How Does It Work
Radiation specialists use a synchrotron machine to accelerate protons up to 60% the speed of light. The speed of the protons creates a high amount of energy and pushes the protons through a nozzle directed at the body.
The protons travel to a specified depth in the body, where they deliver high doses of radiation to the tumor.
Radiation creates breaks within the DNA inside the cancer cells to destroy them.
Possible Side Effects Of Proton Beam Therapy
Like most cancer treatments, proton beam therapy can cause side effects and complications. Even though proton beam therapy is delivered to a precise area, damage to normal cells near the tumor may occur. Many of the side effects are similar to the side effects of conventional radiation therapy, but due to the precise focus of damage, may be less severe. The most common side effects include:
Types Of Breast Cancer Proton Therapy Can Treat
Proton therapy can be used in breast cancers that have not spread to distant areas of the body. Once breast cancer has metastasized to other organs, proton therapy will most likely not be effective. This means that people with breast cancer in stages 1, 2, or 3 may benefit from proton therapy.
Breast cancers that are locally advanced are also candidates for proton therapy. This means that cancer has spread but has stayed in the same region of the breast. This includes cancer cells in areas like the chest wall, chest skin, or lymph nodes under the arm.
The following types of breast cancer may benefit from proton therapy:
You May Like: Stage 1 Grade 3 Breast Cancer
Pencil Beam And Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy
The team at MD Anderson Proton Therapy Center continues to expand ways to use proton therapy to benefit patients. The team pioneered pencil beam proton therapy, also called scanning beam, and intensity modulated proton therapy . We are one of the few centers worldwide offering these types of proton therapy to our patients.
Pencil beam technology and IMPT build on the benefits of proton therapy. With a proton beam just millimeters wide, these advanced forms of proton therapy combine precision and effectiveness, offering unmatched ability to treat a patients tumor and minimizing the effect on a patients quality of life during and after treatment. They rely on complex treatment planning systems and an intricate number of magnets to aim a narrow proton beam and essentially paint a radiation dose layer by layer.
Pencil beam is very effective in treating the most complex tumors, like those in the prostate, brain, eye, and cancers in children, while leaving healthy tissue and other critical areas unharmed. IMPT is best used to deliver a potent and precise dose of protons to complex or concave-shaped tumors that may be adjacent to the spinal cord or embedded head and neck or skull base, including nasal and sinus cavities, oral cavity, salivary gland, tongue, tonsils, and larynx.
What is Proton Therapy?
Pencil beam scanning builds on proton therapys success
Preparing for pencil beam scanning treatment
Limitations Of The Studys Design

The study leaders and other experts noted several limitations to the studys design.
For instance, this observational study cant establish a cause-and-effect relationship between proton therapy and fewer side effects. In addition, all of the study participants were treated at a single institution, which can make it difficult to generalize the findings to a larger population.
Those are very significant limitations that shouldnt be understated, Dr. Buchsbaum emphasized.
Although single-institution studies have inherent limitations, Dr. Baumann noted, all patients in this study received high-quality treatment at a large academic medical center, regardless of whether it was proton or traditional radiation therapy, which suggests that the benefit of proton therapy that we saw is meaningful.
Also, because patients were not randomly assigned to treatment groups, there were differences between patients who got proton and traditional radiation, and that may have skewed the results.
For instance, patients who received proton therapy were, on average, older and had more health issues.
The proton therapy group may also have included more patients from privileged backgrounds, Drs. Park and Yu noted. Socioeconomic status and social support can affect treatment outcomes, they wrote.
In addition, fewer people with head and neck cancerwho are more likely to suffer from radiation-associated side effectswere included in the proton therapy group, the editorialists added.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Lymph Cancer
What Is Proton Therapy For Breast Cancer
Proton therapy is a precise type of radiation therapy that allows your medical team to better target cancer cells than traditional X-ray radiation therapy. Your medical team may consider proton therapy as part of your treatment plan for breast cancer if you have a large tumor, underwent a mastectomy, or when cancer cells have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Proton therapy can be used in breast cancers that have not spread beyond the region of the breast. Metastatic cancerscancers that have spread to distant parts of the bodyare not eligible for proton therapy. This is because proton therapy closely targets the cancerous tumor and cannot be used systemically .
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
A sentinel lymph node biopsy is a procedure in which the sentinel lymph node is removed for examination under a microscope to determine whether cancer cells are present to determine if the cancer has spread.
When breast cancer is diagnosed, tests will be done to find out if the cancer has spread from the breast to other parts of the body. This is called staging and is an important step toward planning a treatment program.
Loma Linda University Medical Center provides additional information about the Stages of Breast Cancer as defined by the American Joint Committee on Cancer.
You May Like: What Organs Does Breast Cancer Affect
Benefits Of Proton Therapy
When the amount of radiation to the heart and lungs is decreased, so is the risk of developing side effects such as heart disease, reduced lung function, or secondary cancer. The proton therapy advantage may be more likely in cases where cancer has developed in the left breast, since it is situated so close to the heart. Whether cancer develops in the right breast or left breast, proton therapy may provide an optimal treatment and decrease the amount of radiation the heart and lungs receive. Additionally, proton therapy may provide better dose coverage to the lymph node regions as compared with conventional radiation.
University of Florida Health Proton Therapy Institute currently treats:
- Stage I, stage II and stage III breast cancer
- Locally advanced breast cancer
Eligible patients include those who are:
- ER, PR positive or negative
- Her2Neu positive or negative
- With or without implants
Proton Therapy Vs Standard Radiation Therapy
Both photon therapy and standard radiation therapy use radiation to damage or destroy cancer cells. However, these treatments use slightly different methods to deliver radiation.
Standard radiation therapy delivers radiation through high energy particles, such as X-rays or electrons. This method deposits radiation to any tissue along its path, which can harm healthy cells near the tumor.
Due to its accuracy, proton therapy can spare more healthy tissue than standard radiation therapy. It also involves a lower risk of heart-related complications.
You May Like: Milk Duct Cancer Symptoms
Acute Toxicity: Skin Dermatitis And Desquamation
The rates of acute skin toxicities in the MSK/Procure series were similar to what would be expected for patients receiving PMRT with photon irradiation using bolus. To confirm this finding, doses to the surface of the skin were measured by optically stimulated luminescent dosimeters with passive scattering proton therapy, photon therapy, and photon therapy with bolus among 14 patients undergoing post-operative EBRT for breast cancer . As shown in , while there is significant skin sparing with photons without bolus, there were no significant differences between patients treated with photons + bolus and passive scattering protons . Thus, it is not surprising that skin toxicity seems comparable to historical reports of PMRT. In the post lumpectomy setting, protons would be expected to have higher skin toxicity and perhaps compromised cosmesis compared to photon tangent fields because of the higher skin dose.
Mean surface dose among 14 patients treated with photon ± bolus or passive scattering proton therapy.
Planning And Uncertainty Mitigation
Another potential challenge for the delivery of breast cancer patients is the increasing use of immediate tissue expander reconstruction. The metal port in the tissue expander placed after breast reconstruction perturbs the proton dose distribution. Large gradients of proton energy loss created by the variability of the stopping powers of the materials used in the tissue expanders creates an unacceptable dose profile. With apreture/compensator techniques, anterior beams are used and a cold spot is created behind the metallic port. The alternative is to increase the beam range to compensate for the increased density through the metal, but at the expense of more dose delivered to the heart and lung. Thus, with traditional techniques , expanders have been a contraindication to proton therapy. A similar issue exists when using photons, as attenuation of beam creates a cold spot. However, the opposing tangent can compensate for this. Similarly with PBS and use of multifield optimization, the cold spot behind the port can be filled and a similar dose distribution can be created. This technique is currently in use at several facilities in the United States and clinical reports with this technique are awaited.
DVH envelopes corresponding with worst-case-scenario robustness planning analysis using uncertainty shifts of ±3 mm, ±2% for a patient undergoing post mastectomy proton therapy.
You May Like: How Bad Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Where Is Proton Beam Therapy Available
There are still a limited number of cancer centers in the United States and globally which provide the option of proton beam therapy. A map of proton therapy centers can show you whether this treatment is offered near your location. If you will need to travel, it’s important to weigh the potential benefits of proton beam therapy relative to those of radiation therapy, to evaluate your insurance coverage and out-of-pocket costs, and ask yourself how far you are willing to travel.
Breast Cancer Proton Therapy
Stage IV
At this IV, breast cancer has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes to other parts of the body. Drug therapy such as chemotherapy and/or hormone therapy are the main treatments recommended for women with stage IV breast cancer. At this stage, proton radiation treatment may be used to shrink tumors or control pain.
Also Check: Is Breast Cancer Curable
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
In general, cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Palliative care focuses on improving how you feel during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after a cancer diagnosis. People who receive palliative care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, and report that they are more satisfied with treatment.
Palliative treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies. You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the cancer, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
-
Music therapy, meditation, stress management, and yoga for reducing anxiety and stress.
-
Meditation, relaxation, yoga, massage, and music therapy for depression and to improve other mood problems.
-
Meditation and yoga to improve general quality of life.
-
Acupressure and acupuncture to help with nausea and vomiting from chemotherapy.
Proton Beams Can Hit The Tumor From Different Directions
This also helps to lessen any damage to the surrounding cells, reducing the risk of complications that people usually associate with radiation therapy.
This video explains how conventional radiation and proton therapy affect the body.
Video credit: Lomalindahealth
There are two main reasons for choosing proton beam therapy.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Breast Cancer Spreading
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation
Bush et al. for the Loma Linda Group reported in 2014 on 100 patients treated for invasive non-lobular carcinoma with a maximal tumor dimension of 3 cm, having undergone partial mastectomy with negative margins and negative axillary LN sampling. Postoperative proton RT was delivered as 4 Gy in 10 fractions, 1 treatment daily over 2 weeks. Multiple fields were treated daily, and skin-sparing techniques were used. At a median follow-up of 60 months, ipsilateral recurrence-free survival was 97%, no cases of grade 3 or higher acute skin reaction were noted, and late skin reactions included 7 cases of grade 1 telangiectasia. These encouraging data resulted in a prospective clinical trial initiated by the Proton Therapy Cooperative Group which has completed accrual and is presently in its follow-up phase.
Early data indicate that proton therapy for partial breast irradiation is non-inferior to modern photon techniques. However, in light of the overall small target volumes and the excellent capability of photon therapy to obtain target volume coverage, it remains to be determined whether there is a distinct long-term advantage for proton therapy.
What To Expect During Proton Therapy Treatment
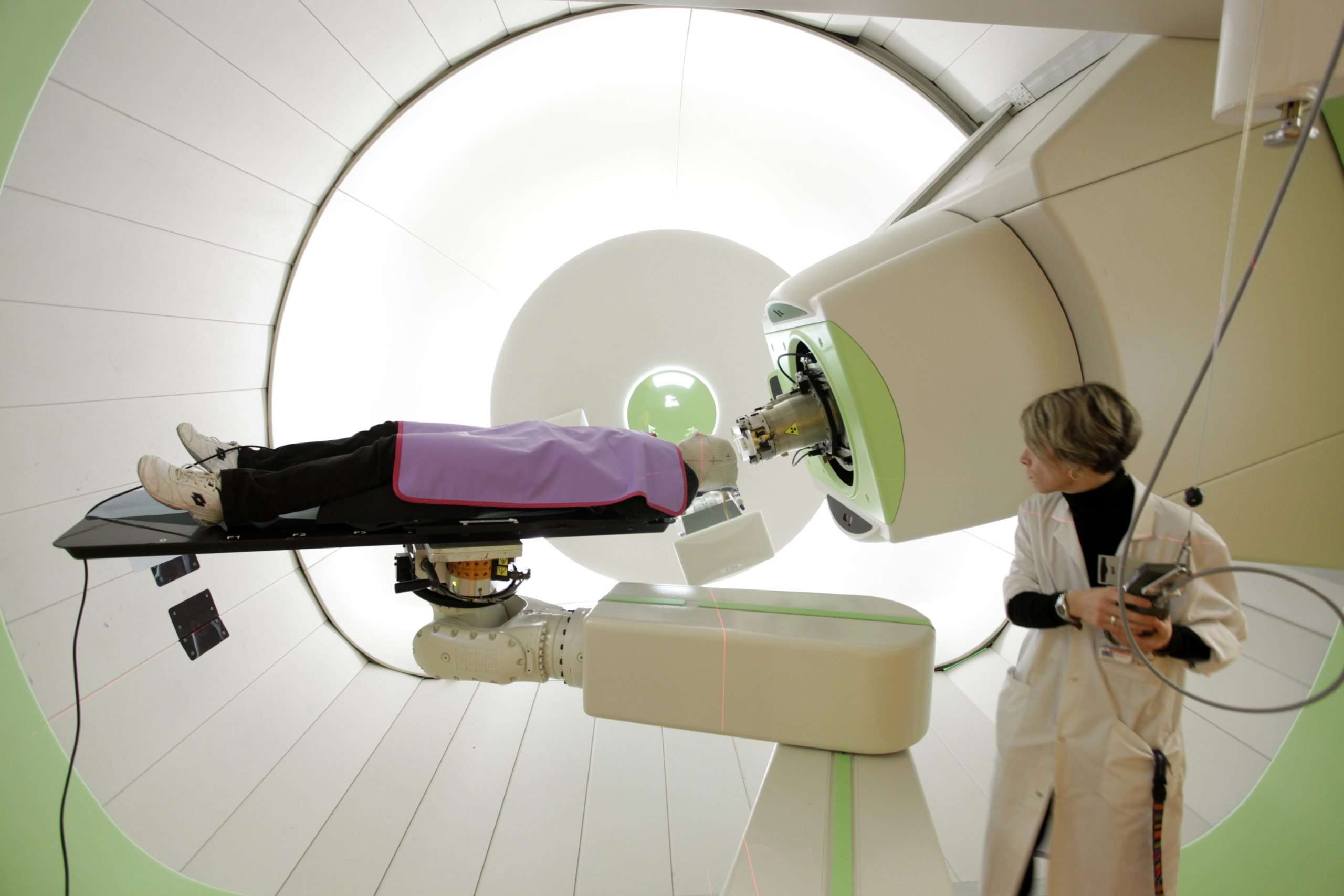
Each session should be about 15 to 30 minutes. Youâll go to a special room where your treatment team will put you in the right position for a technician to aim the protons at the tumor.
You could be on a table or in a chair. A laser will help center the radiation machine on the target area. The doctors will take an X-ray or CT scan to double check the position.
The medical team will leave the room to protect themselves from the radiation. Theyâll be able to see and hear you through a video system.
Some proton therapy rooms have a large mechanical arm called a gantry that moves around you to send radiation at several different angles. You shouldnât feel anything at all during the process.
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3b Cancer Mean
When Is Radiation Therapy Used
Radiation therapy can be used to treat all stages of breast cancer.
Pregnant women should not have radiation therapy because it can harm the unborn baby. Read about Treatment for Breast Cancer During Pregnancy.
Radiation therapy after lumpectomy
Radiation therapy is recommended for most people who have lumpectomy to remove breast cancer. Lumpectomy is sometimes called breast-conserving surgery. The goal of radiation after lumpectomy is to destroy any individual cancer cells that may have been left in the breast after the tumor was removed. This reduces the risk of the cancer coming back and the risk of passing away from breast cancer.
Heres a good analogy for understanding the role of radiation therapy after surgery:If you drop a glass on the kitchen floor, you must first sweep up all of the big pieces of glass and throw them away you can think of breast surgery in this way, says Marisa Weiss, M.D., founder and chief medical officer of Breastcancer.org and director of breast radiation oncology at Lankenau Medical Center. Radiation therapy is like vacuuming the area after you sweep, getting into the corners and under the furniture, to get rid of any tiny shards of glass that might be left behind.
Radiation therapy after mastectomy
Radiation therapy may be recommended after mastectomy to destroy any cancer cells that may be left behind after the surgery. During mastectomy, it’s difficult for surgeons to take out every cell of breast tissue.
Time Needed For Each Treatment
In general, a proton radiation treatment lasts about 15 to 30 minutes, starting from the time you enter the treatment room. The time will depend on the part of the body being treated and the number of treatments. It will also depend on how easily the team can see the tumor site with x-rays or CT scans during the positioning process.
Ask your health care team how long each treatment will take. Sometimes, the doctor will need to give treatment from different gantry angles. Ask your team if this will happen for your treatment. Find out if they will come back into the room during treatment to move the gantry or if the gantry will be rotated around you.
It is also important to know that total time in the treatment room may vary from day to day. This is because the doctor may target different areas that require other radiation âfields.” This may require using various kinds of proton beam segments. For example, one treatment may deliver a part of the total radiation dose to lymph nodes and healthy tissues around the tumor that may contain tiny amounts of tumor. Another treatment may deliver a radiation dose to the main tumor.
Other factors can also affect the total time needed, such as waiting for the proton beam to be moved after another person’s treatment is finished. Most proton treatment centers have only one proton machine.
Also Check: What Is Stage 3 Cancer In Lymph Nodes
Pbrt In The Elderly Breast Cancer Population
PBRT offers elderly breast cancer patients similar potential for disease control with reduced toxicity as the general population. In elderly patients with early stage and low-risk breast cancer, APBI delivered with protons can provide excellent cosmesis and good disease control . Dosimetric analysis of APBI by protons demonstrates improved target coverage and homogeneity while reducing cardiopulmonary toxicity . Compared to APBI delivered with brachytherapy, proton APBI provides patients the ability to avoid additional procedures required with brachytherapy . This reduces the risk of pain, bleeding and infection conferred by catheter implantation during brachytherapy. PBRT also has fewer anatomical restrictions allowing more elderly patients to receive APBI.
Figure 1Figure 2
In elderly breast cancer patients not eligible for APBI, WBI delivered with protons reduces radiation dose to the lung and heart . The reduction in cardiac toxicity is particularly pronounced in women with left-sided breast cancer . Breast cancer RT doses to the heart may result in increased risk of cardiovascular disease and cardiac mortality .