagnosis may increase your risk of developing breast cancer. For information about your specific risk factors, speak with your health care provider.
A number of screening methods, including mammograms in women, can help find and diagnose breast cancer. The decision to have a mammogram or use any other screening method may be a difficult decision for some women. While screening for breast cancer is often recommended, it is not mandatory. Speak with your health care provider for information regarding how to get screened, the facts and myths about screening tests, how to maintain your breast health, and to get help making an informed decision.
For more information about breast cancer and breast cancer screening, visit:
If you have questions about breast cancer or medications, speak with your health care provider or call 8-1-1 to speak with a registered nurse or pharmacist. Our nurses are available anytime, every day of the year, and our pharmacists are available every night from 5:00 p.m. to 9:00 a.m.
How Is It Treated
You and your doctor will decide which mix of treatments is right for you based on many things. These include facts about your cancer as well as your family history, other health problems, and your feelings about keeping your breast.
Breast cancer is usually treated with surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or targeted therapy.
In some cases, you may need to decide whether to have surgery to remove just the cancer or surgery that removes the entire breast .
Treatments can cause side effects. Your doctor can let you know what problems to expect and help you find ways to manage them.
When you find out that you have cancer, you may feel many emotions and may need some help coping. Talking with other women who are going through the same thing may help. Your doctor or your local branch of the Canadian Cancer Society can help you find a support group.
Read Also: Did Anne Hathaway Have Cancer
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
In a sentinel lymph node biopsy , the surgeon finds and removes the first lymph node to which a tumor is likely to spread . To do this, the surgeon injects a radioactive substance and/or a blue dye into the tumor, the area around it, or the area around the nipple. Lymphatic vessels will carry these substances along the same path that the cancer would likely take. The first lymph node the dye or radioactive substance travels to will be the sentinel node.
After the substance has been injected, the sentinel node can be found either by using a special machine to detect radioactivity in the nodes, or by looking for nodes that have turned blue. To double check, both methods are often used. The surgeon cuts the skin over the area and removes the node containing the dye or radioactivity.
The few removed lymph nodes are then checked closely for cancer cells by a pathologist. Sometimes, this is done during the surgery. Because there is a chance that other lymph nodes in the same area will also have cancer if cancer is found in the sentinel lymph node, the surgeon may go ahead with a full axillary dissection to remove more lymph nodes while you are still on the operating table. If no cancer cells are seen in the node at the time of the surgery, or if they are not checked by a pathologist at the time of the surgery, they will be examined more closely over the next several days.
Based on the studies that have looked at this, skipping the ALND may be an option for:
Your Insurance Should Cover Breast Cancer Screening

Thanks to the Affordable Care Act, all health insurance plans should cover yearly mammograms with no out-of-pocket costs for women 40 and older. If your doctor says youre at a higher risk of breast cancer because of family history, an inherited gene mutation or other risk factors, your screening should be covered even if youre under 40. CBEs and screening breast MRIs should also be covered if your doctor recommends them. Medicare and Medicaid also cover breast cancer screening. Check with your insurance provider to find out where you should go for screenings and make sure theyll cover whatever services you need.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
I Found A Lump In My Breast What Should I Do
Maybe it happened in the shower. Or during an intimate moment with your partner. You could have been putting on lotion before bed. And there it isa breast lump. Finding one is understandably anxiety-provoking for women.
But before you jump to conclusions, stop and breathe.
Although the most common symptom of breast cancer is a lump or mass, many breast lumps are either benign or a symptom of a condition unrelated to cancer. So how do you tell the difference, and will it disappear on its own?
David Eddleman, MD, medical director of breast surgery at REX Breast Care Specialists, explains what to do if you find a lump.
Questions You Might Want To Ask Your Gp
- Do I need to see a specialist? Is it urgent?
- When will I see them?
- Where will I see them?
- Will I find out about my appointments by post or telephone?
- Do I need tests? What will they involve?
- How long should I expect to wait?
- Where can I find out more about tests?
- Do I have to do anything in preparation for this test?
- When will I get the results and who will tell me?
Your GP might not be able to answer all of your questions. They will tell you what they can at this point. Not knowing is difficult to cope with and can make you anxious.
Speaking to a friend or relative about how you feel might help.
Read Also: Types Of Breast Cancer Estrogen Positive
Can Breast Cancer Be Prevented
At this time, there is no sure way to prevent breast cancer.
Some risk factors, such as your age and being female, cannot be controlled. But you may be able to do things to stay as healthy as you can, such as having a healthy diet and being active. Knowing your risk of getting breast cancer also can help you choose what steps to take.
Talk to your doctor about your risk. Find out when to start having mammograms and how often you need one. If your doctor confirms that you have a high or very high risk, ask about ways to reduce your risk, such as getting extra screening, taking medicine, or having surgery.
If you have a strong family history of breast cancer, ask your doctor about genetic testing. The test can check for gene changes that increase your risk for getting breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Are There Any Risks Of Breast Cancer Self
Consider your breast cancer self-examination as a necessary precaution not an ultimate diagnosis. In some countries such as China and Russia, there was a sudden surge of unnecessary biopsies that turned out to be a huge waste of resources. Plus, many women suffered baseless physical and mental trauma such as stress over having cancer and blood loss because of surgeries.Bottomline: Dont panic at every little abnormality! Instead, seek multiple professional opinions before beginning a solid treatment.
You May Like: Positive Lymph Nodes Breast Cancer
How To Perform A Breast Check
Step 1 – Look
Begin by looking at your breasts in the mirror with your shoulders straight and your arms on your hips.
Here’s what you should see:
- Breasts that are their usual size, shape, and colour
- Breasts that are evenly shaped without visible distortion or swelling
But if you see any of the following changes, bring them to your doctor’s attention:
- Dimpling, puckering, or bulging of the skin
- A nipple that has changed position or an inverted nipple
- Redness, soreness, rash, or swelling
Step 2 – Raise your arms
Look again at your breasts with your raise your arms above your head and look for the same changes.
Step 3 – Lean forward
Now, lean forward so that there is a pendulum affect in your breasts, look for any dimpling, puckering or bulging of the skin.
Step 4 – Fluids?
While you’re at the mirror, look for any signs of fluid coming out of one or both nipples .
Step 5 – Feel lying down
Next, feel your breasts while lying down, using your right hand to feel your left breast and then your left hand to feel your right breast.
Use a firm, smooth touch with the first three finger pads of your hand, keeping the fingers flat and together. Use a circular motion, about the size of a 2p coin. Check the entire breast from top to bottom, side to side from your collarbone to the top of your abdomen, and from your armpit to your cleavage.
When you’ve reached the deep tissue, you should be able to feel down to your rib cage.
Step 6 – Feel standing or sitting