Effect Of Hormonal Changes On Breasts
As women develop from pre-puberty through puberty, pregnancy and to menopause, the breasts will be affected by a variety of fluctuations in hormones.
During puberty, hormones produced by the ovaries cause growth and development of the breast. After puberty, the hormones oestrogen and progesterone will change throughout a womans monthly menstrual cycle. This may cause women to have swollen or tender breasts at different times of the month.
During pregnancy the body will produce additional oestrogen and progesterone, which trigger further growth and development of the breast to prepare mothers for breastfeeding.
Around the time of menopause , the ovaries stop producing female hormones including oestrogen. Without oestrogen, the breast tissue decreases in size. After menopause , monthly menstrual periods stop.
When Should I Start Having A Mammogram
All women should have a mammogram. Many women start having regular mammograms every year at about age 40. Alberta Health Care covers one mammogram per year starting at that age. If you have a concern about your breasts earlier than that, you should see your doctor and arrange to have appropriate imaging of your breasts. This may be a mammogram, ultrasound, or both. To get a screening mammogram, you will need to speak to your doctor about your family history, when to start screening, and how frequently you should be screened.
Mayfair Diagnostics recommends screening mammography every year from age 40 to 49, then every two years between age 50 and 74, if there are no risks factors that would necessitate a shorter interval. After age 75, screening frequency will depend on a number of factors, including your medical history.
Women with the following risk factors are considered high risk and may be encouraged to start screening earlier and more frequently:
- Personal history of breast or ovarian cancer.
- First-degree relative diagnosed with breast or ovarian cancer.
- BRCA1, BRCA2 positive.
- Three or more second-degree relatives with breast or ovarian cancer.
- Volpara D breast density* score.
- Chest wall radiation at an age younger than 30.
- History of lobular carcinoma in situ or atypical hyperplasia on previous breast biopsy.
Men And Breast Cancer
- About 1 percent of all cases of breast cancer occur in men.
- A family history of breast cancer is a risk factor for men as well as for women.
- Breast cancer in men is often not detected until the cancer is advanced and more difficult to treat.
- Breast cancer in men usually shows up as a lump beneath the breast area, fixation of skin to the lump, and discharge from the nipple.
- Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the lump, followed by chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Treatment and cure rates for men are similar to those for women.
Read Also: Brca1 Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer And Teenage Girls
If youre a teenage girl, you might be worried about your risk of getting breast cancer.
Developing breast cancer when youre a teenager is extremely rare. Its also uncommon in women in their 20s and 30s. The vast majority of breast cancers are diagnosed in women over the age of 50.
There can be a lot of unreliable information and scare stories on the internet, so its important to use reputable websites or talk to your GP if youre worried about any changes to your breasts. You can also call our Helpline free on 0808 800 6000 to speak with one of our experts.
How Breast Cancer Spreads And Recurs
Breast cancer is frightening enough without the fear that it could travel to other parts of the body. Metastasis is the term for the spread of cancer. About 250,000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer and roughly 40,000 will die from the disease each year. When breast cancer is diagnosed in the early stages, many women go on to live cancer-free lives.
Yet for others, the disease is metastatic at the time of diagnosis or later recurs. It’s thought that metastatic disease is responsible for around 66% of the deaths related to breast cancer. How does breast cancer spread or recur?
Also Check: Breast Cancer Treatment Stage 2
Can I Be Screened For Breast Cancer
BreastScreen Australia offers a free screening program for women at risk of breast cancer:
- If youre aged between 50 and 74 years, youll be invited to access a free mammograms every 2 years. This is because nearly 4 in 5 breast cancers occur in women aged over 50.
- If youre aged between 40 and 49 years or over 75 years, you are also eligible but wont be contacted about it.
- Women under 40 years of age are usually not offered breast screening because the density of their breast tissue makes it harder to detect cancers on mammograms.
Younger women with a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer, or women with breast cancer diagnosed in the last 5 years may also benefit from breast screening. For more details, call BreastScreen Australia on 13 20 50 or visit their website.
Other Types Of Breast Cancer
Other less common types of breast cancer include invasive lobular breast cancer, which develops in the cells that line the milk-producing lobules, inflammatory breast cancer and Paget’s disease of the breast.
It’s possible for breast cancer to spread to other parts of the body, usually through the lymph nodes or the bloodstream. If this happens, it’s known as “secondary” or “metastatic” breast cancer.
Also Check: What Is Adjuvant Therapy For Breast Cancer
The Complex Field Of Endocrine Disruptors
Following the publication of Rachel Carsonâs Silent Spring, researchers continued to make connections between chemical exposures and adverse outcome in animals and human beings. Soon after the massive introduction of the pesticide Dichloro-Diphenyl-Trichloroethane and other synthetic chemicals into the environment, evidence emerged linking environmental exposure with a variety of developmental and reproductive abnormalities, while laboratory studies revealed that some of these compounds had oestrogenic activity. This led to the enunciation of the endocrine disruptor hypothesis at the Wingspread Conference, held in Racine, Wisconsin, in 1991. The term endocrine disruptor was coined because the participants proposed that developmental alterations observed in diverse animal species were due to exposure to multiple chemicals that, through different modes of action, disrupted the endocrine systems of metazoan organisms during organogenesis and development at large .
Morphometric parameters in the mammary gland of ovariectomized pubertal mice demonstrate non-monotonic doseâresponse curves in response to oestradiol. The dashed line denotes the number of terminal end buds and the solid line denotes TEB area. * or â indicates the dose where the maximal response was observed, which is statistically different from both its ovariectomized control and the highest administered dose .
What Are Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small, rounded structures of about 1 mm to 25 mm that are found throughout the body.
The lymph nodes form part of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is an important part of the immune system that protects the body from disease and infection. It contains a network of thin tubes called lymph vessels that are found throughout the body. These lymph vessels transport a clear fluid called lymph between the lymph nodes. The lymph nodes filter the lymph to trap or remove substances harmful to the body, such as bacteria or cancer cells. This helps to protect the body from disease or infection. The lymph then passes back to the blood.
The closest lymph nodes to the breast are those in the armpit, which are known as axillary nodes. The axillary nodes drain lymph from nearby tissues, including the breast. There are also lymph nodes under the breastbone and in the neck . The number of lymph nodes varies between different people. There are usually about 15-30 lymph nodes in the armpit.
Because the lymph vessels carry lymph away from the breast, in the case of breast cancer, cancer cells can enter the lymph vessels and begin to grow in the lymph nodes. The axillary nodes are often the first place of cancer spread outside the breast. Usually, surgery is used to remove one or more of the axillary nodes to help check for cancer spread. Cancer found in the lymph nodes affects the staging and treatment of breast cancer.
You May Like: How Do Doctors Treat Breast Cancer
How Does Breast Density Affect Breast Cancer Risk
Dense breast tissue increases the risk of breast cancer, especially in older women. For women with dense breast tissue in 75 percent or more of their breasts, their breast cancer risk is double relative to the general population.
You can’t tell by look or feel, whether or not you have dense breasts. It is a diagnosis that can only be assessed by mammography. Dense breasts have less fat and more glandular and connective tissue. This makes a mammogram harder to read, so smaller cancers may be hidden.
Dense breasts are normal. Breast tissue can change with age, usually becoming less dense as you get older and go through menopause. However, some women continue to have dense breast regardless of age. Dense breasts may be affected by taking certain types of hormone therapies, such as hormone treatments for menopause.
Its important to be aware of your breast density. At Mayfair, we explain your breast score after your mammogram and include your density level in the report that is sent to your referring doctor. Our mammography machines are equipped with the Volpara Health Technologies program which standardizes the density score from A to D:
When To Euthanize A Dog With Breast Cancer
Putting a beloved pet to sleep is never easy but must be considered once mammary cancer has spread or progressed too far.
If your pet shows any of the following signs, you may need to discuss possible euthanization with your veterinarian:
- Refusal to eat for extended periods
- Continual vomiting or diarrhea
- Lethargy
- Difficulty moving
If you notice any drastic negative change in your dogs behavior, monitor them carefully and consult your vet to discuss your options.
Also Check: Estrogen Resistant Breast Cancer
How Quickly Breast Cancer Develops
You may have heard remarks that cancer has been present for five years before it is diagnosed, and this may sometimes be true.
The actual time it takes for breast cancer to grow from a single cancer cell to a cancerous tumor is unknown, as estimates based on doubling time assume that this is constant throughout the duration of tumor growth.
If doubling time were constant, cancer with a doubling time of 200 days would take 20 years to develop into a detectable tumor, and a doubling time of 100 days would take 10 years to be evident on exam.
In contrast, a breast tumor with a doubling time of 20 days would take only 2 years to develop.
Since the majority of studies have found the average doubling time to be between 50 days and 200 days, it’s likely that most breast cancers that are diagnosed began at least 5 years earlier .
When To Go For A Mammogram

So, you are wondering when should you start screening for your breast cancer. Here are the details-
All women aged between 40-49 need a yearly mammogram after their doctors suggest so
All women aged 50 and above must go for it once every two years
For some patients with higher risks, the screening needs to start even before they are 40.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Stage 4 How Long To Live
Invasive Breast Cancer Symptoms
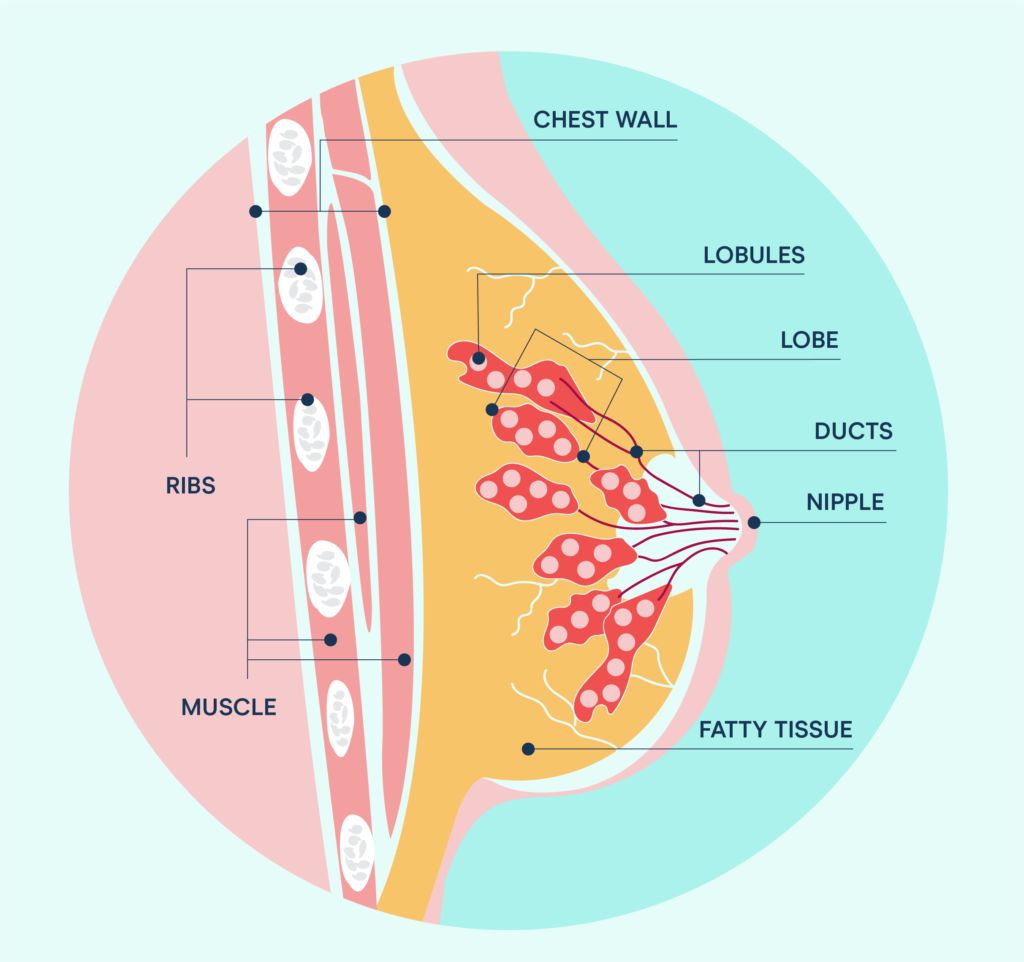
Most breast cancers start in the ducts, or the tubes that carry milk to the nipple, or in the lobules, the little clusters of sacs where breast milk is made. Invasive breast cancer refers to breast cancer that spreads from the original site to other areas of the breast, the lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body. In these cancers that form in the ducts or lobules, invasive ductal carcinoma or invasive lobular carcinoma , the cancer spreads from the ducts or lobules to other tissue. Depending on the stage, you may notice symptoms.
Invasive breast cancer symptoms may include:
- A lump or mass in the breast
- Swelling of all or part of the breast, even if no lump is felt
- Skin irritation or dimpling
- A lump or swelling in the underarm lymph nodes
What Happens After The Local Breast Cancer Treatment
Following local breast cancer treatment, the treatment team will determine the likelihood that the cancer will recur outside the breast. This team usually includes a medical oncologist, a specialist trained in using medicines to treat breast cancer. The medical oncologist, who works with the surgeon, may advise the use of the drugs like tamoxifen or anastrozole or possibly chemotherapy. These treatments are used in addition to, but not in place of, local breast cancer treatment with surgery and/or radiation therapy.
After treatment for breast cancer, it is especially important for a woman to continue to do a monthly breast examination. Regular examinations will help you detect local recurrences. Early signs of recurrence can be noted in the incision area itself, the opposite breast, the axilla , or supraclavicular region .
Maintaining your follow-up schedule with your physician is also necessary so problems can be detected when treatment can be most effective. Your health care provider will also be able to answer any questions you may have about breast self-examination after the following procedures.
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 3 Cancer
Stage Of Breast Cancer
When your breast cancer is diagnosed, the doctors will give it a stage. The stage describes the size of the cancer and how far it has spread.
Ductal carcinoma in situ is sometimes described as Stage 0. Other stages of breast cancer describe invasive breast cancer .
- Stage 1 the tumour measures less than 2cm and the lymph nodes in the armpit aren’t affected. There are no signs that the cancer has spread elsewhere in the body.
- Stage 2 the tumour measures 2-5cm or the lymph nodes in the armpit are affected, or both. There are no signs that the cancer has spread elsewhere in the body.
- Stage 3 the tumour measures 2-5cm and may be attached to structures in the breast, such as skin or surrounding tissues. The lymph nodes in the armpit are affected. However, there are no signs that the cancer has spread elsewhere in the body.
- Stage 4 the tumour is of any size and the cancer has spread to other parts of the body .
This is a simplified guide. Each stage is divided into further categories: A, B and C. If you’re not sure what stage you have, ask your doctor.
Guidelines For Elective Surgical Options
Women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations face a significant risk of breast and ovarian cancer. Prophylactic removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries is recommended by about age 40. Many women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations will also elect to have their breasts removed. Nipple-sparing mastectomy is an effective option for these women.
Making the decision to have an elective preventive double mastectomy and removal of the ovaries is personal and should be based on many life factors. You must balance where you are in your childbearing years, what your future choices may be, and whether you would prefer to follow a rigorous screening schedule instead of making such a life-altering choice.
Whatever your decision, we encourage you to make an informed choice. If you do elect to have a preventive double mastectomy, our breast specialists will guide you in the appropriate breast surgery reconstruction to help restore your body image after treatment.
If you are interested in discussing ovary removal surgery , we will refer you to one of our gynecological oncologists.
Show me more…
Don’t Miss: Is Weight Gain A Symptom Of Breast Cancer
What Role Does The Brca Gene Test Have In Breast Cancer
The BRCA gene test analyses DNA to look for harmful mutations in two breast cancer genes . This test is performed as a routine blood test. The test should only be performed on patients who have specific types of breast cancers or have a family history suggesting the possibility of having an inherited mutation. These mutations are uncommon, and inherited BRCA gene mutations are responsible for about 10% of breast cancers.
Screening For Breast Cancer
Women aged between 50 and 74 are invited to access free screening mammograms every two years via the BreastScreen Australia Program.
Women aged 40-49 and 75 and over are also eligible to receive free mammograms, however they do not receive an invitation to attend.
It is recommended that women with a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer, aged between 40 and 49 or over 75 discuss options with their GP, or contact BreastScreen Australia on 13 20 50.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Recurrence After 10 Years
Can A Woman With Breast Cancer Get Pregnant
For young women, a breast cancer diagnosis also creates uncertainty about having a family. Because cancer treatments can affect ovarian function, specialists with expertise in working with women with cancer can help preserve fertility before treatment begins by freezing eggs or embryos, through a process called cryopreservation. In Connecticut, insurance carriers cover the cost of cryopreservation for men and women under the age of 40 who have cancer.
It also may happen that a young woman is already pregnant when diagnosed with breast cancer, which requires careful conversations between the provider and patient.
Breast cancer is the most common cancer we see in pregnant women, says Dr. Silber. Because pregnancy brings about a variety of changes in the breastand pregnant women arent getting mammogramsit may make the disease harder to diagnose, she notes, but it doesnt mean the prognosis is worse.
In such cases, she explains, Our goal is to do what we can to treat the cancer and protect the pregnancy, adding that there are some types of chemotherapy treatments that can be given during pregnancy to treat breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Does It Feel Like To Have Breast Cancer