What Are Breast Cancer Stages
The stage of a cancer describes the size of the cancer and how far it has spread.
Your breast cancer may be described as stage 1, stage 2, stage 3 or stage 4.
An early form of breast cancer called DCIS is sometimes referred to as stage 0 breast cancer.
The stage takes into account:
- The size of the cancer
- Whether the lymph nodes are affected
- If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
The stage of your cancer may not be fully known until after you have had surgery.
Treatment Of Breast Cancer By Stage
This information is based on AJCC Staging systems prior to 2018 which were primarily based on tumor size and lymph node status. Since the updated staging system for breast cancer now also includes estrogen receptor , progesterone receptor , and HER2 status, the stages may be higher or lower than previous staging systems. Whether or not treatment strategies will change with this new staging system are yet to be determined. You should discuss your stage and treatment options with your doctor.
The stage of your breast cancer is an important factor in making decisions about your treatment options. In general, the more the breast cancer has spread, the more treatment you will likely need. But other factors can also be important, such as:
- If the cancer cells have hormone receptors
- If the cancer cells have large amounts of the HER2 protein
- If the cancer cells have a certain gene mutation
- Your overall health and personal preferences
- If you have gone through menopause or not
- How fast the cancer is growing and if it is affecting major organs like the lungs or liver
Talk with your doctor about how these factors can affect your treatment options.
Stage 0 cancers are limited to the inside of the milk duct and are non-invasive .
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a stage 0 breast tumor.
Box 1 How Rapid Autopsy Studies Can Inform On Metastatic Dissemination And Relapse
Definitions
-
Rapid autopsy: rapid post-mortem collection, examination and biobanking of tissuesfresh, snap-frozen and fixedfrom deceased patients shortly after death.
-
Rapid autopsy cancer programme: coordinated effort among oncologists, pathologists and scientists aimed at collecting specimens from cancer patients within a post-mortem interval of 68h before key biological information within the tissues of interest is lost.
Advantages
-
Multiregional biopsies: to conduct extensive, spatial sampling of tissuesprimary and metastatic, cancerous and normalfor in-depth, high-resolution multi-omics analysis.
-
Physiological model: to analyse DTCs in their natural metastatic niche.
-
to generate novel, ex vivo living patient-derived modelsautopsy-derived xenografts and organoids of metastatic tumours from sites that would otherwise be difficult to sample for functional evaluation .
-
Cancer evolution: to study the phylogenetic relationship of each sampled site to each other and infer the complete clonal evolution of a neoplasm.
-
Dormancy: to examine why some DTCs lodged in certain organs of the human body become dormant for years to decades.
-
Drug resistance: to study why DTC spread across different sites responds differently to therapy, with some developing resistance and others remaining sensitive to treatment.
-
Recurrence: to understand why only some DTCs residing in certain sites of the human body give rise to active metastases, ultimately responsible for patients relapse.
Also Check: Does Nipple Piercing Cause Breast Cancer
Tumor Grades: How The Cells Look
The tumor grade, sometimes called the cell grade, is a scale of G1 to G3 that identifies how abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope.
Cells in grade 1 tumors look almost normal and grow and spread slowly. Grade 3 cells are the most abnormal and grow the fastest. Grade 2 cells fall between grades 1 and 3.
Part of a womans prognosis, or long-term outcome, depends on the cancers stage and the tumors grade. Other factors that affect prognosis include the type of breast cancer a woman has, the hormones or proteins involved, and how quickly tumor cells are dividing and the tumor is growing.
Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Stage 3 breast cancer is divided into three groups:
- Stage 3A
- Stage 3C
Stage 3A can mean:
No cancer is seen in the breast, but cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast measures up to 5cm and cancer is found in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is larger than 5cm, and cancer is found in up to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone.
Stage 3B means the cancer in the breast can be any size and has spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall. Cancer is found in up to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breast bone.
Stage 3C means the cancer in the breast can be any size, may have spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall and cancer is found in 10 or more lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone, or to nodes above or below the collarbone.
Also Check: Her2 Positive Breast Cancer Survival Rates 2013
How Can I Prevent Breast Cancer Recurrence
Healthcare providers dont know why some people experience breast cancer recurrence. A recurrence isnt your fault. You didnt do anything wrong to cause it or fail to do something more to prevent it.
Certain medications may reduce the risk of breast cancer recurrence in people who have early stage breast cancer. For estrogen-receptive breast cancer, hormonal therapies including tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors block either the activity of estrogen or the bodys production of estrogen. Chemotherapy may also be recommended to reduce risk of breast cancer recurrence.
Early diagnosis may make it easier to treat a recurrence. Follow your healthcare providers recommendations for mammograms and other screenings. You should also perform regular breast self-exams. Get familiar with how your breasts look and feel so you can see your provider quickly if you notice changes. And remember that most breast changes occur for reasons other than cancer.
You May Like: Stage 4 Breast Cancer Symptoms Treatments
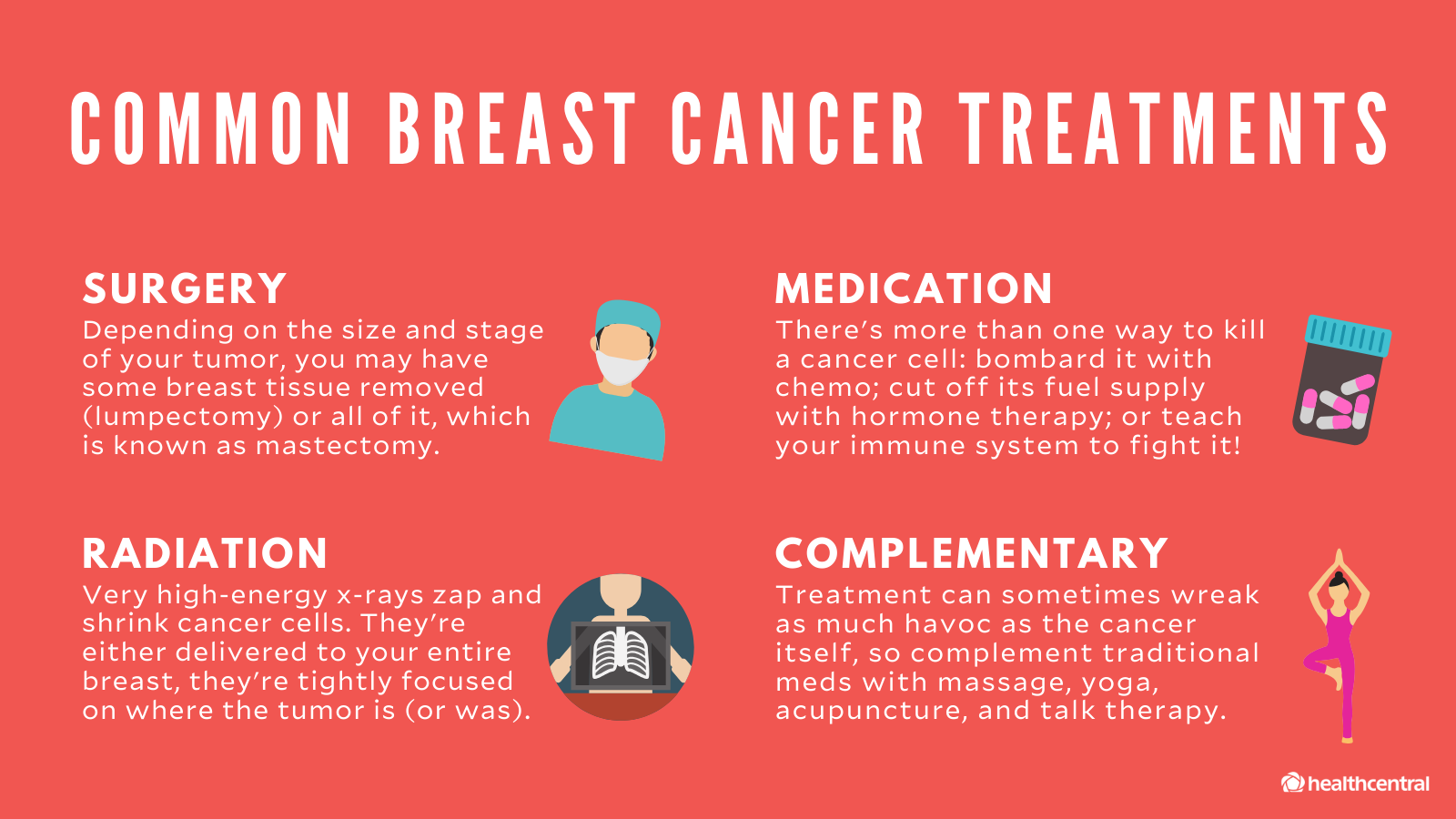
Treatment For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
The most common for stage 2 breast cancer is surgery.
Surgery
In most cases, treatment involves removing the cancer. The person may undergo a lumpectomy or mastectomy. The doctors and the individual can decide based on the size and location of the tumor. The surgeon may also remove one or more lymph nodes.
Combination therapy
A doctor may recommend a combination of radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy to people with stage 2A or 2B breast cancer.
Neoadjuvant therapy
In some cases, a doctor may recommend neoadjuvant therapy, which is chemotherapy before surgery to reduce the size of a tumor.
are 3A, 3B, and 3C.
3A breast cancer is an invasive breast cancer where:
- There is no tumor in the breast, or a tumor of any size is growing alongside cancer found in four to nine axillary lymph nodes or the lymph nodes by the breastbone.
- A person has a tumor greater than 5 cm. They also have clusters of breast cancer cells in the lymph nodes that are between 0.22 mm in diameter.
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm. The cancer has also spread to one to three axillary lymph nodes or the lymph nodes near the breastbone.
Stage 3B breast cancer is invasive breast cancer where:
- A tumor of any size has spread into the chest wall or skin of the breast, causing swelling or an ulcer to develop.
- Cancer cells may also be present in to up to nine axillary lymph nodes.
- They may be present in lymph nodes by the breastbone.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Breast Cancer In Teenagers
Breast Cancer May Return Even 20 Years Later Researchers Find
This means women with the most common type of breast cancer, called estrogen-positive or hormone-positive breast cancer, need to think carefully about whether they want to stop taking the pills, even if they cause side-effects, doctors said.
These breast cancers have a lingering smoldering quality and carry substantial risk of late recurrence after five years of therapy, said Dr. Harold Burstein of the Dana Farber Cancer Institute, who was not involved in the study.
Many patients think. OK, I made it to five years. I know Im safe, said Dr. Jennifer Litton, an oncologist at the MD Anderson Cancer Center. But for estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer, its a continued lifelong risk.
Related: Breast Cancer Drug Can Also Prevent Cancer
Breast cancer is the second-biggest cancer killer of American women, after lung cancer. The American Cancer Society says every year, itâs diagnosed in 200,000 women and a few men, and kills around 40,000.
Most breast cancers are fueled by estrogen, and drugs called hormone blockers are known to cut the risk of recurrence in such cases.
Tamoxifen long was the top choice, but newer drugs called aromatase inhibitors sold as Arimidex, Femara, Aromasin and in generic form do the job with less risk of causing uterine cancer and other problems. The longer women take them, the lower their risk of having the cancer come back.
However, they do cause side-effects.
Related: Gel Works As Well As Pill to Prevent Breast Cancer
Warning Signs And Words To Know
The most common symptom or warning sign of breast cancer is a lump in the breast. But both Cance and Cruz said not all lumps are cancerous. Women should also watch for nipple discharge and changes in breast shape or size.
Cance says vocabulary such as local, regional or distant may be used to describe a patient’s diagnosis. Local refers to the area where the cancer is confined within the breast. Regional may be used when the lymph nodes, primarily those in the armpit, are involved. The term distant is used when the cancer is found in other parts of the body as well, according to Cance.
Another term typically introduced after a breast cancer diagnosis is T-N-M. T represents the tumor size N relates to the involvement of nearby lymph nodes and M refers to whether the cancer has spread beyond the breast, according to Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
Recommended Reading: Whats Stage 3 Cancer
Prognosis For Breast Cancer
The prognosis is the likely outcome of a disease.
If the test results show breast cancer, you may wish to speak with your treatment team about the prognosis.
The doctors will look at the type and stage of the cancer as well as your age and general health to give a prognosis, but no doctor can predict the exact outcome for you.
What Does Stage 1a Breast Cancer Mean
Stage 1 breast cancer means the cancerous cells are invading the surrounding breast tissue. Stage 1 breast cancer has two subcategories â1A and 1B. People with stage 1A breast cancer have breast cancer with: A tumor measuring no more than 2 centimeters in diameter that has not spread outside the breast.
You May Like: Hormone Therapy For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Don’t Miss: 3b Cancer
Risk Of Late Recurrence Is Underestimated
A survey led by the Canadian Breast Cancer Network found that women often underestimate their risk of late recurrence. In the survey, only 10% were aware of the risk of recurrence after five years of tamoxifen therapy, and 40% felt that they were cured after hitting the five-year mark.
Many breast cancer survivors underestimate their risk of late recurrence.
Read Also: What Do Breast Cancer Patients Need
Where Do These Numbers Come From

The American Cancer Society relies on information from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for breast cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the breast.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the breast to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
Recommended Reading: Estrogen Responsive Breast Cancer
Don’t Miss: Third Stage Cancer
Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Stage 2 breast cancer is divided into two groups:
- Stage 2A
- Stage 2B
Stage 2A can mean:
No cancer is seen in the breast but cancer is found in one to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is 2cm or smaller and cancer is found in one to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone.
The cancer in the breast is larger than 2cm but smaller than 5cm and no cancer is found in the lymph nodes under the arm.
Stage 2B can mean:
The cancer in the breast is larger than 2cm but smaller than 5cm. Cancer is found in one to three lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone
The cancer in the breast is larger than 5cm and no cancer is found in the lymph nodes under the arm.
How Is Breast Cancer Recurrence Managed Or Treated
Your treatment depends on the type of cancer recurrence, as well as past treatments. If cancer develops in a reconstructed breast, your surgeon may want to remove the breast implant or skin flap.
Treatments for local and regional breast cancer recurrence may include:
- Mastectomy: Your surgeon removes the affected breast and sometimes lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy:Chemotherapy circulates in blood, killing cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy:Tamoxifen and other hormone therapies treat cancers that thrive on estrogen .
- Immunotherapy:Immunotherapy engages your bodys immune system to fight cancer.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy X-ray beams damage and destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Treatments target specific cancer cell genes or proteins.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Stages Survival Rate
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma: The Most Common Kind
The most common form of breast cancer is invasive ductal carcinoma , sometimes also called infiltrating ductal carcinoma. About 80 percent of all new breast cancer cases in women, and nearly all breast cancer in men, are IDC. The risk of IDC also increases as people grow older.
IDC starts in the ducts just as DCIS does, but the cancer then grows beyond the ducts and invades, or infiltrates, the fatty tissue surrounding the ducts. Without treatment, the cancer continues to metastasize, or spread, into the lymph nodes and bloodstream.
The options available to treat IDC depend on the type of breast cancer it is, what mutations it does or does not have, how aggressive it is, and other factors. One of the most important of those other factors is the cancer stage.
Intrinsic Subtypes And Late Recurrence
A number of different methods have been evaluated for the ability to predict late recurrence. Some of these include:
Higher expression of estrogen-responsive genes: A 2018 study found that people with ER+/HER2 negative breast cancers who had higher expression of estrogen-responsive genes and were not treated with extended hormonal therapy had a high risk of recurrence after five years.
Multigene assays: Several multigene assays may help predict late recurrence, but using this information to figure out when to extend hormonal therapy requires more research. A 2018 evaluation of an 18-gene, 10-year signature found that the information regarding prognosis was similar to other tests including Oncotype DX Recurrence Score, Prosigna PAM50 risk of recurrence score, Breast Cancer Index and IHC4.
Don’t Miss: Stage 1 Grade 3 Breast Cancer
Treatment For Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Doctors can offer a variety of for stage 1 breast cancer, although surgery is the primary treatment.
Surgery
A lumpectomy or mastectomy are both viable surgical options for people with stage 1 breast cancer. A doctor will decide what surgery is most appropriate depending on the location of the primary tumor, how large it is, the size of the breast, family history, genetics, and the persons preference.
The doctor may also carry out a biopsy on one or more lymph nodes.
After removing the tissue, they will send it to a laboratory for further tests. The results will help inform decisions on the next stage of treatment.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a standard treatment for stage 1 breast cancer. However, the decision will depend on factors such the age of the person, the type of cancer, the size of the tumor, and whether there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes.
Hormone therapy
If the breast cancer is ER+ or PR+, hormone therapy may be effective. Hormone therapy works by preventing the growth of estrogen, which helps cancer grow, by blocking estrogen from attaching to tissue and fuelling cancer growth, or both.
Hormone therapy can reach cancer cells in the breast, as well as other areas of the body, and it can reduce the risk of cancer returning.
Chemotherapy
also has subcategories known as 2A and 2B.
Stage 2A breast cancer is invasive cancer:
What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Because stage 1 breast cancer is the earliest stage, you may not notice or experience any symptoms.
However, if symptoms do develop, they may include:
- a lump in your breast tissue or under your arm
- redness, dimpling, or swelling in your breast
- an , which means that the nipple has pulled inward
- non-breast milk nipple discharge
Having these symptoms does not always mean that you have breast cancer, but it is important to let your doctor know so that they can evaluate you.
Recommended Reading: Baking Soda For Breast Cancer
Checking The Lymph Nodes
The usual treatment is surgery to remove the cancer. Before your surgery you have an ultrasound scan to check the lymph nodes in the armpit close to the breast. This is to see if they contain cancer cells. If breast cancer spreads, it usually first spreads to the lymph nodes close to the breast.
Depending on the results of your scan you might have:
- a sentinel lymph node biopsy during your breast cancer operation
- surgery to remove your lymph nodes
You may have other treatments after surgery.