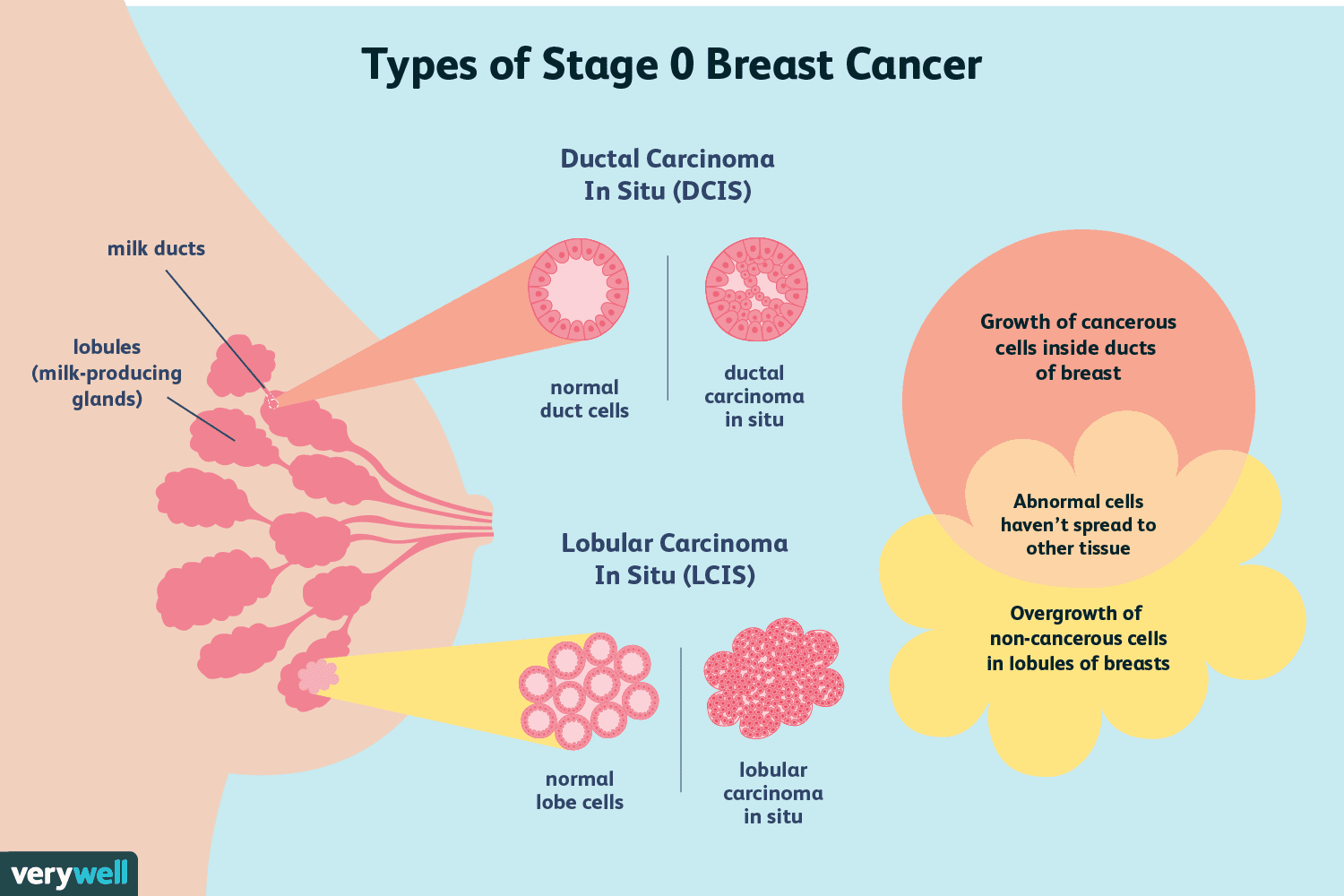
Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
Lobular carcinoma is cancer of the glands that produce breast milk. These glands are called the lobes, or lobules.
Lobular carcinoma in situ is a stage of lobular cancer that does not usually spread. However, it does increase a persons risk of developing other types of breast cancer. Most women get lobular carcinoma before menopause when they are between 4050 years of age.
Fewer than 1 in 10 women get this type of cancer after menopause.
For this reason, a diagnosis of LCIS may mean that a woman will need more frequent breast cancer screenings in the future.
What Medication Treat Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Tamoxifen may be prescribed for woman of all ages who have been treated for DCIS. In those women past menopause, the doctor may prescribe an aromatase inhibitor. These medications help lower the risk of DCIS or another type of cancer developing in either breast. If either is prescribed, it is suggested that these drugs be taken for five years after surgery.
What Are Some Advantages Of Receiving Treatment For Dcis At Msk
At MSK, we have a very thoughtful approach to personalizing treatment for each person with DCIS. The doctors and patients make treatment decisions as a team. Much of the research determining risk factors for DCIS-related recurrence was done at MSK, and we have a computerized prediction model that can help calculate an individuals risk of recurrence, which helps us decide what treatments are best. Weve tried to figure out who really needs additional treatments, such as radiation or hormone therapy, and who may be able to avoid certain treatments. Our goal is to find the right treatment for each patient, so that they can remain cancer free with an excellent quality of life moving forward.
You May Like: What Is Hr Positive Breast Cancer
Risk Of Developing Invasive Breast Cancer After Dcis
After treatment for DCIS, theres a small risk of:
- DCIS recurrence
- Invasive breast cancer
These risks are higher with lumpectomy plus radiation therapy than with mastectomy . However, overall survival is the same after either treatment .
Higher grade DCIS appears more likely than lower grade DCIS to progress to invasive cancer after treatment .
With close follow-up, invasive breast cancer is usually caught early and can be treated effectively.
Learn more about tumor grade.
If youve been diagnosed with DCIS, Susan G. Komen® has Questions to Ask Your Doctor resources that may be helpful. For example, we have a Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Breast Cancer Surgery resource and a Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Radiation Therapy and Side Effects resource.
You can download and print these resources and take them with you to your next doctor appointment. Theres plenty of space to write down the answers to these questions, which you can refer to later.
There are other Questions to Ask Your Doctor resources on many different breast cancer topics you may wish to download. They are a nice tool for people recently diagnosed with breast cancer, who may be too overwhelmed to know where to begin to gather information.
What Is Dcis Breast Cancer

In This Article
DCIS breast cancer is a non-invasive breast cancer. Ductal carcinoma refers to cancerous growth initiates from milk duct and surrounded breast tissue that covers the internal organs. The term in situ refers to in its original place.
The growth of Ductal carcinoma in situ is restricted only in the milk duct and does not spread to internal organs. therefore the risk of a fatal outcome is negligible. But there is always a risk of progression of an invasive breast cancer later stage of life1.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
What Type Of Follow
Each patient is different, and the doctor will work with each individual on a follow-up plan after surgery and radiation therapy. Typically, a patient can expect to see the doctor for a physical exam every six to 12 months for five years after treatment, then annually after that. An annual mammogram will also be recommended.
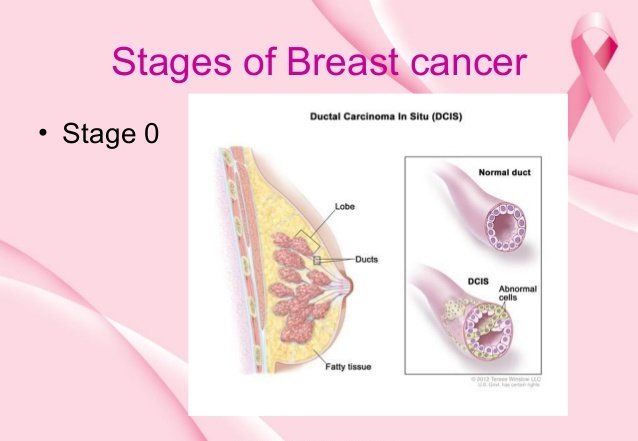
What Is Stage 0 Lcis
Lobular carcinoma in situ at Stage 0 generally is not considered cancer. Although it has carcinoma in the name, it really describes a growth of abnormal but non-invasive cells forming in the lobules. Some experts prefer the name lobular neoplasia for this reason because it accurately refers to the abnormal cells without naming them as cancer. LCIS, however, may indicate a woman has an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
If you have been diagnosed with LCIS, your doctor may recommend regular clinical breast exams and mammograms. He or she may also prescribe Tamoxifen, a hormone therapy medication that helps prevent cancer cells from growing.
Also Check: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Grading Of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Determined By Size And Shape Of Nuclei And Patterning
All DCIS is considered stage 0 breast cancer or the earliest stage possible. Once DCIS as an early stage cancer is confirmed, it may be given a specific DCIS grade based upon the particular kinds of cells which are growing, the characteristics of their nuclei and their growth patterns. The lower the grade, the more slowly the cancer cells grow and the more closely they resemble normal breast cells. Based on this information, the pathologist will describe the DCIS as either grade one , grade two or grade three .
If You Think You Are At High Risk For Breast Cancer
If you are concerned about your risk for breast cancer, talk with your doctor. He or she can help you understand your risk if you have a strong family history of breast cancer. Based on your risk, your doctor will recommend a screening schedule for you.
Your doctor may talk with you about genetic testing, the risks and benefits of taking hormone therapy, or even surgery if your risk is very high.
For more information, see:
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate Of Breast Cancer Stage 4
Who Is Most At Risk For Dcis
We consider anyone who has previously had DCIS or other types of breast cancer, older women, and women with certain previous breast histories such as atypical hyperplasia, a precancerous condition that affects cells in the breast, to be most at risk for Stage 0 cancer, explains Helen Cappuccino, MD, FACS, Assistant Professor of Oncology. Also at risk are women with radial scars, the benign breast lesions that may be detected as a kind of star-shaped feature that can be detected by mammograms, and intraductal papillomas, benign tumors that grow within the milk ducts of the breast. We also look for a family history of breast cancer and prior breast biopsies, as well as women who have a child at age 30 or older, women who have never had a baby, and women who have had fewer full-term pregnancies.
Stage 0 Breast Cancer: When Should You Wait And See
In cancer, as in other areas of medicine, early detection can save lives. But the screening tests used to find early tumors also detect disease that would never cause problems disease you’ll die with but not from. Managing those cases means giving potentially harmful treatment to patients who won’t benefit.
DCIS, or ductal carcinoma in situ, is the poster child of this dilemma. Before routine mammograms, only about 1 percent of U.S. breast cancer cases were DCIS. Now nearly 65,000 women a year about 22 percent of those with breast cancer are diagnosed with DCIS.
DCIS, also known as Stage 0 breast cancer, is not life-threatening, and not all cases will progress to invasive cancer. But because there is no reliable way to determine which ones will, nearly all DCIS is surgically removed with a lumpectomy or mastectomy . Most DCIS patients also are offered radiation and drugs.
While many experts believe this simply is the price that must be paid to save lives, an increasingly vocal minority are working to find ways to reduce overdiagnosis and overtreatment, especially of DCIS.
A small minority women under 35, African-Americans and those with especially aggressive molecular features had a significantly higher chance of dying of breast cancer. Ironically, they did so despite the aggressive treatment they received.
A few U.S. centers already are allowing some low-risk DCIS patients to skip surgery after being informed of the risks and benefits.
Also Check: Can Cancer Come Back In The Same Breast
Beware Of Other Conditions That Can Mimic Stage 0 Breast Cancer:
Differential diagnosis for pathologic nipple discharge :
-
papilloma- most common
-
Post-menopausal use of estrogen and progesterone hormone replacement therapy.
-
Overweight status in post-menopausal women.
-
Mammographic density.
LCIS is more likely to occur in younger women and is more common in white women than in black women.
A Mammogram Can Reveal Dcis
A routine mammogram is usually the way DCIS is discovered and diagnosed. When DCIS is present, it will typically show up as a cluster of calcifications of varying shapes and sizes within a breast duct .
These calcifications are the result of tiny specks of calcium that form in the cells of old cancer cells that have died off and piled up. If calcifications are seen on a mammogram, a biopsy will then be performed to confirm the diagnosis of DCIS.
While the incidence of DCIS has risen sharply since the 1970s, this increase has been attributed primarily to the increased use of screening mammograms.
You May Like: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Body Image And Sexual Problems
Your feelings about your body may change after treatment for breast cancer. Managing body image issues may involve talking openly about your concerns with your partner and discussing your feelings with your doctor. Your doctor may be able to refer you to groups that can offer support and information.
Sexual problems can be caused by the physical or emotional effects of cancer or its treatment. Some women may feel less sexual pleasure or lose their desire to be intimate. For more information, see the topic Sexual Problems in Women.
What Is Stage 0 Dcis
Stage 0 breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ is a non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. In Stage 0 breast cancer, the atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts or lobules into the surrounding breast tissue. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ is very early cancer that is highly treatable, but if its left untreated or undetected, it can spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Also Check: Type 3 Breast Cancer
It’s Confusing Even For Doctors
A recent study in the Annals of Internal Medicine found that pathologists disagree with one another about 8% of the time when diagnosing breast biopsy samples, and that cases of DCIS were the most difficult to reach a conclusion about. About 19% of DCIS cases were overinterpreted in the study, meaning they were mistakenly categorized at a higher grade or as invasive cancer, and about 12% were underinterpreted, or mistakenly categorized at lower grades.
The authors write that non-invasive breast lesions represent a “gray zone” in medicine, where there’s not always a right or wrong diagnosis. They say that revised guidelines are needed to make sure DCIS patients get a consistent diagnosis they can trust.
Managing Your Mental Health
When you learn you have stage 0 breast cancer, you have some big decisions to make. Its important to talk with your doctor about your diagnosis in depth. Ask for clarification if you dont quite understand the diagnosis or your treatment options. You can also take the time to get a second opinion.
Theres a lot to think about. If youre feeling anxious, stressed, or experiencing difficulty coping with the diagnosis and treatment, talk with your doctor. They can refer you to support services in your area.
Here are some other things to consider:
- Reach out to friends and family for support.
- Talk with a therapist or another mental health professional.
- Join an online or in-person support group. The American Cancer Society Support Programs and Services page provides information about resources, either online or in your area. You can also live chat with a representative or, if youre in the United States, call the helpline at 1-800-227-2345.
Strategies to ease stress and anxiety include:
- exercise
Read Also: Type 4 Breast Cancer
Can Breast Cancer Be Prevented
At this time, there is no sure way to prevent breast cancer.
Some risk factors, such as your age and being female, cannot be controlled. But you may be able to do things to stay as healthy as you can, such as having a healthy diet and being active. Knowing your risk of getting breast cancer also can help you choose what steps to take.
Talk to your doctor about your risk. Find out when to start having mammograms and how often you need one. If your doctor confirms that you have a high or very high risk, ask about ways to reduce your risk, such as getting extra screening, taking medicine, or having surgery.
If you have a strong family history of breast cancer, ask your doctor about genetic testing. The test can check for gene changes that increase your risk for getting breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Surgery That Removes All Of The Breast
Mastectomy procedures include:
- Total or simple mastectomy, which is the removal of the whole breast.
- Modified radical mastectomy, which is the removal of the whole breast and the lymph nodes under the arm .
- Radical mastectomy, which is the removal of the breast, chest muscles, and all of the lymph nodes under the arm . This surgery is rarely used.
Depending on the location of the tumour in the breast or other factors, some women may be able to have a skin-sparing or nipple-sparing mastectomy. Skin-sparing mastectomy leaves most of the skin, except for the nipple and the areola. Nipple-sparing mastectomy saves the skin as well as the nipple and areola.
Also Check: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
What Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
According to the American Cancer Society, DCIS is non-invasive orpre-invasive breast cancer, which means the cells that line the ductshave changed to cancer cells but havent spread through the walls ofthe ducts into the nearby breast tissue.
DCIS is considered a pre-cancer because sometimes it can become aninvasive cancer. This means that over time, DCIS may spread out of theducts into nearby tissue, and could metastasize. Currently, theres nogood way to predict which will become invasive cancer and which wont.Therefore, almost all women with DCIS will be treated.
In most cases, a woman with DCIS can choose betweenbreast-conserving surgery and simple mastectomy. In cases wherethe area of DCIS is very large, the breast has several areas of DCIS,or BCS cannot remove the DCIS completely, mastectomy might be a better option.
When Helen Spencer learned she had DCIS,she began a journey of decisions ranging from which hospital tochoose, to the type of surgery, to whether adjuvant hormone therapywould be worth the potential side effects. Readher story.
What Is Risk After Lumpectomy And No Radiation For Dcis
- Tags:Early-stage: Stage 0 — DCIS , Ductal Carcinoma In Situ, Radiation to the Breast, Radiation After Surgery , Planning/Considering Radiation, Lumpectomy, Planning/Considering Surgery, and Preparing for/Undergoing Surgery
DCIS is the most common form of non-invasive breast cancer and is considered stage 0 cancer. While DCIS isnt considered life threatening, it does increase the risk of developing invasive breast cancer later in life.
DCIS usually is treated with surgery to remove the cancer — lumpectomy in most cases. After surgery, hormonal therapy may be recommended if the DCIS is hormone-receptor-positive . Radiation therapy also is recommended for many women. Both hormonal therapy and radiation help reduce the risk of the DCIS recurring , as well as the risk of invasive cancer.
Routine radiation therapy after DCIS was common in the past, but some newer DCIS treatment guidelines say that women at low-risk for recurrence may be able to skip radiation therapy after surgery. Still, the definition of low-risk isn’t always clear.
A study has found that for women diagnosed with DCIS considered to have a low risk of recurrence treated with lumpectomy without radiation, the risk of DCIS recurrence or developing invasive disease in the same breast increased through 12 years of follow-up and didnt level off.
The study included 665 women diagnosed with DCIS that was considered low-risk based on the characteristics of the disease.
- 14.4% for group one
- 24.6% for group two
Recommended Reading: Cancer Stage 3b
What Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Also known as locally advanced breast cancer, the tumor in this stage of breast cancer is more than 2 inches in diameter across and the cancer is extensive in the underarm lymph nodes or has spread to other lymph nodes or tissues near the breast. Stage 3 breast cancer is a more advanced form of invasive breast cancer. At this stage, the cancer cells have usually not spread to more distant sites in the body, but they are present in several axillary lymph nodes. The tumor may also be quite large at this stage, possibly extending to the chest wall or the skin of the breast.
Stage 3 breast cancer is divided into three categories:
Stage 3A: One of the following is true:
- No tumor is found in the breast, but cancer is present in axillary lymph nodes that are attached to either other or other structures, or cancer may be found in the lymph nodes near the breast bone, or
- The tumor is 2 cm or smaller. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that are attached to each other or other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breastbone, or
- The tumor is 2 cm to 4 cm in size. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that are attached to each other or to other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breast bone, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm. Cancer has spread to axillary lymph nodes that may be attached to each other or to other structures, or cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the breastbone.
Stage 3C: