Where Do Cancers Spread
Most cancers have the ability to spread to any region of the body, but some sites of metastases are more common than others.
- The most common sites of metastasis overall include the bones, liver, and lungs.
- The most common sites for breast cancer to metastasize;are the bones, the brain, the liver, and the lungs.
- The most common sites for lung cancer to spread;are the adrenal glands, the bones, the brain, the liver, and elsewhere in the lungs.;
- The most common sites for colon cancer to metastasize are the liver, the lungs, and the peritoneum .
- The most common distant sites to which prostate cancer spreads are the adrenal glands, the bone, the liver, and the lungs.
What Factors Increase The Risk Of Developing Breast Cancer
Although there is no way to predict whether or not your pet may develop mammary cancer, some factors could increase its chances:
- Gender: Female dogs are 62 times more likely to develop mammary cancer than male dogs . Male dogs with mammary cancer also typically only develop benign tumors, which provide a better prognosis than malignant ones.
- Spayed status: The age at which a dog is spayed or neutered could also play a role in the risk of cancer development. If a dog is spayed before her first heat cycle, the chance of developing mammary tumors is 0.5%. If spayed before her second heat cycle, the probability is 8%
- Breed: Some breeds of dogs are more prone to developing tumors. The complete list of breeds can be found below.
- Age: Dogs over six years of age are more likely to have mammary cancer than younger ones
- Diet: Feeding your dog a diet of home-made food consisting of lots of beef and pork, as well as obesity early on in your dogs life, could increase its chances of developing mammary tumors
What Is Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer is most often used to describe cancers that cannot be cured.;This means cancers that wont totally go away and stay away completely with treatment. However, some types of advanced cancer can be controlled over a long period of time and are thought of as an ongoing illness.
Even if advanced cancer cant be cured, treatment can sometimes:
- Shrink the cancer;
- Help relieve symptoms
- Help you live longer
For some people, the cancer may already be advanced when they first learn they have the disease. For others, the cancer may not become advanced until years after it was first diagnosed.
Advanced cancers can be locally advanced or metastatic.
Locally advanced means that cancer has grown outside the body part it started in but has not yet spread to other parts of the body.;For example, some cancers that start in the brain may be considered advanced because of their large size or closeness to important organs or blood vessels. This can make them life-threatening even though they havent spread to other parts of the body. But other locally advanced cancers, such as some prostate cancers, may be cured.
Metastatic cancers have spread from where they started to other parts of the body. Cancers that have spread are often thought of as advanced when they cant be cured or controlled with treatment. Not all metastatic cancers are advanced cancers. Some cancers, such as testicular cancer, can spread to other parts of the body and still be very curable.
Don’t Miss: Can Asbestos Cause Breast Cancer
Why Do Cancers Spread
Normal cells do not spread beyond the area where they belong. For example, lung cells do not travel to the heart even though they are nearby. The reason for this is that normal cells have “adhesion chemicals” that act somewhat like glue, that keep the different cells together in their area of origin. The metastatic process is not yet entirely understood. Sometimes cancer cells, may loose the adhesion chemicals, and break off from a tumor becoming “loose” and mobile, and free to travel through lymphatic vessels or bloodstream . In general, normal cells communicate with other nearby cellsin essence, being continuously under control and reminded of their boundaries. Some cancer cells have devised ways to ignore these communication signals, so they can travel free and invade nearby tissues.;There are other differences between cancer cells and normal cells that allow the cancer cells that have traveled to set up residence in a new location.
Palliative And Supportive Care
Palliative and supportive care focuses on symptom control and support. Its an extremely important part of the care and treatment for many people living with secondary breast cancer and can significantly improve quality of life for them and their families.
People often associate palliative care with end-of-life treatment. However, many people value having it at any stage of their illness, alongside their medical treatment, to help prevent and relieve symptoms such as pain or fatigue. It can also help with the emotional, social and spiritual effects of secondary breast cancer.
The palliative and support care teams are based in hospitals, hospices and the community. You can be referred by your treatment team, GP or breast care nurse depending on your situation.
You May Like: How Treatable Is Breast Cancer
When To Euthanize A Dog With Breast Cancer
Putting a beloved pet to sleep is never easy but must be considered once mammary cancer has spread or progressed too far.;
If your pet shows any of the following signs, you may need to discuss possible euthanization with your veterinarian:
- Refusal to eat for extended periods
- Continual vomiting or diarrhea
- Lethargy
- Difficulty moving
If you notice any drastic negative change in your dogs behavior, monitor them carefully and consult your vet to discuss your options.
Lymph Node Surgery For Breast Cancer
If breast cancer spreads, it typically goes first to nearby lymph;nodes under the arm. It can also sometimes spread to lymph nodes near the collarbone or near the breast bone. Knowing if the cancer has spread to your lymph nodes helps doctors find the best way to treat your cancer.
If you have been diagnosed with breast cancer, its important to find out how far the cancer has;spread. To help find out if the cancer has spread outside the breast, one or;more of the lymph nodes under the arm are removed and;checked in the lab. This is an important part of staging. If the;lymph nodes contain cancer cells, there is a higher chance that cancer cells;have also spread to other parts of the body. More imaging tests;may be done if this is the case.
Lymph node removal can be done in different ways, depending;on whether any lymph nodes are enlarged, how big the breast tumor is, and other;factors.
Recommended Reading: Where To Find Breast Cancer Lumps
About Metastatic Breast Cancer
Cancer begins when healthy cells change and grow out of control, forming a mass or sheet of cells called a tumor. A tumor can be cancerous or benign. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. A benign tumor means the tumor can grow but will not spread.When breast cancer is limited to the breast and/or nearby lymph node regions, it is called early stage or locally advanced. Read about these stages in a different guide on Cancer.Net. When breast cancer spreads to an area farther from where it started to another part of the body, doctors say that the cancer has metastasized. They call the area of spread a metastasis, or use the plural of metastases if the cancer has spread to more than 1 area. The disease is called metastatic breast cancer. Another name for metastatic breast cancer is “stage IV breast cancer if it has already spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis of the original cancer.
Doctors may also call metastatic breast cancer advanced breast cancer. However, this term should not be confused with locally advanced breast cancer, which is breast cancer that has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body.
Understanding Your Cancer And Treatment
Not all breast cancers are alike. Someone elses experience with their treatment may be completely different from yours. Understanding your type and stage can help make sense of your doctors recommendations. This may help you feel better about your treatment choices.
A big part of cancer treatment is the relationship between you and your oncology team. Here are some things youll want to know about early on so youre well informed about your specific type of breast cancer:
Oncologists meet with cancer patients every day and its their job to see you as a whole person. Express your wants and needs. Rest assured that no question is too insignificant to ask.
You May Like: What Do Nipples Look Like When You Have Breast Cancer
Median Overall Survival In Total Study Population4
- OS was a prespecified secondary endpoint. OlympiAD was not powered to show statistical significance in OS for LYNPARZA monotherapy vs chemotherapy.4* OS did not achieve statistical significance4
- The OlympiAD study protocol was amended in March 2018 to allow exploratory follow-up of patients for survival status and serious adverse events beyond the prespecified final OS survival analysis5
- At the prespecified OS cutoff , 13% of patients remained on LYNPARZA and no patients remained on chemotherapy4
- 18 patients remained on LYNPARZA for 36 months and no patients remained on chemotherapy5
*HCPs chemotherapy of choice .1,2
Tumour Dormancy And Reawakening
Tumour dormancy is generally defined as a prolonged state of asymptomatic micrometastatic disease. In cancer of the breast or prostate, cancer cells can remain dormant for years and even decades before recurring as metastatic disease. During this latent period, patients are considered to be disease-free due to the lack of any symptoms of illness and because they have no detectable neoplasms by clinical imaging. Often described as one of the most wicked cancer;cell misbehaviours, tumour dormancy shares many features in common with chronic diseases. Yet, its nature appears to be reversible, as myriad mechanisms have been shown to induce a switch to reawaken indolent DTCs . Furthermore, tumour dormancy is not exclusively a phenomenon of end-stage tumorigenesis, as it can apply to the presence of occult neoplasms until clinical diagnosis , and/or to MRD left behind after treatment . Attention, however, must be paid to the molecular underpinnings of these two scenarios as mechanistic differences between primary and metastatic dormancy might exist.
Also Check: How To Not Get Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Cell Growth
Cancer begins when a normal breast cell undergoes a number of mutations in genes that control the growth of the cell. These mutations may occur over a long period of time, even decades, before a cancer cell forms.
A cancer cell must divide on average 30 times before it forms a mass that can be felt in the breast. Since tumor cells multiply and divide exponentiallyone cell becomes two, two cells become four, and so ona tumor will increase more rapidly in size the larger it is.
That said, not all cells are dividing at one time, and growth can be different at different stages in the formation of a tumor. Compared with many types of cancer, breast cancer has a “low growth fraction,” meaning that the proportion of cancer cells that are in an active cell cycle is low.
Some tumors, such as some leukemias and lymphomas, have much higher growth fractions .
Breast Cancer Is A Heterogeneous Disease

Based on the presence or absence of the oestrogen receptor and progesterone receptor , and the expression and amplification of the human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 , breast cancer can be divided into three clinical subtypes: hormone-receptor -positive , HER2-positive and triple-negative ., In the United States, 71% of breast cancers are HR+, 17% are HER2+ and 12% are TN. Following the discovery of five intrinsic molecular subgroups of the disease based on a 50-gene expression classifier luminal A, luminal B, HER2-enriched, basal-like and normal-likeit became apparent that a large degree of unappreciated molecular heterogeneity exists across and within each subtype of breast cancer. While TN and HER2+ patients often present with basal-like and HER2-enriched cancers, respectively, HR+ women are usually diagnosed with luminal A or luminal B tumours. However, despite sharing some common traits, luminal A cancers are generally ER+, PR high and Ki67 low, resulting in low-grade, slow-proliferating neoplasms, whereas luminal B tumours are typically ER+, PR variable and Ki67 variable, translating into more aggressive cancers with a higher proliferative rate.
Read Also: What Chemo Drugs Are Used For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
When Do People Get A Metastatic Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Metastatic breast cancer can occur at different points:
- De novo metastatic breast cancer: About 6% of women and 9% of men have metastatic breast cancer when theyre first diagnosed with breast cancer.
- Distant recurrence: Most commonly, metastatic breast cancer is diagnosed after the original breast cancer treatment. A recurrence refers to the cancer coming back and spreading to a different part of the body, which can happen even years after the original diagnosis and treatment.
When Metastatic Cancer Can No Longer Be Controlled
If you have been told your;cancer can no longer be controlled, you and your loved ones may want to discuss end-of-life care. Whether or not you choose to continue;treatment;to shrink the cancer or control its growth, you can always receive palliative care to control the symptoms of cancer and the side effects of treatment. Information on coping with and planning for end-of-life care is available in the Advanced Cancer section of this site.
Don’t Miss: What Does Pt1c Mean In Breast Cancer
Disseminated Tumour Cells As Culprits For Metastatic Recurrence
Metastatic relapse is attributed to the outgrowth of cancer cells that have escaped from the primary tumour and take up residence in secondary sites. Cancer cells that physically detach from a primary source and seed distant sites are known as disseminated tumour cells . The process whereby DTCs transform a localised cancer into a systemic disease is called the metastatic cascade . In the next few sections, the seven key steps comprising this complex biological process are discussed with the goal to shed light on the when and how of DTC dissemination. Importantly, while depicting the metastatic cascade as an orderly series of sequential eventsstarting from the primary tumour and ending in a distant metastatic siteit should be noted that DTC spread can take place through multiple routes and different directions. Accordingly, clinical evidence of self-seedingwhereby a metastatic cell re-infiltrates its primary tumourand of metastasis-to-metastasis spread, has been documented, with one such study in HR+ breast;cancer patients reporting a common origin between lymph;node and distant metastases in up to 25% of cases.
Fig. 2: Tumour cell dissemination: the route to metastatic success or failure.
Possible Symptoms Of Advanced And Metastatic Cancer
General signs and symptoms of advanced and metastatic cancer can include:
- Loss of energy and feeling tired and/or weak: This can get so bad that you may have a hard time doing everyday tasks like bathing or getting dressed. People with advanced cancer often need help with these things.
- Weight loss
- Pain
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing
Advanced and metastatic cancers can cause many other symptoms, depending on the type of cancer and where it has spread.
Also Check: What Kind Of Doctor Do You See For Breast Cancer
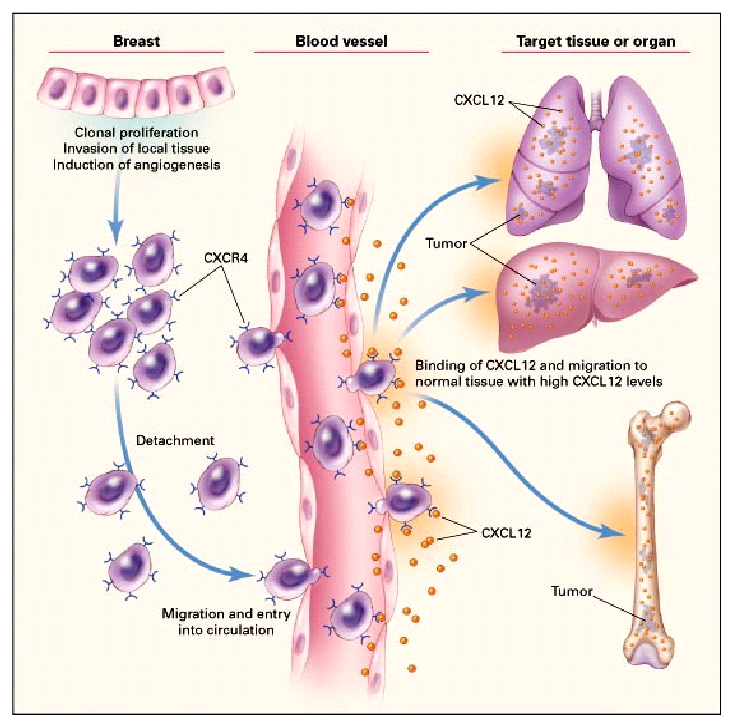
Where Breast Cancer Tends To Go
Breast cancer most often spreads to these organs:
Bones. Breast cancer travels to the bones through the bloodstream. The ribs, spine, pelvis, and long bones of the arms and legs are the most common bones that breast cancer reaches. Bone pain and tenderness are signs the cancer is in your bones. Breast cancer cells can also get into bone marrow — the spongy tissue inside bones where blood cells are made.
Liver. Cancer cells can get into the liver through the bloodstream because the liver filters the blood.
Lungs. The lungs are another common site for metastatic breast cancer to spread because your blood flows through them to pick up oxygen.
Brain. Any type of breast cancer can spread to the brain, but HER2-positive and triple-negative cancers are most likely to reach this organ. Signs of cancer in the brain include headaches, seizures, vision changes, and dizziness.
Why Does Metastatic Breast Cancer Happen
Most often, metastatic cancer occurs because treatment didnt destroy all the cancer cells. Sometimes, a few cells remain dormant, or are hidden and undetectable. Then, for reasons providers dont fully understand, the cells begin to grow and spread again.
De novo metastatic breast cancer means that at the time of initial diagnosis, the breast cancer has already spread to other parts of the body. In the absence of treatment, the cancer spreads.
There is nothing you can do to keep breast cancer from metastasizing. And metastatic breast cancer doesnt happen because of something you did.
Recommended Reading: Does Stress Cause Breast Cancer
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several types of breast cancer, and any of them can metastasize. Most breast cancers start in the ducts or lobules and are called ductal carcinomas or lobular carcinomas:
- Ductal carcinoma. These cancers start in the cells lining the milk ducts and make up the majority of breast cancers.
- Lobular carcinoma. This is cancer that starts in the lobules, which are the small, tube-like structures that contain milk glands.
Less common types of breast cancer include:
-
Medullary
-
Metaplastic
-
Papillary
-
Inflammatory breast cancer is a faster-growing type of cancer that accounts for about 1% to 5% of all breast cancers.
-
Pagets disease is a type of cancer that begins in the ducts of the nipple.
Breast cancer can develop in women and men. However, breast cancer in men is rare. Less than 1% of all breast cancers develop in men.
Surgery To Remove Liver Metastasis
Surgery to remove metastatic breast cancer isn’t common, but a small study suggests that some women can benefit from surgery to remove breast cancer that has metastasized to the liver if the cancer has certain characteristics:
- hormone-receptor-positive
- responded to chemotherapy before surgery
- didn’t grow in the time between metastatic diagnosis and surgery
Right now, we don’t know if women who have surgery to remove metastatic breast cancer in the liver have better outcomes than women who don’t have surgery. Still, if you have liver metastases, you may want to ask your doctor about the benefits and risks of surgery in your unique situation.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer