Genetics And Family History
Treatment for breast cancer may depend partly on having a close relative with a history of breast cancer or testing positive for a gene that increases the risk of developing breast cancer.
Patients with these factors may choose a preventive surgical option, such as a bilateral mastectomy.
Clinical trials are studies in which patients volunteer to try new drugs, combinations of drugs, and methods of treatment under the careful supervision of doctors and researchers. Clinical trials are a crucial step in discovering new breast cancer treatment methods.
Emerging treatments for breast cancer being studied in clinical trials include:
- PARP inhibitors that block protein used to repair DNA damage that occurs during cell division are being used and tested for TNBC.
- Drugs that block androgen receptors or prevent androgen production are being used and tested for TNBC.
If youre interested, ask your oncologist for information about available trials.
How Long Can You Wait For Radiation After Lumpectomy
Radiation therapy usually begins three to eight weeks after surgery unless chemotherapy is planned. When chemotherapy is planned, radiation usually starts three to four weeks after chemotherapy is finished. You will likely get radiation therapy as an outpatient at a hospital or other treatment facility.
Also Check: Chances Of Getting Breast Cancer Twice
Customized Treatment For Breast Cancer
Consultation and collaborative decision making with our multidisciplinary team at the Smith Breast Care Center ensures that your treatment is optimized to meet your unique needs. Your team uses both innovative and tried-and-true solutions to help you manage your complete health while in our care. We work with you every step of the way to help you control and manage side effects. We work with you to decide the best plan of attack for you.
You May Like: Can Birth Control Cause Breast Cancer
Testing A Sequential Versus Concurrent Radiation Boost
The trial included 2,262 women with early-stage breast cancer who had a lumpectomy and an elevated risk of recurrence in the same breast. Risk factors for recurrence included higher tumor grade, being younger than 50 years old, having cancer in lymph nodes in the armpit region, and having a hormone receptornegative breast cancer.
In addition, Dr. Vicini said, 60% of participants had received chemotherapy prior to radiation, which is another sign that a persons risk of recurrence may be higher.
The trial, known as NRG Oncology/RTOG 1005, was run by the NCI-funded NRG Oncology clinical trials group.
Half of the participants were randomly assigned to receive conventional whole-breast radiation given 5 days a week for 35 weeks, followed by a boost given over 67 days . The other half received the boost doses during 3 weeks of hypofractionated whole-breast radiation given 5 days a week . Participants were followed for a median of 7.4 years.
Cancer recurrence rates after 5 and 7 years were very similar in women who received a sequential boost and in those who received a concurrent boost. The percentage of people who had severe side effects was also about the same. Side effects of radiation therapy may include fatigue, hair loss, and effects on nearby organs, including the heart.
| Recurrence/side effect rate | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rate of severe side effects | 3.3% | 3.5% |
Where You Have Chemotherapy
You usually have treatment into your bloodstream at the cancer day clinic. You might sit in a chair for a few hours so its a good idea to take things in to do. For example, newspapers, books or electronic devices can all help to pass the time. You can usually bring a friend or family member with you.
You have some types of chemotherapy over several days. You might be able to have some drugs through a small portable pump that you take home.
For some types of chemotherapy you have to stay in a hospital ward. This could be overnight or for a couple of days.
Some hospitals may give certain chemotherapy treatments to you at home. Your doctor or nurse can tell you more about this.
Clare Disney : Hello, my name is Clare and this is a cancer day unit.
So when you arrive and youve reported into with the receptionist, one of the nurses will call you through when your treatment is ready, sit you down and go through all the treatment with you.
Morning, Iris. My name is Clare. I am the nurse who is going to be looking after you today. Were going to start by putting a cannula in the back of your hand and giving you some anti sickness medication. And then I am going to come back to you and talk through the chemotherapy with you and the possible side effects you may experience throughout your treatment. Is that okay?
Each chemotherapy is made up for each individual patient, depending on the type of cancer they have and where it is and depending their height, weight and blood results.
Don’t Miss: Is Breast Cancer Considered Internal Cancer
Ovarian Ablation Or Suppression
In women who have not yet experienced the menopause, oestrogen is produced by the ovaries.
Ovarian ablation or suppression stops the ovaries working and producing oestrogen.
Ablation can be done using surgery or radiotherapy. It permanently stops the ovaries from working and means you’ll experience the menopause early.
Ovarian suppression involves using a medicine called goserelin, which is a luteinising hormone-releasing hormone agonist .
Your periods will stop while you’re taking it, although they should start again once your treatment is complete.
If you’re approaching the menopause , your periods may not start again after you stop taking goserelin.
Goserelin comes as an injection you have once a month.
If All The Cancer Was Removed With Surgery Why Do I Need Any Additional Treatment
It has long been recognized that breast cancer is not always cured by locoregional treatment alone.
The goal of treating early breast cancer is to remove the cancer and keep it from coming back . Most people diagnosed with breast cancer will never have a breast cancer recurrence. However, everyone who has had breast cancer is at potential risk of recurrence, and that is why in most cases, there is a recommendation for treatment in addition to surgery, which is known as adjuvant therapy. The risk of recurrence can never be entirely eliminated, but the aim of adjuvant therapy is to reduce recurrence risk to the absolute minimum.
You May Like: Is Stage 1b Breast Cancer Curable
What Are The Long Term Side Effects Of Radiation For Breast Cancer
Long-term side effects can include:Breast changes: The breasts may shrink or become more dense after radiation. Brachial plexopathy: Radiation to the breast or chest wall can sometimes damage the nerves that run through the arm, wrist, and hand. Lymphedema: Lymphedema is swelling of the arm, hand, or chest.
Chemo And Radiation Do Different Jobs
Chemotherapy is to wipe out cells that are floating around in your blood or lymph and this is a systemic treatment. Radiation is to take care of where the cancer was or is and wipe out the cancer. It is a localized treatment.
You should have both to give yourself the best odds.
Doris
Recommended Reading: Can Breast Biopsy Spread Cancer
Possible Side Effects Of Chemo For Breast Cancer
Chemo drugs can cause side effects, depending on the type and dose of drugs given, and the length of treatment. Some of the most common possible side effects include:
- Hot flashes and/or vaginal dryness from menopause caused by chemo
Chemo can also affect the blood-forming cells of the bone marrow, which can lead to:
- Increased chance of infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
These side effects usually go away after treatment is finished. There are often ways to lessen these side effects. For example, drugs can be given to help prevent or reduce nausea and vomiting.
Other side effects are also possible. Some of these are more common with certain chemo drugs. Ask your cancer care team about the possible side effects of the specific drugs you are getting.
Risk Factors For Overall Recurrence
There are several risk factors that raise the risk of recurrence overall . These include:
- Tumor size: Larger tumors are more likely to recur than smaller ones both early and late.
- Positive lymph nodes: Tumors that have spread to lymph nodes are more likely to recur at any time than those that have not.
- Age at diagnosis: Breast cancer recurrence is more common in younger people.
- Treatments received and response to treatments: Both chemotherapy and hormonal therapy reduce the risk of recurrence in the first five years.
- Tumor grade: More aggressive tumors are more likely to recur than less aggressive tumors , especially in the first five years
There are also factors that do not appear to affect the risk of recurrence. Recurrence rates are the same for women who have a mastectomy or lumpectomy with radiation and are also the same for women who have a single vs. double mastectomy.
Recommended Reading: What Is De Novo Metastatic Breast Cancer
You May Like: How To Prepare For Breast Cancer Surgery
Internal Beam Radiation Or Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a type of radiation therapy that generates radiation from within the body. In comparison with external beam radiation, which projects particles of radiation from outside the body, brachytherapy can deliver higher doses of radiation in a precise fashion, resulting in fewer side effects and shorter treatment times.
The type of brachytherapy that doctors use depends on the location of the tumor, how much the cancer has spread, and the persons overall health.
Intracavity brachytherapy
The doctor will use a tube or cylinder to deliver a radioactive substance into the body and place it in the tumor.
Interstitial brachytherapy
The doctor will use a needle or catheter to place radioactive material within a cavity either a natural one or one that surgery has created. For breast cancer, they will place it in the breast.
Brachytherapy can also involve either high-dose-rate or low-dose-rate treatments.
High dose rate
This type consists of multiple treatment sessions in which doctors place radioactive material in the body for about 1020 minutes before removing it.
Low dose rate
This type uses substances that release a constant, low dose of radiation over 17 days, during which time a person will likely stay in the hospital. Doctors will remove the radiation source after a designated amount of time.
Read Also: Where Can Breast Cancer Lumps Appear
Is Chemotherapy The Only Treatment For Breast Cancer
No. Occasionally, chemotherapy is the only breast cancer treatment, but most often, healthcare providers use chemotherapy with other treatments, such as:
- Lumpectomy: Removing the tumor and a small amount of surrounding breast tissue.
- Mastectomy: Removing one or both breasts.
- Hormone therapy: Taking medicines that lower estrogen or block estrogens effects on cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Taking medicines that target the changes in cancer cells to destroy them or slow their growth.
- Radiation therapy: Using high-energy X-rays to destroy cancer cells.
Recommended Reading: Is Stage Four Breast Cancer Terminal
What Happens Before Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
A few days before your chemotherapy treatment, youll have blood tests. The blood tests tell your oncologist and pharmacist how to tailor your treatment based on your laboratory values and body mass index .
You may receive chemotherapy through a large, sturdy tube called a central venous catheter . If your healthcare provider recommends a CVC, it will be surgically implanted before treatment. It stays in place until you finish chemotherapy. Types of CVCs include:
- Central line: Long, plastic tube inserted near your heart or in a neck vein.
- Peripherally inserted central catheter : A central line that goes in through an arm vein.
- Port-a-cath : A small, implantable chamber where your nurse gives drug injections.
How Is Brachytherapy Done For Breast Cancer
Intracavitary brachytherapy: This is the most common type of brachytherapy for women with breast cancer. A device is put into the space left from BCS and is left there until treatment is complete. There are several different devices available, most of which require surgical training for proper placement. They all go into the breast as a small catheter . The end of the device inside the breast is then expanded like a balloon so that it stays securely in place for the entire treatment. The other end of the catheter sticks out of the breast. For each treatment, one or more sources of radiation are placed down through the tube and into the device for a short time and then removed. Treatments are typically given twice a day for 5 days as an outpatient. After the last treatment, the device is deflated and removed.
Also Check: Metastatic Breast Cancer In Liver
Are Some Therapies More Effective Based On Stage
The type of radiation treatment you get depends on the stage of breast cancer. People with early to stage 3 breast cancer will benefit most from radiation treatment. Radiation can also help ease side effects in people with advanced breast cancer.
External whole breast radiation works best:
- for early stage to stage 3 breast cancer
- for tumors that are an inch or smaller
- if the cancer is in one spot
- if you had breast-saving surgery or a mastectomy
External beam radiation can also help treat side effects of advanced breast cancer.
Internal radiation works best:
- for early stage breast cancer
- if the cancer is in one spot
- if you had breast-saving surgery or a mastectomy
Sometimes, a person with advanced breast cancer will have internal radiation.
Intraoperative radiation works best:
- during early stage breast cancer
- when the tumor is too close to healthy tissue for external radiation to be possible
Not everyone can have intraoperative radiation or internal beam radiation. Whether you can have these procedures depends on:
- size and location of the tumor
- size of your breast
Can Chemo And Radiation Be Used Together To Treat Cancer
Some cancers can be treated with just radiation. These are most often cancers caught earlybefore they’ve grown large or started to spread.
Most of the time, cancer treatment plans will contain multiple treatments. These treatments can include radiation, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, surgery, targeted therapies, or immune therapies. When your doctor combines multiple treatments at once, its called a combination treatment plan.
Combination treatments are used for many reasons. Treatments may be more effective when theyre combined. For example, chemotherapy may make radiation treatments more effective.
If your doctor suggests undergoing one type of treatment before others, its called neoadjuvant treatment. Neoadjuvant treatments are typically used to shrink a tumor or destroy metastases before the primary tumor is surgically removed.
Treatments that come after others are called adjuvant treatments and are typically used to reduce the risk that cancers will return or spread after initial treatment or surgery on the primary tumor.
Recommended Reading: What Is Metastatic Breast Cancer
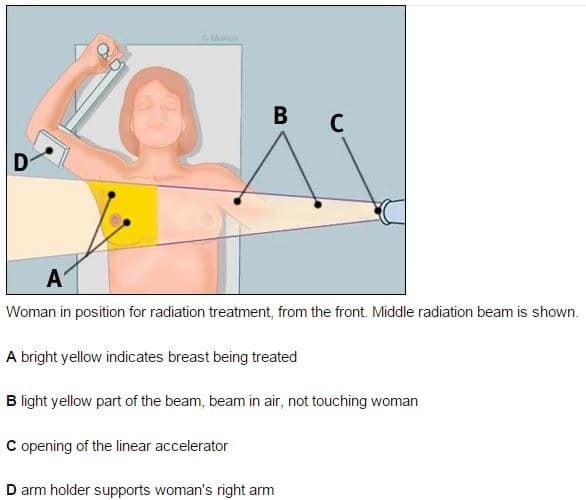
What Are The Types Of Radiation Therapy For Breast Cancer
There are different ways to receive radiation therapy. Your healthcare provider will choose the best method based on the cancer location, type and other factors.
Types of radiation therapy for breast cancer include:
- External beam whole-breast irradiation: During external beam whole-breast radiation therapy, a machine called a linear accelerator sends beams of high-energy radiation to the involved breast. Most people get whole-breast radiation five days a week for one to six weeks. The time frame depends on factors including lymph node involvement. In some cases, intensity-modulated radiation therapy may be used.
- External beam partial-breast: This treatment directs radiation to the tumor site only, not the entire breast over 1 to 3 weeks with 3-dimensional conformal radiation or IMRT.
- Brachytherapy: Some people get internal radiation therapy or brachytherapy. Your provider places an applicator or catheter. A radioactive seed is moved into the tumor site. The seeds give off radiation for several minutes before your provider removes them. You receive two treatments every day for five days.
- Intraoperative:Intraoperative radiation therapy takes place in the operating room before your provider closes the surgical site. Your provider delivers a high dose of radiation to the tumor area of the exposed breast tissue.
The Effects Of Chemotherapy And Natural Chemicals
Chemotherapy is like pouring weed killer on a garden. The flowers get as damaged and die right along with the weeds, but then even more resistant weeds find their way to the surface. Chemotherapy attacks every cell in the body. Hair cells stop their ability to hold onto the hair follicle in many chemo treatments because the chemo has attacked a healthy cell. Neuropathy is induced because the chemo attacks healthy nerve cells. Organs such the heart and kidneys, even bones can be permanently damaged because chemotherapy indiscriminately attacks healthy cells and cancer cells.
To the contrary several natural chemicals can create a specific programmed cell death of cancer cells by penetrating the cancer cell membrane. Apoptosis attaches a genetic message for a cell to self-destruct. Omega 3s, Resveratrol, Vitamin C, pine tree bark and an exhaustive list of morphing substances found in nature can have this miraculous affect, especially when delivered directly into the bloodstream intravenously. It would not be fair to say that alternative cancer therapy is without side effects, but those effects in no way rank in the same caustic category of chemotherapies.
Also Check: Metastatic Breast Cancer Survival Rate By Age
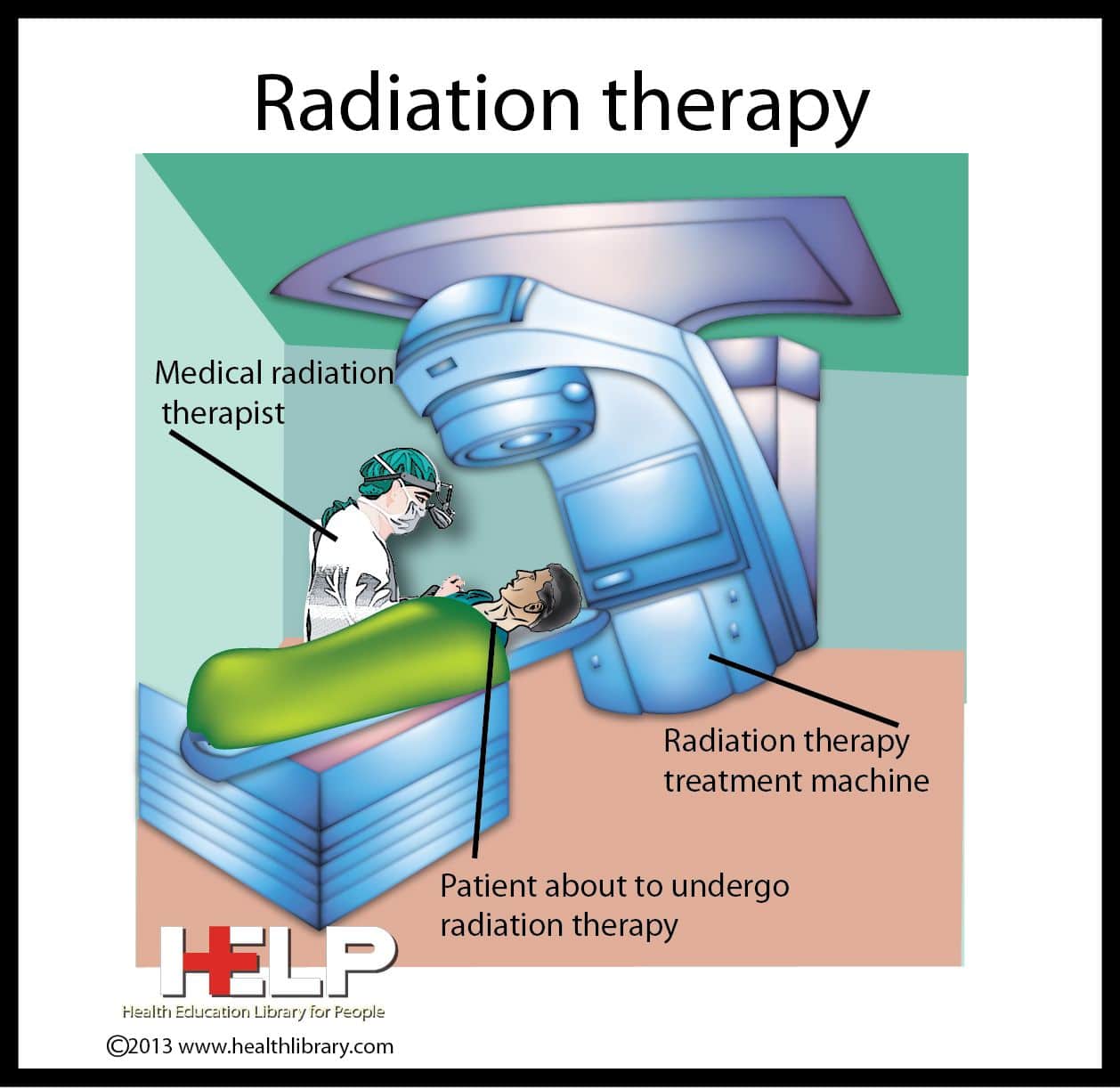
What Is Radiation Therapy For Breast Cancer
Radiation for Breast Cancer. Radiation therapy is treatment with high-energy rays that destroy cancer cells. Some women with breast cancer will need radiation, in addition to other treatments. Radiation therapy is used in several situations: After breast-conserving surgery , to help lower the chance that
Contacting Webmd About Your Personal Information Or Privacy
Please send us an email by using the Contact Us link at the bottom of every page of the WebMD Sites if you have any questions about this Privacy Policy or the personal information we maintain about you. We will respond to your request within a reasonable timeframe.
You can also contact WebMDs Privacy Office at:
WebMD LLC
Don’t Miss: What Is The Prognosis For Breast Cancer