What Is Hormone Therapy
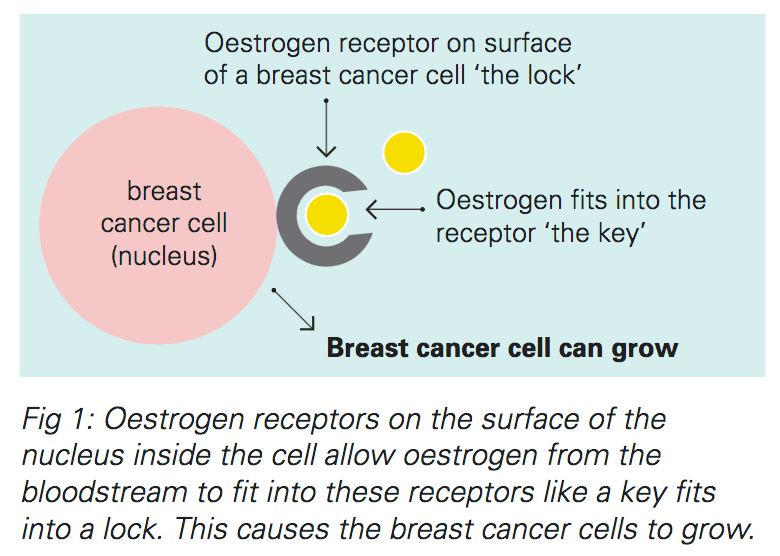
Hormone therapy slows or stops the growth of hormone-sensitive tumors by blocking the bodys ability to produce hormones or by interfering with effects of hormones on breast cancer cells. Tumors that are hormone insensitive do not have hormone receptors and do not respond to hormone therapy.
Hormone therapy for breast cancer should not be confused with menopausal hormone therapy treatment with estrogen alone or in combination with progesterone to help relieve symptoms of menopause. These two types of therapy produce opposite effects: hormone therapy for breast cancer blocks the growth of HR-positive breast cancer, whereas MHT can stimulate the growth of HR-positive breast cancer. For this reason, when a woman taking MHT is diagnosed with HR-positive breast cancer she is usually asked to stop that therapy.
Feminism And The Breast Cancer Wars
The breast cancer wars were a series of conflicts between advocates and others about the causes, treatments, and societal responses to breast cancer. Women in the late 1980s and 1990s followed the successful approach used by ACT-UP and other AIDS awareness groups, of staging media-friendly protests to increase political pressure. Prominent women who made the “wrong” choice were publicly excoriated, as when Nancy Reagan chose mastectomy over lumpectomy followed by six weeks of radiation therapy. The abortionâbreast cancer hypothesis was formulated when an early study showed a connection between voluntary abortions and the development of breast cancer in premenopausal women, which pitted breast cancer advocates against abortion rights advocates.
Seeking Support For A Breast Cancer Diagnosis
If youve been diagnosed with breast cancer, its a great idea to talk to a therapist. A therapist can help you cope throughout your breast cancer journey.
The APA recommends a combination of group therapy, which allows women to share emotional support, and individual therapy, which helps women learn problem-solving skills and alter patterns of negative thinking. A therapist can also help you work through body image or sexuality issues related to a mastectomy or treatment in general.
While breast cancer and mental illness may both feel like insurmountably large problems, you can take simple steps every day to feel better. Staying as active as you can, focusing on healthy eating including lots of fruits and vegetables, and reaching out to friends, family, a support group, or a faith group can all help, says the CDC.
You also dont have to be a medical professional to give support to people in your life with breast cancer. Social support matters, too. Research shows that having supportive intimate partners and family members increases breast cancer survivors overall wellbeing.
Read Also: How To Donate To Breast Cancer Charity
Symptoms Of Secondary Breast Cancer
The symptoms of secondary breast cancer depend on where in the body the cancer has spread to. If it has spread to the bones there might be a painful area in a bone. If it has spread to a lung it may cause breathlessness.
Some people have general symptoms. They may feel generally unwell for no obvious reason. Tell your doctor or nurse if you have any new symptoms. If you are worried, we have more information about the symptoms of secondary breast cancer.
Blood Tests For Tumor Markers
In some cases, blood tests for tumor markers may be used to help monitor metastatic breast cancer.
For example, you may have blood tests every few months for cancer antigen 15-3 or cancer antigen 27.29 . These tests are similar. Health care providers usually check one, but not both of these blood tests.
Whether the tumor marker test score rises or falls over time may give some information on tumor response to a drug or tumor spread.
Tumor marker tests are not helpful in every case. Some people with rising tumor marker levels dont have tumor growth, and some people with tumor growth have normal or unchanged tumor marker levels.
Health care providers dont make treatment decisions based on serum tumor marker testing alone. They may combine findings from a tumor marker test with information on symptoms and findings from imaging tests . This combined information can help your health care providers understand if a treatment is working well for your cancer.
Talk with your health care provider about whether tumor marker testing is right for you.
Also Check: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
What Is Stage Ii Breast Cancer
Stage II describes cancer that is in a limited region of the breast but has grown larger. It reflects how many lymph nodes may contain cancer cells. This stage is divided into two subcategories.
Stage IIA is based on one of the following:
- Either there is no tumor in the breast or there is a breast tumor up to 20 millimeters , plus cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, but cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage IIB is based on one of these criteria:
- A tumor of 20 to 50 millimeters is present in the breast, along with cancer that has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
- A tumor in the breast is larger than 50 millimeters, but cancer has not spread to any lymph nodes.
Your Personal History Of Breast Cancer
If youve been diagnosed with breast cancer in the past, you are more likely to develop a new cancer in the other breast or in another part of the same breast. This is not considered a recurrence but a new breast cancer.
What to do: Follow your cancer teams instructions on monitoring to stay on top of this risk. Ask your doctor whether you should see a genetic counselor.
Also Check: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
What Are Some Of The Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
While finding a lump in your breast or having one appear on a mammogram doesnt automatically mean you have cancer, it does indicate there is a need for further evaluation. Other conditions can cause lumps in the breast includes cysts, benign tumors and certain noncancerous disorders.
According to the Mayo Clinic, the most common sign of breast cancer is a lump or thickening in one breast that can be felt. It may be painless, or it may be tender with some associated pain. Many cancerous lumps are firm, with irregular borders and develop in the upper portion of the breast near the armpit. In the early stages of cancer, there may not be other signs or symptoms.
Since even an experienced healthcare provider cant always tell if a lump is benign or malignant, all lumps and changes to the breast should be examined and evaluated, with a full medical history, physical exam and imaging tests. If further studies are needed, a biopsy may be necessary. Diagnosing breast cancer is generally a step-by-step procedure that can take several days. Many women say the worst part is the waiting and the uncertainty of knowing whether or not they have cancer.
Are There Complications Of Breast Cancer
Possible complications from breast cancer treatment include:
- Lymphoedema in some cases, removing your lymph nodes may cause swelling, discomfort and pain in the arm, shoulder and upper body.
- Early menopause certain treatments, especially chemotherapy and hormone therapy, can cause menopause symptoms, such as hot flushes, joint pain, or a change in sex drive, to occur earlier than usual.
- Anxiety and depression research shows that anxiety and depression are common among women with breast cancer. One study found that up to 50 per cent of women with early breast cancer may experience anxiety and/or depression in the year after diagnosis.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
When Should I See My Doctor
See your doctor or healthcare professional if you notice symptoms of possible breast cancer, such as a lump, pain, itch, nipple discharge or dimpling, or if you have any concerns about your breast cancer risk.
Your doctor or healthcare professional will assess you and work out if you need further tests. If required, they can refer you to a local service and provide necessary follow-up care.
Normal Breast Changes Through Life
The female breast will go through various normal changes over the course of a lifetime. Many of these changes are driven by hormones. They can be related to the menstrual cycle, pregnancy or the normal aging process. Most breast changes are not cancer, however, if you do notice an unusual breast change, it is important that you speak with your doctor so that it can be checked as soon as possible.
Normal breast changes throughout life include:
Also Check: Can Getting Hit In Your Breast Cause Cancer
Circulating Tumor Cell Test
A circulating tumor cell test can check for blood biomarkers that show whether normal cells are transforming into cancer cells. CTC tests can help diagnose and screen patients who have a risk of developing cancer, such as a family history of the disease.
CTC tests are helpful in the early detection of cancer as well as monitoring treatment effectiveness over time. The only test currently approved for this purpose is called CellSearch CTC, which offers different prostate, colorectal, and breast cancer assays.
Will A Biopsy Confirm A Diagnosis Of Breast Cancer

Yes it will. In fact a biopsy is the god standard in diagnosing most infective, inflammatory and malignant diseases.
A biopsy requires the extraction of a small number of cells to view their characteristics under a microscope. A high degree of specificity allows for a correct pathology confirmation of cancer in cases with a strong suspicion of malignancy .
As mentioned before, a breast ultrasound or an x-ray helps guide the extracting needle towards the area under suspicion, to increase the probability of finding abnormal cells.
Dr. Naoko says,
Before taking any further steps, any woman who receives a positive biopsy for breast cancer, should immediately consult with a breast cancer specialist to help categorise the type of cancer..since treatment depends on so many factors..such as size, grading, type of cancer and of course the womans health context.
Recommended Reading: Can Asbestos Cause Breast Cancer
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
- Stage 3A:
- The cancer has spread to 49 axillary lymph nodes or has enlarged the internal mammary lymph nodes, and the primary tumor can be any size.
- Tumors are greater than 5 cm, and the cancer has spread to 13 axillary lymph nodes or any breastbone nodes.
Abemaciclib Palbociclib And Ribociclib And Hormone Therapy
The CDK4/6 inhibitors FDA-approved for metastatic breast cancer treatment are:
- Abemaciclib
- Palbociclib
- Ribociclib
CDK4 and CDK6 are enzymes important in cell division. CDK4/6 inhibitors are a class of drugs designed to interrupt the growth of cancer cells.
Although the CDK4/6 inhibitors abemaciclib, palbociclib and ribociclib have not been compared directly to one another, studies show similar results with each drug .
A CDK4/6 inhibitor in combination with hormone therapy can be used to treat hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancers. Compared to treatment with hormone therapy alone, this combination can give people more time before the cancer spreads and increase overall survival .
The CDK4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib may also be used alone to treat hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative cancers that have progressed during past hormone therapy and chemotherapy .
Abemaciclib, palbociclib and ribociclib are pills.
The table below lists some possible side effects for CDK4/6 inhibitors.
|
For a summary of research studies on the use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in treating metastatic breast cancer, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
Also Check: Baking Soda For Breast Cancer
Common Types Of Breast Cancer In Women
The most common type of breast cancer for individuals to be diagnosed with is invasive breast cancer . This means that the cancerous cells have grown within the duct linings which surround the breast tissue.
The NST is an acronym for no special type which means that breast cancer has no special features and there are no unique features displayed by the cancer cells when analysed under a microscope.
The second most common type of breast cancer is called invasive lobular breast cancer. Lobules are the physiological structures that are responsible for milk production during breastfeeding.
Invasive lobular breast cancer starts in the cells which line these glands and then spreads into the tissues surrounding the lobules.
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare type of breast cancer that involves cancerous cells blocking the lymph channels within the breast.
The lymphatic system is highly important within the immune system and is responsible for the drainage of lymphatic fluid from organs and bodily tissues.
Due to the lymph channels being blocked, they are unable to function properly which causes the surrounding skin tissue to become inflamed, red, and irritated. Breast angiosarcomas are a group of cancers that are extremely rare.
This type of cancer originates in cells that make up the lining of the blood vessel walls and lymphatic vessels. Due to the physiological location of angiosarcomas, they can be difficult to treat as they are able to grow and divide rapidly.
What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
The most common types of breast cancer are:
- Infiltrating ductal carcinoma. This cancer starts in the milk ducts of the breast. It then breaks through the wall of the duct and invades the surrounding tissue in the breast. This is the most common form of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of cases.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ is ductal carcinoma in its earliest stage, or precancerous . In situ refers to the fact that the cancer hasn’t spread beyond its point of origin. In this case, the disease is confined to the milk ducts and has not invaded nearby breast tissue. If untreated, ductal carcinoma in situ may become invasive cancer. It is almost always curable.
- Infiltrating lobular carcinoma. This cancer begins in the lobules of the breast where breast milk is produced, but has spread to surrounding tissues in the breast. It accounts for 10 to 15% of breast cancers. This cancer can be more difficult to diagnose with mammograms.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ is a marker for cancer that is only in the lobules of the breast. It isn’t a true cancer, but serves as a marker for the increased risk of developing breast cancer later, possibly in both or either breasts. Thus, it is important for women with lobular carcinoma in situ to have regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Local And Regional Recurrence Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer that comes back in the breast, chest, scar or lymph nodes nearby is called a local or regional recurrence. This is not secondary breast cancer. If you have a local or regional recurrence, you may have tests to check the cancer has not spread to other parts of the body.
We have more information about breast cancer recurrence.
See also
Cytotoxics And Targeted Therapies
are a relatively new class of cancer drugs that can overcome many of the issues seen with the use of cytotoxics. They are divided into two groups: small molecule and antibodies. The massive toxicity seen with the use of cytotoxics is due to the lack of cell specificity of the drugs. They will kill any rapidly dividing cell, tumor or normal. Targeted therapies are designed to affect cellular proteins or processes that are utilised by the cancer cells. This allows a high dose to cancer tissues with a relatively low dose to other tissues. Although the are often less severe than that seen of cytotoxic chemotherapeutics, life-threatening effects can occur. Initially, the targeted therapeutics were supposed to be solely selective for one protein. Now it is clear that there is often a range of protein targets that the drug can bind. An example target for targeted therapy is the BCR-ABL1 protein produced from the , a genetic lesion found commonly in and in some patients with . This has enzyme activity that can be inhibited by , a drug.
Also Check: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
Prognostic Impact Of Tumor
It has been previously reported that tumor-specific expression of the rate-limiting enzyme, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutharyl-coenzyme A reductase , in the mevalonate pathway is associated with more favorable tumor parameters in breast cancer. In the present study, it is examined the prognostic value of HMG–CoAR expression in a large cohort of primary breast cancer patients with long-term follow up.
Social Role Of The Woman With Breast Cancer

The marketing of breast cancer awareness allows people to incorporate support for awareness into their personal identity or lifestyle. Socially aware, pro-woman individuals, businesses, politicians, and organizations use pink ribbons and other trappings of breast cancer awareness to signal their support for women, health, and mainstream medicine.
Don’t Miss: Baking Soda And Honey For Cancer
How Herceptin Works
Cancer cells grow in an uncontrolled fashion. Herceptin works on the surface of the cancer cell by blocking the chemical signals that can stimulate this uncontrolled growth.
Genes are like instruction manuals that tell each cell of your body how to grow, what kind of cell to become, and how to behave. Genes do this by ordering the cell to make special proteins that cause a certain activity such as cell growth, rest, or repair.
Some cancer cells have abnormalities in genes that tell the cell how much and how fast to grow. Sometimes the cancer cells have too many copies of these genes with abnormalities. When there are too many copies of these genes, doctors refer to it as “overexpression.” With some forms of gene overexpression, cancer cells will make too many of the proteins that control cell growth and division, causing the cancer to grow and spread.
Some breast cancer cells make too many copies of a particular gene known as HER2. The HER2 gene makes a protein known as a HER2 receptor. HER2 receptors are like ears, or antennae, on the surface of all cells. These HER2 receptors receive signals that stimulate the cell to grow and multiply. But breast cancer cells with too many HER2 receptors can pick up too many growth signals. This causes them to start growing and multiplying too much and too fast. Breast cancer cells that overexpress the HER2 gene are said to be HER2-positive.