Stage Of Breast Cancer
When breast cancer is diagnosed, your doctors will give it a stage. The stage describes the size of the cancer and how far it has spread, and is used to predict the outlook.
Ductal carcinoma in situ is sometimes described as stage 0. Other stages of breast cancer describe invasive breast cancer and include:
- stage 1 the tumour measures less than 2cm and the lymph nodes in the armpit are not affected. There are no signs that the cancer has spread elsewhere in the body
- stage 2 the tumour measures 2 to 5cm, the lymph nodes in the armpit are affected, or both. There are no signs that the cancer has spread elsewhere in the body
- stage 3 the tumour measures 2 to 5cm and may be attached to structures in the breast, such as skin or surrounding tissues, and the lymph nodes in the armpit are affected. There are no signs that the cancer has spread elsewhere in the body
- stage 4 the tumour is of any size and the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
This is a simplified guide. Each stage is divided into further categories: A, B and C. If you’re not sure what stage you have, talk to your doctor.
Getting A Breast Biopsy
In a breast biopsy, the doctor takes out small pieces of breast tissue to check them for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have breast cancer.
There are many types of biopsies. Ask your doctor what kind you will need. Each type has risks and benefits. The choice of which type to use depends on your own case.
Sometimes, surgery is needed to take out all or part of the lump to find out if its cancer. This is often done in a hospital using local anesthesia . You might also be given medicine to make you sleepy.
Look Into Fertility Preservation
If youre hoping to get pregnant in the future and are undergoing chemo, ask about fertility preservation options like egg freezing. Chemo can diminish fertility. Its very important to address that prior to starting treatments, says Dr. Rosenblatt, who refers patients to her hospitals fertility center.
Don’t Miss: Metastatic Breast Cancer Mbc
Theres No Such Thing As A Silly Question
After reviewing and discussing the patients case in detail, the tumor board provides a consensus treatment recommendation. The plan is unique and based on many factors.
No one element alone — staging, hormone sensitivity, HER2 status — tells the whole story, says Morikawa. For example, two patients with the same stage cancer may not receive the same treatment recommendation.
In many, if not most, cases of early stage cancer, the patient will be a candidate for surgery to remove her primary tumor. Surgery may or may not be performed first.
In some cases, drug therapy like chemotherapy might be recommended to shrink a tumor before surgery is performed, explains Morikawa, noting that additional treatment recommendations could include hormone therapy, radiation therapy or a combination of therapies.
A number of factors will determine what additional therapies a patient might benefit from, and how soon those follow-up treatments should start.
Just Diagnosed With Breast Cancer: Answers From An Expert

Dr. Norah Lynn Henry is an Associate Professor in the University of Utah’s Division of Oncology in the Department of Medicine. She is Leader of the Womens Cancers Disease Center at the Huntsman Cancer Institute. Dr. Henry is the Cancer.Net Associate Editor for Breast Cancer.
Most people know someone who has breast cancer. But do you know how common the disease really is? In the United States, 1 in 8 women will be diagnosed in her lifetime. That means more women are diagnosed with this cancer than any other, excluding skin cancer. The good news is that there are fewer deaths from breast cancer each year, in part because of new treatments.
Here are 9 key facts about breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: Can Getting Hit In The Breast Cause Cancer
Ask Your Doctor For A Survivorship Care Plan
Talk with your doctor about developing a survivorship care plan for you. This plan might include:
- A suggested schedule for follow-up exams and tests
- A schedule for other tests you might need in the future, such as early detection tests for other types of cancer, or tests to look for long-term health effects from your cancer or its treatment
- A list of possible late- or long-term side effects from your treatment, including what to watch for and when you should contact your doctor
- Diet, physical activity, and other lifestyle modification suggestions
Is My Cancer Invasive Or Noninvasive
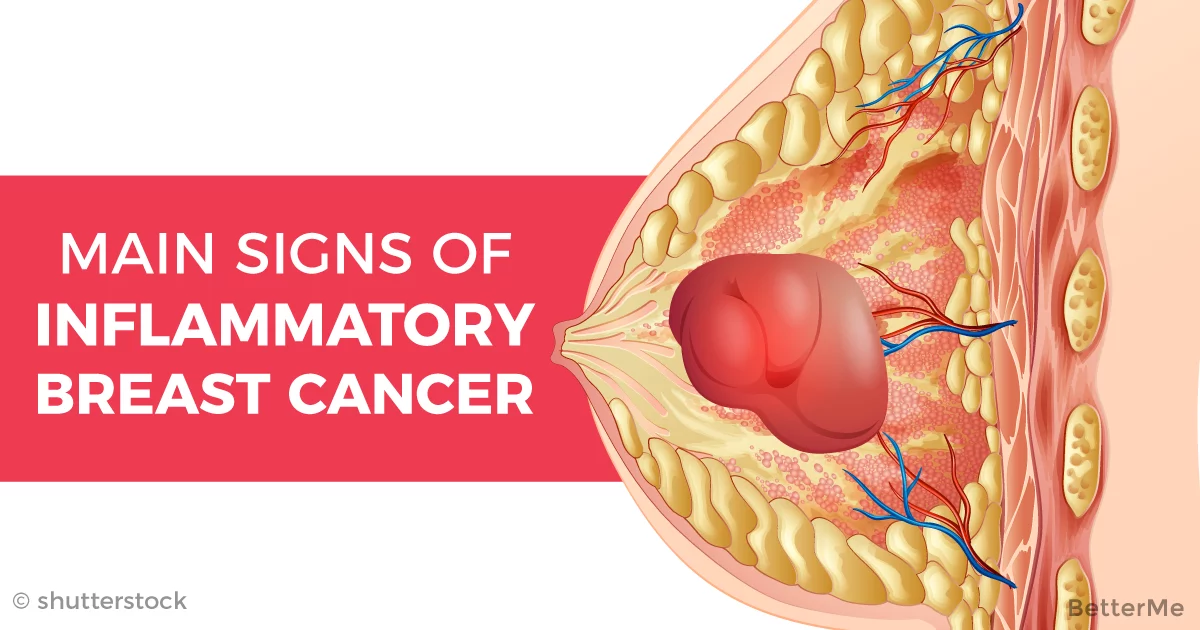
A tumor is an abnormal growth that may be benign or malignant. Benign breast tumors are not life-threatening and do not spread to other parts of the body. Malignant breast tumors are cancers that impact your health and may spread to other parts of the body. A malignant tumor that grows into surrounding tissue is considered invasive. Invasive tumors are more likely to spread to other parts of the body than non-invasive tumors. Non-invasive breast cancer cells remain in a particular area of the breast without spreading to surrounding tissue, lobules or ducts.
Read Also: Stage 3 Lymph Nodes Cancer
People With Breast Cancer Are Often Treated By A Cancer Care Team
Many different people with different specialties are often included in the cancer care team. This is called a multidisciplinary team. A breast cancer care team may include:
Surgeons. A surgeon generally removes the tumor in the breast and surrounding lymph nodes.
Radiation oncologists. A radiation oncologist treats cancer using radiation therapy, which is often given after surgery to decrease the risk of cancer coming back in the breast and chest area.
Medical oncologists. Medical oncologists treat breast cancer with drugs such as chemotherapy, anti-hormone therapy, and other targeted therapies to decrease the chance of cancer returning or to treat cancer that has spread throughout the body.
Oncology nurse. Oncology nurses serve many roles in cancer care. An oncology nurse may give physical examinations, give chemotherapy and other medications, coordinate care with the other members of the cancer care team, provide education and counseling to patients and families, and more.
Social workers. Clinical social workers help patients, family members, and other caregivers cope with everyday tasks and challenges before, during, and after breast cancer treatment.
Genetic counselors. Genetic counselors discuss whether or not genetic testing is appropriate based on an individuals personal and family history of breast cancer and other cancers.
Financial counselors. Financial counselors help with insurance-related issues and financial aid.
Who Gets Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women other than skin cancer. Increasing age is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer, with 66% of breast cancer patients being diagnosed after the age of 55.
In the US, breast cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death in women after lung cancer, and it’s the leading cause of cancer death among women ages 35 to 54. Only 5 to 10% of breast cancers occur in women with a clearly defined genetic predisposition for the disease. The majority of breast cancer cases are “sporadic, meaning there is no definitive gene mutation.
Also Check: Stage 3a Breast Cancer Survival
Gather Your Support Team
Assemble a band of people you can count on to offer both emotional and practical support. Designate family and friends to help you with everyday tasks that may become difficult, such as driving to appointments and doing laundry. Support from family and friends is crucial, says Dr. Barcenas.
If youre older, ask your doctor about extra assistanceanything from transportation to meals on wheels to additional nurse checks. Your care team is there to help with these kinds of social supports too, says Dr. Rosenblatt. Figuring out these details early on will give you a sense of control,” says Cross.
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several types of breast cancer, and theyre broken into two main categories: invasive and noninvasive, or in situ.
While invasive cancer has spread from the breast ducts or glands to other parts of the breast, noninvasive cancer has not spread from the original tissue.
These two categories are used to describe the most common types of breast cancer, which include:
- Ductal carcinoma in situ. Ductal carcinoma in situ is a noninvasive condition. With DCIS, the cancer cells are confined to the ducts in your breast and havent invaded the surrounding breast tissue.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ. Lobular carcinoma in situ is cancer that grows in the milk-producing glands of your breast. Like DCIS, the cancer cells havent invaded the surrounding tissue.
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. Invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer. This type of breast cancer begins in your breasts milk ducts and then invades nearby tissue in the breast. Once the breast cancer has spread to the tissue outside your milk ducts, it can begin to spread to other nearby organs and tissue.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Invasive lobular carcinoma first develops in your breasts lobules and has invaded nearby tissue.
Other, less common types of breast cancer include:
The type of cancer you have determines your treatment options, as well as your likely long-term outcome.
1 and 5 percent of all breast cancer cases.
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Recurrence Symptoms Pain
Breast Cancer Screening & Early Detection
After the age of 45, women should go for annual mammograms, breast exams, and cancer screenings to be proactive in detecting an abnormality. Catching cancer in its early stages is crucial for increasing a patient’s survival rate. If women are at a high risk due to family history or risk factors such as being overweight or having a previous exposure to chest radiation, they may want to consider scheduling mammograms earlier. If something irregular is detected, doctors may also order a breast ultrasound or a needle biopsy to further inspect the area. Patients should understand the proper protocols for detection, and doctors should communicate recommendations and offer insights about potential concerns.
If a doctor fails to order age-based cancer screenings, ignores a patient’s symptoms and concerns that may align with a breast cancer diagnosis, or fails to consider previous health conditions and red flags, a patient may not be receiving the standard of care that is to be expected. If a breast cancer diagnosis is delayed, leading to a more invasive breast cancer in its later stages, patients may be eligible to file a breast cancer misdiagnosis lawsuit and be awarded compensation for costly cancer treatments, pain, and suffering.
Why You Have Follow Up
At each follow up your doctor or nurse checks how you are coping with any ongoing treatment, for example hormone therapy.
Your healthcare team can give you information and support to help you cope. Your appointments are also a good opportunity to raise any concerns and ask questions that you might have.
You May Like: Treatment For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Anyone Can Get Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is more common after menopause, but younger women can develop it too. Men can also be diagnosed with the disease, although its rare. There are some factors that increase the risk of developing breast cancer, including being overweight and greater amounts of alcohol use. However, for most people diagnosed with breast cancer, doctors cant identify a specific cause.
Quality Of Life After Treatment
Most people report a good quality of life after they complete breast cancer treatment . However, you may have some late effects of treatment.
You may have some long-term side effects or new side effects may occur months or even years after treatment ends. These may include hot flashes and other menopausal symptoms, fatigue, chronic breast pain, lymphedema and a loss of sex drive.
It can be hard to plan for or cope with these late effects since they vary from person to person.
However, there are things you can do to ease some symptoms.
Learn about :
Read Also: Hormone Therapy For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Can Blood Work Detect Breast Cancer
Yes. Cancerous tumors produce specific proteins that can be found in blood marker tests. Certain markers, such as CA 15.3, TRU-QUANT, and CA 27.29, typically indicate breast cancer may be present or if there is a cancer recurrence. Other markers, like CEA , can indicate that breast cancer is present and can also determine if it has traveled to other areas of the body. Doctors will often order blood tests before treatment and throughout the process to help diagnose the cancer, as well as to see how the cancer is responding to treatment methods. A blood test is a supplement to other breast cancer detection strategies, but it is not a foolproof method and should not be used in place of other cancer screenings.
Do I Still Need A Second Opinion If My Mammogram Came Back Positive
Mammograms are about 87% effective in detecting invasive breast cancer cells. Depending on the doctor and his or her interpretation of the mammogram, test results can still yield a false-negative or false-positive. You should always follow-up and get a specialist’s second opinion to confirm the diagnosis and to get more information about your treatment options and next steps.
Recommended Reading: Mayo Clinic Breast Cancer Stages
Should I Consider Participating In A Clinical Trial
Breast cancer treatment has improved tremendously over the years, thanks to advances made possible because of patients who have been willing to participate in studies exploring treatment options, drug protocols or other approaches before they can be granted federal approval. These clinical trials may offer participants new treatment options that may have otherwise been unavailable to them, especially after exhausting conventional treatments. If you qualify for such a trial, ask your doctor about any concerns or questions you may have about participating, so that you may determine if its a good fit for you.
Just Diagnosed With Breast Cancer: Now What Questions To Ask Your Doctor
Few women are truly prepared to receive a breast cancer diagnosis. Knowing what to ask your doctor is a challenge for the newly diagnosed. The challenge is made even greater by ongoing improvements in how we manage breast cancer. The following list of questions will help you get off to a great start with your doctors.
Am I eligible for a clinical trial? A clinical trial is a research study involving people that aims to test news ways to prevent, detect or treat a medical condition. The most advanced and innovative breast cancer treatments are first only accessible via clinical trials. Participants in clinical trials are also monitored more closely than non-trial patients and clinical trial treatments are often available at no additional cost to the patient, although some may experience some out-of-pocket expenses.
Also Check: Bob Red Mill Baking Soda Cancer
Follow Up Care After Breast Cancer Treatment
Many women are relieved or excited to be finished with breast cancer treatment. But it can also be a time of worry, being concerned about the cancer coming back, or feeling lost without seeing their cancer care team as often.
For some women with advanced breast cancer, the cancer may never go away completely. These women may continue to get treatments such as chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or other treatments to help keep the breast cancer under control and to help relieve symptoms from it. Learning to live with breast cancer that doesnt go away can have its own type of uncertainty.
Even if you have completed breast cancer treatment, your doctors will want to watch you closely. Its very important to go to all of your follow-up appointments. During these visits, your doctors will ask if you are having any problems, and will probably examine you. Lab tests and imaging tests aren’t typically needed after treatment for most early stage breast cancers, but they might be done in some women to look for signs of cancer or treatment side effects.
Here Is A List Of Questions That You May Want To Ask Your Health Care Team:
Since Ive been diagnosed, Ive been overwhelmed. How can I better cope with my diagnosis? A cancer diagnosis turns a persons world upside down emotionally and physically. Your team of doctors, nurses and social workers are valuable sources of support as you cope with a cancer diagnosis. Oncology social workers are licensed professionals who counsel people affected by cancer, providing emotional support and helping people access practical assistance. CancerCares oncology social workers provide individual counseling, support groups and locate services face-to-face, online or on the telephone, free of charge. To learn more, visit www.cancercare.org or call 800-813-HOPE .
Is my tumor invasive or noninvasive? Invasive breast tumors are tumors that have started growing into nearby healthy breast tissues. Noninvasive, or in situ tumors, are confined to the milk ducts this is the earliest stage of breast cancer. As is true for most cancers, breast cancer in the earliest stage usually has the best chance of being effectively managed.
What stage is my tumor? A tumors stage refers to its size and extent of spread in the bodye.g., whether it has spread to lymph nodes or other organs. Cancer confined to the breast may be called localized cancer. Cancer that has spread to other organs is called metastatic cancer. A cancers stage is often denoted by a Roman numeral . The higher the numeral, the more the cancer has spread within the body.
Recommended Reading: What Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer