What Is Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Stage IV is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. It has spread to nearby lymph nodes and to distant parts of the body beyond the breast. This means it possibly involves your organs such as the lungs, liver, or brain or your bones.
Breast cancer may be stage IV when it is first diagnosed, or it can be a recurrence of a previous breast cancer that has spread.
Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Breast cancer survival rates vary widely based on many factors.
Two of the most important factors are the type of cancer you have and the stage of the cancer at the time you receive a diagnosis. Other factors that may play a role include:
shows theres a higher mortality rate in People of Color with breast cancer diagnoses compared with white people. One reason for this may be healthcare disparities.
The good news is breast cancer survival rates are improving.
According to the ACS , in 1975, the 5-year survival rate for breast cancer in women was 75.2 percent. But for women diagnosed between 2008 and 2014, it was 90.6 percent.
The 5-year survival rates for breast cancer differ depending on the stage at diagnosis. They range from 99 percent for localized early stage cancers to 27 percent for advanced metastatic cancers.
Breast Cancer Is Sometimes Caused By Inherited Gene Mutations
The genes in cells carry the hereditary information that is received from a persons parents. Hereditary breast cancer makes up about 5% to 10% of all breast cancer. Some mutated genes related to breast cancer are more common in certain ethnic groups.
Women who have certain gene mutations, such as a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, have an increased risk of breast cancer. These women also have an increased risk of ovarian cancer, and may have an increased risk of other cancers. Men who have a mutated gene related to breast cancer also have an increased risk of breast cancer. For more information, seeMale Breast Cancer Treatment.
There are tests that can detect mutated genes. Thesegenetic tests are sometimes done for members of families with a high risk of cancer. For more information, see Genetics of Breast and Gynecologic Cancers.
You May Like: Can You Get Breast Cancer From Getting Punched
Treatment Of Locally Advanced Or Inflammatory Breast Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Targeted therapy .
- Clinical trials testing new anticancer drugs, new drug combinations, and new ways of giving treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Breast Cancer Treatment . Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Don’t Miss: Can You Live With Metastatic Breast Cancer
What Causes Breast Cancer
Breast cancer develops when abnormal cells in your breast divide and multiply. But experts dont know exactly what causes this process to begin in the first place.
However, research indicates that are several risk factors that may increase your chances of developing breast cancer. These include:
- Age. Being 55 or older increases your risk for breast cancer.
- Sex. Women are much more likely to develop breast cancer than men.
- Family history and genetics. If you have parents, siblings, children or other close relatives whove been diagnosed with breast cancer, youre more likely to develop the disease at some point in your life. About 5% to 10% of breast cancers are due to single abnormal genes that are passed down from parents to children, and that can be discovered by genetic testing.
- Smoking. Tobacco use has been linked to many different types of cancer, including breast cancer.
- Alcohol use. Research indicates that drinking alcohol can increase your risk for certain types of breast cancer.
- Obesity. Having obesity can increase your risk of breast cancer and breast cancer recurrence.
- Radiation exposure. If youve had prior radiation therapy especially to your head, neck or chest youre more likely to develop breast cancer.
- Hormone replacement therapy. People who use hormone replacement therapy have a higher risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer.
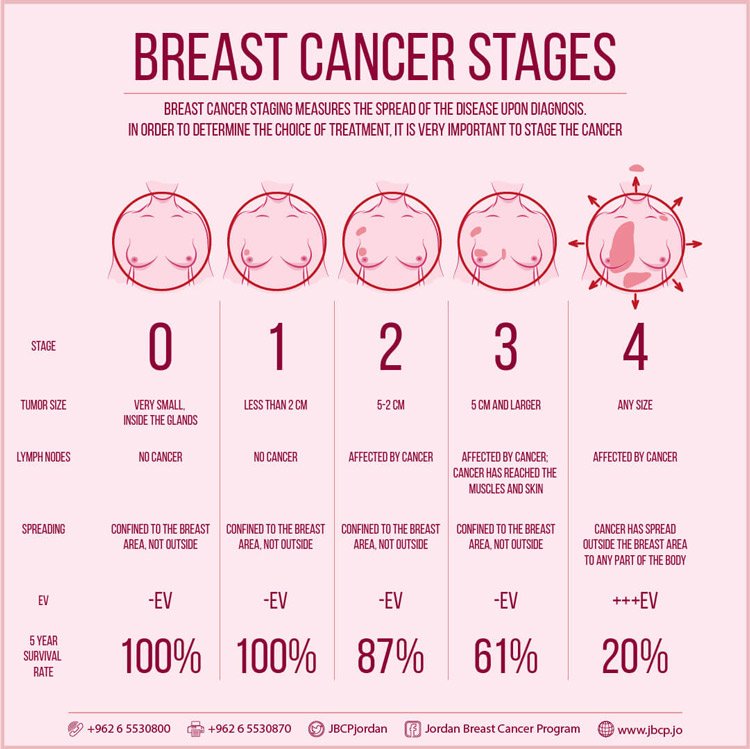
How Is Breast Cancer Staged
Breast cancer in men and women is staged the same, into five groups. This article will focus on early/moderate stage breast cancer in women. Learn more about male breast cancer here.
Staging is based on:
- The size of your tumor on the mammogram and what is found after surgery.
- Any evidence of spread to other organs .
- Surgery to test if your lymph nodes have cancer cells.
Staging is important because it helps guide your treatment options. Stages 0, I, and II are early or moderate stages.
The staging system is very complex. Below is a summary of the staging system. Talk to your provider about the stage of your cancer.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ : abnormal cells line a gland in the breast. This is a risk factor for future cancer, but this is not thought to be cancer itself.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ : abnormal cells linea duct in the breast. Women with DCIS have a higher risk of getting invasive breast cancer in that breast. Treatment options are similar to patients with Stage I breast cancers.
Don’t Miss: How Does Tamoxifen Work In Treating Breast Cancer
What Can I Expect If I Have Breast Cancer
If youve been diagnosed with breast cancer, your healthcare provider will talk with you in detail about your treatment options. Treatment and recovery will be different for everyone, so they can tell you what to expect in your situation.
Is breast cancer fatal?
People with early-stage breast cancer often manage their condition successfully with treatment. In fact, many people whove received a breast cancer diagnosis go on to live long, fulfilling lives. Late-stage breast cancer is more difficult to treat, however, and can be fatal.
What is the survival rate for breast cancer?
The overall five-year survival rate for breast cancer is 90%. This means that 90% of people diagnosed with the disease are still alive five years later. The five-year survival rate for breast cancer that has spread to nearby areas is 86%, while the five-year survival rate for metastatic breast cancer is 28%. Fortunately, the survival rates for breast cancer are improving as we learn more about the disease and develop new and better approaches to management.
Keep in mind that survival rates are only estimates. They cant predict the success of treatment or tell you how long youll live. If you have specific questions about breast cancer survival rates, talk to your healthcare provider.
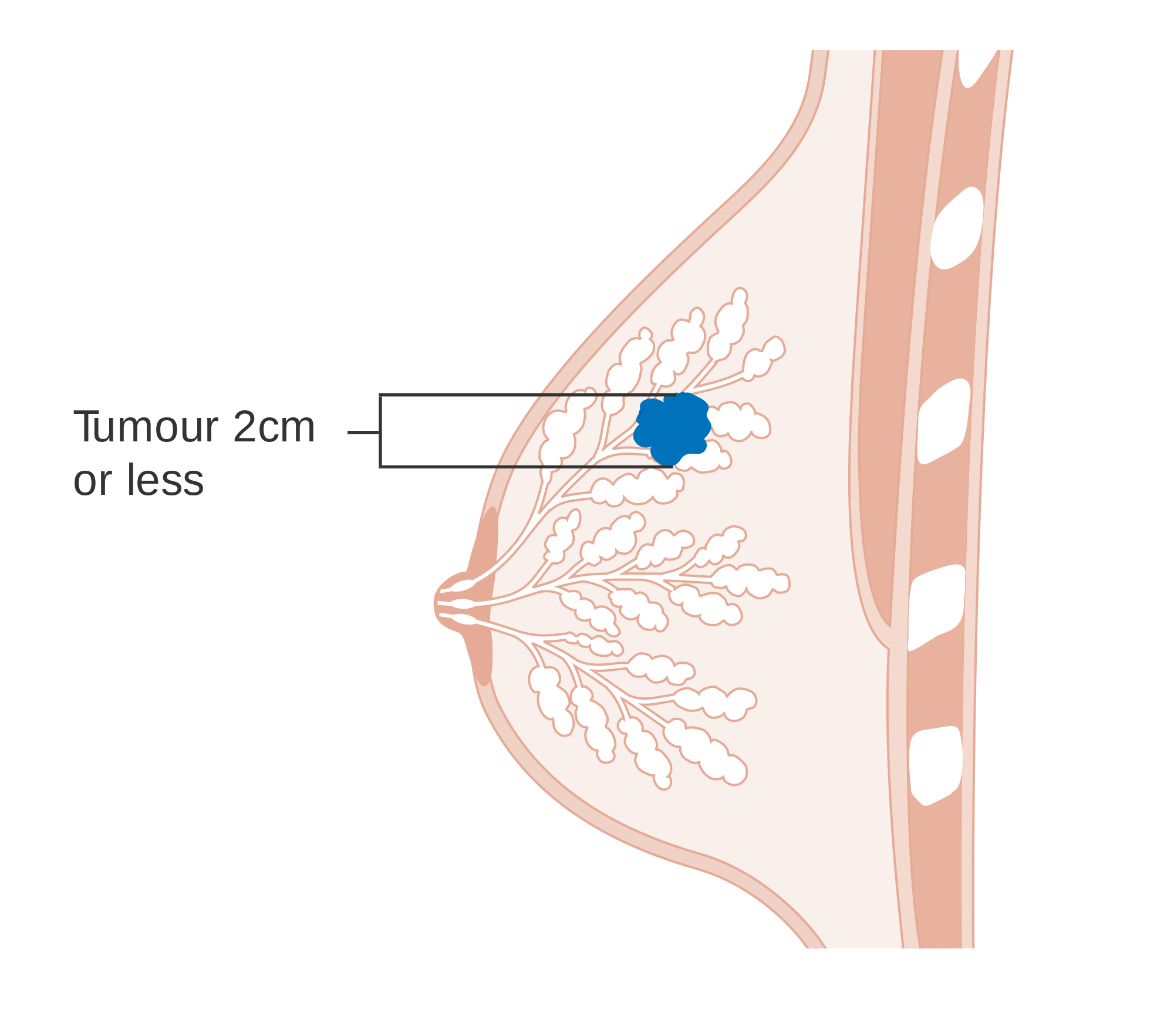
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Recommended Reading: What To Eat During Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
What To Expect If You Are Diagnosed With Early
When found early, breast cancer patients have a very high likelihood of living a long and happy life as a cancer survivor. The American Cancer Society reports that localized breast cancer survivors have a 99% chance of 5-year survival. Regional cancer that is still early stage but has moved to local lymph nodes has an 86% chance of 5-year survival. Compare this to patients with distant breast cancer who have an average of a 28% 5-year survival rate, and you’ll quickly see why regular mammograms and self-monitoring can be lifesavers!
You will definitely have cancer treatments and a journey ahead of you, but it will most likely be shorter than if it was found at a later stage.
Dramatic Rise In Cancer In People Under 50
Women diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer often can choose to have a lumpectomy, which removes only cancerous tissue and a thin margin of surrounding healthy cells instead of the entire breast. Current cancer guidelines for most women under 65 recommend following lumpectomy with radiation therapy, which targets stray cancer cells that might otherwise cause breast cancer to recur or spread to other parts of the body.
A new study presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology could eventually expand an option for skipping radiation to some women as young as 55.
The study involved 500 women ages 55 and older with early-stage breast cancers similar to established criteria for skipping radiation during treatment. It also allowed women to enroll if the margin of normal breast tissue removed was very thin . The analysis used an extra test on tumor cells removed during lumpectomy to confirm that they were slow-growing.
Over an average follow-up of five years, the study revealed that the rate of breast cancer recurrence in the same breast was 2.3% in women who skipped radiation after lumpectomy and took endocrine blockers instead the same rate expected with radiation use, which was impressive, said Nadine Tung, director of the Cancer Risk and Prevention Program and Breast Medical Oncology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Also Check: How Can We Prevent Breast Cancer
What Should A Person With Stage 0 Or Stage 1 Breast Cancer Expect Regarding Treatment
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered non-invasive, it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors. Like stage 0, Chemotherapy is often not necessary for earlier stages of cancer.
Material on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
Medically Reviewed on April 15, 2020
The Importance Of Staging In Breast Cancer Treatment Options
The stage of breast cancer is determined largely by the size of the tumor and whether it has spread beyond the breast to lymph nodes and/or other areas of the body. Early-stage breast cancer is smaller and hasn’t spread at all or only to a couple of lymph nodes closest to the breast where cancer was found. Learn more about breast cancer staging.
Among the various classifications of breast cancer, one category assigned is based on the extent to which the cancer has spread. The patient will be identified as one of:
- Early-stage breast cancer: Breast cancer is contained within the tissues of the breast or the axillary lymph nodes . This includes patients with ductal carcinoma in situ as well as stages 1, 2A, 2B, and sometimes 3A breast cancers.
- Locally advanced breast cancer: Cancer has spread beyond the breast tissues and affected many axillary lymph nodes. This includes the various levels of stage 3.
- Metastatic breast cancer: Also referred to as distant breast cancer, there are cancer cells found in other areas of the body. This is also referred to as stage 4. The most common places that breast cancer cells will move to include the bones, liver, and lungs/chest wall.
Also Check: Can You Have Pain With Breast Cancer
N Categories For Breast Cancer
N followed by a number from 0 to 3 indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are involved.
Lymph node staging for breast cancer is based on how the nodes look under the microscope, and has changed as technology has gotten better. Newer methods have made it possible to find smaller and smaller groups of cancer cells, but experts haven’t been sure how much these tiny deposits of cancer cells influence outlook.
Its not yet clear how much cancer in the lymph node is needed to see a change in outlook or treatment. This is still being studied, but for now, a deposit of cancer cells must contain at least 200 cells or be at least 0.2 mm across for it to change the N stage. An area of cancer spread that is smaller than 0.2 mm doesn’t change the stage, but is recorded with abbreviations that indicate the type of special test used to find the spread.
If the area of cancer spread is at least 0.2 mm , but still not larger than 2 mm, it is called a micrometastasis . Micrometastases are counted only if there aren’t any larger areas of cancer spread. Areas of cancer spread larger than 2 mm are known to influence outlook and do change the N stage. These larger areas are sometimes called macrometastases, but are more often just called metastases.
NX: Nearby lymph nodes cannot be assessed .
N0: Cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes.
N1c: Both N1a and N1b apply.
N3: Any of the following:
N3a: either:
N3b: either:
Breast Exam By Your Doctor
The same guidelines for self-exams provided above are true for breast exams done by your doctor or other healthcare professional. They wont hurt you, and your doctor may do a breast exam during your annual visit.
If youre having symptoms that concern you, its a good idea to have your doctor do a breast exam. During the exam, your doctor will check both of your breasts for abnormal spots or signs of breast cancer.
Your doctor may also check other parts of your body to see if the symptoms youre having could be related to another condition.
Read Also: What Does Stage 1a Breast Cancer Mean
Radiation Therapy For Early
Oncologists recommend radiation therapy after breast cancer surgery because it lowers the likelihood that cancer will return by killing the remaining cancer cells.
External radiation therapy is a common way to treat breast cancer. The patient comes into the office 5 days a week for 6-8 weeks for a short treatment with the linear accelerator. It doesn’t hurt but is very time-consuming. There are also some side effects like fatigue, redness, and sensitivity of the skin where the radiation is aimed.
For patients with early-stage breast cancer, another type of radiation therapy may be an option called High Dose Rate Brachytherapy. For this type of internal radiation treatment, a tube is inserted in the breast and left there. Over the course of 5 days , a radioactive pellet is inserted into the tube to treat the area inside the breast where the cancer was located. The pellet is removed and then replaced again a few times each day. Once the five days are over, the tube is removed and the treatment is complete. This comes with fewer side effects compared to external radiation and it shortens the overall treatment time.
Your radiation oncologist, who works closely with your breast surgeon and medical oncologist, will determine if HDR internal radiation therapy is an option for you.
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for breast cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the breast.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the breast to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
You May Like: How Does Hormone Therapy Work For Breast Cancer
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone