What Is Stage I
Stage I is the earliest point of invasive cancer when tumor cells have started to spread to surrounding, normal breast tissue, Cruz said. In this stage the spread is contained to a small area.
Stage I is divided into categories IA and IB based on the size of a tumor and where cancer cells are detected. In IA, the tumor is about the size of a grape, Cruz said. Stage IB indicates the tumor is smaller or nonexistent, but there are small clusters of cells in the lymph nodes.
Ending cancer as we know it?:National Cancer Institute Director Ned Sharpless lays out his vision
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 cancer means the breast cancer has extended to beyond the immediate region of the tumor and may have invaded nearby lymph nodes and muscles, but has not spread to distant organs. Although this stage is considered to be advanced, there are a growing number of effective treatment options.
This stage is divided into three groups: Stage 3A, Stage 3B, and Stage 3C. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and surrounding tissue.
How Does Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
Cancer can spread from where it started to other parts of the body.
When cancer cells break away from a tumor, they can travel to other areas through either the bloodstream or the lymph system. If they travel through the lymph system, the cancer cells may end up in lymph nodes. Most of the escaped cancer cells die or are killed before they can start growing somewhere else. But one or two might settle in a new area, begin to grow, and form new tumors. This spread of cancer to a new part of the body is called metastasis.
In order for cancer cells to spread to new parts of the body, they have to go through several changes. They must become able to break away from the original tumor and attach to the outside wall of a lymph or blood vessel. Then they must move through the vessel wall to flow with the blood or lymph to a new organ or lymph node.
When cancer does spread to lymph nodes, it usually spreads to nodes near the tumor itself. These are the nodes that have been doing most of the work to filter out or kill the cancer cells.
Also Check: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Biopsy Of An Enlarged Lymph Node
If any of the lymph nodes under the arm or around the collar bone are swollen, they may be checked for cancer directly with a needle biopsy, either a fine needle aspiration or a core needle biopsy. Less often, the enlarged node is removed with surgery. If cancer is found in the lymph node, more nodes will need to be removed during an axillary lymph node dissection .
You Must Know How Breast Cancer Spread Faster
In the United States, Breast cancer is the most common cancer diagnosis among women these days.
It is complicated to estimate how a persons breast cancer will change over a year. Several types of breast cancer grow at different rates, and many parts affect its growth and spreading chances.
Here we discuss how breast cancer can spread faster, the common ways it can progress, and the long-term risk for the disease.
Dont Miss: Where Does Breast Cancer Usually Spread
You May Like: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
T: Tumor Size Categories For Breast Cancer
T followed by a number from 0 to 4 describes the primary tumors size and its spread to the skin or the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor or wider spread to tissues near the breast.
- TX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed
- T0: No sign of primary tumor
- Tis: Carcinoma in situ
Survival And Mortality Rates
Survival depends on mortality. You start with 100 percent of the people in the group.
100 percent mortality rate = survival rate
Say, the mortality rate in the group of people is 5 percent. Survival would be 95 percent .
Similarly, the number of people in a group who survive depends on the number of people who die. Say, 500 people are in the group and 1 person dies. This means 499 people survived .
Read Also: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Limited Arm And Shoulder Movement
You might also have limited movement in your arm and shoulder after surgery. This is more common after ALND than SLNB. Your doctor may advise exercises to help keep you from having permanent problems .
Some women notice a rope-like structure that begins under the arm and can extend down toward the elbow. This is sometimes called axillary web syndrome or lymphatic cording. It is more common after ALND than SLNB. Symptoms may not appear for weeks or even months after surgery. It can cause pain and limit movement of the arm and shoulder. This often goes away without treatment, although some women may find physical therapy helpful.
The Number Staging System
Breast cancer can also be divided into four number stages. We have put these into a table to make them easier to understand. You can .
This information is about stage 1 to 3 breast cancer.
Stage 1 breast cancer is when the cancer is 2cm or smaller. There may be no cancer cells in the lymph nodes in the armpit or tiny numbers of cancer cells are found. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast, but cancer cells have spread to lymph nodes in the armpit.
Stage 2 breast cancer is when the cancer is up to or bigger than 5cm. It may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes under the arm. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast. But cancer cells have spread to 1 to 3 lymph nodes in the armpit or near the breast bone.
Stage 3 breast cancer is sometimes called locally advanced breast cancer. The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the armpit and sometimes to other lymph nodes nearby. It may have spread to the skin of the breast or to the chest muscle. The skin may be red, swollen or have broken down. Sometimes the cancer cannot be found in the breast or is small but has spread to 4 to 9 lymph nodes in the armpit.
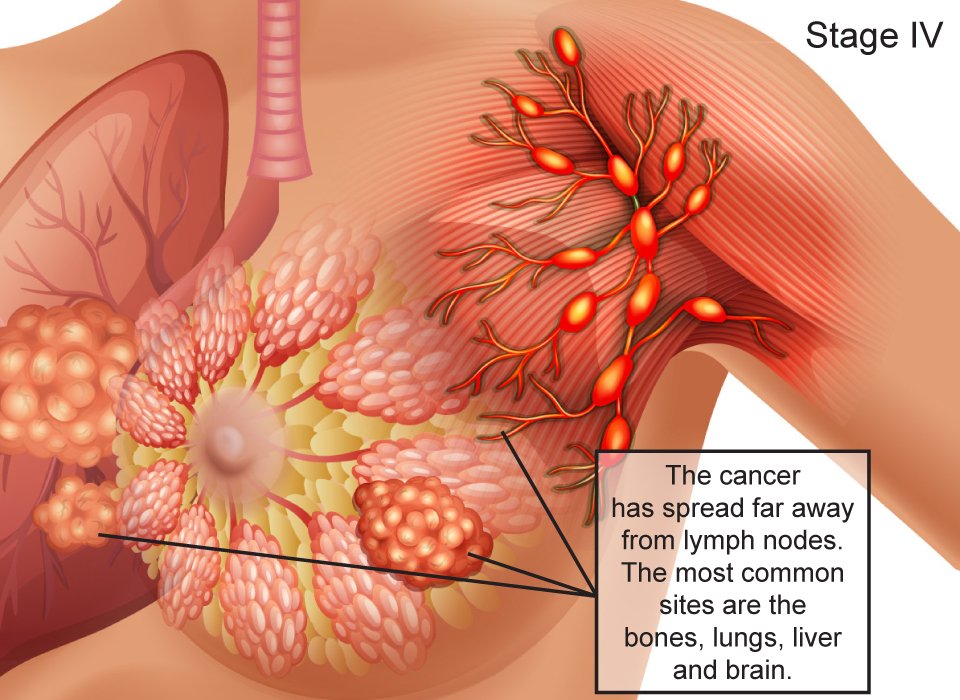
Stage 4 breast cancer is also called secondary or metastatic breast cancer. This is when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones, the liver or lungs. We have separate information about secondary breast cancer.
Read Also: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
Stages Of Breast Cancer
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how much cancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is often called the extent of cancer. Information from tests is used to find out the size of the tumour, what part of the breast has cancer, whether the cancer has spread from where it first started and where the cancer has spread. Your healthcare team uses the stage to plan treatment and estimate the outcome .
The most common staging system for breast cancer is the TNM system. For breast cancer there are 5 stages stage 0 followed by stages 1 to 4. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I, II, III and IV. Generally, the higher the stage number, the more the cancer has spread. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about staging.
When describing the stage of breast cancer, sometimes doctors group them as follows:
In situ breast cancer The cancer cells are only in the duct or lobule where they started and have not grown into nearby breast tissue . It is stage 0.
Early stage breast cancer The tumour is smaller than 5 cm and the cancer has not spread to more than 3 lymph nodes. It includes stages 1A, 1B and 2A.
Locally advanced breast cancer The tumour is larger than 5 cm. The cancer may have spread to the skin, the muscles of the chest wall or more than 3 lymph nodes. It includes stages 2B, 3A, 3B and 3C. Inflammatory breast cancer is also considered locally advanced breast cancer.
Find out more about .
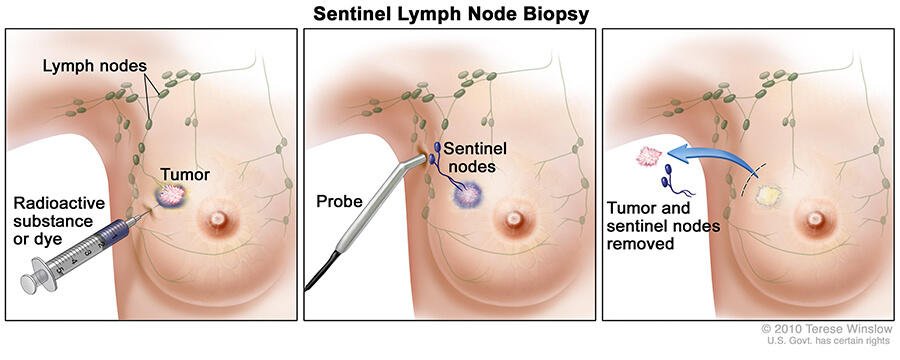
Types Of Lymph Node Surgery
Even if the nearby lymph nodes are not enlarged, they will still need to be checked for cancer. This can be done in two different ways. Sentinel lymph node biopsy might be needed.
Lymph node surgery is often done as part of the main surgery to remove the breast cancer, but in some cases it might be done as a separate operation.
Also Check: Can Getting Hit In Your Breast Cause Cancer
Tumor Grades: How The Cells Look
The tumor grade, sometimes called the cell grade, is a scale of G1 to G3 that identifies how abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope.
Cells in grade 1 tumors look almost normal and grow and spread slowly. Grade 3 cells are the most abnormal and grow the fastest. Grade 2 cells fall between grades 1 and 3.
Part of a womans prognosis, or long-term outcome, depends on the cancers stage and the tumors grade. Other factors that affect prognosis include the type of breast cancer a woman has, the hormones or proteins involved, and how quickly tumor cells are dividing and the tumor is growing.
What Is The Life Expectancy For Stage 3 Breast Cancer
The life expectancy for people with breast cancer is improving, according to the American Cancer Society. It points out that current survival rates are based on people who were diagnosed and treated at least 5 years ago and treatments have advanced over that time.
Your life expectancy with stage 3 breast cancer depends on several factors, such as:
- your age
- the size of the tumors
You should talk with your doctor about how these factors may apply to you.
Don’t Miss: How To Donate To Breast Cancer Charity
What Is Stage 0
Stage 0 is the least invasive stage of breast cancer and usually detected early in patients, according to the American Cancer Society. In this stage, cancer cells or non-cancerous abnormal cells are only in the part of the breast in which they formed and haven’t spread.
“At this stage of breast cancer, we tell patients not to be too worried. Stage 0 is extremely treatable and we ask people not to shed a tear over the diagnosis just yet,” said Cruz.
Remembering Sarah Harding:Sarah Harding of British pop group Girls Aloud dies at 39 after breast cancer battle
The Stages Of Breast Cancer Are As Follows:
Stage 0 is sometimes used to describe abnormal cells that are not invasive cancer. For example, Stage 0 is used for ductal carcinoma in situ . DCIS is diagnosed when abnormal cells are in the lining of a breast duct, but the abnormal cells have not invaded nearby breast tissue or spread outside the duct. Although many doctors dont consider DCIS to be cancer, DCIS sometimes becomes invasive breast cancer if not treated.
Stage I is an early stage of invasive breast cancer. Cancer cells have invaded breast tissue beyond where the cancer started, but the cells have not spread beyond the breast. The tumor is no more than 2 centimeters across.
Stage II is one of the following:
- The tumor is no more than 2 centimeters across. The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- The tumor is between 2 and 5 centimeters . The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- The tumor is between 2 and 5 centimeters . The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- The tumor is larger than 5 centimeters . The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
Stage III is locally advanced cancer. It is divided into Stage IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC.
You May Like: Don Harrington Breast Cancer Center
How Can I Prevent Breast Cancer Recurrence
Healthcare providers dont know why some people experience breast cancer recurrence. A recurrence isnt your fault. You didnt do anything wrong to cause it or fail to do something more to prevent it.
Certain medications may reduce the risk of breast cancer recurrence in people who have early stage breast cancer. For estrogen-receptive breast cancer, hormonal therapies including tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors block either the activity of estrogen or the bodys production of estrogen. Chemotherapy may also be recommended to reduce risk of breast cancer recurrence.
Early diagnosis may make it easier to treat a recurrence. Follow your healthcare providers recommendations for mammograms and other screenings. You should also perform regular breast self-exams. Get familiar with how your breasts look and feel so you can see your provider quickly if you notice changes. And remember that most breast changes occur for reasons other than cancer.
Lymph Node Status And Breast Cancer Treatment
After the tissue from your biopsy has been examined, your Rocky Mountain Cancer Centers oncologist will go over the results . The pathology report will show how many lymph nodes were removed and how many were involved . This is referred to as lymph node status.
Breast cancer that has not spread to nearby lymph nodes, is referred to as node-negative status. If the report indicates that cancer is present in the lymph nodes, this is referred to as node-positive status. Positive results also mean that the cancer may have already or could possibly spread to other organs, such as the bones, lungs, liver, and brain. In order to determine that, your RMCC oncology team would need to conduct further tests.
The pathology report will also show how much cancer is in each node. Cancer cells can range from small in size and few in number to large in size and many in number. This information may be reported as:
- Microscopic , meaning only a few cancer cells are in the node and that a microscope is needed to find them.
- Gross , meaning there is a lot of cancer in the node and that it can be seen or felt without the use of a microscope.
- Extracapsular extension, meaning the cancer has spread outside the wall of the node.
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
T Categories For Breast Cancer
T followed by a number from 0 to 4 describes the main tumor’s size and if it has spread to the skin or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast.
TX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed.
T0: No evidence of primary tumor.
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
T1 : Tumor is 2 cm or less across.
T2: Tumor is more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm across.
T3: Tumor is more than 5 cm across.
T4 : Tumor of any size growing into the chest wall or skin. This includes inflammatory breast cancer.
Less Lymph Node Surgery Equivalent Survival
The trial, called ACOSOG Z0011, was designed to compare whether sentinel lymph node biopsy alone provided equivalent survival benefits to ALND after breast-conserving surgery among a subset of women who also received radiation and systemic therapy. The research team enrolled 891 participants into the study from 1999 to 2004.
Women who had stage I or II cancer and metastases in only one or two sentinel nodes were eligible to join the study. All women had undergone SLNB at the time of breast-conserving surgery.
Half of the trial participants received no further surgery, and the other half underwent ALND. Almost 90% of women in both groups had radiation therapy after surgery, and almost all received some type of systemic therapy.
In the initial results from the trial, published in 2010 and 2011, women who had only SLNB did not have worse overall survival than women who underwent full ALND. The two groups also had similar rates of disease-free survival and cancer recurrence in the lymph nodes.
These early results were absolutely practice changing, and at this point the overwhelming majority of surgeons are not doing a full axillary lymph node dissection in patients with one or two positive nodes, said Larissa Korde, M.D., head of Breast Cancer Therapeutics in NCIs Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis.
However, the cancer research community had lingering concerns about the trial, the authors of the new paper explained.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage