What Is A Histological Work
Determining your type of breast cancer begins with a histological workup, a summary prepared by the pathologist after you undergo a biopsy. Essentially, the histological evaluation is the microscopic analysis of the chemical and cellular properties associated with a suspicious breast tumor. The pathologists here at Providence Saint Johns will also confirm the size of the breast tumor where necessary for breast cancer staging purposes. The histological evaluation is essential to determine the most effective treatment recommendations following surgery.
Mammogram Findings: Types Of Microcalcifications
If the microcalcifications are Powderish, with either a fine, indescernible, or cotton ball appearance, then the probability of DCIS is about 47% and most frequently results in a low-grade cancer.
When the microcalcifications have the Crushed Stone characteristic, appearing either as coarse, granular, angular, broken-needle-tip, arrowhead, or a spearhead shape, then the probability of DCIS is about 61%. A breast cancer classified as low to intermediate-grade. But if the microcalcifications have a Casting appearance, then the probability of DCIS is about 96%, the breast cancer is classified as high-grade.
Casting microcalcifications typically appear in two variations. Variant A is called dense casting, with linear and branched, fragmented or irregular features. Variant B is called dotted casting, with granular and branched, dotted or snakeskin-like features.
Note, while DCIS is generally considered a milder breast abnormality, it must be stressed that not all kinds of DCIS with microcalcifications are highly curable.
There is a new line of scientific evidence which identifies a highly aggressive-invasive subtype of casting microcalcification in the micropapillary DCIS subtype, which has a poor prognosis and should be treated with mastectomy.
The relative ratio between the carbonate content and the protein matrix within the microcalcification may also have some relationship to the type of grade of ductal carcinoma associated with them.
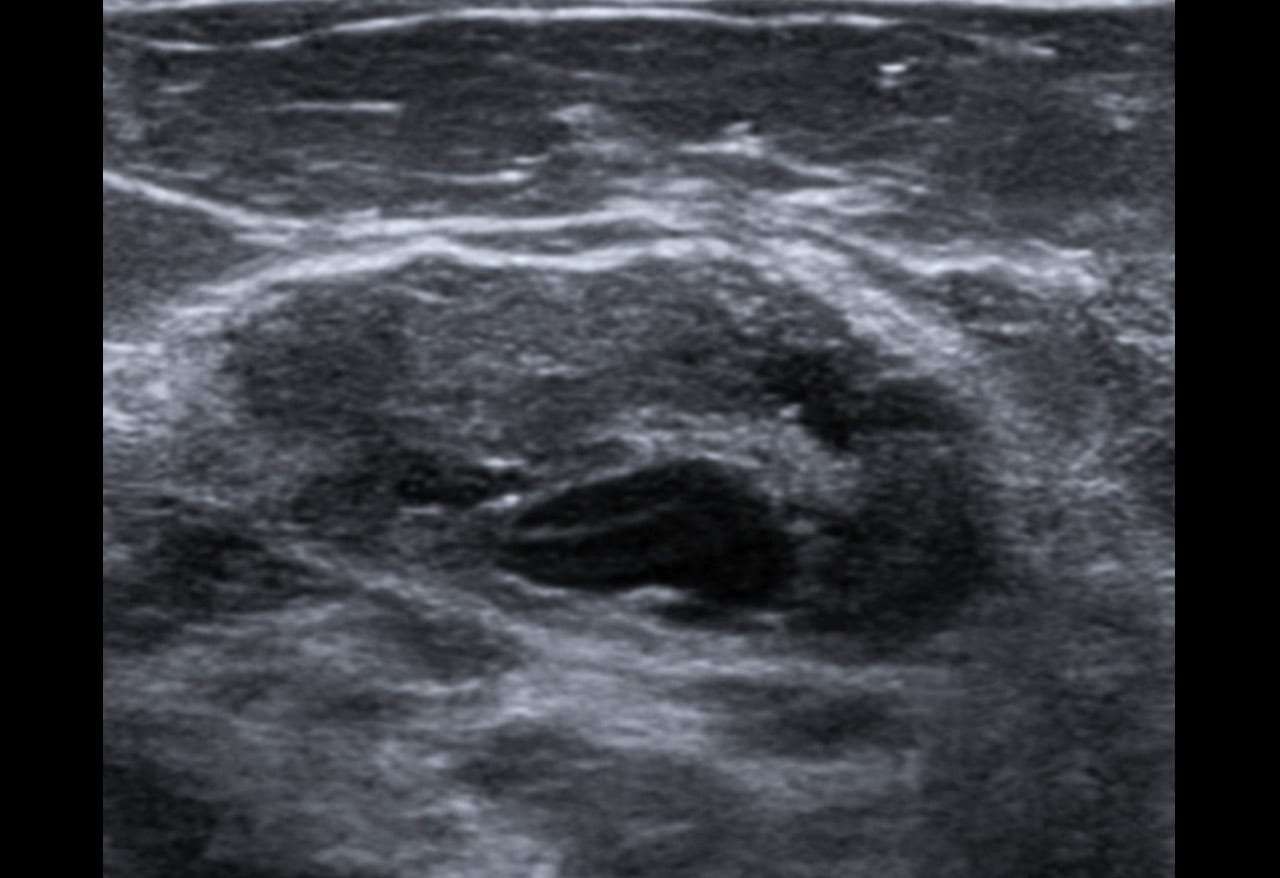
Ultrasound Differentiation Of A Benign Versus Malignant Solid Mass
Specialists will consider a mass malignant when it contains any single malignant feature found on ultrasound.
Mammogram shows Mass: Malignant Features
- Size greater than 1 cm
- Growth non-parallel to the skin.
Mammogram shows Mass: Benign Features
Radiologists will consider a mass benign, until proven otherwise, if it has no malignant features. Plus:-
- Few lobulations
- Intense uniform hyperechogenicity
- Thin Echogenic capsule
Furthermore, radiologists will call a breast mass indeterminate if there are no malignant features and none of the benign combinations.
In the ultrasound image below, one notes a suspicious hypoechoic mass with microlobulations. This mass would definitely need a biopsy. A radiologist would probably give a BI-RADS classification of either category 4C, or 5.
Also Check: How Is Breast Cancer Formed
Breast Cancer Tumor Cells
Under the microscope, breast cancer cells may appear similar to normal breast cells. They also may look quite different, depending on the tumor’s growth and grade.
Cancer cells differ from normal cells in many ways. The cells may be arranged in clusters. They also may be seen invading blood vessels or lymphatic vessels.
The nucleus of cancer cells can be striking, with nuclei that are larger and irregular in shape. These centers will stain darker with special dyes. Often, there are extra nuclei rather than just one center.
Other Indications That It Might Be Cancer
You know that a lump may be a sign of breast cancer. But some types, like inflammatory breast cancer, dont usually cause a lump. So, its worth knowing other signs and symptoms of breast cancer, such as:
- swelling around your breast, armpit, or collarbone
- dimpling of your skin, which can resemble an orange peel
- red or discolored, dry, flaky, or thickening skin on your breast or nipple
- unusual nipple discharge, especially blood
- the nipple is turning inward
- any change in size or shape of a breast
- pain
If cancer has advanced beyond your breast, symptoms may include:
- unexplained weight loss
- shortness of breath
- bone pain
Symptoms in men are very much the same. Of course, having one or more symptoms doesnt mean you have breast cancer, but the only way to know for certain is to call a doctor as quickly as possible.
Breast cancer is most common in people who:
- are female
- with age, especially after 50
- have a personal or family history of breast cancer
- have their first period before 12 years old or menopause after 55 years old
- experience physical inactivity
- take hormonal contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy
- consume alcohol
Its important to note that the stress of enduring racism, discrimination, and other racist systems may play a part in developing the disease beyond genetic factors.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can You Live Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Radial Scar/complex Sclerosing Lesion
Radial scar is a pseudo-infiltrative lesion characterized by afibroelastotic core with entrapped ducts and surrounding radiating ductsand lobules demonstrating a range of epithelial hyperplasia.20The term radial scar is used for lesions < 1cm and the termcomplex sclerosing lesion is used for lesions > 1 cm in size. Theepithelial component can display a variety of atypia and may represent anidus for development of ductal carcinoma in situ. RS are commonly seenincidentally in pathology specimens obtained for other reasons, but canalso be seen as non-palpable lesions detected on screening mammography.
Why Are Heterogeneous Masses Difficult To Treat
Some heterogeneous masses on the ovaries resolve on their own. Wikipedia goes on to explain that the heterogeneity of cancerous masses makes it difficult to treat cancer because the cells have different forms, gene expressions, motility and metabolism.
What kind of cancer has a heterogeneous mass?
Drug administration, one treatment option for cancer, does not kill all the different kinds of cancerous cells in a tumor. Cancers that have heterogeneous masses include breast cancer, prostate cancer, colon cancer, brain cancer, myeloma and leukemia, Wikipedia states.
What does a hypoechoic mass look like on an ultrasound?
Some of the features that show as a hypoechoic mass on ultrasound that are indicative of a malignant breast mass include: or a duct extension. and spiculation, which probably has the highest positive predictive value for malignant breast cancer. Benign breast lesions on the other hand tend to appear on ultrasound with:
How often does an oval shape on an ultrasound indicate Benignity?
Also, an oval shape indicates a benign lesion about 84% of the time. Breast lesions with a parallel orientation are predictive of benignity almost 80% of the time. Medics sometimes refer to the quality of the margins of a breast lesions on ultrasound as the capsule .
Recommended Reading: What Causes Hormonal Breast Cancer
How To Perform A Male Self
A person can perform the following steps:
Why Monitoring Your Breasts Is Important
By performing a monthly breast self-exam, youll get to know how your breasts normally look and feel. It may help you notice small changes early on. Although you may have some idea whats causing a lump or other abnormality, you cant know for certain. Thats why its important to talk with a doctor about your concerns.
When it comes to breast cancer screening, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends a mammogram every 2 years for average-risk women between 50 to 74 years old. Younger women, or those with a higher chance of developing the condition, may want to start screening earlier.
You May Like: What Does Triple Negative Breast Cancer Mean
Characteristics Of Mass Shape Margin And Density Can Suggest Malignancy
In terms of shape, if it is round, oval or slightly lobular, the mass is probably benign.
But, if the mass has a multi-lobular contour, or an irregular shape, then it is suggestive of malignancy. refer to the characteristics of the borders of the mass image.
When the margin is circumscribed and well-defined the mass is probably benign. If the margin is obscured by more than 75% by adjacent tissue, it is moderately suspicious of malignancy.
Likewise, there is moderate suspicion if the margin is microlobulated . If the margin is indistinct or spiculated then there is also high suspicion of malignancy.
Density is usually classified as either fatty, low, iso-dense or high. The mass is probably benign for fatty and low densities, moderately suspicious of malignancy for an iso-density and highly suspicious of malignancy at high densities. The mammographic characteristics of breast masses is quite a complex and detailed study.
How Is A Fibroadenoma Diagnosed
Contact your healthcare provider anytime you notice a breast lump or breast changes. Some fibroadenomas are too small to notice. If you or your provider finds a lump, your provider may perform these tests to confirm a fibroadenoma:
- Imaging scans, including mammogram and/or ultrasound.
- Image-guided core needle breast biopsy.
Also Check: Can You Die From Stage 0 Breast Cancer
Signs Of Cancerous Masses
Cancerous masses in the breast are often very firm, like a rock. They have an irregular shape and size. They can be mobile but are often fixed, meaning they feel like they are attached to the skin or nearby tissue. You can’t really move them around by pushing on them. They’re also not likely to be painful, though they can be in some cases.
On exam, other changes may be present as well. These changes may include:
- Dimpling of the skin, with a texture like orange peel
- Nipple retraction, where the nipple turns inward instead of outward
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit
One type of breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer, does not usually cause a lump. Instead, you may see redness, swelling, and sometimes a rash on the skin of the breast.
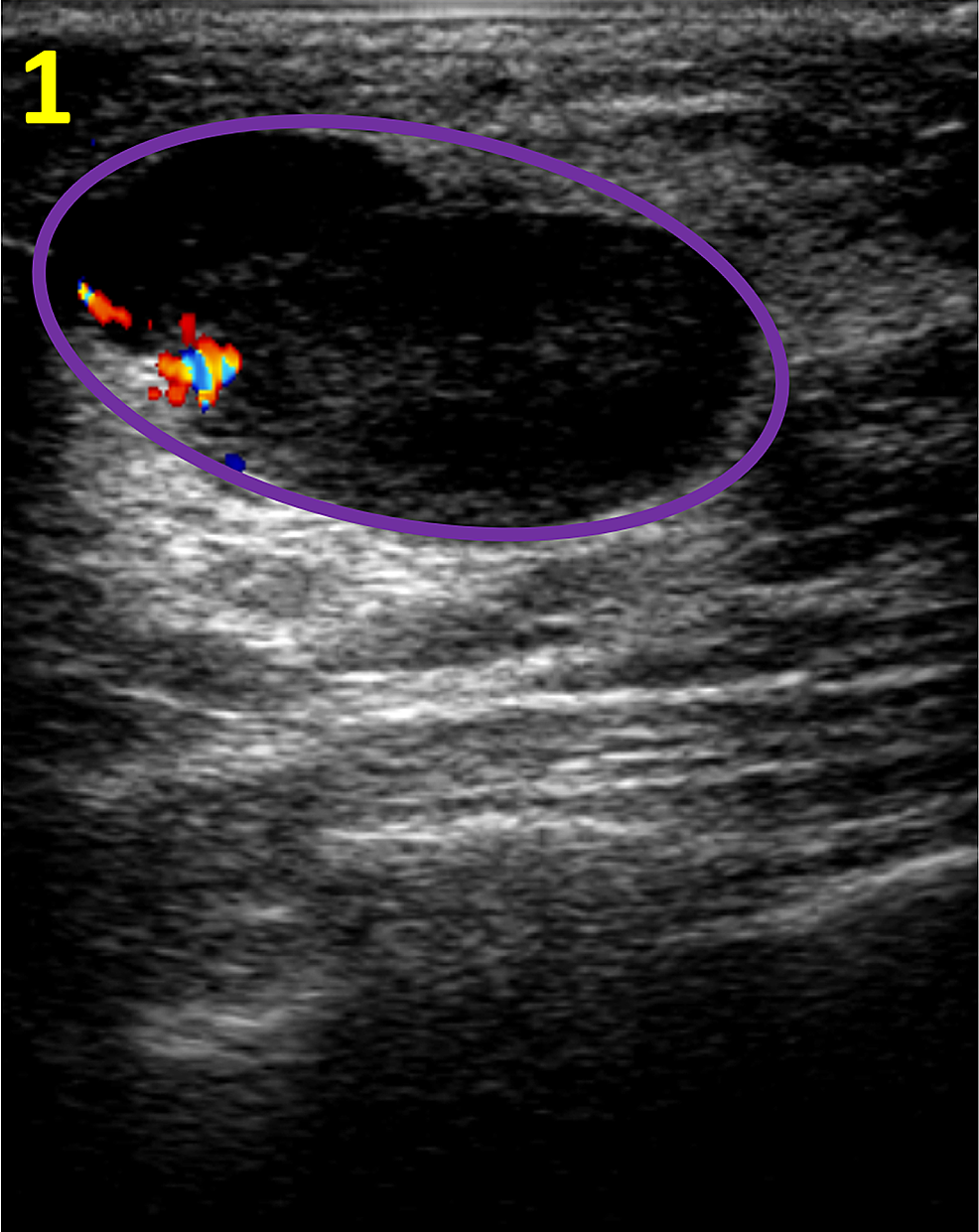
Microlobulations And Duct Extensions On Ultrasound
Microlobulations on breast ultrasound indicate the presence of lots of very small lobulations on the surface of a solid breast nodule. So, these lobulations will be quite similar to mammogram findings. As the number of these microlobulations increase, the probability that the breast mass is malignant also increases.
A duct extension appears on ultrasound as a radially oriented projection that seems to arise from the lesions an axis oriented towards the nipple.
These projections often occur both within or around breast duct. Sometimes, you will see a duct extensions/projection has developed as a bridge between multi-focal malignancies. This is different from a branch pattern in which multiple extensions arise from the mass but extend away-from the nipple. A branching pattern tends to indicate a tumor growth advancing away from the nipple. Any apparent growth that is long enough to visibly fill a duct and branch, no matter what direction is goes, will be suspicious for malignancy. So, in this case, a biopsy will be necessary.
You May Like: What Were Your First Signs Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Global Asymmetry Focal Asymmetry Developing Asymmetry
When there is asymmetric density on a mammogram image, it can mean that a mass is developing, but it is far more likely that it is something else.
There are different types of asymmetry global, focal, and developing, and the chances of malignancy, though low, tend to increase if there are new developments from previous mammograms, and if the lesion is, or becomes, palpable.
Global asymmetry
means that the area of density includes a significantly large portion of the breast. In most cases this is the result of normal variations in hormone levels.
However, if something is palpable, the possibility for malignancy is as high as 10%, and the lesion will require further evaluation. Now, if the lesion appears to be a solid mass, or has suspicious microcalcifications, or an architectural distortion, then a biopsy will be necessary.
Focal asymmetry
Means the suspect asymmetry-mass is much smaller, and has a similar shape on two views. It lacks the clear borders that we see in a true mass, and it usually appears as an island of normal , yet dense fibroglandular tissue. The likelihood of malignancy with focal asymmetry is less than 1%.
Follow-up procedures will, to some degree, depend upon whether or not this is a first or subsequent screening. If there are previous mammograms and the focal asymmetry seems to be stable, then a radiologist will consider this mass to be benign. However, yearly screenings may be necessary for monitoring purposes.
Developing Asymmetry
Common Causes Of Enlarged Lymph Nodes
Common benign causes of benign lymphadenopathy might also include reactive nodal hyperplasia, or collagen vascular disease. An acute bacterial infection or tuberculosis might also bring about the condition.
If the lymphadenopathy is actually caused by a malignant carcinoma, it is often associated with breast cancer development in the previously unaffected breast.
Recommended Reading: How I Knew I Had Inflammatory Breast Cancer
What Are The Types Of Fibroadenomas
Fibroadenomas are along a spectrum of changes in the breast supporting tissue.
- Simple fibroadenomas are the most common. These lumps dont tend to increase breast cancer risk.
- Complex fibroadenomas, fibroepithelial lesions, benign phyllodes tumors are also on this spectrum of breast changes. These lumps need to be excised.
Appearance On An Ultrasound
Breast ultrasound can detect some lumps that a mammogram cannot. It is also used to help diagnose masses found on a mammogram.
Ultrasound can help tell the difference between fluid-filled cysts, which aren’t likely to be cancerous, and hard cysts that need further testing. Hard cysts are more likely to be cancerous.
On an ultrasound report, the term “hypoechoic” refers to an area that appears darker in the images. This means the area is solid.
Recommended Reading: What Does Breast Cancer In Men Feel Like
Differential Diagnosis For A Solitary Well
A mass suspicious of breast cancer is a space-occupying lesion seen on at least two mammogram projections. Furthermore, cancerous tumors also tend to be more dense in the middle than at the edges.
Radiologists tend to describe breast masses according to their shape, margin, and density. Density more or less refers to the amount of fat tissue in the mass in comparison to the surrounding breast tissues.
So, when deciding whether or not the mass is likely to be breast cancer, the screening physicians must consider a differential diagnosis for a number of common ailments.
For relatively non-fatty masses: Cyst, fibroadenoma, solitary intraductal papilloma, dermal lesion, hematoma, abscess, phyllodes tumor, circumscribed malignancy.
For relatively fatty masses: lymph node, cytosteatonecrosis , lipoma, hamartoma, galactocele.
Survivorship Care After Treatment For Phyllodes Tumors Of The Breast
Phyllodes tumors can come back, either in the breast, if you had lumpectomy, or in the skin and underlying tissues of the breast, if you had mastectomy. In very, very rare cases, phyllodes tumors may come back in a part of the body away from the breast.
So you and your doctor will develop a survivorship care plan that will likely include more frequent screening, including:
Don’t Miss: What Is An Oncotype Test For Breast Cancer
Breast Lumps: Why Size Movability And Pain Matter
Your breasts are made up of fat, nerves, blood vessels, fibrous connective tissue, and glandular tissue, as well as an intricate system of milk-producing lobules , and ducts . This anatomy in and of itself creates a lumpy, uneven terrain.
A lump in the breast distinguishes itself from this background of normal irregularities. Harmless breast lumps can be solid and unmovable, like a dried bean or movable, soft, and fluid-filled you can roll it between your fingers like a grape. A lump may be pea-size, smaller than a pea, or even several inches across, although this larger size is rare.
What typically differentiates a benign breast lump from a cancerous breast lump is movement. That is, a fluid-filled lump that rolls between the fingers is less likely to be cancerous than a hard lump in your breast that feels rooted in place.
Another rule of thumb has to do with pain. Breast cancer does not usually cause pain. Benign conditions sometimes do, although there are exceptions to this rule as well. For instance, a rare form of breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer, may cause symptoms such as aching, tenderness, pain, or burning in the breast.
The only way to know the status of a lump for sure is through medical tests, such as an ultrasound, a mammogram, or a fine needle aspiration , in which your doctor uses a tiny needle to extract a bit of the lump for laboratory examination.
RELATED: What Is a Skin Lump? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
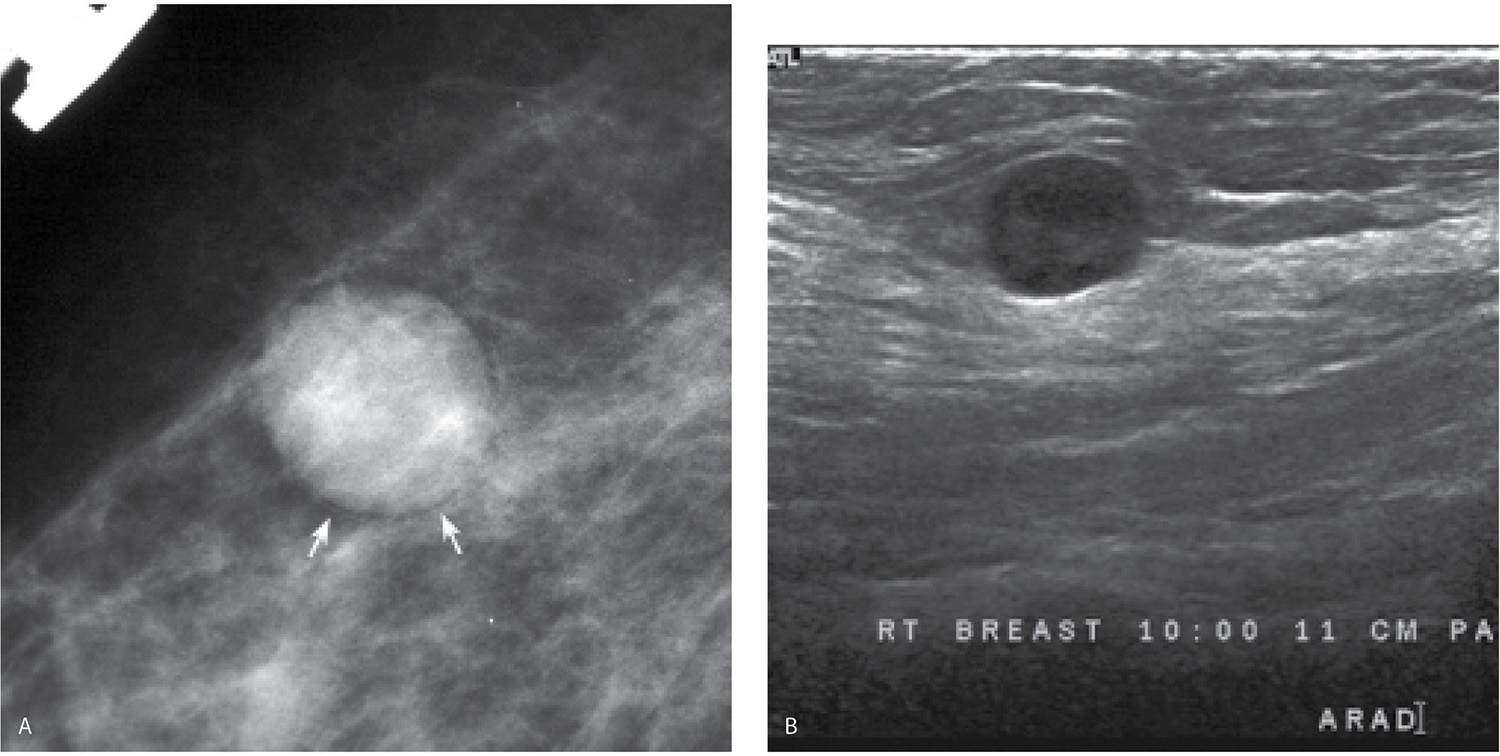
Indirect Signs Of Malignancy
Other indirect or subtle signs that may suggest malignancy include a neodensity, architectural distortion, or asymmetric density . Identifying such subtle signs may require careful comparison with previous examinations. Any new or evolving density that is identified by comparison with previous mammograms should lead to further evaluation. Ultrasonography may be indicated if the neodensity has features suggestive of a cyst.
Architectural distortion is the appearance on a mammogram of spicules without an associated mass . The differential diagnosis includes scarring from previous surgery, radial scar, and carcinoma.
Don’t Miss: How Common Is Metastatic Breast Cancer
Ductal Or Lobular Hyperplasia
Atypical lobular hyperplasia and atypical ductal hyperplasia are considered precancerous conditions. Atypical describes cells that look abnormal under a microscope, and hyperplasia means there is an overgrowth of cells. Breast tumors that have these characteristics are more likely to turn into cancer therefore, close monitoring or surgical excision is required to treat these conditions.
Hypoechoic Nodule Or Solid Lesion In A Breast
Suppose an ultrasound report said there is a hypoechoic mass or nodule, or a hypoechoic lesion in a breast. Also perhaps the report says that the abnormal is solid. What do these words mean?
Hypoechoic means an area looks darker on ultrasound than the surrounding tissue. The surrounding tissue therefore looks brighter/lighter shades of grey. Does hypoechoic mean cancer? No.
A hypoechoic mass means that it is solid, rather than liquid. That is basically all the word means, that the lump or lesion is not a cyst.
Read Also: What Color Is Breast Cancer Pink