Risk Of Lymph Node Metastasis Is Extremely Low In Micro
So, there is agreement that the risk of lymph node metastasis is very low, but the debate then turns to analyzing the various presenting factors in the microinvasive breast cancer tumor which might positively or negatively influence the incidence rate. Some studies have considered the difference in frequency of axillary node metastasis between tumors with measurable invasion, versus those of microfocal invasion. The rate of axillary lymph node metastasis for microinvasive tumors is estimated at around 4%, and about 8%-9% for measurable tumors. Whether or not the statistical difference is significant is still a matter of interpretation. However, the T1 threshold seems to be significant among physicians, and these larger tumors, even if 90% of the tumor is still DCIS, are thought to be more worrisome.
How Quickly Do Breast Cancer Tumors Grow From Stage To Stage
Cancer cells divide and multiply quickly in such a way that as a tumor gets bigger, it divides and grows even faster. The average doubling time for breast cancer tumors is between 50 and 200 days. Breast cancer tumor growth rate is impacted by hormonal factors, such as hormone receptor status and HER2 status.
Grading Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
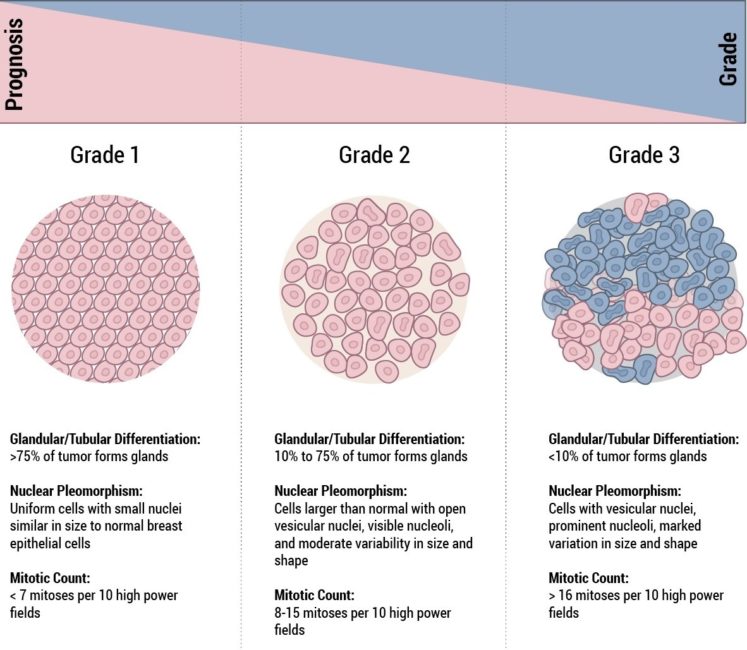
In 1957, Bloom and Richardson first developed a histology grading system for invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast, based on the degree of tubule formation, cell nuclear pleomorphism and mitotic count. This system was replaced or modified in 1991 by the Nottingham grading system, which is still based on a points scoring system of the histologic features of the cancer; mild, moderate or severe or Grade 1, 2 or 3 .
You May Like: What Foods Kill Breast Cancer Cells
What Are The Survival Rates For Stage 3 Breast Cancer By Stage
Survival rates can be confusing. Remember that they dont reflect your individual circumstances.
The relative 5-year survival rate for stage 3 breast cancer is 86 percent, according to the American Cancer Society. This means that out of 100 people with stage 3 breast cancer, 86 will survive for 5 years.
But this figure doesnt consider breast cancer characteristics, like grade or subtype. It also doesnt distinguish between people with stage 3A, 3B, and 3C.
In comparison, the relative 5-year relative survival rate for stage 0 breast cancer is 100 percent. For stages 1 and 2, its 99 percent. For stage 4, the survival rate drops to 27 percent.
The Decision To Proceed With Exploratory Lymph Node Dissection Is A Subject Of Debate With Microinvasive Breast Tumors
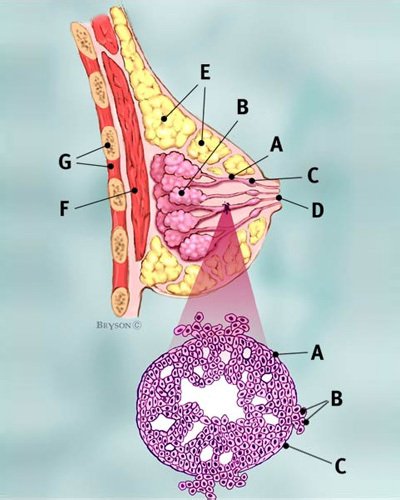
With microinvasive breast cancer, we find a curious situation where physicians can look at the same set of statistics, and yet come to different conclusions; some say that axillary lymph node dissection is warranted, other feel that it is completely unnecessary, also pointing to the cost, discomfort and stress involved. They are many grey area decisions in breast cancer treatment, and an experienced physician will tend to have a feel for the subtleties in all of the diagnostic presentations and risk factors associated with the patient, and make an appropriate decision.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Percentage Of Getting Breast Cancer
How Is Lobular Breast Cancer Different From Other Breast Cancers
Compared to other types of breast cancer, lobular breast cancer:
- Has different symptoms than other more common types of breast cancer.
- May be harder to see on mammogram because it does not cause a firm or distinct lump.
- May not be diagnosed until the cancer is large enough to cause symptoms.
- Is more likely to involve both breasts.
- Can reoccur many years after the first diagnosis and cancer can spread to different-than-typical sites like the stomach, intestine, ovary, kidneys, ureters and eye.
What Is Tumor Grading
After surgery to remove the tumor, a doctor will check it and assign a grade to it. The grade depends on how closely the cancer cells resemble normal cells when viewed under a microscope. Low-grade cancer cells are similar to normal breast cells. Higher grade breast cancer cells look more different. They show the cancer is more aggressive.
The doctor will also test for estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors. This test will show whether the female hormones — estrogen and progesterone — influence the cancer cells. If the test is positive, it means hormones cause the cancer cells to grow. In that case, therapies to suppress or block hormones may help treat the cancer.
The cancer will also be tested for a gene called HER2. If itâs found, additional drugs like trastuzumab can be used.
Other tests will see if the cancer has spread from the breast to other areas of the body.
Read Also: Will My Breast Cancer Come Back
Additional Grading Criteria: A Composite Total Of Tubular Nuclear And Mitotic Index Assesments
As a grade of low, intermediate or high is obtained through a composite sum by assigning a score based on the nuclear assessment, a mitotic index assessment, and a tubular assessment.
The nuclear assessment is based on the nuclear size within the invasive cells. They are described from small to medium to large in size, as well as by their uniformity in size and shape.
The tubular assessment refers to an approximate, quantitative account of the amount of cell groupings which remain in their normal tubular shape. The smaller the percentage of tubular structures in comparison to other shapes, the higher the score. Other structures to appear may include solid trabecula, vacuolated single cells, alveolar nests, and solid sheets of cells.
The mitotic index refers to evident patterns of cell division.Mitosis is a process by which a cell separates into two genetically identical daughter cells. . So, the mitotic index is assessment of the abundance of these pairs of daughter cells, measured in the count per square millimeter. Mitoses are only counted in the invasive area of the lesion .
| Histologic Grade |
| >20 = 3. |
How Are Breast Tumors Tested For Her2
Women newly diagnosed with invasive breast cancers should be tested for HER2.;
A biopsy or surgery sample of the cancer is usually tested with either immunohistochemical stains or Fluorescent in situ hybridization .
See Testing Biopsy and Cytology Specimens for Cancer and Understanding Your Pathology Report: Breast Cancerto get more details about these tests. ;
Recommended Reading: How To Screen For Breast Cancer
What Is Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer, which includes stage IV breast cancer, is cancer that has spread from the breast to another part of the body. Breast cancers most often metastasize to theliver, brain, bones, or lungs. It happens when breast cancer cells break off a breast tumor and move through the body in the bloodstream or lymph system.
Even though its found in a different organ, metastatic breast cancers are still called breast cancers — and not bone cancers or lung cancers, for instance — because they started out as breast cells.
How Are Invasive And Metastatic Cancers Treated
Invasive cancer can spread to distant sites, so the goal is to get treatment before that happens. Your options will depend on the type of cancer you have and the cancer stage at diagnosis. Some types of cancer tend to grow and spread faster than others. If this applies to you, more aggressive treatment may be necessary.
Common treatments for cancer include surgery to remove the primary tumor and radiation to kill any cells that may have been left behind. Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment used to kill cancer cells that may have drifted elsewhere in the body. For some types of cancer, additional targeted treatments are available.
The same therapies can be used for metastatic cancer, but its more difficult to treat. The goal is to control growth, ease your symptoms, and improve your quality of life. Despite where the metastatic tumor is found, some of your treatment options will depend on where the cancer originated.
Other determining factors include your age, overall health, and whatever cancer treatments you may have had in the past.
Research into treatment for metastatic cancer is ongoing.
Read Also: Why Is Left Breast Cancer More Common
What Does Cancer Grade Mean
Breast cancers are given a grade according to:
- How different the cancer cells are to normal breast cells;
- How quickly they are growing
The grade of a cancer is different to the;cancer stage.;
A cancers grade is determined when a doctor looks at the cancer cells under a microscope, using tissue from a biopsy or after breast cancer surgery.
What Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
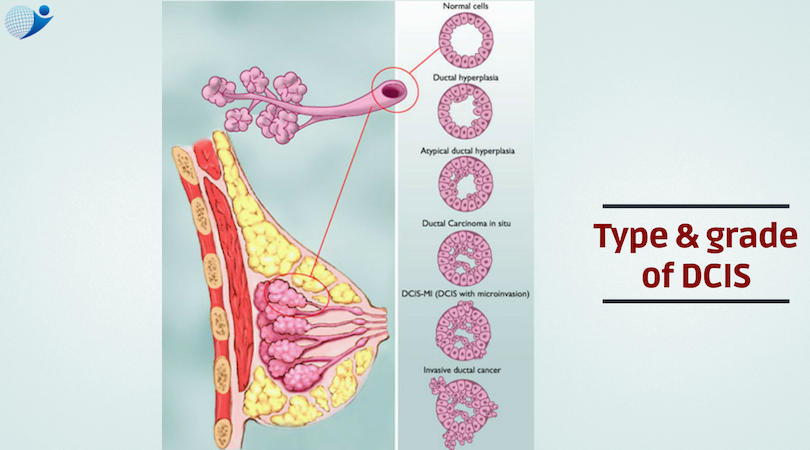
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a very early form of breast cancer thats confined to the milk ducts, which is why its called ductal. Carcinoma is the name for any cancer that begins in cells that line the inner or outer surfaces of tissues, such as the breast ducts. In situ is a Latin term meaning in its original place. DCIS is the most common form of noninvasive breast cancer.
DCIS is classified as low, intermediate, or high;grade. Grades are based on what the cells look like under a microscope. The lower the grade, the more closely DCIS resembles normal breast cells. The higher the grade, the more different it is;from normal cells. DCIS can sometimes involve the nipple, causing it to look red and scaly. This is a rare form of cancer known as Pagets disease of the breast .
In some women, DCIS may not progress to invasive cancer in their lifetime. This has fueled debate about DCIS about whether women with low-risk disease need any treatment, or if they could be safely checked with annual mammograms and breast exams to see if the cancer is progressing. Currently, the standard treatment for DCIS includes surgery, often a lumpectomy.
Recommended Reading: What Is Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer
When Is Radiation Usually Used To Treat Stage 2 Breast Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, radiation therapy may be used after a breast-conserving surgery, or lumpectomy, to mitigate the risk of cancer cells recurring in the same breast or nearby lymph nodes. After a mastectomy, an oncologist may determine that radiation is necessary if the tumor was larger than 5 cm, if there was lymph node involvement, or if cancer was found outside of surgical margins.
How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Diagnosed
Same Day Results
At the Johns Hopkins Breast Center, we know how quickly patients want results from a biopsy or scan if there is a suspicion of breast cancer. We follow strict guidelines for biopsies and pathology reports. Most of our patients will receive the probability of cancer immediately following their biopsy procedure and a pathology confirmation within 24 hours.
Learn more about the steps of diagnosis, including:
- Digital mammography
- Biologic targeted therapy
You May Like: Can Little Girls Get Breast Cancer
Diagnosing Invasive Breast Cancer
In many people the cancer is found during breast screening.
Its important that you see your GP if you have any symptoms. They may refer you to a specialist breast clinic. At the breast clinic the doctor or specialist nurse takes your medical history and examines your breasts. They also feel for any swollen lymph nodes under your arms and at the base of your neck.
You may have some or all of the following tests:
- a mammogram
- an ultrasound
- a biopsy a small sample of cells or tissue is taken from your breast and looked at under a microscope
Changes seen on the mammogram or ultrasound could;be due to cancer, so you may have a biopsy of the breast. You might also have an ultrasound of the lymph nodes under your arm. You may also have lymph node biopsies if they look abnormal.
You should get your results within 1 or 2 weeks at a follow up appointment.;
- drugs that help prevent or slow down bone thinning or bone damage
- a combination of these treatments
You may have surgery to your armpit called a sentinel lymph node biopsy. This means having about 3-5 lymph nodes removed. Sometimes surgeons have to remove more lymph nodes. Your doctor will let you know whether you need this.;
You might have chemotherapy or hormone therapy before surgery called neoadjuvant therapy. The aim is to shrink the cancer down. This means that some people may be able to;have breast conserving surgery, who might;have needed removal of the breast .;
What Is Metaplastic Carcinoma
Also known as metaplastic breast cancer, metaplastic carcinoma is a rare type of invasive breast cancer with a unique characteristic: It contains a mix of two or more types of breast cancer cells, usually carcinoma combined with sarcoma. Metaplastic means that one form is turning into another. Various leading-edge techniques are used to analyze the exact genetics and biology of these confused cancers to find out if the tumor is more similar to carcinoma or sarcoma, since these two types of cancer have very different treatments.
Also Check: How To Help Breast Cancer Awareness
What Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Also known as invasive breast cancer, the tumor in this stage measures between 2 cm to 5 cm, or the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer. Stage 2 breast cancer indicates a slightly more advanced form of the disease. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue, and the tumor is larger than in stage 1 disease. However, stage 2 means the cancer has not spread to a distant part of the body.
At stage 2, a tumor may be detected during a breast self-exam as a hard lump within the breast. Breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.
Stage 2 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 2A: One of the following is true:
- There is no tumor within the breast, but cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast is 2 cm or smaller and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor in the breast measures 2 cm to 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage 2B: One of the following is true:
- The tumor measures 2 cm to 5 cm and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
At stage 2, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Most commonly, stage 2 breast cancer is described as:
How Is Invasive Breast Cancer Treated
Different things will determine the type of breast cancer treatment your doctor recommends, including:
- Size of the tumor
- Results of lab tests done on the cancer cells
- Stage of the cancer
- Your age and general health
- If youâve been through menopause
- Your own feelings about the treatment options
- Family history
Also Check: What Is Hr Positive Breast Cancer
What Are The Signs Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Breast cancer may have no signs or symptoms, especially during the early stages. As the cancer grows, you may notice one or more of the following:
- A lump or thickening in or near the breast or in the underarm that continues after your monthly menstrual cycle
- A mass or lump, which may feel as small as a pea
- A change in the size, shape, or contour of the breast
- A blood-stained or clear fluid from the nipple
- A change in the feel or appearance of the skin on the breast or nipple — dimpled, puckered, scaly, or inflamed
- Redness of the skin on the breast or nipple
- A change in shape or position of the nipple
- An area that is distinctly different from any other area on either breast
- A marble-like hardened area under the skin
You may notice changes when you do a monthly breast self-exam. By doing a regular self-check of your breast, you can become familiar with the normal changes in your breasts.
Less Common Invasive Breast Cancers
- Inflammatory breast cancer is an aggressive form of locally advanced breast cancer. Its called inflammatory breast cancer because the main warning signs are swelling and redness in the breast.
With inflammatory breast cancer, warning signs tend to arise within weeks or months. With other breast cancers, warning signs may not occur for years.
- Paget disease of the breast is a cancer in the skin of the nipple or in the skin closely surrounding the nipple. Its usually found with an underlying breast cancer.
- Metaplastic breast cancers tend to be larger and have a higher tumor grade than more common breast cancers. Metaplastic breast cancers can be hard to diagnose because the tumor cells can look very different from the tumor cells of more common breast cancers.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Have Stage 4 Breast Cancer
What Are The Chances Of Breast Cancer Recurrence After Treatment For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
In women who have breast-conserving treatment, the chance of recurrence is about 3-15% in 10 years, depending on tumor characteristics and margins. Distant recurrence in those who had mastectomy is most influenced by axillary lymph node involvement. When axillary lymph nodes are not cancerous, the recurrence rate is 6% in 5 years. When axillary lymph nodes are cancerous, the recurrence rate is 23% in 5 years with mastectomy but no radiation.
How Often Does Stage 1 Breast Cancer Come Back After Treatment
If stage 1 cancer is treated comprehensively, it rarely comes back. A new, unrelated breast cancer is more likely to emerge after stage 1 breast cancer is treated than a recurrence. Your healthcare provider will recommend a surveillance schedule for you so that new breast cancer or a recurrence can be identified and treated as quickly as possible.
Don’t Miss: Do You Gain Weight With Breast Cancer