Symptoms Of Secondary Breast Cancer
Secondary breast cancer means that a cancer that began in the breast has spread to another part of the body. Secondary cancer can also be called advanced or metastatic cancer.
It might not mean that you have secondary breast cancer if you have the symptoms described below. They can be caused by other conditions.
Cancer In The Lymph Nodes
Cancer can appear in the lymph nodes in 2 ways: it can either start there or it can spread there from somewhere else.
Cancer that starts in the lymph nodes is called lymphoma. You can read more about lymphoma in Hodgkin Lymphomaand Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
More often, cancer starts somewhere else and then spreads to lymph nodes. That is the focus of this section.
Breast Cancer Progression Tends To Be Consistent And Predictable
There are many ways that breast cancer can develop but most of the time it starts in the breast ducts.
While cancer is still confined to the breast ducts, specialists refer to it as ductal carcinoma in situ, or DCIS. The good news is that if breast screening detects cancer at this in-situ stage, the chance of survival is close to 100%.
As cancer moves into the breast duct wall and finally begins to affect the surrounding breast tissue, specialists call it infiltrative or invasive breast cancer.
If treatment does not occur, breast cancer will usually spread to other areas of the body . Very often the first area that cancer usually spreads to is the lymph nodes in the underarm area .
Once cancer enters the lymphatic system, it can and usually does spread to other areas of the body. Sometimes this is called distant metastasis.
Not all breast cancers spread first to the axillary lymph nodes and then to the rest of the body. If the breast tumor occurs near the nipple, cancer may spread first to the internal mammary nodes beneath the sternum. And in some cases, the breast cancer can spread via the bloodstream without involving the lymphatic system.
Also Check: How To Tell If Cancer Has Metastasized
Lymphangiogenesis And Lymphatic Metastasis
While the promoting effect of angiogenesis and vascularization of the tumor in the progression of the disease is well documented, there is little information with regard to lymphangiogenesis and its function in metastasis. Certain studies have indicated that the tumors are devoid of lymphatic vessels, while others have suggested that tumors invade and destroy lymphatic vessels . Furthermore, other studies have indicated that tumor cells may induce lymphangiogenesis, some form of lymphatic sprouting, or hyperplasia in close proximity to the periphery of the tumors . Therefore, the pertinent question is whether lymphangiogenesis is necessary for lymphatic metastasis. Although it is possible for lymphatic metastasis to occur via preexisting vessels that were incorporated into the tumors, there is evidence to suggest that increased lymphatic vessel density due to lymphangiogenesis significantly improves metastasis .
Cancer In Nearby Lymph Nodes
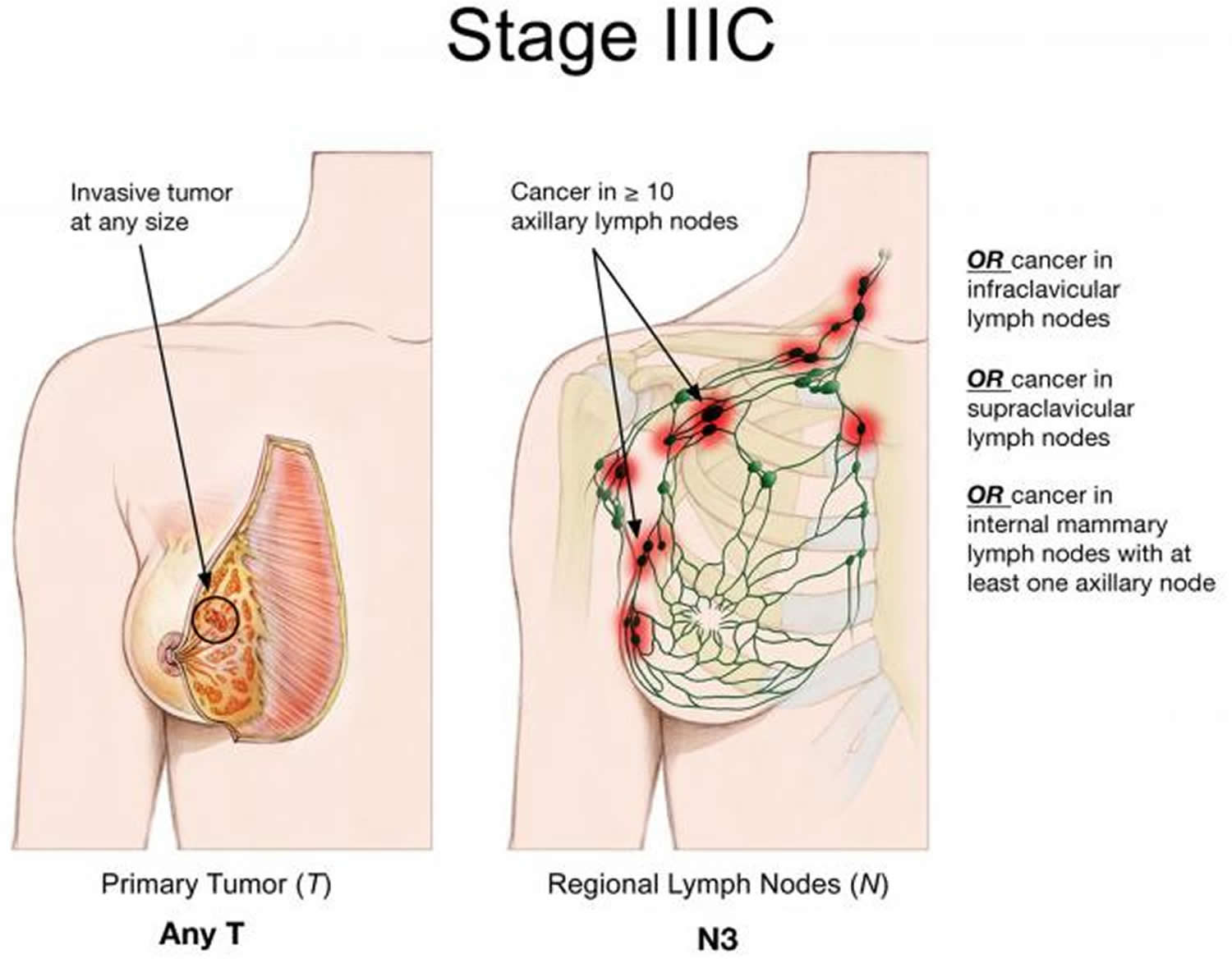
Sometimes cancer is found in lymph nodes that are near to where the cancer started. For example, breast cancer cells may travel to lymph nodes in the armpit or above the collar bone .
If a surgeon removes a primary cancer, they often remove some of the nearby lymph nodes. The lymph nodes are examined to see if there are any cancer cells in them.
The risk of the cancer coming back may be higher if the nearby lymph nodes contain cancer cells. Your doctors may suggest you have more treatment after surgery to reduce the risk.
Cancer in lymph nodes that are further away is called secondary cancer. Cancer found in nearby lymph nodes is usually treated differently to cancer in lymph nodes that are further away from the primary cancer.
Also Check: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rates
What Is Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Stage IV is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. It has spread to nearby lymph nodes and to distant parts of the body beyond the breast. This means it possibly involves your organs such as the lungs, liver, or brain or your bones.
Breast cancer may be stage IV when it is first diagnosed, or it can be a recurrence of a previous breast cancer that has spread.
A Little Bit About The Internal Mammary Lymph Nodes
The internal mammary nodes are located behind the ribs. Ribs are made of bone, but in the front, they turn into cartilage just before they join the sternum.
So, each rib attaches to the sternum with cartilage and each of these cartilage bars is around 5 cm long. Thus, it can be very difficult to remove an internal mammary node. There is an internal mammary artery and vein along with the lymph ducts and other veins.
If you need to remove an internal mammary node, the cartilage in front needs to be cut out. Cartilage, unfortunately, does not grow back or heal and this will leave a gap which makes the rib essentially useless.
So, it is a judgement call by the surgeon as to whether or not one should attempt a surgical approach to remove internal mammary nodes with positive metastasis. This is because surgical removal is just too damaging to the function of the chest and ribs.
However, electron beam radiotherapy is an effective treatment for internal mammary nodes. The electrons penetrate to about the correct depth to reach the internal mammary nodes.
Treatment of Stage IIIa Breast Cancer
The treatment for women with stage IIIa breast cancers tends to be a modified radical mastectomy and locoregional radiotherapy.
Often, chemotherapy is given as adjuvant therapy, but in some cases , pre-operative chemotherapy is also recommended. Breast conservation is generally not a good option with stage IIIa breast cancers.
You May Like: Did Anne Hathaway Have Breast Cancer
What Is Breast Cancer In Men
Breast Cancer in men is a type of cancer that occurs in the non-functional milk ducts, glands, and breast tissues. Mens breasts have fatty tissues, breast cells, and ducts. Breast tissues in men are similar to that of a pre-puberty girl. These tissues in men do not grow much because they have low levels of female hormones. Cancer develops when healthy cells grow out of control, forming a mass of cells called a tumor.
A tumor can be malignant or benign. The tumor is malignant if it grows and spreads to other parts of the body. On the other hand, a benign tumor can grow but doesnt spread to other body parts. When Breast Cancer spreads to the other body parts through the lymph or blood, it is called metastasis.
What Happens After A Sentinel Node Biopsy
If the lymph nodes do not contain cancer cells, you wont need to have any more nodes taken out.
If cancer cells are in the sentinel nodes, you have another operation to remove most or all of the lymph nodes under your arm. This is an axillary lymph node dissection or clearance. You generally have it about 2 weeks after you get the results.
Some people have radiotherapy to the armpit to destroy any remaining cancer cells instead of surgery.
Also Check: Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer Curable
Stage Iv Breast Cancers May Be Recurrences Following Initial Treatment
Up to 5% of initial breast cancer diagnoses are of the most advanced or metastatic stage. However, this number has significantly reduced with the implementation of widespread breast cancer screening programs.
Metastatic breast cancer can appear to be a rapid deterioration of a disease that has been present for some time undetected.
But metastatic breast cancer can also be the result of a recurrence of breast cancer after successful initial treatment. Sometimes the terms local and regional recurrence indicate a return of breast cancer to the original tumor site or elsewhere in the breast or contralateral breast.
If the cancer returns in other areas of the body it is a distant metastasis or distant recurrence.
For more detail on Stage IV survival rates, recurrence rates and treatment please see our new post HERE.
How Is Cancer In Lymph Nodes Found
Normal lymph nodes are tiny and can be hard to find, but when theres infection, inflammation, or cancer, the nodes can get larger. Those near the bodys surface often get big enough to feel with your fingers, and some can even be seen. But if there are only a few cancer cells in a lymph node, it may look and feel normal. Lymph nodes deep in the body cannot be felt or seen. So doctors may use scans or other imaging tests to look for enlarged nodes that are deep in the body. Often, enlarged lymph nodes near a cancer are assumed to contain cancer.
The only way to know whether there is cancer in a lymph node is to do a biopsy. Doctors may remove lymph nodes or take samples of one or more nodes using needles. The tissue thats removed is looked at under the microscope by a pathologist to find out if there are cancer cells in it. The pathologist prepares a report, which details what was found. If a node has cancer in it, the report describes what it looks like and how much was seen.
When a surgeon operates to remove a primary cancer, they may remove one or more of the nearby lymph nodes as well. Removal of one lymph node is considered a biopsy, but when many lymph nodes are removed, its called lymph node dissection. When cancer has spread to lymph nodes, theres a higher risk that the cancer might come back after surgery. This information helps the doctor decide whether more treatment, like chemo,immunotherapy, targeted therapy or radiation, might be needed after surgery.
Don’t Miss: Chances Of Getting Breast Cancer Twice
About The Lymph Nodes
The lymphatic system helps protect us from infection and disease. It also drains lymph fluid from the tissues of the body, before returning it to the blood.
The lymphatic system is made up of fine tubes called lymphatic vessels. They connect to groups of lymph nodes throughout the body.
Lymph nodes are small and bean-shaped. They filter bacteria and disease from the lymph fluid. When you have an infection, lymph nodes often swell as they fight the infection.
Diagnosing Metastatic Breast Cancer
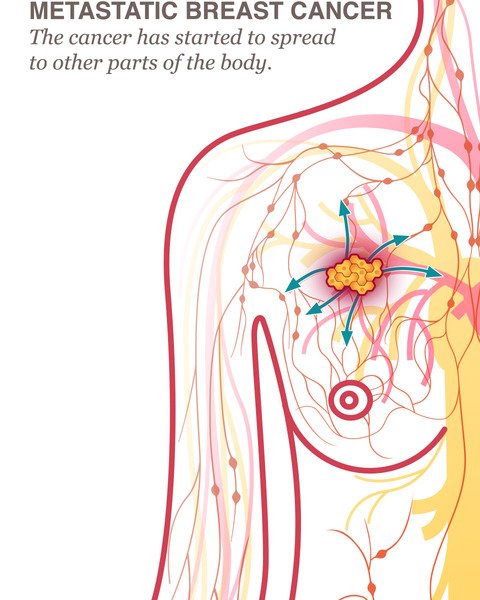
Getting a clear picture of where breast cancer has spread is essential for creating a personalized treatment plan. Your care team will likely use a combination of the following tests and tools to diagnose both localized and advanced breast cancer:
Ultrasound exam: With this imaging technique, sound waves create a picture of internal areas of the body.
Magnetic resonance imaging : This procedure produces detailed images using magnetic fields and radio waves.
Blood chemistry studies: A blood sample is taken to measure the amounts of certain substances that are released by your organs and tissues. A higher or lower amount of a particular substance may be a sign of disease.
Biopsy: A biopsy is the removal of cells or tissues so a pathologist may view them through a microscope. Your original breast cancer diagnosis was likely confirmed with a biopsy.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Integrative Therapies For Metastatic Breast Cancer
You may find it beneficial to add integrative therapies to your treatment plan. There are many evidence-informed integrative modalities to boost the mind and body. Practices like gentle yoga, meditation, massage and music therapy may feel enjoyable and reduce stress and anxiety levels.
To help our patients maintain quality of life after a metastatic breast cancer diagnosis, our team of breast cancer experts may offer supportive care services to help manage side effects of the disease and its treatments. These may include:
Diagnosing Cancer Of The Lymph Nodes
In addition to a biopsy, the TNM system is commonly used to issue a diagnosis and determine which type of treatment is best. The T refers to the size of the tumor or cancerous growth. The N refers to the number of lymph nodes that contain cancerous cells. And, the M is for metastasis, which refers to cancer thats spread to areas far from the originating tumor.5
This categorization is used in addition to other diagnostic tests and tools to determine the cancer stage such as:
- Imaging tests X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and other types of imaging tests can provide a clearer picture and more information about where the cancer is located and how much is present.
- Endoscopy exams An endoscope is a thin, lighted tube with a video camera attached that looks around on the inside of the body for cancerous areas.
In general, cancers assigned as Stage I are less advanced and have a better prognosis and response to treatment. Whereas, a higher stage indicates that the cancer has spread further and requires a more intense or multiple types of treatment. Other factors that affect treatment are:
Also Check: What Is De Novo Metastatic Breast Cancer
Where Does Breast Cancer Spread To
Breast cancer cells seem to prefer to settle into:-
- long bones in the arms and legs
- ribs
- skull
With an osteolytic metastasis, the cancer kind of eats away at the bone, creating holes.
With an osteoblastic bone metastasis, the bone mineral density actually increases, but this can cause the bones to fracture more easily. This requires a little more explanation. Breast cancer metastases tend to be lytic when they are untreated, and then they become densely sclerotic as they respond to treatment.
Even if no treatment is given yet, an osteoblastic metastasis from breast cancer generally indicates that the persons own body is trying to fight cancer with some success.
A CT scan may also be used to check for metastasis to the lungs or liver. A CT scan is essentially an X-ray linked to a computer. The breast cancer doctor injects a contrast dye agent into the bloodstream and this makes any cancer cells in the liver and chest easier to see.
Surgery To Remove Lymph Nodes
Breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body. If it does spread, it usually first spreads to the lymph nodes in the armpit close to the breast. These lymph nodes drain the lymphatic fluid from the breast and arm.
It is important to know if there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes in the armpit and how many. This helps the doctors work out the stage of your cancer and plan the best treatment for you.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
What Happens When Breast Cancer Spreads
Breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body. This happens primarily through the lymph nodes, and a much smaller portion through the blood vessels. Here is a discussion of the role of the lymphatic system in breast cancer.
For a quick refresher, lymph nodes are kidney bean shaped organs that are scattered all over the body, but have 5 concentrated areas, one of which is the underarms. The lymph nodes in the underarms primarily take care of the breast and arm on the same side. They help to stimulate your immune system to fight off intruders. They also transport fighter cells to the bone marrow. When cancer cells are trapped in the lymph nodes, they may be destroyed by the immune system, or they may spread to other areas from there.
When there is breast cancer in your lymph nodes, you may not notice any symptoms at all. In fact, it is not until the lymph nodes are overloaded with cancer and swollen that you may notice a lump in the underarm or even swelling of the arm or breast on the same side.
Once breast cancer leaves the lymph nodes, it is considered metastatic, or stage IV.
There are times when breast cancer is metastatic, or spread to other organs, when it is first diagnosed. In these cases, breast cancer was not detected in the breast before it spread to other parts of the body.
Types Of Lymph Node Surgery
Even if the nearby lymph nodes are not enlarged, they will still need to be checked for cancer. This can be done in two different ways. Sentinel lymph node biopsy might be needed.
Lymph node surgery is often done as part of the main surgery to remove the breast cancer, but in some cases it might be done as a separate operation.
You May Like: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
If breast cancer has spread to the chest wall or skin of the breast, or the lymph nodes around the chest, neck and under the breast bone, but has not spread to other areas of the body, its called locally advanced breast cancer. Sometimes breast cancer is locally advanced when it is first diagnosed.
People who have locally advanced breast cancer are thought to have an increased risk of cancer cells spreading to other areas of the body, compared to those with stage 1 or 2 breast cancers.
How Is A Local Recurrence After Lumpectomy Diagnosed
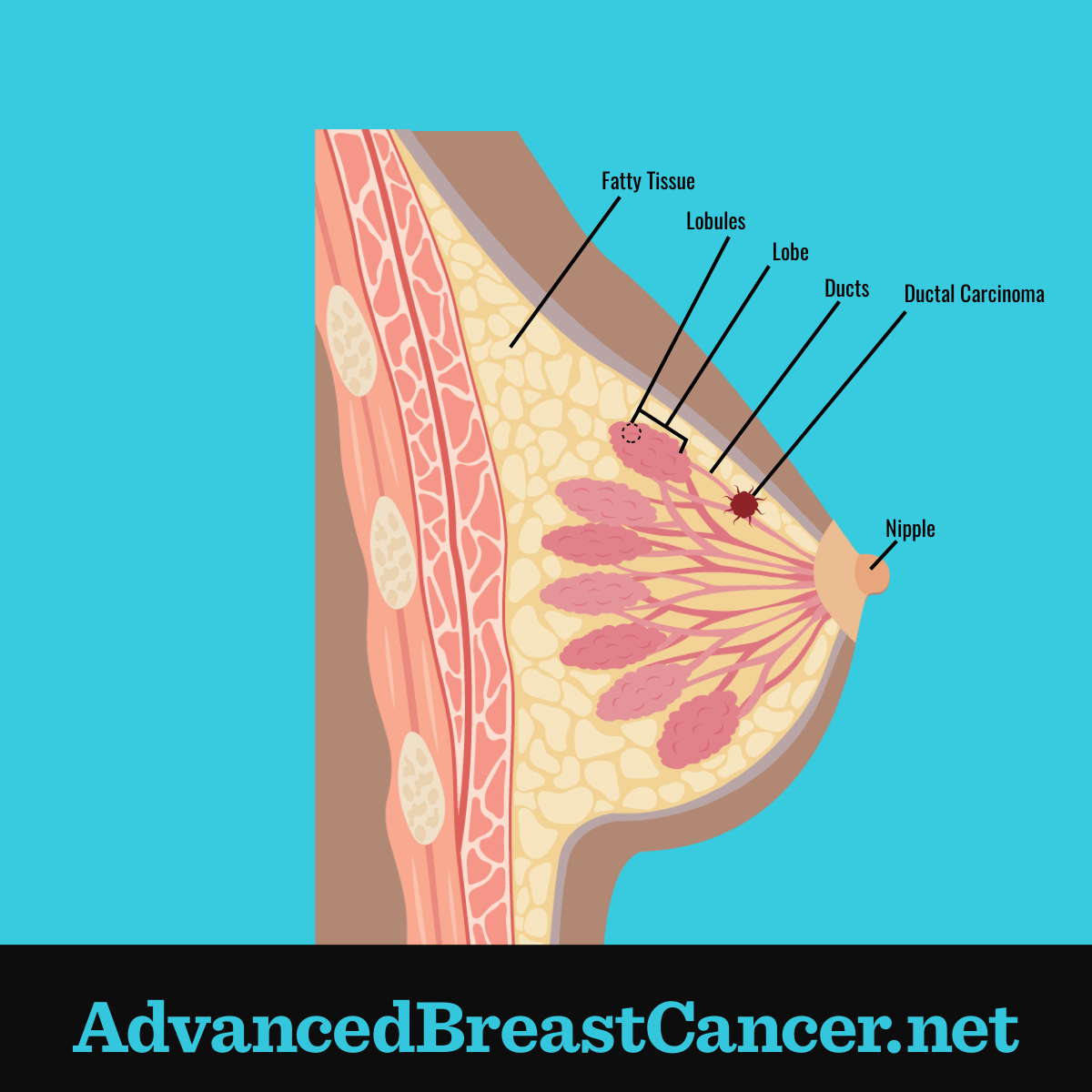
After a diagnosis of early stage breast cancer, any remaining breast tissue should be evaluated annually with scans .
Most local recurrences within the breast after lumpectomy are detected on routine annual breast imaging, which usually takes the form of mammography and ultrasound, and on occasions MRI.
If you have a local recurrence or new primary breast cancer, you may find symptoms similar to an initial breast cancer. This includes:
- A new lump in the breast, armpit area or around the collarbone
- A change in breast size or shape
- Changes to the nipple, such as sores or crusting, an ulcer or inverted nipple
- Clear or bloody nipple discharge
- Changes to the skin including redness, puckering or dimpling
- Breast tenderness or pain
Once a local recurrence has been diagnosed, we do tests to see whether there are signs of cancer elsewhere in the body. These may include a chest X-ray, CT scan, bone scan or PET scan, and blood tests , then we have to figure out how best to treat the tumour in the breast. Usually in these cases we do a mastectomy, as the prior less drastic surgery and radiation didnt take care of it.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer Curable In The 3 Stage
Read Also: Is Breast Cancer Curable