If You Notice A Change In Your Breasts
If you find or feel a lump or notice any other change to your breasts, its important to get checked by your GP as soon as possible. Book an emergency appointment with your doctor, who may refer you to a breast clinic where you will be seen within two weeks.
Many symptoms of breast cancer, including breast lumps, are non cancerous and caused by normal breast changes. But it remains vital that you pay attention to your body and seek help if you notice anything that isnt normal for you.
Money And Financial Support
If you have to reduce or stop work because of your cancer, you may find it difficult to cope financially.
If you have cancer or you’re caring for someone with cancer, you may be entitled to financial support, for example:
- if you have a job but can’t work because of your illness, you’re entitled to Statutory Sick Pay from your employer
- if you don’t have a job and can’t work because of your illness, you may be entitled to Employment and Support Allowance
- if you’re caring for someone with cancer, you may be entitled to Carers Allowance
- you may be eligible for other benefits if you have children living at home, or if you have a low household income
Find out what help is available to you as soon as possible. The social worker at your hospital will be able to give you the information you need.
Key Points To Remember
- Chemotherapy is sometimes used after surgery for early-stage breast cancer to help lower the chances that your breast cancer will come back.
- Some types of cancer have a very small chance of coming back. Women who have these types of cancer may not need chemo. There are gene tests that may show whether having chemo will help you reduce your chances that the cancer will return.
- Your age, type of cancer, tumour size, and hormone receptor status have an effect on how well chemo will work to keep your cancer from coming back.
- Different medicines used for chemo have different side effects. Your doctor can give you other medicines to help you deal with side effects like nausea and vomiting. Some women are bothered a lot by the side effects, but some aren’t.
You May Like: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
What Is Breast Cancer
Cells in the body normally divide only when new cells are needed. Sometimes, cells in a part of the body grow and divide out of control, which creates a mass of tissue called a tumor. If the cells that are growing out of control are normal cells, the tumor is called benign. If, however, the cells that are growing out of control are abnormal and don’t function like the body’s normal cells, the tumor is called malignant .
Cancers are named after the part of the body from which they originate. Breast cancer originates in the breast tissue. Like other cancers, breast cancer can invade and grow into the tissue surrounding the breast. It can also travel to other parts of the body and form new tumors, a process called metastasis.
Your Breast Is Changing Colors

Another symptom of inflammatory breast cancer is when your breast skin turns pink or reddish on more than half the breastsomething that can be hard to tell in those with darker skin tones. Sometimes these changes in coloration can be difficult to find in African Americans and in obese patients with very large breasts,Ricardo H. Alvarez, MD, leads the Breast Cancer Center Institute at Cancer Treatment Centers of America , said on the CTCA website. And for harmful habits you should be aware of, check out 30 Things You Had No Idea Could Cause Cancer.
Also Check: How Do Doctors Treat Breast Cancer
Genetic Tests For Hereditary Cancer Syndromes
Genetic tests for mutations that cause hereditary cancer syndromes are usually requested by a persons doctor or other health care provider. Genetic counseling can help people consider the risks, benefits, and limitations of genetic testing in their particular situations.
A genetic counselor, doctor, or other health care professional trained in genetics can help an individual or family understand their test results and explain the possible implications of test results for other family members.
People considering genetic testing should understand that their results may become known to other people or organizations that have legitimate, legal access to their medical records, such as their insurance company or employer, if their employer provides the patients health insurance as a benefit. Legal protections are in place to prevent genetic discrimination, including the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act of 2008 and the Privacy Rule of the Health Information Portability and Accountability Act of 1996.
The page on Genetic Testing for Inherited Cancer Susceptibility Syndromes has more information on what tests are available and who may want to consider them.
Invasive Breast Cancer Symptoms
Most breast cancers start in the ducts, or the tubes that carry milk to the nipple, or in the lobules, the little clusters of sacs where breast milk is made. Invasive breast cancer refers to breast cancer that spreads from the original site to other areas of the breast, the lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body. In these cancers that form in the ducts or lobules, invasive ductal carcinoma or invasive lobular carcinoma , the cancer spreads from the ducts or lobules to other tissue. Depending on the stage, you may notice symptoms.
Invasive breast cancer symptoms may include:
- A lump or mass in the breast
- Swelling of all or part of the breast, even if no lump is felt
- Skin irritation or dimpling
- A lump or swelling in the underarm lymph nodes
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 1 Breast Cancer
What Is A Normal Breast
No breast is typical. What is normal for you may not be normal for another woman. Most women say their breasts feel lumpy or uneven. The way your breasts look and feel can be affected by getting your period, having children, losing or gaining weight, and taking certain medications. Breasts also tend to change as you age. For more information, see the National Cancer Institutes Breast Changes and Conditions.external icon
A New Lump Or Thickening
A lump or thickening is not always a sign of cancer but show your doctor to rule it out, especially if it’s only in one breast.
Lumps might be felt in the breast, armpit area or around the collarbone. Cancerous lumps often feel hard but sometimes it could be just a thickening in the breast tissue which feels different to the rest of your breast. It doesn’t move around in the breast but it will continue to grow over time. Breast cancers are usually not painful.
The average size of a lump found by a woman checking her breasts is 22mm, but a mammogram can detect lumps as small as 2mm.
If you notice any changes in your breasts, see your doctor.
Read Also: Cure Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Palliative And Supportive Care
Palliative and supportive care focuses on symptom control and support. Its an extremely important part of the care and treatment for many people with secondary breast cancer and can significantly improve quality of life for them and their families.
People often think of palliative care as being associated with end-of-life treatment. However, many people value having it at any stage of their illness, alongside their medical treatment, to help prevent and relieve symptoms such as pain or fatigue. It can also help with the emotional, social and spiritual effects of secondary breast cancer.
You can be referred by your specialist team, GP or breast care nurse depending on your situation. Some people may be able to refer themselves.
Knowledge Is Power And We Can Be Powerful Together
Your greatest asset in the fight against breast/ovarian cancer is knowledge of both the scientific facts and your own biology. This includes being educated on HBOC and the intrinsic link between breast and ovarian cancer. If caught and treated early, ovarian cancer patients 5-year survival rate is 92%. However, only 20% of cases are actually diagnosed this early. We need to change this. Please share this article with friends and family members. Keep up with us on social media for helpful tips, inclusive events, and up-to-date facts.
Katherine Wellander
Higher Risk in the Ashkenazi Jewish Population
Why is the Ashkenazi Jewish population at higher risk?
- Breast cancer
Ready to take action? Knowledge is power. Take this short quiz to be proactive about your health.
Genes 101
If the DNA sequence is changed, like a spelling mistake, the instructions may not make sense. The technical term for this change is mutation, meaning there is a change to the usual genetic code that may change the instructions stored in the gene. A mutation in a gene that repairs DNA damage or controls cell growth can increase the risk of developing cancer.
Sporadic vs Hereditary Cancers:
BRCA 1 and BRCA 2: Most Common hereditary breast and ovarian cancer
Don’t Miss: What Is Hr Positive Breast Cancer
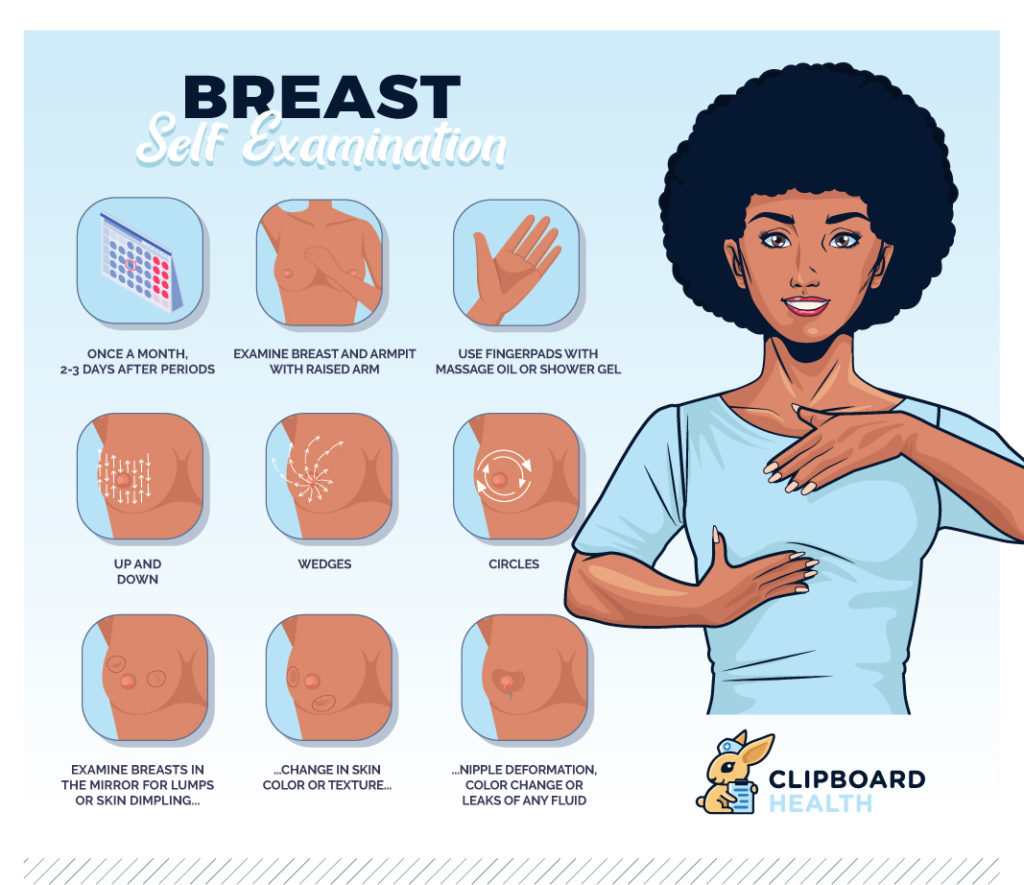
How Should I Check My Breasts
Take the time to get to know how your breasts normally look and feel through normal regular activities .
You dont need to use a special technique, but ensure you look at and feel your breasts regularly. Make sure this includes all parts of your breast, your armpit and up to your collarbone.
For women of all ages, it is recommended that you be breast aware. Breast awareness is being familiar with the normal look and feel of your breasts, so that you can identify any unusual changes .
How Can I Protect Myself From Breast Cancer

Follow these three steps for early detection:
- Get a mammogram. The American Cancer Society recommends having a baseline mammogram at age 35, and a screening mammogram every year after age 40. Mammograms are an important part of your health history. Recently, the US Preventive Services Task Force came out with new recommendations regarding when and how often one should have mammograms. These include starting at age 50 and having them every two years. We do not agree with this, but we are in agreement with the American Cancer Society and have not changed our guidelines, which recommend yearly mammograms starting at age 40.
- Examine your breasts each month after age 20. You will become familiar with the contours and feel of your breasts and will be more alert to changes.
- Have your breast examined by a healthcare provider at least once every three years after age 20, and every year after age 40. Clinical breast exams can detect lumps that may not be detected by mammogram.
You May Like: Chances Of Breast Cancer Survival
Metastatic Breast Cancer Symptoms
Metastatic breast cancer symptoms depend on the part of the body to which the cancer has spread and its stage. Sometimes, metastatic disease may not cause any symptoms.
- If the breast or chest wall is affected, symptoms may include pain, nipple discharge, or a lump or thickening in the breast or underarm.
- If the bones are affected, symptoms may include pain, fractures, constipation or decreased alertness due to high calcium levels.
- If tumors form in the lungs, symptoms may include shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, coughing, chest wall pain or extreme fatigue.
- If the liver is affected, symptoms may include nausea, extreme fatigue, increased abdominal girth, swelling of the feet and hands due to fluid collection and yellowing or itchy skin.
- If breast cancer spreads to the brain or spinal cord and forms tumors, symptoms may include pain, confusion, memory loss, headache, blurred or double vision, difficulty with speech, difficulty with movement or seizures.
Symptoms Of Male Breast Cancer
One study found that male breast cancer is on the rise, with a 25% increase over the 25 years from 1973 to 1988. But its still rare. Its unclear whether the reported rise means the disease is slowly becoming more common, or whether men better understand the symptoms and report their symptoms, leading to diagnoses that might have been missed in the past.
If you notice any persistent changes to your breasts, you should contact your doctor. Here are some signs to watch for:
- a lump felt in the breast
- nipple pain
- sores on the nipple and areola
- enlarged lymph nodes under the arm
Its important to note that enlargement of both breasts is usually NOT cancer. The medical term for this is gynecomastia. Sometimes the breasts can become quite large. Non-cancer-related enlargement of the breasts can be caused by medications, heavy alcohol use, weight gain, or marijuana use.
A small study about male breast cancer found that the average time between first symptom and diagnosis was 19 months, or over a year and a half. Thats a very long time! This is probably because people dont expect breast cancer to happen to men, so there is little to no early detection.
Earlier diagnosis could make a life-saving difference. With more research and more public awareness, men will learn that just like women they need to go to their doctor right away if they detect any persistent changes to their breasts.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
The most common types of breast cancer are:
- Infiltrating ductal carcinoma. This cancer starts in the milk ducts of the breast. It then breaks through the wall of the duct and invades the surrounding tissue in the breast. This is the most common form of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of cases.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ is ductal carcinoma in its earliest stage, or precancerous . In situ refers to the fact that the cancer hasnt spread beyond its point of origin. In this case, the disease is confined to the milk ducts and has not invaded nearby breast tissue. If untreated, ductal carcinoma in situ may become invasive cancer. It is almost always curable.
- Infiltrating lobular carcinoma. This cancer begins in the lobules of the breast where breast milk is produced, but has spread to surrounding tissues in the breast. It accounts for 10 to 15% of breast cancers. This cancer can be more difficult to diagnose with mammograms.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ is a marker for cancer that is only in the lobules of the breast. It isnt a true cancer, but serves as a marker for the increased risk of developing breast cancer later, possibly in both or either breasts. Thus, it is important for women with lobular carcinoma in situ to have regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Rid Of Breast Cancer
Your Breast Looks Like It Has Been Bruised
If your breast is starting to have a bruised appearance with no other reason for the discoloration, the Mayo Clinic says it could be a sign of inflammatory breast cancersomething that can easily be confused with an infection. And for things you can do to improve your overall well-being, check out 100 Easy Ways to Be a Healthier Woman.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Cancer Prognosis
A Change In Your Breast May Be An Early Sign Of Breast Cancer Heres What To Look For
Breast cancer affects approximately one in eight women in their lifetime. But today, breast cancer is becoming more and more treatable especially when its caught early.
There are a few signs and symptoms to watch out for, says Mona Duncan, MD, general surgeon at Geisinger. Thats why its so important to go for your regular checkups and mammograms, and to perform monthly breast self-exams at home.Learn how to perform a breast self-exam.
Recommended Reading: Do You Gain Weight With Breast Cancer
Does A Benign Breast Condition Mean That I Have A Higher Risk Of Getting Breast Cancer
Benign breast conditions rarely increase your risk of breast cancer. Some women have biopsies that show a condition called hyperplasia . This condition increases your risk only slightly.
When the biopsy shows hyperplasia and abnormal cells, which is a condition called atypical hyperplasia, your risk of breast cancer increases somewhat more. Atypical hyperplasia occurs in about 5% of benign breast biopsies.
You May Like: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Grade Of Breast Cancer
The grade describes the appearance of the cancer cells.
- Low grade the cells, although abnormal, appear to be growing slowly.
- Medium grade the cells look more abnormal than low-grade cells.
- High grade the cells look even more abnormal and are more likely to grow quickly.
Want to know more?
- Breast Cancer Now: Secondary breast cancer
Signs Of Breast Cancer Recurrence
Despite initial treatment and success, breast cancer can sometimes come back. This is called recurrence. Recurrence happens when a small number of cells escape the initial treatment.
Symptoms of a recurrence in the same place as the first breast cancer are very similar to symptoms of the first breast cancer. They include:
- a new breast lump
- redness or swelling of the breast
- a new thickening near the mastectomy scar
If breast cancer comes back regionally, it means that the cancer has returned to the lymph nodes or near to the original cancer but not exactly the same place. The symptoms may be slightly different.
Symptoms of a regional recurrence may include:
- lumps in your lymph nodes or near the collarbone
- chest pain
- pain or loss of sensation in your arm or shoulder
- swelling in your arm on the same side as the original breast cancer
If youve had a mastectomy or other surgery related to breast cancer, you might get lumps or bumps caused by scar tissue in the reconstructed breast. This isnt cancer, but you should let your doctor know about them so they can be monitored.
As with any cancer, early detection and treatment are major factors in determining the outcome. Breast cancer is easily treated and usually curable when detected in the earliest of stages.
The best way to fight breast cancer is early detection. Talk with your doctor about when you should start scheduling regular mammograms.
Don’t Miss: How To Detect Breast Cancer Early