Surgery To Remove Lymph Nodes
Breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body. If it does spread, it usually first spreads to the lymph nodes in the armpit close to the breast. These lymph nodes drain the lymphatic fluid from the breast and arm.
It is important to know if there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes in the armpit and how many. This helps the doctors work out the stage of your cancer and plan the best treatment for you.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are part of a system of tubes and glands in the body that filters body fluids and fights infection.
The most common symptom if cancer has spread to the lymph nodes is that they feel hard or swollen. You might have any of the following symptoms if your cancer has spread to the lymph nodes:
- a lump or swelling under your armpit
- swelling in your arm or hand
- a lump or swelling in your breast bone or collar bone area
One of the first places breast cancer can spread to is the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer. This is not a secondary cancer.
Living With Metastatic Breast Cancer
An advanced breast cancer diagnosis often elicits a flood of emotions: fear, confusion, sadness, anger and worry. You may wonder, Why me? You may think its unfair that this has happened to you. All of these emotions and feelings are normal, so take the time to process your thoughts, speak with your care team to understand your diagnosis, and connect with loved ones and close friends for support.
Over time, as the shock wears off, many patients find that they get on with their lives, adjusting to what some call their new normal. You may continue to work, enjoy life and spend time with family and friends, even if sometimes you have less energy than before.
Try to eat a nutritious diet to feel stronger and better tolerate treatments. Maintaining good nutrition may also help lower your risk of infection and provide you with more energy for enjoying life.
Light exercise may give your mind and body’s boost, helping you feel energized, especially if you spend time in the fresh air. Always seek medical advice before making any changes to your diet or exercise routines.
You May Like: When Do You Need Radiation For Breast Cancer
How Fast Does Metastatic Breast Cancer Spread
Like all cells, breast cancer cells grow by cellular division. But because cancer cells are mutated, their growth rate can be difficult to predict.
According to the Robert W. Franz Cancer Research Center at Providence Portland Medical Center, breast cancer cells need to divide at least 30 times before they are detectable by physical exam.
Each division takes about 1 to 2 months, so a detectable tumor has likely been growing in the body for 2 to 5 years.
Generally speaking, the more cells divide, the bigger the tumor grows. The larger the tumor, the greater the odds that it may invade nearby tissues, the lymphatic system, or the circulatory system, and spread to other organs.
Breast cancer grading and staging can provide some clues to how aggressive your cancer is.
Grade 3 breast cancer is likely to spread faster than grade 1 or 2, for example.
that can affect how quickly your breast cancer may spread include:
Grading and staging are the two primary metrics used to assess breast cancer.
Treatment For Secondary Breast Cancer
A team of specialists will meet to discuss the best possible treatment for you. This is called a multidisciplinary team .
Your doctor and nurse will talk to you about the best treatment for you. They will also ask you about your preferences. They will talk to you about things to consider when making treatment decisions. You may have some treatments as part of a clinical trial.
Secondary breast cancer can be controlled, often for many years, but it cannot be cured. Because of new and improved treatments, women with secondary breast cancer are living for longer. The aim of treatment is to control the cancer, improve the symptoms and help you to live well for longer.
The treatment you have will depend on:
- where the cancer is in your body
- if it is ER positive or HER2 positive
- previous breast cancer treatment you have had.
You may have a combination of treatments.
Treatments for secondary breast cancer include:
Recommended Reading: How Can Breast Cancer Kill You
Checking The Lymph Nodes
Before your treatment you have an ultrasound scan to check the lymph nodes in the armpit close to the breast. This is to see if they contain cancer cells. If breast cancer spreads, it usually first spreads to the lymph nodes close to the breast.
Depending on the results of your scan you might have:
- a sentinel lymph node biopsy during your breast cancer operation
- surgery to remove your lymph nodes
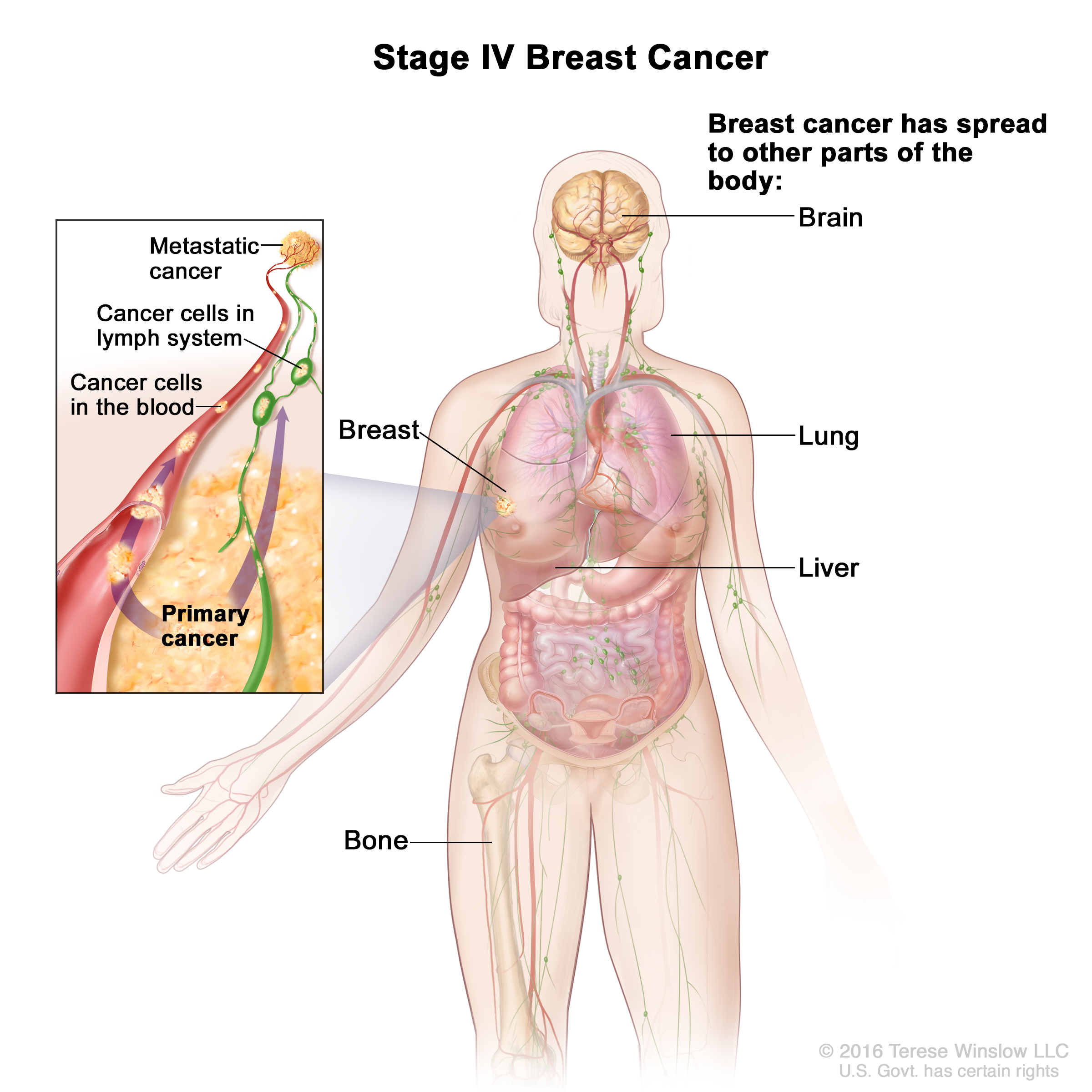
What Are The Signs That Breast Cancer Has Spread
Metastatic breast cancer is a secondary cancer the cancerous cells originate in breast tissue and then travel to other parts of the body. The most common areas of breast cancer metastasis are the bones, lungs and liver.
Following an initial breast cancer diagnosis, a patient will receive a personalized monitoring plan for metastatic reoccurrence from their care team. Depending on the specific parts of the body affected, the symptoms of metastatic breast cancer can vary.
Read Also: What Are The Side Effects Of Radiotherapy For Breast Cancer
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several different types of breast cancer, which develop in different parts of the breast.
Breast cancer is often divided into either:
- non-invasive breast cancer found in the ducts of the breast which has not spread into the breast tissue surrounding the ducts. Non-invasive breast cancer is usually found during a mammogram and rarely shows as a breast lump.
- invasive breast cancer where the cancer cells have spread through the lining of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. This is the most common type of breast cancer.
Other, less common types of breast cancer include:
- invasive lobular breast cancer
- inflammatory breast cancer
It’s possible for breast cancer to spread to other parts of the body, usually through the blood or the axillary lymph nodes. These are small lymphatic glands that filter bacteria and cells from the mammary gland.
If this happens, it’s known as secondary, or metastatic, breast cancer.
What Is Chest Wall Cancer
Comprising less than five percent of all thoracic malignancies, cancers of the chest wall are rare and difficult to treat. Chest wall tumors can develop in the bones, soft tissues and cartilage of the chest cavity, which contains the heart, lungs and other organs. These tumors typically involve invasion or have metastasized from adjacent thoracic tumors, and are malignant in more than half of cases.
The most common chest wall cancer is sarcoma of the chest wall, including:
Other chest wall cancers include metastatic cancer, desmoid tumor and neurogenic tumors.
Tumors in the chest wall typically manifest as painful, quickly growing and easily palpable masses. Surgery is often necessary, and may be followed by plastic surgery reconstruction to recreate a normal appearance.
Physicians and surgeons at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Lung Center provide comprehensive, specialized care for patients with chest wall cancer. As the thoracic surgical and pulmonary medicine specialists for Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, our physicians collaborate with other specialists to provide patients with a highly informed diagnosis and a cohesive treatment plan.
You May Like: Can Blood Test Show Breast Cancer
Treating Chest Wall Pain
Treatment for chest wall pain will depend on whats causing it.
If its found that your breast pain is caused by a pulled muscle in your chest, this is likely to improve over time and can be treated with pain relief.
Chest wall pain can also affect the area under the arm and towards the front of the chest, and this may be due to:
- costochondritis inflammation of parts of the ribs
- Tietzes syndrome inflammation of the costal cartilages and swelling
Your GP or specialist may be able to tell that the costal cartilages are painful if pressure is put on them. Sometimes this inflammation can feel similar to heart pain. You may feel tightness in the chest and a severe, sharp pain. The pain may also spread down the arm and can be worse when you move.
You may find it helpful to rest and avoid sudden movements that increase the pain. Pain relief such as paracetamol or a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory such as ibuprofen may help.
Your specialist may suggest injecting the painful area with a local anaesthetic and steroid.
Smoking can make the inflammation worse, so you may find that your pain lessens if you cut down or stop altogether.
The NHS website has more information about costochondritis and Tietzes syndrome.
Pain caused by other medical conditions, such as angina or gallstones, may be felt in the breast. Your GP or specialist will advise you on the most appropriate treatment.
Possible Questions To Ask Your Doctor
Read Also: What Does Breast Cancer In Men Feel Like
Malignant Chest Wall Tumors
- Soft tissue sarcomas: Include malignant fibrous histiocytoma, liposarcoma, and neurofibrosarcoma
- Chondrosarcomas: Malignant tumor of cartilage, usually on the front of the chest where the ribs and sternum connect
- Osteosarcoma: Tumor of the bone
- Ewing sarcoma: A group of bone and soft tissue tumors
- Solitary plasmacytoma: Rare plasma-cell tumor in the bone
- Liposarcoma: Tumor of fatty tissue
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
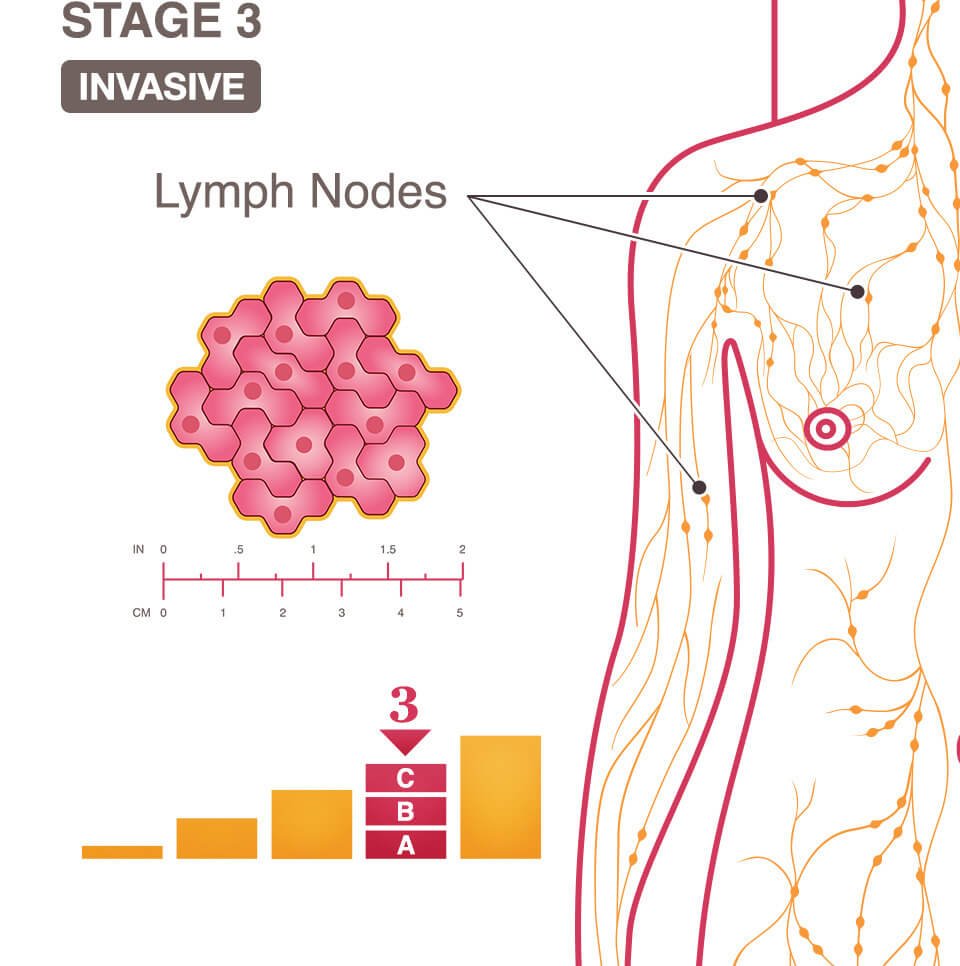
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
Also Check: Can Breast Cancer Metastasis If Not In Lymph Nodes
How Does Breast Cancer Spread
Breast cancer can invade and grow into the tissue surrounding the breast or it can travel to other parts of the body and form a new tumor there. Nearly all types of cancer have the ability to spread , but whether or not it will spread is often linked to what type of breast cancer you have.
Breast cancer can spread in three ways:
Every cancer is different, but the type of breast cancer you have typically plays a role in how aggressive or slow moving it is and where its most likely to spread, says Dr. Roesch.
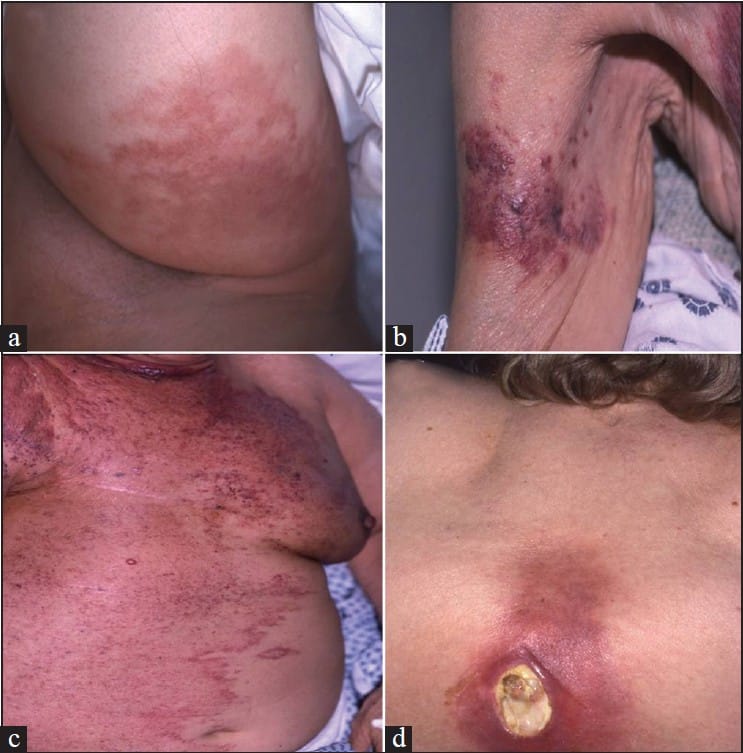
Symptoms Of Angiosarcoma Of The Breast
Another rare form of breast cancer, angiosarcoma forms inside the lymph and blood vessels. Only a biopsy may definitively diagnose this type of cancer. Angiosarcoma can cause changes to the skin of your breast, such as the development of purple-colored nodules that resemble a bruise. These nodules, if bumped or scratched, may bleed. Over time, these discolored areas may expand, making your skin appear swollen in that area. You may or may not have breast lumps with angiosarcoma. If you also have lymphedema, which is swelling caused by a buildup of lymphatic fluid, angiosarcoma may occur in the affected arm. Cancer treatment sometimes damages the lymph vessels, which may lead to lymphedema.
Recommended Reading: Who Is More Likely To Get Breast Cancer
Integrative Therapies For Metastatic Breast Cancer
You may find it beneficial to add integrative therapies to your treatment plan. There are many evidence-informed integrative modalities to boost the mind and body. Practices like gentle yoga, meditation, massage and music therapy may feel enjoyable and reduce stress and anxiety levels.
To help our patients maintain quality of life after a metastatic breast cancer diagnosis, our team of breast cancer experts may offer supportive care services to help manage side effects of the disease and its treatments. These may include:
Before starting any integrative therapies, however, ask your care team for advice on which ones are most suited to you and fit into your overall treatment plan, as well as how to do them safely.
What Causes Chest Wall Tumors
Scientists dont know exactly what causes chest wall tumors. But in some cases, genetics seem to play a role. Also, lifestyle factors may raise your risk, especially for secondary chest wall tumors. For example, lung cancer can spread to your chest wall. So, smoking increases your risk for lung cancer, as well as for chest wall tumors.
Recommended Reading: How Big Are Breast Cancer Tumors
What Is Cancer Staging
Staging is a way of describing how extensive the breast cancer is, including the size of the tumor, whether it has spread to lymph nodes, whether it has spread to distant parts of the body, and what its biomarkers are.
Staging can be done either before or after a patient undergoes surgery. Staging done before surgery is called the clinical stage, and staging done after surgery is called the pathologic stage. Doctors use diagnostic tests to find out the cancer’s stage, so staging may not be complete until all of the tests are finished. Knowing the stage helps the doctor recommend the best kind of treatment and can help predict a patient’s prognosis, which is the chance of recovery. There are different stage descriptions for different types of cancer.
This page provides detailed information about the system used to find the stage of breast cancer and the stage groups for breast cancer, such as stage IIA or stage IV.
What Causes Breast Cancer
Breast cancer develops when abnormal cells in your breast divide and multiply. But experts dont know exactly what causes this process to begin in the first place.
However, research indicates that are several risk factors that may increase your chances of developing breast cancer. These include:
- Age. Being 55 or older increases your risk for breast cancer.
- Sex. Women are much more likely to develop breast cancer than men.
- Family history and genetics. If you have parents, siblings, children or other close relatives whove been diagnosed with breast cancer, youre more likely to develop the disease at some point in your life. About 5% to 10% of breast cancers are due to single abnormal genes that are passed down from parents to children, and that can be discovered by genetic testing.
- Smoking. Tobacco use has been linked to many different types of cancer, including breast cancer.
- Alcohol use. Research indicates that drinking alcohol can increase your risk for certain types of breast cancer.
- Obesity. Having obesity can increase your risk of breast cancer and breast cancer recurrence.
- Radiation exposure. If youve had prior radiation therapy especially to your head, neck or chest youre more likely to develop breast cancer.
- Hormone replacement therapy. People who use hormone replacement therapy have a higher risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer.
Also Check: Is Metastatic Breast Cancer Genetic
How Can I Prevent Chest Wall Tumors
You may not be able to prevent chest wall tumors. But you can lower your risk of many forms of cancer with lifestyle changes, including:
- Avoid smoking and tobacco products.
- Get recommended vaccines, including the HPV vaccine.
- Get screening tests as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Keep a healthy weight.
- Limit or eliminate alcohol consumption.
Talk with your healthcare provider about your risk for various cancers and what lifestyle changes you should make.
Https Www Google Earth
2021. 1. 6. ·Jeffrey M. Rothschild, MD, MPH. A painless lump on the chest can most commonly be caused by a skin condition like an abscess, wart, or cysts. Rare causes for a painless chest wall lump include non cancerous cell. . Rib or chest pain after breastcancer may be costochondritis. Physical Therapy can help by increasing tissue flexibility and decreasing inflammation. … Also known as anterior chestwall pain, it causes discomfort in the chestwall around the breastbone or sternum and pain can range from mild to severe. … Costochondritis symptoms oftentimes.
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 2 Breast Cancer Mean