Treatment For Stage 0 Breast Cancer
There is a variety of treatment options for stage 0 breast cancer, including:
Surgery
A lumpectomy involves removing cancerous cells from the breast. It is an option when the cells remain in one area. This is a relatively short and simple procedure, and a person should be able to go home after the surgery on the same day.
If cancerous cells appear throughout the breast, the doctor may recommend a mastectomy, which involves removing the entire breast. Plastic surgeons can rebuild the breast at the same time or a later date.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy can help kill cancer cells and inhibit them from spreading. A person will typically undergo radiation therapy once the breast surgery site has healed. This is usually 4-6 weeks after surgery.
Hormone treatment
The hormone estrogen, found naturally in the body, can impact some types of breast cancer. If a person has estrogen receptor-positive or progesterone receptor-positive breast cancer, a doctor may suggest hormone treatment in addition to surgery.
The person may also require radiation therapy to manage the levels of these hormones in the body.
Stage 1 breast cancer means the cancerous cells are invading the surrounding breast tissue. Stage 1 breast cancer has two subcategories 1A and 1B.
People with stage 1A breast cancer have breast cancer with:
- A tumor measuring no more than 2 centimeters in diameter that has not spread outside the breast.
Prognosis Of Late Vs Early Cancer Recurrence
Late recurrence is associated with a better prognosis than early recurrence in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. A 2018 study in Clinical Breast Cancer found that survival after recurrence was significantly longer in people with a late versus early recurrence . In this study, the lungs were the most common site of late distant recurrence.
Treatment For Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Doctors can offer a variety of treatment options for stage 1 breast cancer, although surgery is the primary treatment.
Surgery
A lumpectomy or mastectomy are both viable surgical options for people with stage 1 breast cancer. A doctor will decide what surgery is most appropriate depending on the location of the primary tumor, how large it is, the size of the breast, family history, genetics, and the persons preference.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a standard treatment for stage 1 breast cancer. However, a doctor may not recommend radiation therapy for people over 70 years old, particularly if hormone therapy is suitable.
Hormone therapy
If the breast cancer is ER+ or PR+, hormone therapy may be effective. Hormone therapy works by preventing the growth of estrogen, which helps cancer grow. Hormone therapy can reach cancer cells in the breast as well as other areas of the body and reduces the risk of the cancer coming back.
Chemotherapy
Before recommending chemotherapy, a doctor will test to see whether the cancer is hormone receptive.
If the test results show that the cancer is not receptive to estrogen and progesterone or to another protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 , it is known as triple-negative breast cancer .
Hormone therapy is ineffective against this cancer type, and people who have TNBC will usually need chemotherapy.
Stage 2 breast cancer also has subcategories known as 2A and 2B.
Stage 2A breast cancer is an invasive cancer where:
You May Like: What Is Stage 2 Cancer Of The Breast
Breast Cancer May Return Even 20 Years Later Researchers Find
This means women with the most common type of breast cancer, called estrogen-positive or hormone-positive breast cancer, need to think carefully about whether they want to stop taking the pills, even if they cause side-effects, doctors said.
These breast cancers have a lingering smoldering quality and carry substantial risk of late recurrence after five years of therapy, said Dr. Harold Burstein of the Dana Farber Cancer Institute, who was not involved in the study.
Many patients think. OK, I made it to five years. I know Im safe, said Dr. Jennifer Litton, an oncologist at the MD Anderson Cancer Center. But for estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer, its a continued lifelong risk.
Related: Breast Cancer Drug Can Also Prevent Cancer
Breast cancer is the second-biggest cancer killer of American women, after lung cancer. The American Cancer Society says every year, it’s diagnosed in 200,000 women and a few men, and kills around 40,000.
Most breast cancers are fueled by estrogen, and drugs called hormone blockers are known to cut the risk of recurrence in such cases.
Tamoxifen long was the top choice, but newer drugs called aromatase inhibitors sold as Arimidex, Femara, Aromasin and in generic form do the job with less risk of causing uterine cancer and other problems. The longer women take them, the lower their risk of having the cancer come back.
However, they do cause side-effects.
Related: Gel Works As Well As Pill to Prevent Breast Cancer
Recurrence Can Mean Different Things
For some women, a recurrence can be metastatic — the cancer has come back not in the breast , but elsewhere in the body as well. That’s a much more serious situation . Or, it may have come back much as the first time you were diagnosed, as a “new” cancer, and is treated as such.
Be aware that many people talk about recurrence and metastasis in the same breath. But they are not the same thing. If you have had a local recurrence, when the cancer remains confined to your breast, the good news is that your prognosis is not necessarily any worse than it was the first time.
“Whether it’s a recurrence of the original cancer or a new primary cancer in the other breast, in both cases we assume we’re dealing with a curable situation, and we attempt to think about those patients as we would anyone with a new presentation,” says Clifford Hudis, MD, chief of the Breast Cancer Medicine Service at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
If, for example, you finished treatment for breast cancer seven or eight years ago, any recurrence or new cancer would be treated largely as an entirely new problem.
“That woman will not only undergo surgery, but may well receive additional therapy that doesn’t ignore the fact that she had a previous cancer, but recognizes that seven years out, her prognosis from the first cancer is excellent,” says Eric Winer, MD, director of the Breast Program at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston.
You May Like: Is Breast Cancer Inherited From Mother Or Father
Introduction To Breast Cancer Recurrence
Breast cancer can recur at any time, but most recurrences occur in the first three to five years after initial treatment. Breast cancer can come back as a local recurrence or as a distant recurrence somewhere else in the body. The most common sites of recurrence include the lymph nodes, the bones, liver, or lungs.
What’s The Risk Of Recurrence
Everyone who has had breast cancer has some risk of recurrence, but its typically low.;;
In general, the more time that goes by, the lower the risk of recurrence. Cancer is most likely to recur in the first two years after treatment, and once people get to five years of living cancer-free after treatment, its considered to be a significant milestone to be celebrated. Recurrence after that five year markrare, but possibleis called late recurrence.;
Theres still so much that is unknown about cancer recurrence, but researchers have found some patterns in recent years that point to clues about why it happens. These factors might be linked to a higher risk of breast cancer recurrence:;
- Having high blood sugar
- Not eating enough fruits and vegetables
- Having had a surgical site infection after your surgery
Certain characteristics of your original cancer also might mean a higher risk of recurrence, such as:
- A tumor of more than five centimeters across
- Cancer cells that are HER2-positive;
- Cancer cells that are triple negative;
- Cancer cells in four or more axillary lymph nodes at the time of surgery
- Cancer cells in the chest muscles or breast skin
You might be at higher risk for late recurrence if you had:
- A tumor of more than two centimeters
- A high number of affected lymph nodes
- A hormone receptor-positive cancer
- A HER2-negative cancer
- Hormone therapy for only a short time after surgery;
Also Check: Can Breast Cancer Spread To Bones
Treatment For Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Treatment for people with stage 3 breast cancer includes chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation. Typically, doctors administer the chemotherapy before performing the surgery in an attempt to shrink a tumor.
People with stage 3 breast cancer will probably need radiation therapy to kill off any remaining cancer cells. Doctors may also recommend hormone therapy, as well as additional targeted therapies, if necessary.
Box 1 How Rapid Autopsy Studies Can Inform On Metastatic Dissemination And Relapse
Definitions
-
Rapid autopsy: rapid post-mortem collection, examination and biobanking of tissuesfresh, snap-frozen and fixedfrom deceased patients shortly after death.
-
Rapid autopsy cancer programme: coordinated effort among oncologists, pathologists and scientists aimed at collecting specimens from cancer patients within a post-mortem interval of 68h before key biological information within the tissues of interest is lost.
Advantages
-
Multiregional biopsies: to conduct extensive, spatial sampling of tissuesprimary and metastatic, cancerous and normalfor in-depth, high-resolution multi-omics analysis.
-
Physiological model: to analyse DTCs in their natural metastatic niche.
-
to generate novel, ex vivo living patient-derived modelsautopsy-derived xenografts and organoids of metastatic tumours from sites that would otherwise be difficult to sample for functional evaluation .
-
Cancer evolution: to study the phylogenetic relationship of each sampled site to each other and infer the complete clonal evolution of a neoplasm.
-
Dormancy: to examine why some DTCs lodged in certain organs of the human body become dormant for years to decades.
-
Drug resistance: to study why DTC spread across different sites responds differently to therapy, with some developing resistance and others remaining sensitive to treatment.
-
Recurrence: to understand why only some DTCs residing in certain sites of the human body give rise to active metastases, ultimately responsible for patients relapse.
Read Also: Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer Bad
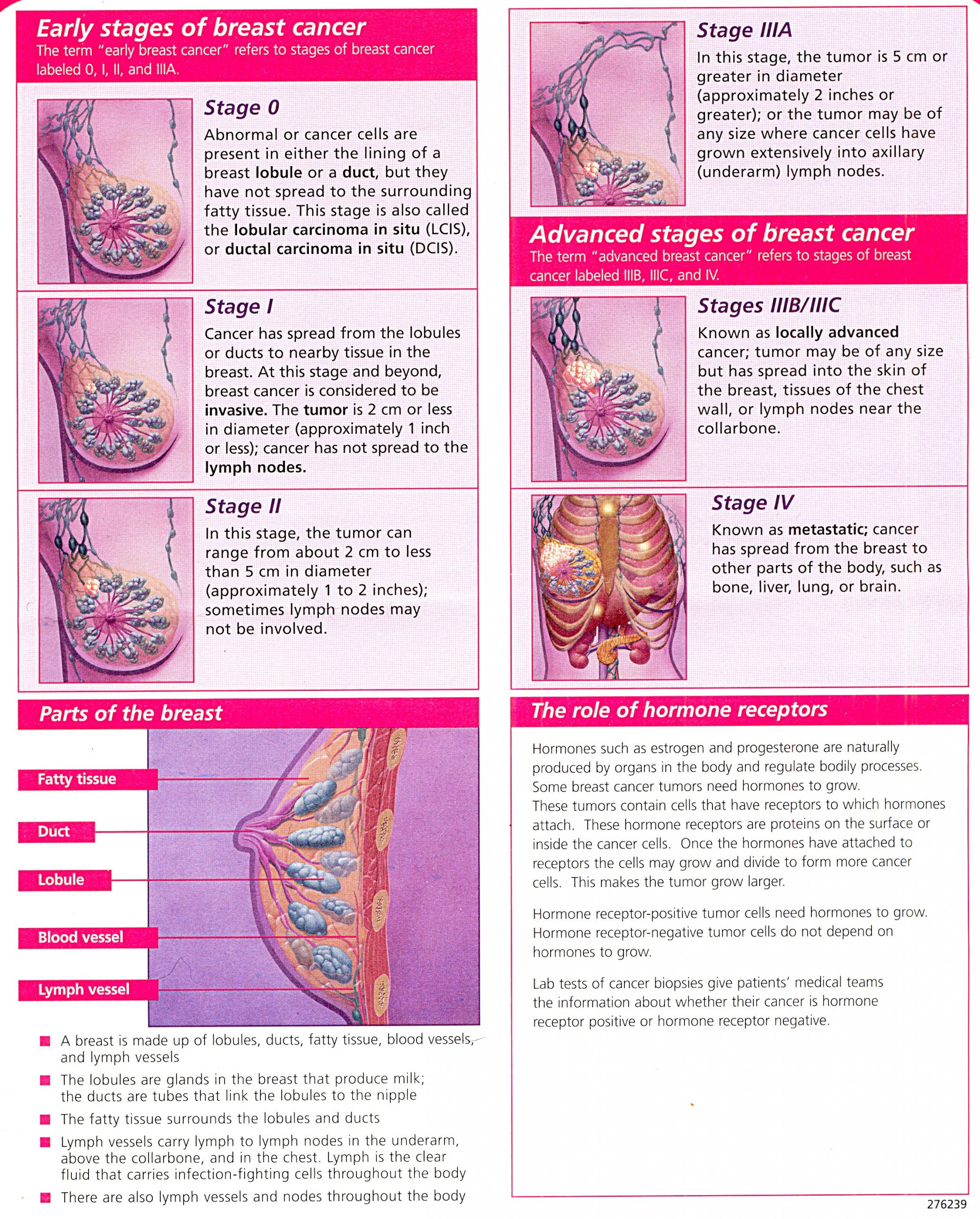
How Is Breast Cancer Stage Determined
The breast cancer staging process helps doctors determine how much cancer there is and where its located. The higher the breast cancer stage number, the more advanced the disease.
Breast cancer staging is so important because it provides cancer care teams which include breast surgeons, oncologists, pathologists, radiologists and many others an agreed upon way to talk about the disease. This makes it easier for them to understand diagnoses and collaborate on treatment plans.
The Myth And Stigma Of The 5
Many people still believe that breast cancer, even hormone-positive disease, is essentially cured after five years; this can lead to misunderstandings in families. Loved ones who don’t understand late recurrence may downplay your feelings, or criticize you when you think “brain tumor” each time you get a headache.
Until information on late recurrence becomes more widely known, and even though it’s frustrating, you may need to educate loved ones about the risk, and why you should be concerned when you develop new or unexplained symptoms.
Read Also: Can You Work During Breast Cancer Treatment
How The Breast Cancer Staging Process Starts
The breast cancer staging process begins with diagnostic testing. Depending on previous screening results, if any breast cancer symptoms are present, and other factors, your doctor may recommend one of the following tests:
- Diagnostic mammogram A mammogram involves using an X-ray to take photos of your breast tissue at different angles. To do this, your breasts are gently compressed between two plates so the X-ray can be taken.
- Ultrasound An ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that bounces soundwaves of your breast tissue to create a picture of the inside of your breast.
- MRI An MRI is another non-invasive imaging test that uses radio waves and a magnetic field to create an image of your breast tissue. This can help doctors determine the size and placement of tumors.
- Biopsy A biopsy removes small masses and growths from your breast so they can be examined under a microscope by a pathologist and determine if theyre cancerous.
If cancer is detected, a CT scan may be ordered to look for any distant metastasis or local invasion to other organs. And youll likely be connected with a breast surgeon right away, either through a nurse navigator or your doctor.
What Are The Complications Of Breast Cancer Recurrence

Breast cancer that comes back can be harder to treat. The same therapy isnt always effective again. Tumors can develop a tolerance to certain treatments like chemotherapy. Your healthcare provider will try other therapies. You may be able to try drugs under development in clinical trials.
If breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, your healthcare providers still treat it like breast cancer. For instance, breast cancer cells that move to the lungs cause breast cancer in the lungs not lung cancer. Metastatic breast cancer is more difficult to treat than cancer in only one part of the body.
You may feel stressed, depressed or anxious. A mental health counselor and support groups can help.
You May Like: Does Breast Cancer Cause Hot Flashes
Treatment For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Typically, treatment for stage 4 breast cancer includes a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy .
Targeted therapy is a treatment that targets the protein that allows cancer cells to grow and this type of therapy may also be an option for people with stage 4 breast cancer.
Sometimes, surgeons will operate to try and remove tumors though this is not usually the first option for treatment.
Doctors, however, may recommend surgery to help with pain relief by treating some of the issues that may develop as a result of having stage 4 breast cancer. These include spinal cord compression, removing single masses caused by metastasis, and fixing any broken bones.
A doctor may also prescribe medication to treat related symptoms such as:
- antidepressants to help mood
- anticonvulsants to manage pain or neurologic conditions
- local anesthetics to manage pain
New treatments and therapies are emerging all the time, and anyone who has breast cancer at any stage can volunteer to try out these new treatments. People considering this should talk to their doctor to see whether any trials are available in their area.
Trials for a new treatment called immunotherapy are currently taking place. Immunotherapy works by raising the bodys natural ability to fight off cancer and has fewer side effects than chemotherapy.
As well as numbers, a zero or an X often follow the letters T, N, and M. According to the AJCC, the meanings are as follows:
These include:
Local Recurrence After Mastectomy
Even though the entire breast is removed in a mastectomy, breast cancer can still return to the chest area. If you notice any changes around the mastectomy scar, tell your health care provider.
The more lymph nodes with cancer at the time of the mastectomy, the higher the chances of breast cancer recurrence.
Local recurrence after a mastectomy is usually treated with surgery, and radiation therapy if radiation therapy wasnt part of the initial treatment.
Treatment may also include chemotherapy, hormone therapy and/or HER2-targeted therapy.
You May Like: What Is Unilateral Breast Cancer
Risk Factors For Overall Recurrence
There are several risk factors that raise the risk of recurrence overall . These include:
- Tumor size: Larger tumors are more likely to recur than smaller ones both early and late.
- Positive lymph nodes: Tumors that have spread to lymph nodes are more likely to recur at any time than those that have not.
- Age at diagnosis: Breast cancer recurrence is more common in younger people.
- Treatments received and response to treatments: Both chemotherapy and hormonal therapy reduce the risk of recurrence in the first five years.
- Tumor grade: More aggressive tumors are more likely to recur than less aggressive tumors , especially in the first five years
There are also factors that do not appear to affect the risk of recurrence. Recurrence rates are the same for women who have a mastectomy or lumpectomy with radiation and are also the same for women who have a single vs. double mastectomy.
Risk Of Late Recurrence Is Underestimated
A survey led by the Canadian Breast Cancer Network found that women often underestimate their risk of late recurrence. In the survey, only 10% were aware of the risk of recurrence after five years of tamoxifen therapy, and 40% felt that they were cured after hitting the five-year mark.
Many breast cancer survivors underestimate their risk of late recurrence.
Read Also: What Do Breast Cancer Patients Need
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 1 Breast Cancer
In Stage 1 breast cancer, cancer is evident, but it is contained to only the area where the first abnormal cells began to develop. The breast cancer has been detected in the early stages and can be very effectively treated.
Stage 1 can be divided into Stage 1A and Stage 1B. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and the lymph nodes with evidence of cancer.
Intrinsic Subtypes And Late Recurrence
A number of different methods have been evaluated for the ability to predict late recurrence. Some of these include:
Higher expression of estrogen-responsive genes: A 2018 study found that people with ER+/HER2 negative breast cancers who had higher expression of estrogen-responsive genes and were not treated with extended hormonal therapy had a high risk of recurrence after five years.
Multigene assays: Several multigene assays may help predict late recurrence, but using this information to figure out when to extend hormonal therapy requires more research. A 2018 evaluation of an 18-gene, 10-year signature found that the information regarding prognosis was similar to other tests including Oncotype DX Recurrence Score, Prosigna PAM50 risk of recurrence score, Breast Cancer Index and IHC4.
Read Also: Can Roundup Cause Breast Cancer